A nursing study on five-animal frolics in improving anxiety and depression of inpatients
2021-06-25XiaoxinLIXuWANGFangRENJinyuGUOShufenZHANGLingTANGDepartmentofNursingBeijingChangpingNankouHospitalBeijingChinaDepartmentofInternalMedicineBeijingChangpingNankouHospitalBeijingChinaDepartmentofSurgeryBeijingChangpingNanko
Xiaoxin LI, Xu WANG, Fang REN, Jinyu GUO,Shufen ZHANG, Ling TANGDepartment of Nursing, Beijing Changping Nankou Hospital,Beijing, China; Department of Internal Medicine, Beijing Changping Nankou Hospital, Beijing, China; Department of Surgery, Beijing Changping Nankou Hospital, Beijing, China;Department of Medicine, Beijing Changping Nankou Hospital,Beijing, China; Department of Nursing, Dongfang Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
ABSTRACT
Objective: The objective is to investigate the effect of five-animal frolics on anxiety and depression of hospitalized inpatients.
Materials and Methods: Totally 50 inpatients from departments of Internal Medicine, Surgery and General Medicine with hospital admission date between January 2019 and July 2020 were included. All patients exercise five-animal frolics under the professional guidance of the nurse in charge. The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) was used to assess the conditions of anxiety and depression of patients before and after taking five-animal frolics exercise.
Results: The overall score of anxiety patients was significantly lower after five-animal frolics exercise than before [6.0 (5.0, 8.0) vs. 10.0(8.0, 12.0), Z=-5.466, P < 0.001]; the overall depression score of patients was significantly lower after five-animal frolics exercise than before[ 6.5 (4.0, 8.0) vs. 10.0 (8.0, 14.0), Z=-5.175, P < 0.001]. There were 26 (52.0%) very effective cases after exercise, 16 (32.0%) effective cases,8 (16.0%) invalid cases, and the effective rate was 84.0%
Conclusion: Taking five-animal frolics exercise can improve anxiety and depression of inpatients.
Keywords: Anxiety, depression, five-animal frolics, inpatients, traditional Chinese medicine nursing
INTRODUCTION
In traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), anxiety and depression belong to the category of depression syndrome in TCM,and are caused by emotional distress, stagnation of Qi,and dysfunction of viscera and organs.[1,2]Chen Bo’s[3]study showed that the incidence of anxiety and depression was high in hospitalized patients in general hospitals. Anxiety and depression, as a negative emotions, can aggravate the condition of illness,[4]reduce immune function and quality of life,[5,6]increase the occurrence of complications,[7]change the pregnancy outcome,[8]and mode of delivery[9]and have adverse effects on the treatment, rehabilitation and prognosis of the disease. Five-animal frolics were created by Hua Tuo, a famous medical scientist in the Eastern Han Dynasty in China,according to the guiding techniques in medical books such asHuangdi’sCanonofInternalMedicineandSynopsisofGolden Chamber. It is created according to the morphology of five kinds of animals, tiger, deer, bear, ape and bird, combined with the health-preserving thought. Some studies have shown that five-animal frolics can strengthen the body, correct people’s psychological disorders and psychological diseases,regulate people’s emotions, improve people’s depression,anxiety and tension, improve people’s willpower, and keep the harmony between man and nature.[10]The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of five-animal frolics on improving anxiety and depression of hospitalized patients,and to provide reference for clinical nursing interventions.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
General information
In this study, 50 patients with anxiety/depression tendencies who were hospitalized in internal medicine, surgery and general departments of a secondary hospital in Beijing from January 2019 to July 2020 were selected as the study subjects using self-controlled clinical design scheme and convenient sampling method. There were 31 males and 19 females, aged 56.68 ± 16.49 years old. Nine cases were with paralysis,7 cases with stroke, 6 cases with trauma, 6 cases with vertigo, 6 cases with diabetes, 5 cases with tumors, 4 cases with arthritis, and others 7 cases. Among the 50 patients,39 cases (78.0%) were with anxiety, including 20 (51.3%) cases with mild anxiety, 15 (38.4%) cases with moderate anxiety,and 4 (10.3%) cases with severe anxiety; 36 (72.0%) cases were with depression, including 19 (52.8%) cases with mild depression, 9 (25.0%) cases with moderate depression, and 8 (22.2%) cases with severe depression; 26 (52%) cases were with anxiety and depression.
Inclusion criteria were (1) meeting the diagnostic criteria of anxiety/depression according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV);[11](2) the total score of the General Hospital Anxiety/Depression Emotion Scale was ≥8; (3) aged 18–90 years; (4) patients with stable disease determined by the doctor in charge and suitable to participate in five-animal frolics exercise; (5) patients who could persist in exercising five times a week for 30 min each time and had accumulated exercise time during hospitalization for 14 days;and (6) patients who voluntarily agreed to participate in the research.
Intervention process of five-animal frolics
The responsible nurses issued pictures and brochures about five-animal frolics to patients so that they could get a sense of the process and benefits of five-animal frolics exercise.Before formal exercise, 1–2 responsible nurses in different departments led their patients to warm up for 5 min, in a place with spacious environment, warm in winter, shade in summer, or fresh air circulation, so that the patients gradually enter and adapt to the exercise state. During five-animal frolics exercise, the background music was Taiji Qigong Music from Shi Fu’s album. Exercise time is during 15:00 p. m–16:00 p. m. every day. Exercise frequency is 5 days a week, once a day, 30 min each time. The exercise cycle is 14 days. The principle of five-animal frolics exercise is to highlight the joy, relax, and ease of movements. After finishing movements, patients are required to take 5 min of relaxation exercise to gradually restore to a calm state and avoid discomfort.
Evaluation indicators and methods
The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) was used to assess anxiety and depression status of inpatients after 14 days of exercise. HADS includes two subscales of anxiety and depression. Each subscale consists of 7 items with a total of 14 items. Each item is scored in four grades: 0, 1, 2,and 3. A total score of 0–7 indicates normal; 8–10 indicates mild anxiety/depression; 11–14 indicates moderate anxiety/depression; and 15–21 indicates severe anxiety/depression.[12]According to Xieet al.’s study,[13]the Cronbach’s α coefficients of HADS, anxiety subscale and depression subscale were 0.904, 0.869, and 0.807, with good reliability and validity.
According to the evaluation criteria of efficacy in the Diagnosis and Treatment Program of Depression, Published by National Administration of TCM in 2017, the reduction rate = (preexercise score-postexercise score)/Preexercise score ×100%, the reduction rate ≥50% indicates significant/very effective, 25% ≤the reduction rate ≤50% indicates effective, and the reduction rate <25% is ineffective. The total effective rate = significant rate + effective rate. The larger the difference of score before and after exercise, the higher the degree of improvement of anxiety/depression.
Treatment of adverse reactions
During the exercise of five-animal frolics, patients may have adverse reactions such as chest tightness, breath-holding,dizziness, and palpitation due to improper posture, improper exertion, physical and mental tension and poor breathing or illness aggravating. When the above symptoms occur, nurses should immediately stop the patient’s exercise, give monitoring of vital signs and assess the condition. For patients whose symptoms disappear after a short rest, they can continue to participate in exercise with special attention and instructions on action essentials. For patients with more severe symptoms,nurses should stop patients’ exercise, inform the doctor in charge immediately, and take corresponding treatment and nursing measures according to the situation.
Ethical considerations
This study has been approved by the Ethics Committee of Nankou Hospital, Changping District, Beijing. Approval number for this study is 20180923. The purpose, significance,research institution, research process, research method and duration, precautions and possible benefits of participating in the study have been informed in detail to patients before exercise, and the clinical data collected are promised to be used only for this study. Any public report on the results of this study will not disclose the personal privacy information of the patients and the informed consent forms were obtained from the patients.
Statistical analysis
SPSS version 22.0 statistical software (IBM, Armonk, New York,USA) was used to input and analyze data, and the frequency and composition ratio of counting data were described. Median (M)and percentile (P25, P75) are used to express measurement data if they obey normal distribution and mean ± standard deviation is used to express measurement data if they do not obey normal distribution. Paired samplet-test was used for data that conformed to normal distribution. For data with nonnormal distribution, nonparametric Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used, withP< 0.05 as the significant difference.
RESULTS
All patients completed the trail and no patients withdraw from the study. After exercise, the scores of mild and moderate anxiety patients and the overall scores of anxiety patients were lower than those before five-animal frolics exercise, and the difference was statistically significant (P< 0.05) [Table 1].The depression scores of patients at all levels were lower than those before five-animal frolics, and the difference was statistically significant (P< 0.05) [Table 2]. There were 26 (52.0%) cases effectiveness after exercise, 16 (32.0%)effective cases, 8 (16.0%) invalid cases, and the effective rate was 84.0%. No patients experienced adverse events/reactions during the course of this exercise.
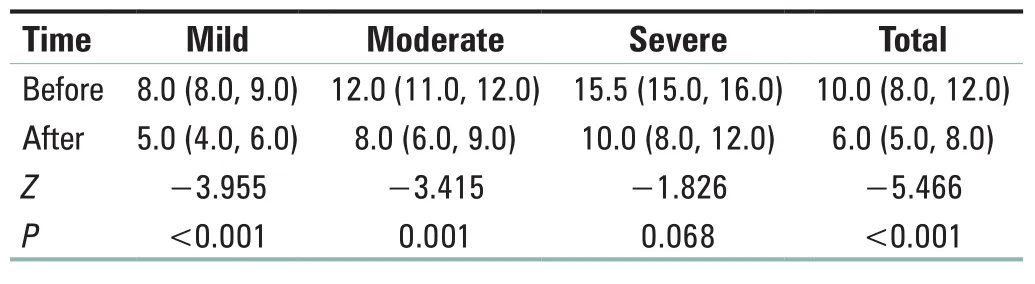
Table 1: Comparison of Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale score of anxiety patients before and after exercise

Table 2: Comparison of Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale depression score of patients before and after exercise
DISCUSSION
Anxiety and depression patients, as a special group, suffer from illness pain physically, while their psychology will also be affected to varying degrees. In the face of enormous disease, many patients will have serious psychosocial problems. As far as the spectrum of psychiatric disorders is concerned, the most common symptoms are depression,anxiety and somatization.[14]According to the theory of TCM,abnormal mood can cause diseases by injuring Zang and Fu organs, making qi-movement disturbance and qi-blood imbalance.[15,16]They can interact with each other and form a vicious circle in the course of disease. Therefore, it is of great significance to explore effective interventions to improve the anxiety and depression status of hospitalized patients.
Mechanism of five-animal frolics
Five-animal frolics is created by imitating the morphology of five kinds of animals, tiger, deer, bear, ape, and bird,combined with the health-preserving thought. This study shows that five-animal frolics exercise can reduce anxiety and depression in hospitalized patients. From the perspective of TCM theory,[17]the attribute of tiger play is fire, representing the heart. Tiger play can make the bones firm and strong,the spirit full and relaxed, the Qi and blood harmonized, and the meridians unobstructed. The attribute of deer play is wood, representing the liver. The deer play takes briskness as its main purpose to make the body and mind active and the mood happy. And it can strengthen the bones and muscles, purge the liver fire, and replenish the essence of Qi to the brain to relieve pressure. The attribute of bear play is earth, representing the spleen. Bear play can converge Yang Qi, strengthen the gallbladder and invigorate the spleen,ventilate blood smoothly and energetically to regulate mood.The attribute of ape play is metal, representing the lung.The ape play can stretch the bones and muscles, strengthen the waist and kidney, so as to promote Yang Qi and achieve the effect of regulating mood. The attribute of bird play is water, representing the kidney. Bird play has the effect of calming the mind, nourishing Yin and blood. In TCM, one with calming and peaceful mind is full of Qi, enough Qi can generate essence, enough essence cause vigorous spirit, thus making one peaceful in return.
Research and analysis of modern medicine on five-animal frolics
From the perspective of modern medical theory, five-Animal frolics can not only fully stretch body, but also relax mental consciousness, once the cerebral cortical cells get rest, the brain cells are more active. By regulating nerve-body fluids,the tension of sympathetic nervous system can be reduced,therefore the mood gets improved.[18]Studies have confirmed that the prefrontal and hippocampal regions of the brain are closely related to cognitive function and emotional control.[19,20]The changes of N-acetylaspartate (NAA), creatine-phosphate creatine complex (Cr), choline complex (Cho) values may be related to the occurrence of depression, and the changes of their relative content can reduce the occurrence of depression.The study of Chenget al.[21]showed that by observing the effect of 12-week fitness Qigong and five-animal frolics on mild depression, it was found that five-animal frolics could improve the ratio of NAA/Cr, the ratio of Cho/Cr and other metabolic indicators in human prefrontal lobe and hippocampus.Foreign and Chinese Taiwanese scholars have shown through systematic research that Qigong exercise can change the frequency of human brain waves.[22]From the presented data of α and β waves, it is found that Qigong exercise is superior to the control group in both “relaxation” and “positive emotions.”From the perspective of movement theory, the exercise of five-animal frolics should be combined with “shape, spirit, mind and Qi.” When the body is in a highly concentrated state, the brain will form dominant excitation foci, effectively inhibiting the introduction of other adverse information. Therefore,five-animal frolics exercise can enhance the positive mood to reduce the degree of anxiety and depression.
There are some limitations in this study. The type of the study belongs to the self-controlled trial. The decrease in hospitalization rate of patients affected by COVID-19 pandemic, as well as the more bedridden and braked patients,led to the collection of fewer samples. In the future, we need to expand the sample size and carry out randomized controlled trials to verify the results again.
CONCLUSION
In summary, five-animal frolics can decrease anxiety and depression of hospitalized patients, and it is easy to learn and good for physical fitness. In addition, it can be used as an effective intervention in regulating mood and promoting the rehabilitation.
Declaration of patient consent
The informed consent has been obtained from all patients included in this study. In the form the patients have given their consent for clinical information to be reported in the journal. The patients understand that their names and initials will not be published and due efforts will be made to conceal their identity, but anonymity cannot be guaranteed.
Financial support and sponsorship
This work was supported by Changping District Health Science and Technology Development special funds (No.2018-4-08) and Beijing Changping Nankou Hospital.
Con flicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
杂志排行
Journal of Integrative Nursing的其它文章
- Correlation between psychological factors and the expression of galanin and 5-hydroxytryptamine in different subtypes of gastroesophageal re flux disease
- Mediating effect of undergraduate nursing students’professional commitment on positive psychological capital and learning burnout
- Scienti fic publications in nursing journals from East Asia:A survey of literature
- The impacts of resilience on the association between illness uncertainty and sleep quality among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Effect of health locus of control on the quality of life among hemodialysis patients
- lmproving the delivery of medical education in rural medical colleges
