Curling ulcer in the setting of severe sunburn: A case report
2021-01-11AlexanderSchosheimMichelleTobinAnupamaChawla
Alexander Schosheim, Michelle Tobin, Anupama Chawla
Abstract BACKGROUND While sunburns are very common, especially in pediatrics, curling ulcers secondary to sunburns are a very rare entity that has not been noted in the literature in over fifty years. This case is the first addition to the literature since the originally documented case.CASE SUMMARY A previously healthy 17 year old male presents to the emergency room with lethargy, shortness of breath on exertion, dark stools and nausea. His fatigue started to become significantly worse four days prior to admission.Approximately two weeks prior to admission, the patient was on a beach vacation with his family at which time he suffered severe sunburns. He had developed crampy epigastric abdominal pain, which was followed by dark, loose stools. On exam, he is non-toxic appearing, but with pallor and peeling skin on his face and chest with epigastric tenderness. Infectious stool studies were all negative including Helicobacter pylori. He denies use of any non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and also denies alcohol or recreational drug use. While admitted he is found to be significantly anemic with his hemoglobin as low as 6.3 requiring two units of packed red blood cells. Endoscopy revealed several severe and deep ulcerations in the antrum and body of the stomach indicative of stress or curling ulcers.CONCLUSION While the incidence of stress ulcers is not known, it is most common with severe acute illness, most commonly presenting as upper gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding.It is essential to be aware of the risk of curling ulcers secondary to severe sunburns as patients with stress ulcer GI bleeding have increased morbidity and mortality compared to those who do not have GI bleed.
Key Words: Curling ulcer; Sunburn; Stress ulcer; Pediatrics; Gastroenterology;Gastrointestinal bleed; Case report
INTRODUCTION
Stress ulcers are a well-known clinical entity with various findings ranging from asymptomatic superficial lesions and occult gastrointestinal (GI) bleed to overt clinically significant GI bleeding. It is thought that this is typically due to gastric and sometimes esophageal or duodenal mucosal barrier is disruption. When the etiology of the stress ulcer is a burn, they are characterized as curling ulcers. Most cases of curling ulcers in the current literature are secondary to severe systemic burns and although rare, there was one previous case report of curling ulcer secondary to sunburn.
CASE PRESENTATION
Chief complaints
A previously healthy 17 year old male presented to Stony Brook University Hospital from an outside hospital with lethargy, shortness of breath on exertion, dark stools and nausea.
History of present illness
The patient's fatigue had become significantly worse for four days prior to admission.Approximately two weeks prior to admission, the patient was on a beach vacation with his family at which time he suffered severe sunburns. He had developed crampy epigastric abdominal pain that was followed by dark, loose stools.
History of past illness
He has no significant past medical history.
Personal and family history
He and his family have no significant history.
Physical examination
On physical exam, he was pale and tired-appearing with epigastric tenderness.
Laboratory examinations
Infectious stool studies were all negative includingHis complete blood count revealed that he was significantly anemic with a hemoglobin of 6.3 and his complete metabolic panel was within normal limits.
Imaging examinations
No imaging was performed.
Further hospital course
Endoscopy was performed and revealed severe, deep ulcerations in the antrum and body of the stomach (Figure 1).
FINAL DIAGNOSIS
Curling ulcers in the antrum.
TREATMENT
The patient was treated with high dose proton-pump inhibitor and carafate along with iron and folate supplementation.
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
With time, the patient’s symptoms and blood work improved. Five months after his original admission, endoscopy was performed and all previous areas of ulceration had completely resolved.
DISCUSSION
While the incidence of stress ulcers is not known, it typically occurs with severe acute illness, most commonly presenting as upper GI bleeding. Although stress ulcers can lead to perforation, it is very rare with less than 1% incidence. An impaired mucosal barrier where the mucosal glycoprotein breaks down due to increased concentrations of refluxed bile salts or uremic toxins in the setting of critical illness may be the possible pathologic changes that lead to ulceration. Increased secretion of gastric acid secondary to higher secretion of gastrin during stress is likely as well.
CONCLUSION
Curling ulcers secondary to sunburns are a previously described phenomenon, but it is a rare entity that has not been noted in the literature in over fifty years. It is essential to be aware of the risk of curling ulcers secondary to severe sunburns as patients with stress ulcer GI bleeding have increased morbidity and mortality when compared to those without GI bleed.
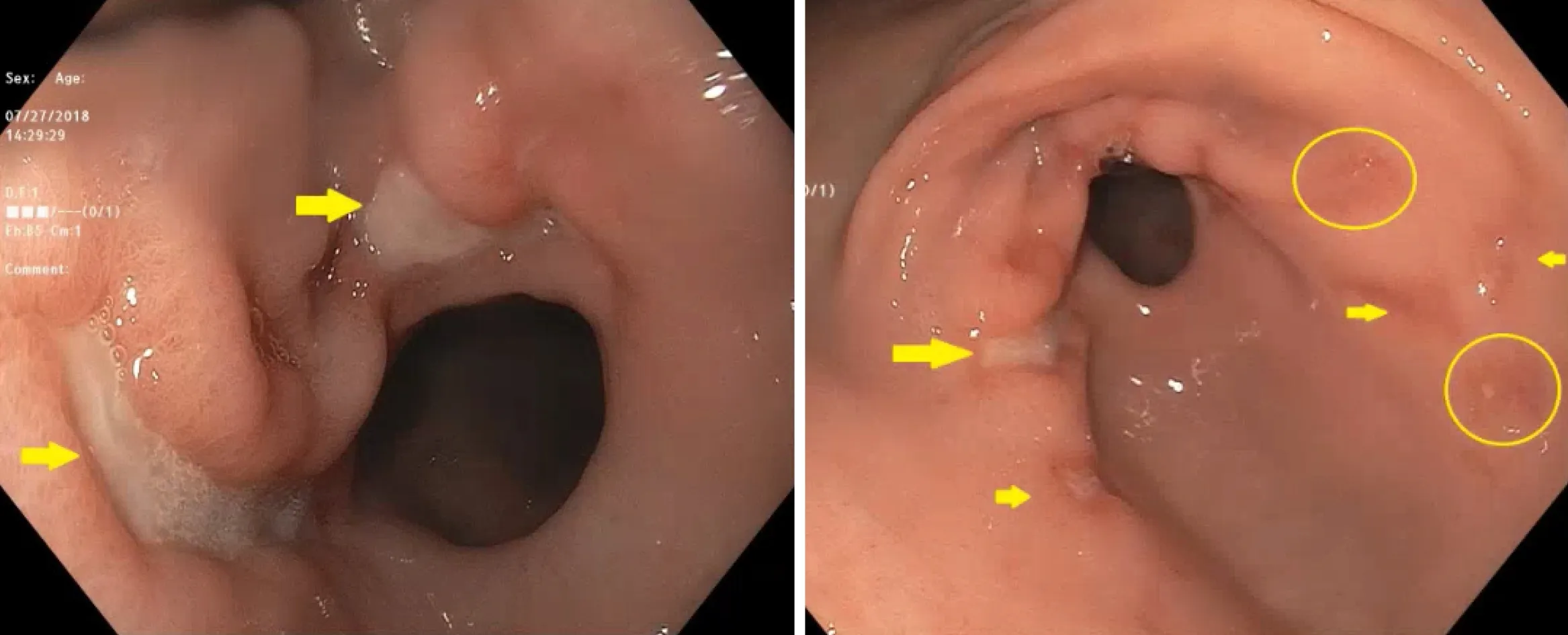
Figure 1 Deep ulcerations in the antrum of the stomach.
杂志排行
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy的其它文章
- Anticoagulation and antiplatelet management in gastrointestinal endoscopy: A review of current evidence
- Peroral traction-assisted natural orifice trans-anal flexible endoscopic rectosigmoidectomy followed by intracorporeal colorectal anastomosis in a live porcine model
- Evaluation of the diagnostic and therapeutic utility of retrograde through-the-scope balloon enteroscopy and single-balloon enteroscopy
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug effectivity in preventing post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Endoscopic ultrasound-guided gallbladder drainage in pancreatic cancer and cholangitis: A case report
- Preemptive endoluminal vacuum therapy after pancreaticoduodenectomy: A case report
