Long noncoding RNA HAND2-AS1 re duce d the viability of hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting microRNA-300/SOCS5 axis
2021-01-07HuaQiangBiZhongHuiLiHuiZhang
Hua-Qiang Bi , Zhong-Hui Li , Hui Zhang
a Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Third Military Medical University (Army Medical University), Chongqing 40 0 038, China
b Department of Radiology, First Affiliated Hospital of Third Military Medical University (Army Medical University), Chongqing 40 0 038, China
c Department of Vascular Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Third Military Medical University (Army Medical University), Chongqing 40 0 038, China
Keywords:Hepatocellular carcinoma Cell survival Heart and neural crest derivatives expressed 2 anti-sense 1 microRNA-300 Suppressor of cytokine signaling 5
A B S T R A C T Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most prevalent human cancers with high mortality. Long non-coding RNA heart and neural crest derivatives expressed 2 anti-sense 1 (HAND2-AS1) is down-regulated in several cancers including HCC, yet the precise mechanisms how HAND2-AS1 regulates cell survival in HCC remains poorly understood.Methods: The expression levels of HAND2-AS1 and miR-300 were measured using quantitative real-time PCR. The protein levels of suppressor of cytokine signaling 5 (SOCS5), Bcl-2, Bax and cleaved caspase-3 were determined by Western blot. Cell viability and cell proliferation were assessed using cell counting kit-8 and clone formation assay, respectively. Cell apoptosis was detected using flow cytometry. The interactions between HAND2-AS1 and miR-300, miR-300 and SOCS5 were validated using luciferase reporter assay.Results: HAND2-AS1 was down-regulated in HCC tissues and cell lines, and the expression level of HAND2-AS1 was positively correlated to patient survival. HAND2-AS1 over-expression reduced viability and proliferation in HCC cells. Elevated HAND2-AS1 level induced apoptosis in HCC cells, accompanied with increased Bax and cleaved caspase-3 levels and decreased Bcl-2 level. We also validated that HAND2-AS1 acted as a sponge of miR-300, and there was a negative correlation between expression levels of HAND2-AS1 and miR-300 in HCC tissues. Furthermore, we found that SOCS5 was a downstream target of miR-300. In addition, miR-300 mimics abolished HAND2-AS1-mediated inhibition of cell viability and proliferation. miR-300 mimics also reversed the HAND2-AS1-induced apoptosis in HCC cells.Conclusion: lncRNA HAND2-AS1 inhibits proliferation in HCC through regulating miR-300/SOCS5 axis.© 2020 First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine in China. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), accounting for more than 90%of primary liver cancer, remains one of the most common and frequent causes of cancer-related death worldwide [1] . HCC is a heterogeneous malignancy which makes the treatment of HCC multidisciplinary and extraordinary difficult. HCC patients are usually diagnosed at advanced tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stages which left them with very limited treatment options, and the five-year survi val rate is unsatisfactory [2] . The most worrisome risk factors for HCC are exposure to hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) and heavy alcohol intake. Besides, type 2 diabetes and obesity are emerging as critical pathogenic factors for hepatocellular carcinogenesis and are responsible for the steadily increase of HCC incidence in recent decades [3] . Therefore, a better understanding of pathogenesis and searching for novel targets for diagnosis and treatment of HCC are of great importance.
About 90% of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the human genome are located in noncoding regions. Noncoding RNAs, including long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) and microRNAs,are emerging as crucial regulators in a variety of cellular processes [4] . LncRNAs are a group of conserved noncoding RNAs longer than 200 nucleotides which are implicated in diverse physiology processes such as cell death, cell differentiation and tumorigenesis [5] . LncRNA heart and neural crest derivatives expressed 2 anti-sense 1 (HAND2-AS1) was found to be downregulated in HCC by Yang et al. in 2017. And the aberrant expression of HAND2-AS1 is predicted to be associated with tumorigenesis, metastasis and angiogenesis in HCC [6] . Yet the role that lncRNA HAND2-AS1 plays in the HCC cell lines remains elusive. microRNAs are endogenous RNAs ranging from 18 to 25 nucleotides which are evolutionarily conserved among species. microRNAs play key roles in cell proliferation, cell apoptosis and metastasis via binding to their complementary sequence of target molecules, and further induce RNA degradation or translational inhibition [7 , 8] .Recent studies demonstrated that miR-300 is implicated in cell proliferation, cell migration, cell invasion and metastasis in several cancers including glioblastoma, breast cancer and HCC [9-11] .
In the present study, we detected the expression of HAND2-AS1 in HCC tissues and HCC cell lines. We also investigated the impact of HAND2-AS1 expression on proliferation and apoptosis in HCC cell. Furthermore, HAND2-AS1 was predicted as a sponge of miR-300, thus we validated their interaction and explored their regulatory effect on survival of HCC cells. Our study might provide a novel therapeutic target for HCC treatment.
Methods
Clinical samples
Surgical tissues were collected from 50 patients without preoperative therapy at the First Affiliated Hospital of Third Military Medical University (Army Medical University). We collected 50 HCC tissues and 50 adjacent non-tumor liver tissues in this study with the consent of patients. All relative experiments were performed according to the ethical guidelines oftheDeclarationof Helsinkiand approved by Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Third Military Medical University (Army Medical University) (Approval No. 2016001).
Cell culture and transfection
HEK-293T cell line, normal liver cell line HL-7702 and HCC cell lines Huh-6, Huh-7 and SK-HEP-1 were obtained from Procell(Wuhan China) and cultured following the provider’s instruction.LncRNA HAND2-AS1 was cloned into pcDNA3.1 between BamH I and Xho I for over-expression. Cells were transfected with plasmids or miR-300 mimics using lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen, California, USA) following the manufactures’ instruction [12] .
Quantitative real-time PCR
Total RNAs of patient samples and HCC cell lines were extracted using trizol reagent (Beyotime, Shanghai China) and reversely tran-scribed using SuperScript IV (ThermoFisher, Massachusetts, USA).Relative expression levels of HAND2-AS1, miR-300 and suppressor of cytokine signaling 5 (SOCS5) were examined using SYBR Green and real-time PCR data was analyzed by the 2-△△CTmethod. Small nuclear RNA RNU6B was used as internal control for miR-300, and GAPDH was used as control for lncRNA HAND2-AS1 and SOCS5.Real-time primers used in this study were shown in Table 1 .

Table 1 Primer sequence.
Cell counting kit-8
Huh7 and SK-HEP-1 showed relative lower HAND2-AS1 level,thus they were chosen for subsequent investigations. Huh7 and SKHEP-1 cells were seeded into 96-well plate and cultured for 24 h(5 × 103cells/well). Cells were then transfected with plasmids or miR-300 mimics and cell proliferation was detected at 1 day, 2 days, 3 days and 4 days after transfection. Cells were incubated with 10 μL CCK-8 (Solarbio, Beijing, China) reagent for 4 h and optical density values at 450 nm were detected using a microplate reader.
Clone formation assay
Huh7 and SK-HEP-1 cells were seeded into a 6-well plate (10 0 0 cells/well) and transfected with plasmids or miR-300 mimics. Then cells were cultured in a culture chamber until confluency. After rinsing with phosphate buffer saline (PBS) buffer for twice, cells were fixed with 5 mL methanol and stained with Giemsa (Beyotime) for 30 min, followed by cell clone counting under a microscope.
Apoptosis detection
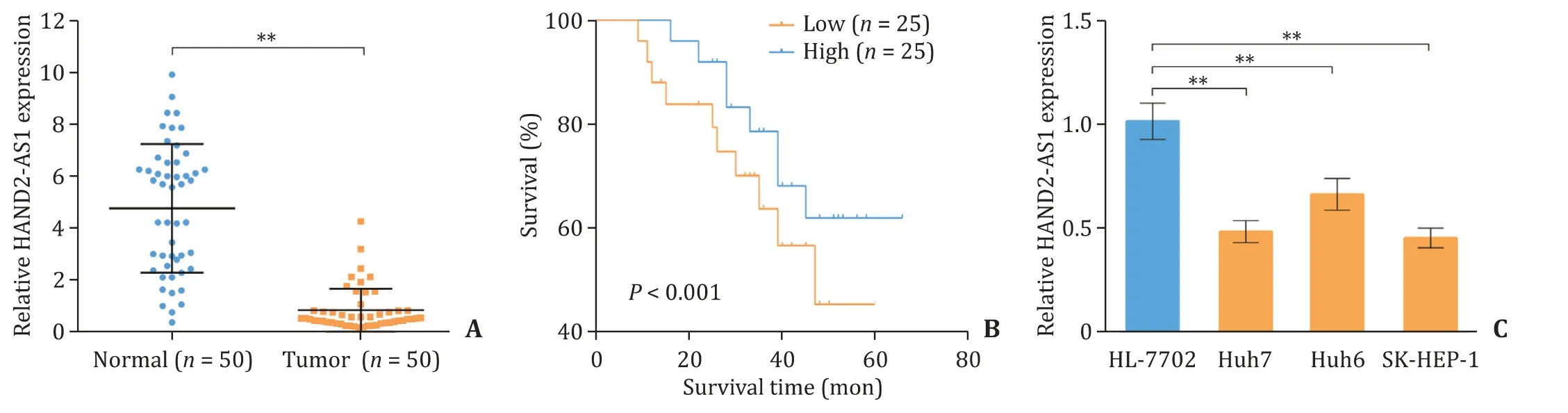
Fig. 1. LncRNA HAND2-AS1 is down-regulated in liver cancer tissues and cell lines. A: The relative mRNA level of HAND2-AS1 in 50 liver cancer tissues and 50 normal liver tissues measured by quantitative real-time PCR; B: The relationship between HAND2-AS1 expression level and the survival of patients; C: The relative mRNA level of HAND2-AS1 in normal liver cell line HL-7702 and liver cancer cell lines Huh7, Huh6 and SK-HEP-1 determined using quantitative real-time PCR. **: P < 0.01. HAND2-AS1:heart and neural crest derivatives expressed 2 anti-sense 1.
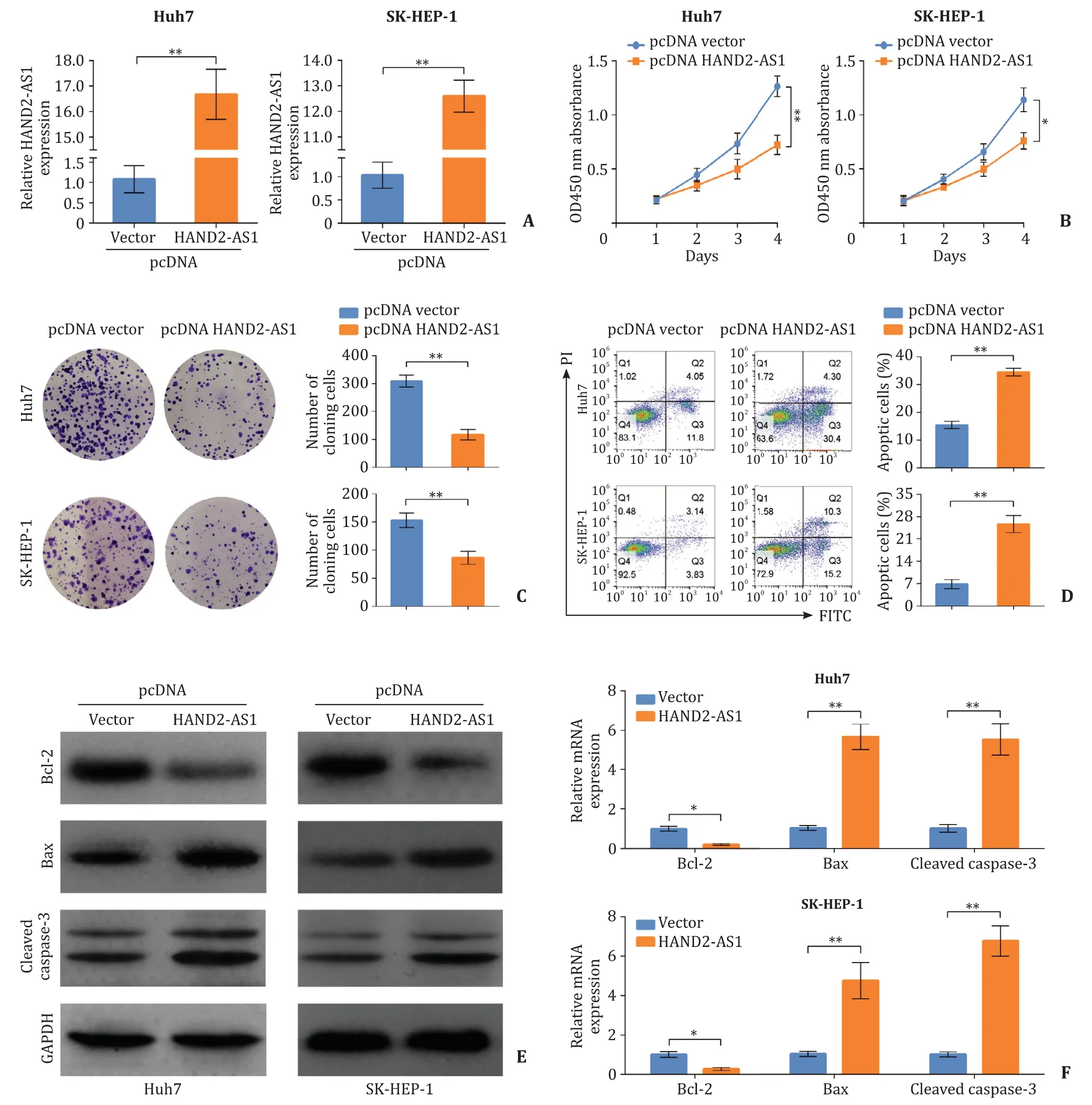
Fig. 2. LncRNA HAND2-AS1 over-expression reduces the proliferation of HCC cells. HAND2-AS1 was cloned into pcDNA3.1 for over-expression and transfected into Huh7 and SK-HEP-1 cells. A: The over-expression of HAND2-AS1 in Huh7 and SK-HEP-1 cells examined using quantitative real-time PCR; B: Cell counting kit-8 performed to assess the cell viability after HAND2-AS1 over-expression; C: Proliferative capacity of Huh7 and SK-HEP-1 cells evaluated using clone formation assay; D: Apoptosis in Huh7 and SK-HEP-1 cells after HAND2-AS1 over-expression detected using flow cytometry; E: The protein levels of Bcl-2, Bax and cleaved caspase-3 in Huh7 and SK-HEP-1 cells were determined by Western blot; F : The mRNA levels of Bcl-2, Bax and cleaved caspase-3 in Huh7 and SK-HEP-1 cells detected using quantitative real-time PCR. *: P < 0.05; **:P < 0.01. HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; HAND2-AS1: heart and neural crest derivatives expressed 2 anti-sense 1.
Cell apoptosis was detected using flow cytometry. Huh7 and SK-HEP-1 cells were harvested and stained using a commercial Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit (Beyotime). In brief, cells were suspended with 195 μL binding buffer, stained with 5 μL Annexin V-FITC and 10 μL propidium iodide for 15 min away from light. Then cell apoptosis was detected using a flow cytometry.
Western blot
Huh7 and SK-HEP-1 cells were transfected with plasmids or miR-300 mimics. Cells were lysed using RIPA buffer (CST, Boston,USA) and supernatant proteins were collected after centrifugation.Proteins were quantified and fractionated using the sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Proteins were then transferred onto a polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane (Millipore, Massachusetts, USA), blocked with skim milk and incubated with primary antibodies at 4 °C overnight. After rinsing with PBS buffer, the PVDF membrane was incubated with secondary antibodies and visualized using electrochemiluminescence (ECL) reagent (Solarbio). Bcl-2 mouse antibody (1:30 0 0,Proteintech, Wuhan, China), Bax antibody (1:50 0 0, Proteintech),cleaved caspase-3 mouse antibodies (1:10 0 0, CST), SOCS5 rabbit antibody (1:10 0 0, Abcam, Cambridge, USA) and GAPDH mouse antibody (1:10 0 0 0, Proteintech) were used as primary antibodies.HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG and HRP-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (1:30 0 0, Proteintech) were used as secondary antibodies.
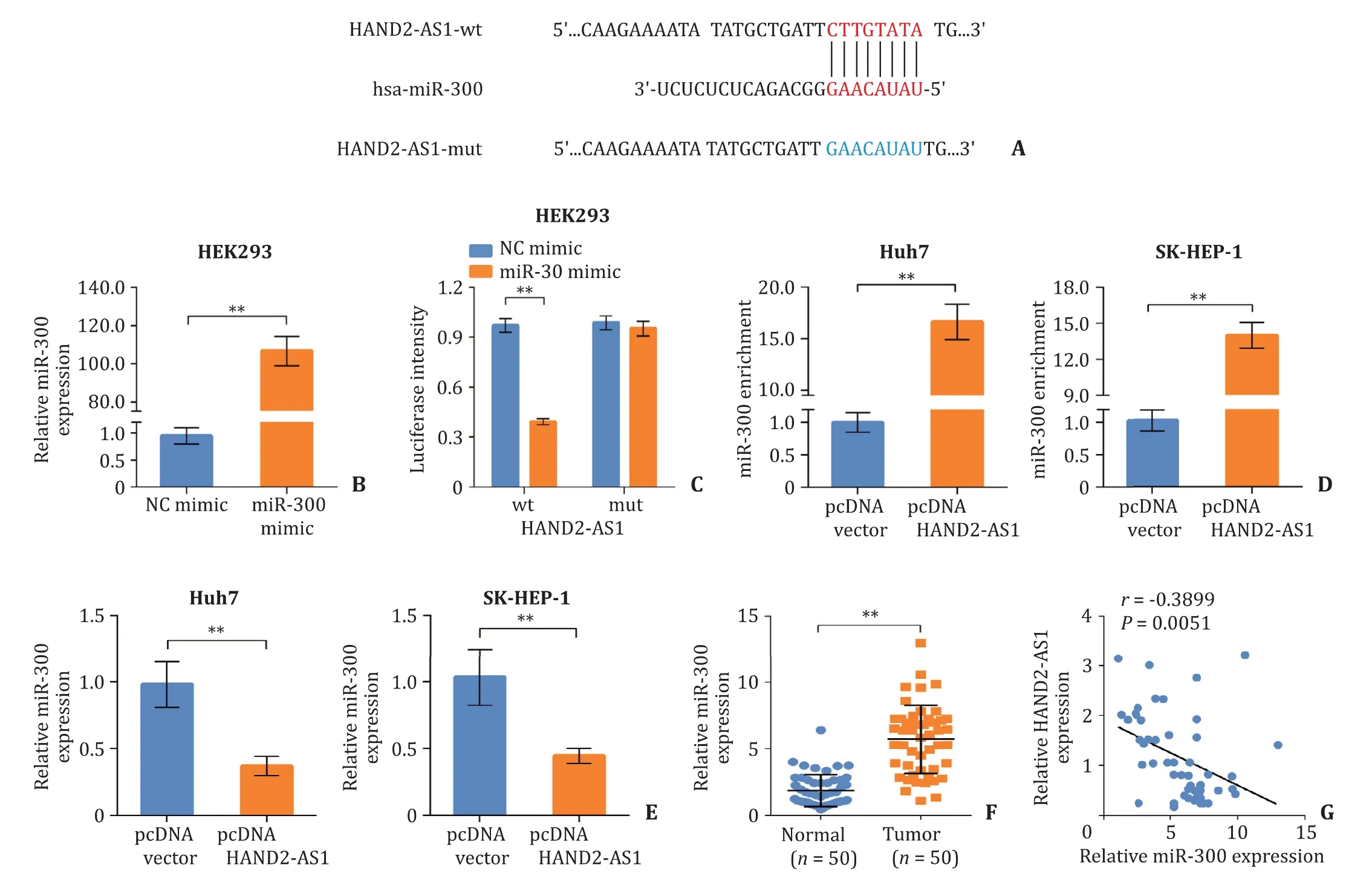
Fig. 3. LncRNA HAND2-AS1 acts as a sponge of miR-300. A: The binding site of miR-300 on HAND2-AS1; B: The efficiency of miR-300 mimics measured using quantitative real-time PCR; C: The interaction between HAND2-AS1 and miR-300 validated by dual-luciferase assay; D: The enrichment of miR-300 in Huh7 and SK-HEP-1 cells after HAND2-AS1 over-expression evaluated using RNA pull down; E: Relative expression level of miR-300 in Huh7 and SK-HEP-1 cells after HAND2-AS1 over-expression measured by quantitative real-time PCR; F: Relative expression level of miR-300 in liver cancer tissues and normal liver tissues determined by quantitative real-time PCR; G: The negative correlation between the expression of HAND2-AS1 and miR-300 in liver cancer tissues. **: P < 0.01. HAND2-AS1: heart and neural crest derivatives expressed 2 anti-sense 1.
Dual-luciferase assay
The wild type and mutant type of lncRNA HAND2-AS1 and SOCS5 were amplified by PCR, and cloned into pmirGLO (Promega,Wisconsin, USA). HEK-293T cells were co-transfected with pmir-GLO plasmids and miR-300/negative control mimics. Luciferase activity was assessed using a commercial luciferase reporter assay kit(Keygen, China) following the manufactures’ protocol.
RNA pull down
Huh7 and SK-HEP-1 cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1-HAND2-AS1 or vehicle, and lysed 48 h after transfection. LncRNA HAND2-AS1 was labelled using biotinylated oligonucleotide probes and incubated with magnetic streptavidin beads (Invitrogen) containing RNase inhibitor solution overnight. Beads were separated from cell lysate using a magnet and incubated with Proteinase-k(Beyotime). Then beads were washed and purified RNAs were detected using quantitative real-time PCR.
Statistical analysis
All experiments in this study were repeated at least three times.Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD). All data analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 7 or SPSS 19.0.Mean values were analyzed with Student’st-test (two groups) or one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) (three or more groups). Results of cell counting kit-8 and dual-luciferase assays were analyzed with two-way ANOVA. The relationship between HAND2-AS1 expression and patients’ survival time was analyzed using Kaplan-Meier method. APvalue<0.05 was regarded statistically significant.
Results
LncRNA HAND2-AS1 is down-regulated in liver cancer tissues and cell lines
We detected the expression level of lncRNA HAND2-AS1 in 50 liver cancer tissues and 50 adjacent non-tumor liver tissues, and a significantly lower HAND2-AS1 level was observed in liver cancer tissues ( Fig. 1 A). Moreover, patients with relative lower HAND2-AS1 expression than median HAND2-AS1 level of 0.53 showed shorter survival time ( Fig. 1 B). We further detected the mRNA level of HAND2-AS1 in normal liver cell line HL-7702 and three liver cancer cell lines. Huh7, Huh6 and SK-HEP-1 cells showed significantly lower HAND2-AS1 expression ( Fig. 1 C).
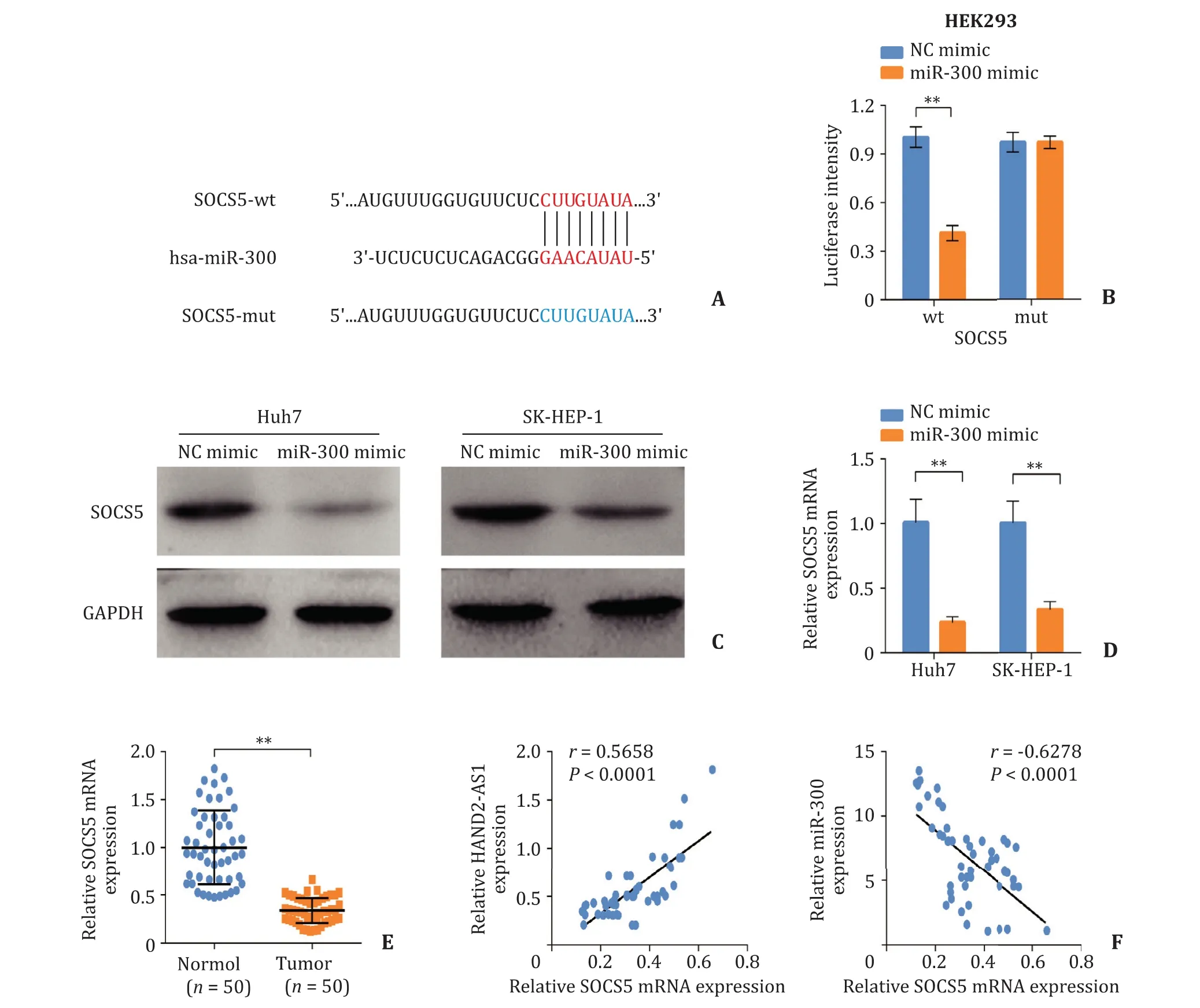
Fig. 4. SOCS5 acts as a downstream target of miR-300. A: The binding site of miR-300 on SOCS5; B: Dual-luciferase assay performed to validate the interaction between HAND2-AS1 and miR-300; C and D: The expression level of SOCS5 in Huh7 and SK-HEP-1 cells after miR-300 mimics transfection determined by Western blot and quantitative real-time PCR; E: The relative mRNA level of SOCS5 in liver cancer tissues and normal liver tissues measured using quantitative real-time PCR; F: The correlation between SOCS5 and HAND2-AS1 or miR-300 in liver cancer tissues. **: P < 0.01. WT: wildtype; MUT: mutant type; SOCS5: suppressor of cytokine signaling 5.
LncRNA HAND2-AS1 over-expression inhibits the proliferation in HCC
We transfected pcDNA3.1-HAND2-AS1 into Huh7 and SK-HEP-1 cells for over-expression, and a significantly elevated mRNA level of HAND2-AS1 was observed ( Fig. 2 A). Cell counting kit-8 revealed that viability of Huh7 and SK-HEP-1 cells was decreased after HAND2-AS1 over-expression ( Fig. 2 B). Proliferation of Huh7 and SK-HEP-1 cells was also significantly inhibited by HAND2-AS1 over-expression ( Fig. 2 C). Further apoptosis detection by flow cytometry showed that HAND2-AS1 over-expression significantly induced apoptosis of Huh7 and SK-HEP-1 cells, accompanied with decreased Bcl-2 expression and increased Bax and cleaved caspase-3 expression at both mRNA and protein levels ( Fig. 2 D-F).
LncRNA HAND2-AS1 acts as a sponge of miR-300
LncRNA HAND2-AS1 was predicted as a decoy of miR-300 on miRDB ( http://www.mirdb.org/ ). Dual-luciferase assay was performed to validate the interaction between HAND2-AS1 and miR-300, and putative binding site was shown in Fig. 3 A. miR-300 mimics transfection significantly increased the expression level of miR-300 in HEK293 cells ( Fig. 3 B). miR-300 mimics significantly inhibited the luciferase activity in the wild type HAND2-AS1 group,but had no notable effect on the mutant type HAND2-AS1 group( Fig. 3 C). Furthermore, RNA pull down showed that enriched miR-300 was significantly increased after pcDNA3.1-HAND2-AS1 transfection ( Fig. 3 D). The expression level of miR-300 in Huh7 and SK-HEP-1 cells was decreased after HAND2-AS1 over-expression( Fig. 3 E). In addition, the expression of miR-300 was up-regulated in liver cancer tissues, which was negatively correlated to that of HAND2-AS1 ( Fig. 3 F, G). Our results indicated that lncRNA HAND2-AS1 act s as a sponge of miR-300.
SOCS5 acts as a downstream target of miR-300
The binding site of miR-300 on SOCS5 was displayed in Fig. 4 A.miR-300 mimics notably suppressed the luciferase activity of SOCS5-WT 3 ′ -UTR, yet had no significant effect on the SOCS5-MUT 3 ′ -UTR ( Fig. 4 B). The expression of SOCS5 in Huh7 and SK-HEP-1 cells was significantly reduced at both mRNA and protein levels after miR-300 mimics transfection ( Fig. 4 C, D). Moreover, the mRNA level of SOCS5 was significantly decreased in liver cancer tissues compared with normal control ( Fig. 4 E). The expression of SOCS5 was positively correlated to HAND2-AS1 level but negatively correlated to that of miR-300 ( Fig. 4 F). These results revealed that SOCS5 acts as a downstream target of miR-300.
LncRNA HAND2-AS1 reduced the viability in HCC through regulating miR-300/SOCS5 axis
Huh7 and SK-HEP-1 cells were co-transfected with pcDNA3.1-HAND2-AS1 and miR-300 mimics. HAND2-AS1 reduced the viability of Huh7 and SK-HEP-1 cells, which was further reversed by miR-300 mimics ( Fig. 5 A). The proliferation of Huh7 and SKHEP-1 cells was inhibited by HAND2-AS1 over-expression, which was abolished by further miR-300 mimics transfection ( Fig. 5 B).HAND2-AS1 significantly promoted the apoptosis of Huh7 and SKHEP-1 cells, which was further abrogated by miR-300 ( Fig. 5 C).In addition, HAND2-AS1 increased the expression of SOCS5, Bax and cleaved caspase-3 at both mRNA and protein levels, which was reversed after miR-300 mimics transfection. The expression of Bcl-2 showed the opposite trend in Huh7 and SK-HEP-1 cells( Fig. 5 D, E). Our results indicated that lncRNA HAND2-AS1 reduced the viability of HCC cell lines through regulating miR-300/SOCS5 axis.
Discussion
More than eight thousand lncRNAs are aberrantly expressed and involved in the development of HCC, yet only approximately nine hundred were annotated by references [6] . LncRNA HAND2-AS1 was first discovered by Yang et al. in 2017, since then it was identified in various malignancies. HAND2-AS1 is down-regulated in endometrioid endometrial carcinoma (EEC) tissues and HAND2-AS1 over-expression suppressed the progression of EEC. HAND2-AS1 expression level is closely related to clinical outcomes of EEC including tumor grade, metastasis and recurrence [13] .HAND2-AS1 also has a lower expression in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and HAND2-AS1 interacts with transforming growth factorβ(TGF-β) to further modulate the migration and invasion in NSCLC cells [14] . The present study found that lncRNA HAND2-AS1 was significantly down-regulated in both HCC tissues and HCC cells, and the survival of HCC patients was positively correlated to HAND2-AS1 level. Moreover, we first found that HAND2-AS1 over-expression inhibited the viability and proliferation in HCC cells. Elevated HAND2-AS1 expression also elevated the pro-apoptotic Bax level but decreased the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 level, which further promoted cytochrome C release and eventually caspase-3 activation. These findings indicated that HAND2-AS1 induces HCC apoptosis through mitochondria-initiated intrinsic pathway [15] .
Since Salmena et al. proposed the "competing endogenous RNA"(ceRNA) hypothesis in 2011, the sponging effect of lncRNAs on microRNAs are attracting increasing attention [16] . LncRNA HAND2-AS1 is implicated in several human cancers via sponging different microRNAs, which refers to that HAND-AS1 binds to microRNAs, reduces the microRNAs amount and attenuates their function [17] . HAND2-AS1 inhibits the progression of colorectal cancer by sponging miR-1275 and further elevates the expression of its target Kruppel like factor 14 (KLF14) [18] . HAND2-AS1 exerts its anti-oncogenic effects in esophagus squamous cell carcinoma through sponging microRNA-21 [19] . HAND2-AS1 also reduces cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in chronic myeloid leukemia cells via regulating micRNA-1275 [20] . In this study, we first discovered a novel interaction between lncRNA HAND2-AS1 and miR-300 in HCC. The expression level of HAND2-AS1 is negatively correlated to that of miR-300 in both HCC tissues and cells, and further luciferase reporter assay validated their interaction. Moreover,miR-300 mimics abolished the HAND2-AS1-induced cell proliferative inhibition and cell apoptosis. miR-300 was reported to be a tumor promoter in liver cancer via facilitating proliferation, invasion, epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis [ 11 , 21 , 22 ].Therefore, our findings demonstrated that HAND2-AS1 reduced the viability of HCC cells by regulating miR-300.
In addition, we found that SOCS5, one of the negative regulators of JAK/STAT signaling, was a downstream target of miR-300. The expression of SOCS5 is negatively correlated to miR-300 level but positively correlated to HAND2-AS1 level. SOCS5 exerts its antitumor function in several cancers and is regulated by different microRNAs. miR-301a enhances invasion and metastasis in pancreatic cancer via regulating SOCS5 [23] . miR-589-5p inhibits the expression of SOCS5 to activate the JAK/STAT signaling and further maintains the stemness in HCC [24] . Furthermore, SOCS5 acts as a target of miR-18a and miR-25, which enhance the tumorigenic properties in HCC [25] . These previous researches imply us that miR-300/SOCS5 is a novel regulatory axis in the survival of HCC, and we will consummate our study by over-expressing SOCS5 to investigate its role in the progression of HCC.
In conclusion, our findings demonstrated that lncRNA HAND2-AS1 reduces the viability of HCC via targeting the miR-300/SOCS5 axis, and this regulatory axis might be a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of HCC.
Acknowledgments
None.
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Hua-Qiang Bi:Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing - original draft.Zhong-Hui Li:Methodology, Writing - original draft.Hui Zhang:Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing - review & editing.
Funding
None.
Ethical approval
All relative experiments were performed according to the ethical guidelines oftheDeclarationofHelsinkiand approved by Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Third Military Medical University (Army Medical University) (Approval no. 2016001).
Competing interest
No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
杂志排行
Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International的其它文章
- Non-operative management of pancreatic trauma in adults
- Serum non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level is increased in Chinese patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Increased CMTM4 mRNA expression predicts a poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
- Folfirinox chemotherapy prolongs stent patency in patients with malignant biliary obstruction due to unresectable pancreatic cancer
- Role of phosphorylated Smad3 signal components in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of pancreas ✩
- Diagnostic accuracy of administrative database for bile duct cancer by ICD-10 code in a tertiary institute in Korea
