Correlation between psychological factors and the expression of galanin and 5-hydroxytryptamine in different subtypes of gastroesophageal re flux disease
2021-06-25YuanYUANHuiWenXUSongZHANGEnTAKASHIKitayamaAKIOJingYanLIANGSchoolofNursingYangzhouUniversityYangzhouChinaDivisionofSatoyamaNursingandTelecareNaganoCollegeofNursingKomaganeJapanDivisionofBasicandClinicalMedicineNaganoC
Yuan YUAN, Hui-Wen XU,Song ZHANG, En TAKASHI, Kitayama AKIO,Jing-Yan LIANGSchool of Nursing, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China; Division of Satoyama Nursing and Telecare, Nagano College of Nursing,Komagane, Japan; Division of Basic and Clinical Medicine, Nagano College of Nursing, Komagane, Japan; Institute of Translational Medicine, Medical College, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China
ABSTRACT
Objective: The aim of this study is to analyze the differences in galanin (GAL) and 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) levels in patients with different subtypes of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and its correlation with anxiety and depression in patients.
Methods: Using the reflux disease questionnaire, 238 patients with GERD were selected as the study group. According to the endoscopic performance, they were divided into the nonerosive reflux disease (NERD) group (114 patients) and the RE group (124 patients). Sixty healthy people were selected as the control group. All research subjects were tested using the self-rating anxiety scale (SAS) and the self-rating depression scale (SDS) to assess the severity of anxiety and depression. The levels of 5-HT and GAL were analyzed using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Results: Compared with the control group, 5-HT level in GERD patients without anxiety and depression was higher (t = 1.97, P < 0.05) and GAL level was lower (t = 1.97, P < 0.05). NERD patients demonstrated more server anxiety (F = 55.92, P < 0.05) and depression problems (F = 36.51,P < 0.05) compared to reflux esophagitis (RE) patients. The 5-HT level was lower (F = 54.53, P < 0.05) and the GAL level was higher (F = 8.00,P < 0.05) in NERD patients compared with the control group. Furthermore, 5-HT level was negatively correlated with SAS (r = −0.789, P < 0.05)and SDS (r = −0.787, P < 0.05) scores; GAL level was positively correlated with SAS (r = 0.688, P < 0.05) and SDS (r = 0.705, P < 0.05) scores;5-HT and GAL level were negatively correlated (r= −0.744, P < 0.05).
Conclusions: 5-HT level is higher and GAL level was lower in GERD patients without anxiety and depression than healthy people; the symptoms of anxiety and depression of NERD patients are more severe compared to those of RE patients; the severity of anxiety and depression was negatively correlated with the level of 5-HT and positively with GAL level.
Keywords: 5-hydroxytryptamine, galanin, Gastroesophageal re flux disease, psychological factors
INTRODUCTION
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a common gastrointestinal disorder worldwide with prevalence estimates ranging from 2.5% to 33.1% and the incidence of it is increasing in both Western and Asian countries.[1-3]GERD can typically be divided into three subtypes: nonerosive reflux disease (NERD),reflux esophagitis (RE), and Barrett’s esophagus.[4,5]Symptoms of the disease vary, and patients may face problems of anxiety,depression, and sleep disorders. In addition, it may affect the patient’s quality of life, particularly for NERD patients.[6,7]The etiology of GERD is multifactorial and the mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of GERD have not been comprehensively determined. Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are the current mainstay therapy for GERD. However, the efficacy of PPIs is not very effective, particularly in NERD patients.[8,9]
Some studies have found that 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)receptor agonists can improve the symptoms of GERD by increasing the pressure of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), enhancing esophageal peristalsis, accelerating the clearance of esophageal acid, and facilitating emptying of the stomach.[10,11]These findings suggest that 5-HT has a specific relationship with the occurrence and development of GERD. At present, the effects of 5-HT on GERD and galanin (GAL) on the digestive tract have been reported,[12,13]but the relationship between GAL and GERD has not yet been reported. The correlation between the levels of 5-HT and GAL and the psychological factors in GERD has also not been reported. This study explored the correlation between the levels of 5-HT and GAL and the psychological factors in GERD to use 5-HT and GAL in the development of new effective drugs in the treatment of GERD.[14]
METHODS
Participant recruitment
The study was a cross-sectional survey. We selected 238 patients with GERD as the study group in Subei People’s Hospital from August 2014 to August 2017 using a reflux disease questionnaire (RDQ). According to the endoscopic performance, the study group was divided into the NERD group and the RE group. Sixty patients recruited from the outpatient health clinic were selected as the control group.This study was approved by the ethical committee of Subei People’s Hospital (Jiangsu, China).
Inclusion criteria were (1) patients were diagnosed as GERD according to expert consensus,[15]with typical symptoms of heartburn, acid and food regurgitation; (2) the total RDQ scores s12; (4) people aged 18; and (5) they were willing to join in the study and sign written informed consent form.
Patients were excluded for the following reasons: previous treatment with a proton pump inhibitor; use of prescribed nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and aspirin; a history of upper gastrointestinal surgery; the incidence of a peptic stricture or duodenal and/or gastric ulcer visible on upper endoscopy; comorbidities, such as diabetes mellitus,autonomic or peripheral neuropathy, functional bowel disorder, or any underlying disease that might increase the acid clearance time or affect the LES pressure; unwillingness or inability to complete the study; and unwillingness or inability to provide informed consent.
Measurement Sociodemographic characteristics questionnaire
The questionnaire was designed by the researchers themselves and included sociodemographic characteristics (including gender, age, body mass index [BMI], etc.,) and RDQ (including the symptom levels and frequencies of heartburn,noncardiogenic chest pain, and acid and food regurgitation in the recent 4 weeks).
Self-rating anxiety scale
The self-rating anxiety scale (SAS) was designed by Zung[16]to assess the severity of anxiety. The SAS consists of 20 questions.Each question was scored on a scale of 1–4 (rarely, occasionally,often, and always). The SAS scores were used to define four categories of anxiety severity: within a normal range or no significant psychopathology (20–44 points); mild to moderate anxiety (45–59 points); severe anxiety (60–74 points); and extreme anxiety (75–80 points).
Self-rating depression scale
Similarly, the self-rating depression scale (SDS) was designed by Zung[17]to evaluate the level of depression. The SDS includes 10 positive items and 10 negative items. Each question was scored on a scale of 1–4 (rarely, occasionally,often, and always). The SDS scores were used to define four categories of depression severity: within a normal range or no significant psychopathology (below 40 points);minimal to mild depression (40–47 points); moderate to marked depression (48–55 points); and severe to extreme depression (56 points and above).
Procedure
After trained and passed the examination, investigators began to conduct the investigation. Investigators explained the purposes and methods of the study to the participants before the study and then sent out questionnaires with their consent. Face to face with them, the researchers explained the meaning of each item clearly and the participants could ask the researchers questions at any moment if they could not understand the questionnaire. With the help of the investigators, participants completed the questionnaire.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
Patients’ plasma samples were collected and centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 20 min. The supernatant was collected to measure the levels of 5-HT and GAL using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. All samples were measured in duplicate. ELISA kits were purchased from Beyotime Biotechnology Company in China. The enzymatic reader was bio-680, which was purchased from BIO-RAD in the United States.
提高资金利用效率,防止资金浪费现象发生,这是PPP投资型项目建设的重要内容。然而调查显示,部分企业在参与PPP投资型项目时,忽视严格审核施工预算方案,未能对资金使用作出科学合理安排,制约项目效益提升。为转变这种情况,有必要健全PPP投资型项目管理制度,对资金使用作出科学合理安排,提高预算方案的科学性与合理性,防止资金浪费,让PPP投资型项目资金得到合理使用。
Statistical analysis
Data were presented as the mean ± standard deviation.Statistical comparisons were performed using one-way analysis of variance ort-tests, and the correlation between the parameters was evaluated using Pearson correlation analysis with SPSS software (version 20.0; SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA).P <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Demographic characteristics
A total of 238 patients and 60 healthy controls were included in this study. Patient demographics and clinical characteristics are shown in Table 1. Significant differences were observed with respect to BMI and smoking among the three groups (P< 0.05). No significant differences were observed with respect to sex, age, or drinking among the three groups (P> 0.05).
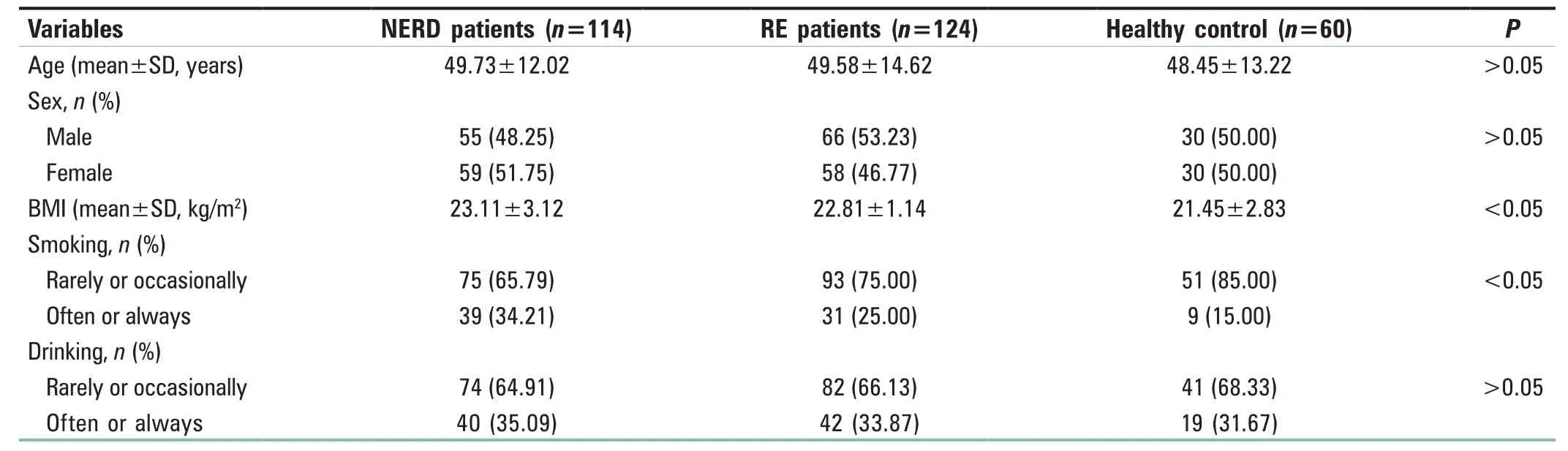
Table 1: Demographic characteristics of the subjects
Comparison of 5-hydroxytryptamine and galanin levels in gastroesophageal re flux disease patients without anxiety and depression and the control group
The 5-HT level was higher in GERD patients without anxiety and depression than the control group (207.78 ± 50.95 ng/mL vs. 173.71 ± 40.99 ng/mL,P< 0.05); the GAL level was lower in GERD patients without anxiety and depression than the control group (17.53 ± 3.75 pg/mL vs. 24.00 ± 9.87 pg/mL,P< 0.05).
Correlation between self-rating anxiety scale and self-rating depression scale scores and 5-hydroxytryptamine and galanin levels
5-HT level was negatively correlated with SAS scores (r= −0.789,P< 0.05) and SDS scores (r= −0.787,P< 0.05); GAL level was positively correlated with SAS (r= 0.688,P< 0.05) and SDS (r= 0.705,P< 0.05) scores; 5-HT GAL level and GAL level were negatively correlated (r= −0.744,P<0.05).
Differences between self-rating anxiety scale and self-rating depression scale scores in the nonerosive re flux disease, RE, and control groups
The SAS and SDS scores of NERD patients and RE patients were higher compared to those of the control group (F= 55.92 and 36.51,P< 0.05), and the SAS and SDS scores of NERD patients were higher than those of the RE patients (F= 55.92 and 36.51,P< 0.05), as shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1: Differences between self-rating anxiety scale scores and self-rating depression scale scores in the nonerosive re flux disease, RE, and control groups
Differences between 5-hydroxytryptamine and galanin levels in the nonerosive re flux disease, RE, and control groups
The 5-HT level was lower and the GAL level was higher in the NERD group compared to those of the control group (F= 54.53 and 8.00,P<0.05), while the 5-HT level was higher and the GAL levels were lower in the RE group compared to those of the control group (F= 54.53 and 8.00,P<0.05), as shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2: Differences between 5-hydroxytryptamine levels and galanin levels in the nonerosive re flux disease, RE, and control groups
DISCUSSION
Effect of 5-hydroxytryptamine and galanin on the digestive tract
Effect of 5-hydroxytryptamine and galanin on anxiety and depression
It has been confirmed that GAL and 5-HT are related to the pathogenesis of many types of mental disorders.[21,22]Clinicians use selective serotonin site inhibitors (SSRIs)to treat mental disorders such as depression. This finding indicates that 5-HT is an important neurotransmitter in the pathogenesis of mental disorders.[23,24]At present, the study of the effect of 5-HT on psychological abnormalities has mainly focused on the deficiency of 5-HT synthesis and barriers of 5-HT transport, among other challenges.[25]GAL has a wide distribution in the peripheral and central nervous systems, and some studies have suggested that GAL and its receptor play an important role in the development of depression.[26,27]A previous study found that the 5-HT level in NERD patients is lower than those of the control group and that the GAL level is higher than those of the control group. This finding demonstrates that there is a specific relationship between psychological factors and NERD. Some studies have also found that NERD and RE patients exhibit an abnormal psychological phenomenon, but the severity of NERD is higher compared to that of RE patients.[28]In this study, the SDS and SAS scores of NERD and RE patients were higher than those of the control group, and the SAS and SDS scores of NERD patients were higher than those of the RE patients, which revealed that the problems of anxiety and depression in NERD patients are more severe compared to those of RE patients.
Correlation between 5-hydroxytryptamine and galanin
GAL is an inhibitory modulator that regulates the release of norepinephrine and 5-HT by hyperpolarization.[29]A few investigations and reports on the relationship between GAL and classical neurotransmitters have been performed, but the research results have not been very consistent.[30,31]The abnormality of 5-HT content or activity may be correlated with the pathogenesis of many types of psychological disorders. Some studies have also shown that the reduction of 5-HT activity can cause anxiety and depression symptoms. In recent years, an increasing number of studies have proposed that GAL and its receptors play an important role in the occurrence and development of depression.[32,33]Some studies have found that the pathogenesis of psychological disorders,such as depression, may be correlated with the regulation of GAL on NE, 5-HT, and dopamine. This study showed that there is a negative correlation between 5-HT and GAL; when the anxiety and depression problems were more serious, the 5-HT level was lower and the GAL level was higher.
Limitations
The study is subjected to two limitations. First, although the sample size meets the sample size requirements after calculation, the larger the sample size is, the smaller the representativeness error of the statistical estimator will be.Therefore, we can continue to expand the sample size to make the results more representative. Secondly, this study is only carried out in Subei People’s Hospital, which may have regional particularity. In the following study, multi-center research can be carried out to compare the research results.
CONCLUSIONS
Overall, this study found that GAL and 5-HT levels play an important role in the occurrence and development of GERD. If GERD patients do not have anxiety and depression problems,then 5-HT levels are increased and GAL levels are decreased.Psychological factors have a large effect on the occurrence and development of NERD; when anxiety and depressive symptoms are more severe, 5-HT levels decrease and GAL levels increase. At present, for the treatment of GERD, PPIs are the first-line medication. However, this treatment may not be suitable for all GERD patients. It can be combined with the use of anti-anxiety and antidepression drugs in the treatment of GERD drugs. The effect of SSRIs on mental and psychological disorders has been proven in the clinic. The study of GAL and its receptors may direct the development of anti-anxiety and antidepression drugs in the future. It also plays a crucial role in the treatment of GERD.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent forms. In the form, the patients have given their consent for clinical information to be reported in the journal. The patients understand that their names and initials will not be published and due efforts will be made to conceal their identity, but anonymity cannot be guaranteed.
Financial support and sponsorship
This study was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81570392), National Key R and D Program of China (2016YFE0126000), Open Project of Key Laboratory of Zoonosis in Jiangsu Province (HX20014), and Key R and D Projects of Yangzhou (YZ2020097).
Con flicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Journal of Integrative Nursing的其它文章
- A nursing study on five-animal frolics in improving anxiety and depression of inpatients
- Mediating effect of undergraduate nursing students’professional commitment on positive psychological capital and learning burnout
- Scienti fic publications in nursing journals from East Asia:A survey of literature
- The impacts of resilience on the association between illness uncertainty and sleep quality among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Effect of health locus of control on the quality of life among hemodialysis patients
- lmproving the delivery of medical education in rural medical colleges
