Scienti fic publications in nursing journals from East Asia:A survey of literature
2021-06-25ZhiChenLIUYaLouPUYongHuaWANGLiGAOJingWANGBaoHuaCAODepartmentofNursingGeneralHospitalofWesternCommandTheaterChengduChinaSchoolofNursingSuzhouVocationalHealthCollegeSuzhouChinaSchoolofNursingTheAirForceMedicalUniver
Zhi-Chen LIU, Ya-Lou PU, Yong-Hua WANG,Li GAO, Jing WANG, Bao-Hua CAODepartment of Nursing, General Hospital of Western Command Theater, Chengdu, China; School of Nursing,Suzhou Vocational Health College, Suzhou, China; School of Nursing, The Air Force Medical University, Xi’an, China;Zhi-Chen LIU and Ya-Lou PU Contributed to the Work Equally
ABSTRACT
Background: East Asia is one of the most important economy and research force in the world. However, the trend of published articles in various areas of East Asia has not been reported.
Methods: We used PubMed and Web of Science databases to search for articles published from China, South Korea, and Japan in 59 nursing journals, from January 2008 to December 2017.
Results: The results indicated that Journal of Clinical Nursing is the most popular journal in East Asia and the number of articles published in China has shown a steady upward trend, surpassing Japan and South Korea (from 204 in 2008 to 320 in 2017). South Korea has increased rapidly since 2013 (from 65 in 2013 to 144 in 2017).
Conclusion: We conclude that China is the most influenced country with the largest number of articles in the field of nursing in East Asia.It is worth noting that the number of articles published in Japan has been slowly declining since 2015.
Keywords: A bibliometric study, East Asia, impact factor, journal citation reports, nursing, science citation index expanded
INTRODUCTION
In recent years, the field of nursing has developed rapidly along with other biomedical research fields. The number of scientific research articles published by a country or region with international influence is an important indicator for evaluating the contribution to innovation in nursing disciplines.[1]Due to the rapid advancement of Internet technology, especially the extensive application of PubMed, Web of Science, Medline, and other databases, the communication of scientific research is more convenient and faster. Large-scale, bibliometric analysis based on these search tools became feasible.
East Asia includes five countries of the mainland China, Japan,South Korea, North Korea, and Mongolia, as well as three regions of Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan. The importance of East Asia is that it includes two developed countries,Japan and South Korea, and China, the most populous and fastest-growing developing country.[2]According to Essential Science Indicators (January 1, 2008, to December 31, 2017),in all fields sorted by articles, showed that mainland China is ranked the second, Japan ranked the seventh, and South Korea ranked the thirteenth. However, the trend of published articles on nursing in various regions of East Asia has not been reported, and the results may differ from those in the above rankings. The aim of this study was to expose the contributions of East Asian countries in nursing research and to provide a basis for the future focus of East Asian nursing research.
METHODS
Search strategy
The methodology used in this study is consistent with previous similar articles.[3-6]On August 26, 2018, Web of Science database was used to retrieve and identify journals related to nursing. A total of 118 professional nursing journals were listed under the “Nursing” category of the 2017 journal citation report (JCR) published by Institute for Scientific Information. “Nursing” category is defined as coverage resources on all aspects of nursing science and practice such as administration, economics, management,education, technological applications, and all clinical care specialties. Because we conducted a 10-year bibliometric analysis, journals that were cited by JCR only in recent years,as well as journals that were not fully cited for 10 years, were excluded. In the end, 59 journals were included in the study.
Web of Science and PubMed online databases were applied for literature searches from August 30, 2018, to September 10, 2018, to screen articles published in these 59 journals from January 1, 2008, to December 31, 2017.Because there is no published articles from Mongolia and North Korea in these 59 journals from January 2008 to December 2017, search by countries/regions was limited to China (Mainland, Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan), Japan,and South Korea. We used the ISSN (print) of the journals to search in Web of Science and PubMed database, the search terms were “0161-9268 OR 1062-3264 OR 0002-936X OR 0897-1897 OR 0883-9417 OR 0813-0531 OR 1099-8004 OR 0730-7659 OR 0162-220X OR 1538-2931 OR 0887-6274 OR 0279-5442 OR 1462-3889 OR 1042-895X OR 0197-4572 OR 0147-9563 OR 0020-7489 OR 0020-8132 OR 1055-3290 OR 0884-2175 OR 1088-4602 OR 0309-2402 OR 0889-4655 OR 0962-1067 OR 0737-0016 OR 0099-1767 OR 1074-8407 OR 0098-9134 OR 0890-3344 OR 1526-9523 OR 0002-0443 OR 1057-3631 OR 0148-4834 OR 1527-6546 OR 0893-2190 OR 8755-7223 OR 1351-0126 OR 0279-3695 OR 1043-6596 OR 1071-5754 OR 0361-929X OR 0266-6138 OR 0260-6917 OR 0363-3624 OR 0029-6465 OR 0969-7330 OR 1320-7881 OR 0029-6554 OR 0029-6562 OR 0190-535X OR 0744-6020 OR 1524-9042 OR 0031-5990 OR 0737-1209 OR 0278-4807 OR 0160-6891 OR 0193-9459 OR 1545-102X OR 1539-0136”AND “China [AD] OR Hong Kong [AD] OR Taiwan [AD]OR Macau [AD]”, “Japan [AD]” and “Korea [AD].” PubMed produced different types of articles, such as clinical trials,reviews, and randomized controlled trials (RCTs), depending on the types of publication. The retrieval work was completed by two librarians who have worked for >10 years.
PubMed only provided the address of the first author in the “Affiliation” field before 2014, but the database update in 2014 contained the address information of all authors.Because some of the articles were international cooperation projects, the number of articles directly added by regions after 2014 was larger than the total number of articles in East Asia. The number of published articles was used for evaluating the number of research outcomes.
Quality appraisal
This study used three methods to compare the quality of published articles. First, the impact factor (IF). According to the 2008–2017 JCR, the accumulated IFs (the IFs of journals multiplied by the number of articles published in journals.)and the mean IFs (the accumulated IFs divided by the number of published articles) were calculated. Second, citation reports from various regions of East Asia were generated through the Web of Science database. Third, the number of articles published by each region in the ten nursing journals with the highest IF was compared. In addition, this study identified five of the most popular nursing journals in East Asia through the number of articles published in journals.
Statistical analysis
The purpose of this paper is to explore the publication trends of research articles on nursing in various regions of East Asia,rather than to test the hypothesis of contributions to research in various regions, so only simple descriptive statistics such as sum and mean are used.
RESULTS
Number of articles
From 2008 to 2017, there were a global total of 52,687 articles published in 59 journals in this field.There were 3972 articles (3972/52,687, 7.54%) from China(2788/3972, 70.2%), South Korea (830/3972, 20.9%), and Japan (374/3972, 9.4%). From Figure 1, we can see the different trends in the number of articles published in the three regions in the past decade. The number of articles published in China has shown a steady upward trend, surpassing Japan and South Korea (from 204 in 2008 to 320 in 2017). South Korea has increased significantly since 2013 (from 65 in 2013 to 144 in 2017).The number of articles published in Japan has remained relatively stable (from 36 in 2008 to 39 in 2017). The share of articles in the three regions is shown in Figure 2. The trend is consistent with the number of articles published.
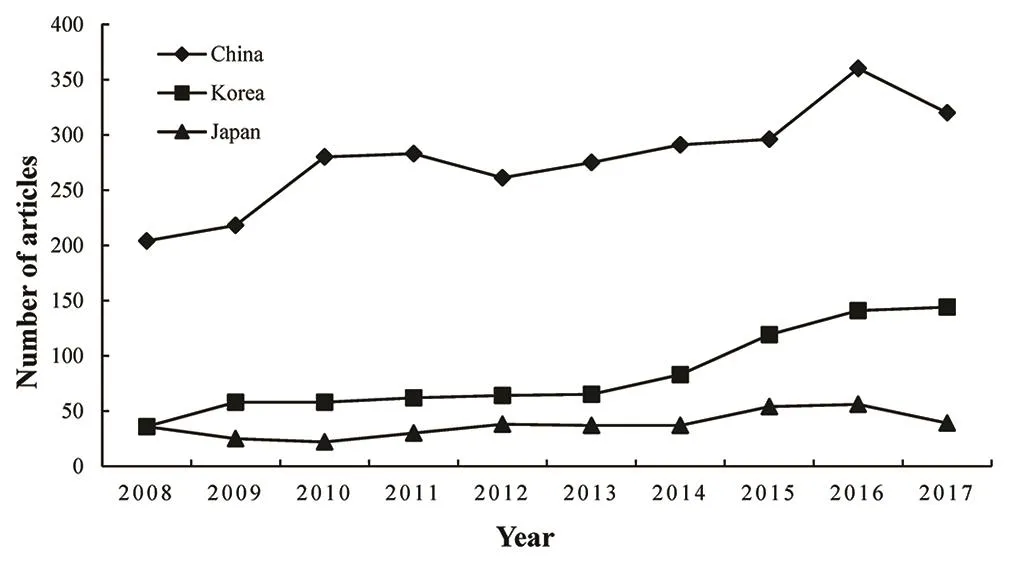
Figure 1: The number of articles from China, South Korea, and Japan in 2008–2017
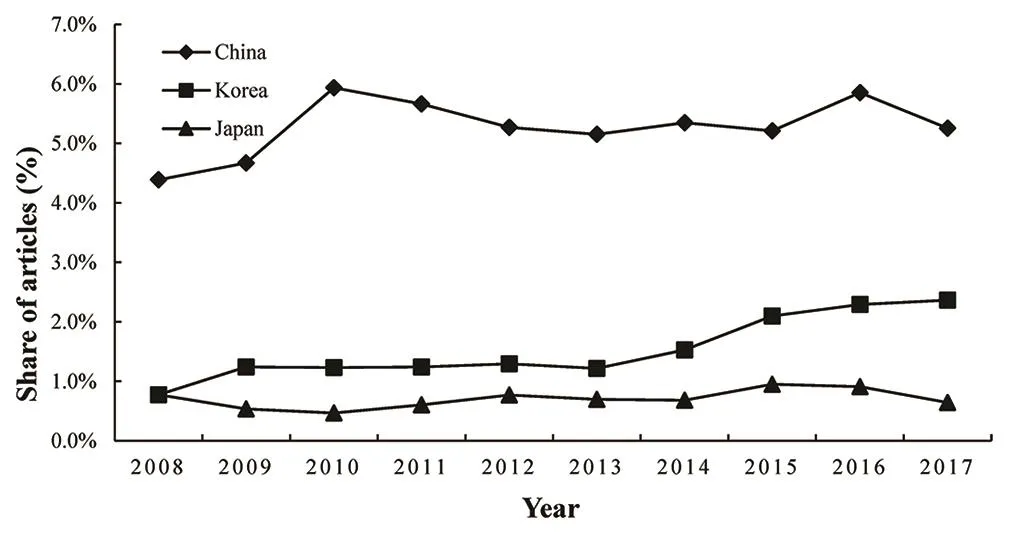
Figure 2: The share of articles from China, South Korea, and Japan in 2008–2017
Article types
In the past 10 years, 2235 clinical trials, 5860 reviews, and 1865 RCTs have been published worldwide. There were 473 clinical trials (21.2%), 260 reviews (4.4%), and 404 RCTs (21.7%) from East Asia. In the analyzed 10 years, China has published the largest number of clinical trials (363), reviews (208), and RCTs (327)compared to Korea (89 clinical trials, 46 reviews, and 64 RCTs)and Japan (23 clinical trials, 7 reviews, and 15 RCTs) [Figure 3].
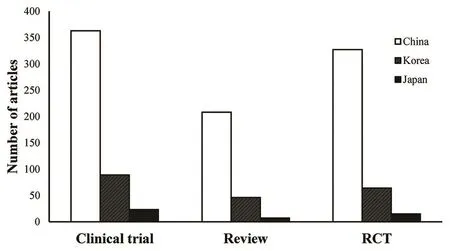
Figure 3: The number of clinical trials, reviews, and randomized controlled trials from China, South Korea, and Japan in 2008–2017
Impact factors
According to the 2017 JCR, 59 journals all had IF for a decade.The accumulated IF of articles published in China (4305.66)was higher than that of South Korea (1175.70) and Japan (528.64). At the same time, China (1.54) also had the highest mean IF compared to South Korea (1.42) and Japan (1.41) [Table 1]. The IF of Chinese published articles was between 0.304 and 3.755, the range of Korea’s IF was 0.310 to 3.755, and that of Japan was between 0.333 and 3.755.

Table 1: Accumulated and mean impact factor of articles from China, South Korea, and Japan
Citations
The “Address” field of Web of Science contained information about all authors, but before 2014, PubMed only contained the address of the first author, so the number of articles in the citation reports was more than the results of the previous search in PubMed. The total number of citations of articles published in China (43,219) from 2008 to 2017 was higher than those in South Korea (11,074) and Japan (4190). At the same time, the average number of citations per article in China (13.45) was also higher than that of South Korea (11.07)and Japan (7.97) [Table 2].

Table 2: Total and mean citations of articles from China,South Korea, and Japan
High-impact nursing journals
A total of 1254 articles in East Asia were published in ten nursing journals with the highest IFs. Among them,990 (78.9%) articles were published inInternational Journal of Nursing Studies,European Journal of Cancer Care,Journal of Advanced Nursing,andNurse Education Today. There were 932 articles published in high-impact nursing journals in China, whereas 230 and 92 articles in South Korea and Japan were, respectively, published in the top ten journals [Table 3].
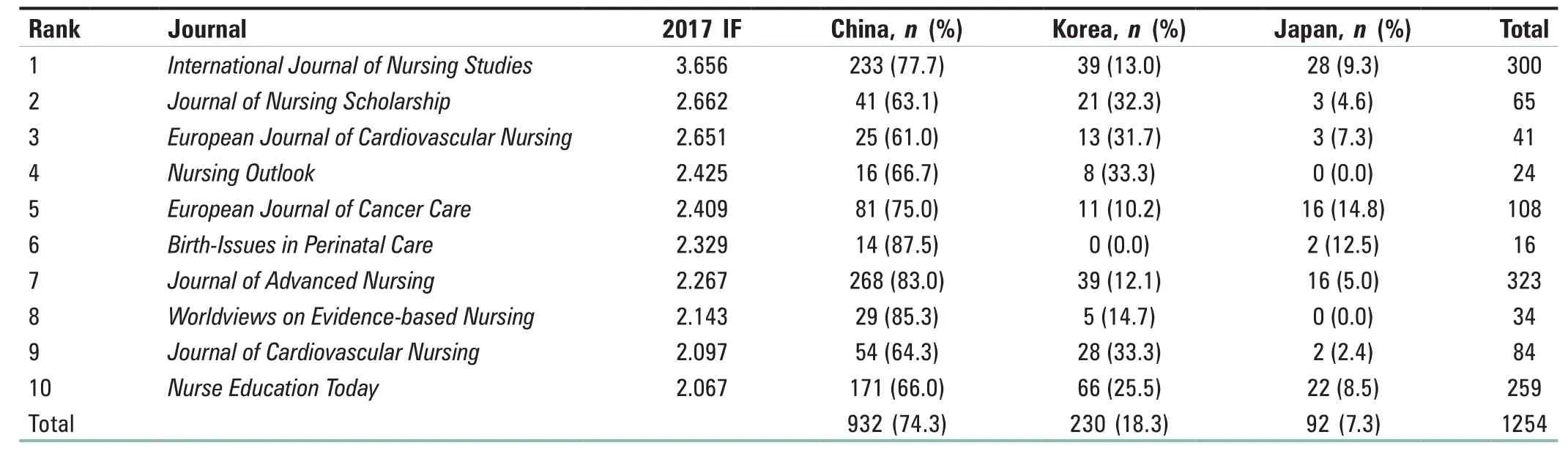
Table 3: Articles published on the ten most influential nursing journals from China, South Korea, and Japan
Popular nursing journals
The most popular journals in various regions of East Asia are shown in Table 4.Journal of Clinical Nursingwas the most popular journal in China and South Korea, but the most popular journal in Japan wasInternational Journal of Nursing studies.Journal of Clinical NursingandNurse Education todayappeared in five of the most popular journals in all regions of East Asia.
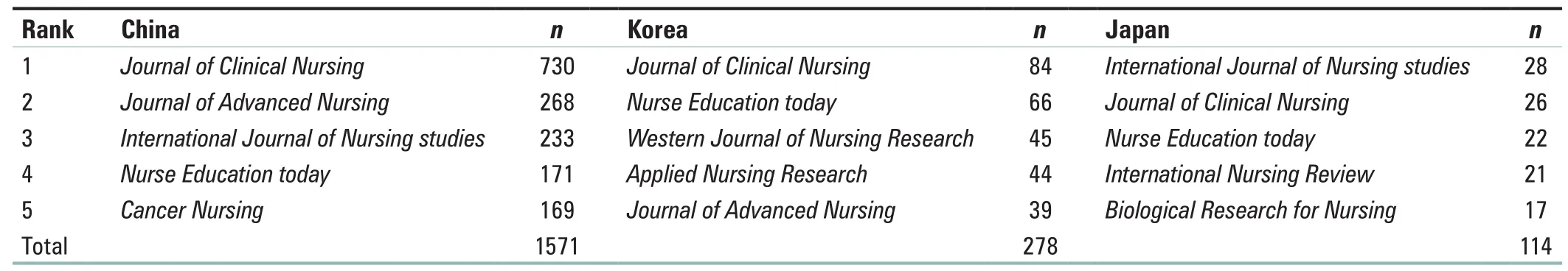
Table 4: The five most popular nursing journals in China, South Korea, and Japan
DISCUSSION
East Asia is a very important area for economic and scientific development. However, the publications of research articles on nursing in various regions of East Asia have not been reported. To our knowledge, this study is the first to survey the quantity and quality of articles published in nursing journals in different regions of East Asia during the decade,exposing the contributions of scholars in East Asia to nursing research. This study provides an overview of the overall landscape of East Asian research in the field of nursing.
Historically, Japan and South Korea have been leading the East Asian region for several decades in medical science research.[2]They have also contributed many excellent research articles to the development of the nursing discipline. Nevertheless,this study found that between 2008 and 2017, the number of articles published in Japan remained basically stable, but there has been a slow decline since 2015. Interestingly, in the past decade, Japan has only published 7 reviews and 15 RCTs in the field of nursing. Compared with Japan, the number of scientific papers published by South Korea has increased significantly since 2013, and China has also steadily increased in 10 years. Perhaps, it is related to two reasons: first, Japan’s economic recession in the past two decades may have led to a reduction in its investment in scientific research. Second,South Korea’s and China’s sustained rapid economic growth.In particular, a study has shown that South Korea’s share of research funding in the past two decades has nearly doubled, making it the country with the highest share of research funding in East Asia.[7]China has the largest scientific workforce in East Asia. There are many studies that have proven China’s continued growth in biomedical fields.[5,8,9]The results of this study indicate that China is no exception in the field of nursing.
This study used IFs and citation reports widely used in previous similar studies to analyze the quality of articles.[6,10,11]China has the most accumulated IF, mean IF, total citation, and mean citation in East Asia, and published the most articles in the ten journals with the highest IF, indicating that China is the most influential region in East Asia in nursing, which is also related to the largest number of articles published in China. However, it is important to note that China includes four regions, namely mainland China, Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan. They also have different characteristics in nursing research.[12]According to one study, Taiwan is the most influential area in China, and Hong Kong is the region with the highest quality of publications. The mainland has the lowest mean IF and means citation compared to Taiwan and Hong Kong.[1]These findings remind us that although China’s overall influence in East Asia is great, the quality of research in mainland China needs to be further improved. We need to recognize that there are still some disciplinary development issues in mainland China. First, in China, the number of nurses per thousand people is 1.83.[13]There is still a gap between the numbers of nurses per thousand people in the world.The shortage of nurses makes nurses unable to spend too much energy on scientific research. Second, the regional distribution of nurses is uneven and has become a hindrance to the coordinated development of various regions. Third,although the education of nursing disciplines is developing rapidly,[14]multi-level nursing education is a huge shortcoming of professional development, and the proportion of highly educated nursing talents in the nursing team is too low.[15,16]These problems are gradually improving in China through medical reforms and other means.[17]
However, there are some controversies about the evaluation method of the quality of the article.[18]The IF is not the most objective criterion for evaluating the quality of the journal,but generally, the IF can reflect the academic level of similar disciplines.[19]In addition, the number of citations in a journal may be concentrated in a few articles, and it does not accurately reflect the academic quality of each article,[20]but in general, the citation number is related to the innovation and scientific nature of the article. Hence, we need to look at the results of this study dialectically.
Journal of Clinical Nursingis the most popular journal in China and South Korea. However, the most popular journal in Japan isInternational Journal of Nursing studies, which has been the most influential journal of nursing disciplines for a decade. From this perspective, the quality of research by most Japanese nursing scholars is high.Journal of Clinical NursingandNurse Education Todayappeared in five of the most popular journals in all regions of East Asia, indicating that their importance in helping East Asia’s nursing research,theory, and practice should be published on international platforms.
Limitations
The study has the following three limitations: First, this study selects journals based on the JCR-differentiated field of nursing, but some journals contain articles that exceed the scope of nursing, and some journals related to nursing are not included in the JCR, which may affect the number of scientific research articles in a certain region. Second, the choice of the articles in this study is limited by the “address” field. If the article only indicates the specific city, it is not stated that China, Korea, Japan, Hong Kong, Taiwan, or Macau are not included in the study. Third, the journal evaluation indicators selected in this study may not be the best choice, but these indicators are widely used in similar reports.
CONCLUSION
From 2008 to 2017, China has published the most nursing-related articles, clinical trials, reviews, and RCTs in East Asia. It is worth considering that the number of articles published in Japan has been slowly declining since 2015, and the number of scientific papers published by Korea since 2013 has increased significantly. From the IF and citation report,China is the country with the highest influence in the field of nursing in East Asia.Journal of Clinical Nursingis the most popular journal in East Asia.
Financial support and sponsorship
This work was supported by the Shaanxi Province Soft Science Research Project (No. 2015KRM120).
Con flicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
杂志排行
Journal of Integrative Nursing的其它文章
- A nursing study on five-animal frolics in improving anxiety and depression of inpatients
- Correlation between psychological factors and the expression of galanin and 5-hydroxytryptamine in different subtypes of gastroesophageal re flux disease
- Mediating effect of undergraduate nursing students’professional commitment on positive psychological capital and learning burnout
- The impacts of resilience on the association between illness uncertainty and sleep quality among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Effect of health locus of control on the quality of life among hemodialysis patients
- lmproving the delivery of medical education in rural medical colleges
