法尼醇X受体(FXR)在药源性胆汁淤积型肝损伤中的作用
2020-10-14陆远富
冯 红,陆远富
(遵义医科大学 基础药理教育部重点实验室暨特色民族药教育部国际合作联合实验室,贵州 遵义 563099)
The farnesoid X receptor (FXR) is a highly specific bile acid receptor that plays an important feature in bile acid metabolism[1],and is highly expressed in the liver and ileum.Assuredly,previous results suggested that FXR deletion results in juvenile onset cholestasis[2]and progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis[3].
Some researchers have shown that drugs,especially Chinese herbal medicine cause liver damage either in a dose-dependent or idiosyncratic manner.In most cases,recovery is seen immediately after withdrawal of the drug,however,some cases may develop to become chronic cholestasis[4].Cholestasis is associated with bile acid dysmetabolism,the main form of drug-induced liver injury which has an increasing incidence[5].Unfortunately,drug-induced cholestasis liver injury (DIC) is often neglected in clinical practice,due to the lack of no gold standard for diagnosis.Altered FXR signaling is commonly involved in the process of bile acid related diseases.Thus,we summarized the roles of FXR in DIC and FXR as a protective factor in DIC.
1 Bile acid and drug-induced cholestatic liver injury
1.1 Bile acid and liver injury Bile acid is a molecule with the characteristics of hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity,as it contains both hydrophilic hydroxyl and carboxyl groups as well as hydrophobic hydrocarbon nuclei and methyl groups.Bile acid participates in lipid,glucose,and energy metabolism.In addition,it is a powerful detergent concentrate,which causes hepatocellular apoptosis,cholestasis,and even cirrhosis due to impaired cell membranes,destroying liver function.
Some studies have confirmed that the degrees of liver damage are caused by bile acids vary according to type and quantity.Glycochenodeoxycholic acid (GCDCA) induces mitochondrial permeability transition in isolated hepatocytes,and also stimulates the generation of reactive oxygen species in hepatocytes and mitochondria in high concentrations,which is accompanied by hepatocellular apoptosis[6].Bile acid-mediated-inflammation is a trigger for toxicity,with bile acids acting as inflammatory cytokines,activating the Erk1/2 pathway that produces pro-inflammatory factors such as interleukin (IL)-10,IL-1β,SCAM-1,which may promote hepatocyte inflammation[7].Invitroexperiments indicate that bile acids cause liver injury in a way of inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress,for instance,deoxycholic acid (DCA),chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA),and lithocholic acid (LCA) induce the expression of TGF-β m RNA,leading to hepatocytes apoptosis,fibrosis,cirrhosis[8].
In general,hydrophobic bile acid is considered to a significant element contributing to liver injury.However,the toxicity of hydrophobic bile acids differs according to the type.It has been certified that unconjugated bile acids have higher toxicity than conjugated bile acids such as taurine conjugated or glycine conjugated,and the sort order of toxicity efficiency is LCA> DCA > CDCA> cholic acid (CA) > ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA)[9].While,the hydrophobicity of conjugated bile acids also displays different toxicities due to structural differences,ranking as follows TDCA> taurochenodeoxycholic acid (TCDCA)> taurocholic acid (TCA)> tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA)> tauro-β-muricholic acid (T-βMCA)[10].
1.2 Bile acid homeostasis and drug-induced liver cholestasis injury DIC is closely associated with damaged bile acid homeostasis,classed as acute and chronic cholestasis according the time horizon.Drug may disrupt bile acid synthesis,transport,and reduce bile flow by direct or indirect,and many studies are concerned in vitro and in vivo studies (Table 1).It is generally accepted that inhibition the function of bile acid export pump (Bsep),multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (Mrp2),multidrug export pump 2 (Mdr2) is the primary reason for drug induced cholestasis[20].
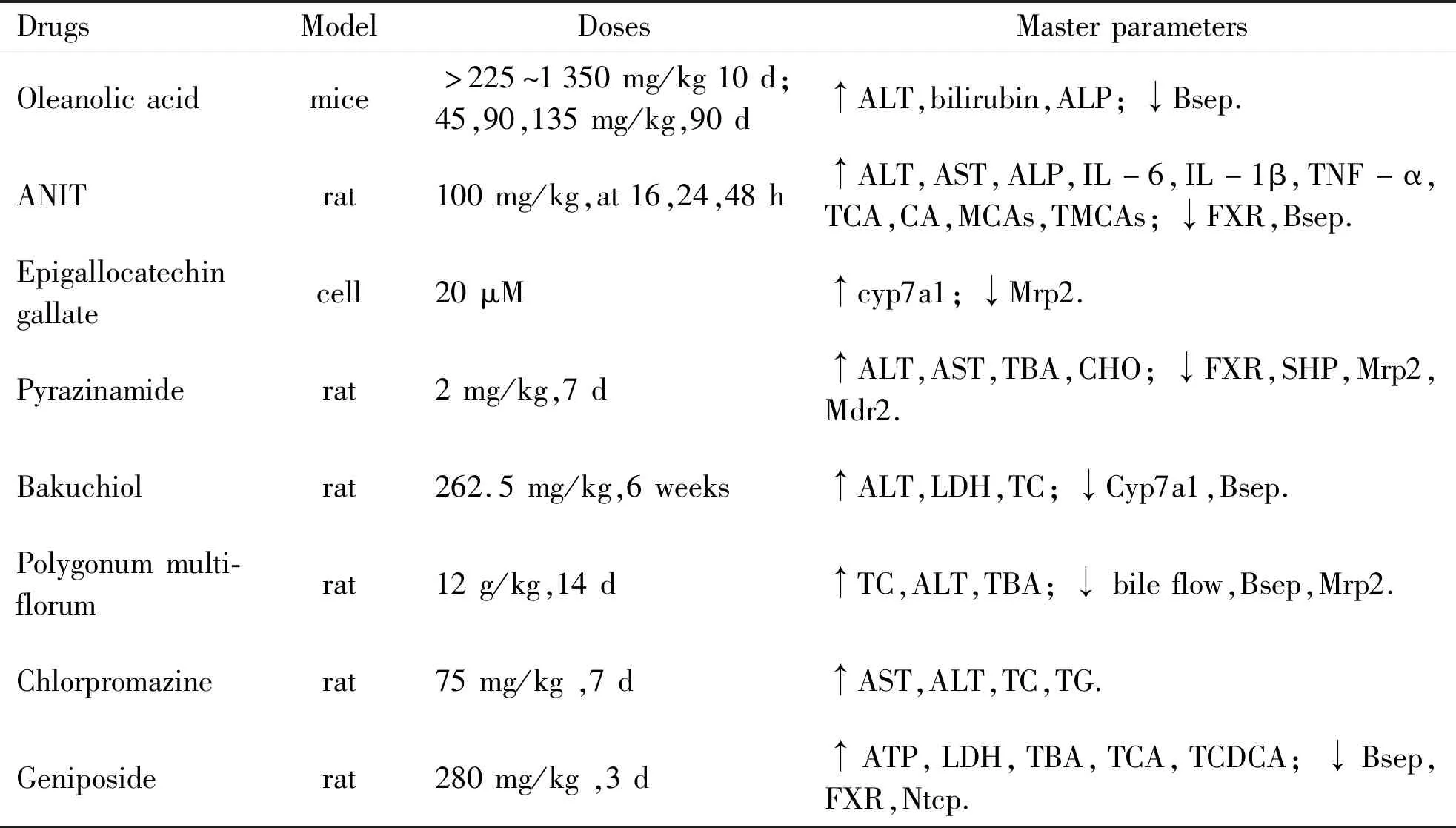
Table 1 Drug-induced cholestatic liver injury
Drugs cause liver toxicity by changing the contents or concentration of the bile acids,with the main pathological features are bile duct hyperplasia,necrosis,inflammation cells,feathery degeneration,and steatosis in cholestatic liver injury,damage types of that are distinguishing due to different drugs[21].Its severity is not only related to drug dose,but exposure time.Disturbances in bile acids composition have been observed in DIC.For instance,Geniposide-induced liver injury is associated with the increased ratio of TCA,TCDCA and tauro-α-muricholic acid (T-αMCA)[19].CA,glycocholic acid (GCA),TCDCA,TCA and T- αMCA are increased after drugs treated and are often considered as diagnostic markers of cholestatic liver damage[22].Tang,etal. reported that ANIT results in serious liver injury because of increased the levels of TCA,CA,αMCA,βMCA and T- αMCA,T- βMCA in liver and serum[23].
2 FXR and bile acid homeostasis
2.1 Bile acid metabolism Bile acids are synthesized via the classic and alternative passage from cholesterol in the liver (Figure 1).CA is synthesized in classic bile acid synthesis pathway with the action of cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase (Cyp7a1),while small amounts of CDCA is also synthesized.Most CDCA is synthesized in alternative pathway through the sterol 27-hydroxylase (Cyp27a1) and oxysterol 7α-hydroxylase (Cyp7b1).The ratio of CA to CDCA is regulated by sterol 12α-hydroxylase (Cyp8b1) to maintain the balance of hydrophobicity and hydrophilicity bile acids in vivo.Muricholic acid (MCA) is the main bile acid in rodents and hydroxylated from CDCA via Cyp2c70.Primary bile acids are combined with taurine or glycine under the catalysis of the enzymes bile acid:CoA synthase (Bacs) and bile acid:amino acid N- acyltransferase (Baat)[24].
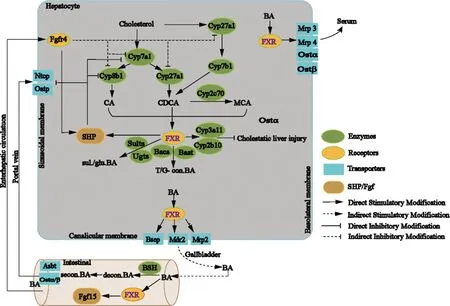
Figure 1 The role of FXR in bile acid synthesis and transport
Cholesterol is converted into the primary bile acids CA and CDCA,which occurs through two routes:‘classical’ and ‘alternative’.The classical pathway is suppressed by Cyp7a1,Cyp8b1,Cyp27a1 and produces CA,which is suppressed by Cyp27a1 and produces CDCA.The alternative pathway is initiated by Cyp27a1 and Cyp7b1 and produces CDCA.In rodents,CDCA is translated into MCA via Cyp2c70.Free bile acids are conjugated to G and T through the Bacs and Baat,after FXR activation.At the same time,FXR activation,Sults and Ugts are activated,and subsequent sul.and glu.bile acids are increased.Meanwhile,increased bile acid excretion and reduced toxicity occurs along with increased Cyp3a11 and Cyp2b10.Simultaneously,Oatp,Ntcp,and bile acids synthetase (Cyp7a1,Cyp8b1) are suppressed by activated FXR via the FXR-SHP way.Primary bile acids are transported into bile via Bsep,Mrp2,and Mdr2 that are induced by activated FXR.When eating,bile will enter the intestinal tract and is decon.under the function of BSH,and with the help of intestinal flora,the secon.bile acids are produced.Conjugated and unconjugated bile acids activate FXR and reduce bile acid synthesis through the FXR-Fgf15 route,accompanying the reduced bile acid synthetase,such as Cyp7a1,Cyp8b1,and Cyp27a1.When cholestasis occurs,Mrp3/4 and Ostα/β will be activated,which is closely related to FXR activation; it also promotes bile acids release into bloodstream across hepatocyte basolateral membrane.
Abbreviations:CA,cholic acid; CDCA,chenodeoxycholic acid; MCA,muricholic acid; Cyp7a1,sterol7α-hydroxylase; Cyp8b1,sterol 12α-hydroxylase; Cyp27a1,27-hydroxylase; Cyp7b1,oxysterol 7α-hydroxylase; Bacs,bile acid:CoA synthase; Baat,bile acid:amino acid N-acyltransferase; decon.,deconjugated; FXR,Farnesoid X receptor; Bsep,bile acid export pump; G,glycine; glu.,glucuronidated; Mrp2,multidrug resistance-associated protein 2; Mrp3,multidrug resistance-associated protein 3; Mrp2,multidrug resistance-associated protein 4; Mdr2,multidrug export pump 2; BSH,bile acid hydrolases; Ntcp,Na+- taurocholate cotransport protein; Oatp,organic anion transporter; Ost α/β,organic solute transporter α/β; secon.,secondary; sul.,sulfated; T,taurine.
Conjugated or free bile acids are transferred into bile duct and stored in gallbladder under the action of transporters such as Bsep,Mdr2,Mrp2.After a meal,the gallbladder contracts to secret bile into intestinal tract,facilitating the digestion and absorption of food.In the intestinal,primary bile acids have undergone deconjugation microbial with bile salt hydrolase (BSH) activity and turned into secondary bile acids[25].To meet the body’s needs,most bile acids are taken up into hepatocytes through enterohepatic circulation mediated by basolateral bile acid uptake transporters Na+-taurocholate cotransport protein (Ntcp) or organic anion transporting polypeptides (Oatp).
2.2 FXR and bile acid regulation It is demonstrated that nuclear receptor FXR has a critical affect in regulating bile acid synthesis,transport,and toxicity (Figure 1).FXR will be activated when bile acids levels increase especially hydrophobic bile acid in hepatocytes.Activated FXR can inhibits the expression of bile acid synthesis enzymes (Cyp7a1,Cyp8b1,Cyp27a1,Cyp7b1) through FXR-SHP,thereby reducing the bile acid synthesis,as well as inhibits the expression of bile acid uptake transporters (Ntcp,Oatp) and reduce bile acid reabsorption.Most important is that,activated FXR also increases Bsep expression,which is well known for the character in the transport of bile acid from the liver to bile.Moreover,the expressions of Mrp2,Mdr2,Mrp3/4 and organic solute transporter (Ost α/β) are increased,which promote bile acid efflux.In addition,the expression of bile acid detoxication enzymes (Cyp3a11,Cyp2b10,Ugtls,Sults) and bile acid binding enzymes (Bacs and Baat) will increase after FXR is activated[26-27],reducing bile acid toxicity by changing the ratio of bile acid components.Intestinal FXR,maybe,is crucial to inhibit bile acid synthesis.Activated FXR is responsible for Fgf15 gene expression,following the Fgfr4 gene high expression,which inhibits bile acid synthesis enzymes expression and limits bile acid synthesis.It may be ascribed to the non-receptor tyrosine kinase (Src) leads to Y67-FXR phosphorylation[28].
Given the influence of FXR on bile acid homeostasis,it is no surprising that the FXR signaling pathways are linked to drug cholestasis.
3 FXR and drug cholestasis
3.1 The possible pathways of FXR in drug cholestasis A lot of researches implied that FXR is associated with the development and potential therapy DIC (Figure 2).Pyrazinamide,a first-line anti-tuberculosis drug,altered bile acids profile and induced rat cholestasis through FXR inhibition[11].Activated cAMP-ERK-LKB1-AMPKα1 signaling pathway contributed to the FXR low expression and then reduced bile flow[29].Metformin disturbed bile acid balance via AMPK-FXR crosstalk in vivo and in vitro.It was also observed that changes in FXR phosphorylation levels were related to glucose levels[30].Drug-induced inflammation is another factor leading to cholestasis.Indomethacin resulted in cholestasis by interfering the signal transducer and activator of transcription3 (STAT3) phosphorylation and activation caspase 9,Sirtuin1 (Sirt1) deficiency was proved to mediate intestinal hepatocytes nuclear factor1α (HNF-1α)-FXR signaling and cause cholestasis[31-32].As a result,interest about how to activate FXR has been raised.
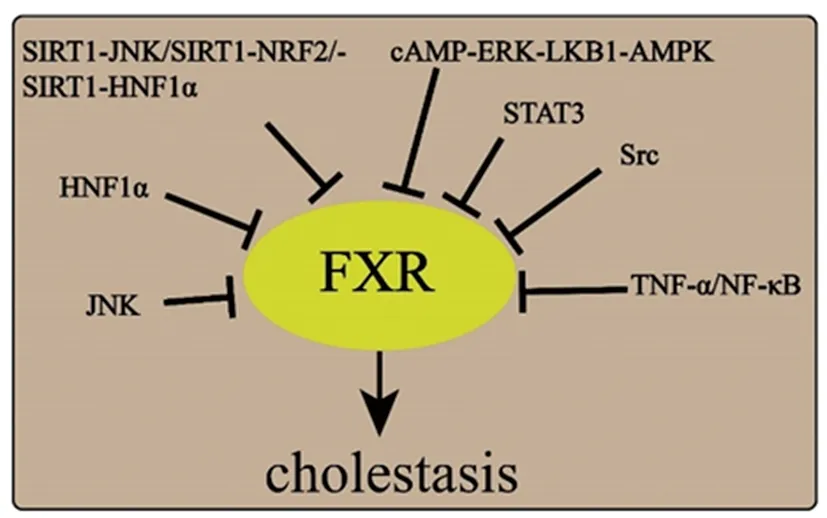
FXR is suppressed by drugs via a variety of pathways.Inhibited FXR results in increased hydrophobic bile acids and reduced bile acids effluent transporters,finally leading to cholestatic liver injury.Abbreviations:HNF1α,hepatic nuclear factor 1α; NF-KB,nuclear factor kappa beta; STAT3,signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TNF-α,tumor necrosis factor α; JNK,c-Jun-terminal kinase; ERK,extracellular signal-related kinase; NRF2,nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2; AMPK,AMP-activated protein kinase; LKB1,Liver kinase B1; Src,Steroid receptor coactivator.Figure 2 The pathway may be involved in FXR inhibition
Drugs activate FXR via a multiple of ways to alleviate liver toxicity.Sirt1 is a potential therapeutic target in liver cholestasis.SRT 1720,a Sirt1 activator,regulated bile acids metabolism and relived CA feeding cholestatic liver injury via FXR-FGF 15 in ileum or FXR-SHP in liver mediated inhibition of Cyp7a1 and Cyp27a1,which along with increased Cyp2b10,also induced efflux transporters in kidney.In the study,interestingly,it was also observed that P-JNK mediated the p53 activation possibly reduces Sirt1 expression in mice livers fed by CA.Furthermore,SRT 1720 protected mice from ANIT-mediated cholestasis by mainly up-regulating the Sirt1-HNF-1α-FXR and Sirt1-Nrf 2 pathways,and by increasing target genes expression (Bsep,Oatp1b2,Ntcp,Mrp2) and the detoxifying enzymes mRNA levels of Cyp3a11 and Cyp2b10[33].
Hydrophilic CDCA and UDCA accelerated protein kinase (PKA) phosphorylation in a dose-dependent and time-dependent manner.PKA phosphorylation results in inhibition of AMPK phosphorylation and couple with the up-regulating expression of FXR and bile acid transporters (Bsep,Oatp1b2,Ntcp,Mrp2),which improved the cholestasis in rat[34].The expression of bile acid transporters was aggrandized in an FXR-dependent manner after glycyrrhetinic acid Derivative TY 501 treated for 8 consecutive days,and intrahepatic cholestasis aroused by hydrophobic bile acid LCA[35].Calycosin alleviates CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity connected with FXR activation and STAT3 phosphorylation in mouse[36].
Altogether,activated FXR has a hepatoprotective influence,while inhibiting FXR will lead to intrahepatic cholestasis.The fundamental character of FXR has been shown in FXR knockout mice.
3.2 FXR knockout FXR whole body knockout mice,under standard conditions,display normal weight,cell proliferation,and high levels of bile acid synthetase (Cyp7a1,Cyp8b1),low expression of FXR,SHP[6].FXR knockout mice are often accompanied inflammation,fibrosis,and liver tumors,importantly,inflammatory cytokines.For instance,Cxcl 2,Foxp 3,Ccl 2,Ccl 17,TNF -α,IL-6,IL-1β have higher expression levels in FXR knockout mice liver[37].
FXR deficient mice develop alcoholic liver diseases (ALD),featured with inhibition Bsep,but there are no distinct differences in the severity of steatosis,inflammation,or fibrosis between wild-type and hepatocyte-specific FXR knockout mice in the development of ALD[38].What is noteworthy is that,conjugated bile acid TCA aggravates CCl4-induced liver injury in FXR knockout mice through TCA-JNK axis[39].FXR is also a factor associated with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC),FXR agonist,GW 4064,did not alleviate LPS-induced liver injury in FXR knockout mice[40-41].
3.3 FXR agonists FXR is considered as a therapeutic target,and FXR agonists are widely used in cholestasis diseases (Table 2).Obeticholic acid (OCA),also called INT-747 or 6α-ethyl-chenodeoxycholic acid,is the most widely used.It ameliorates the cholestasis by upregulating FXR and the downstream genes,including FGF15,SHP,Bsep,Ostα/β in mice,and alleviating inflammation,steatosis,increasing bile acid efflux[42].Findings suggest that OCA has a potential effect on tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) through interfering with IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway[51].Interestingly,OCA activated the intestinal FXR,thereby the expression of interferon-g and natural killer cells expression has been markedly reduced in the bacterial translocation model.Fexaramine-3 (Fex-3),known for a new intestinal-restricted FXR agonist,can promote the expression of Bsep and SHP,while not Cyp7a1[43].WAY-362450 has contributed to the treatment of steatosis through suppressing TNFα-JNK pathway[44].Tropifexor (LJN 452) has shown a significant effect on Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) in phase 2 human clinical trials[52].INT-767,a dual FXR/TGR 5 agonist,can protect against NASH by attenuating the inflammation,collagen deposition,fibrosis,and cirrhosis,one other dual FXR and GPBAR1 agonist,BAR 502,reverses liver fibrosis in high fat diet (HFD) model[45-46].
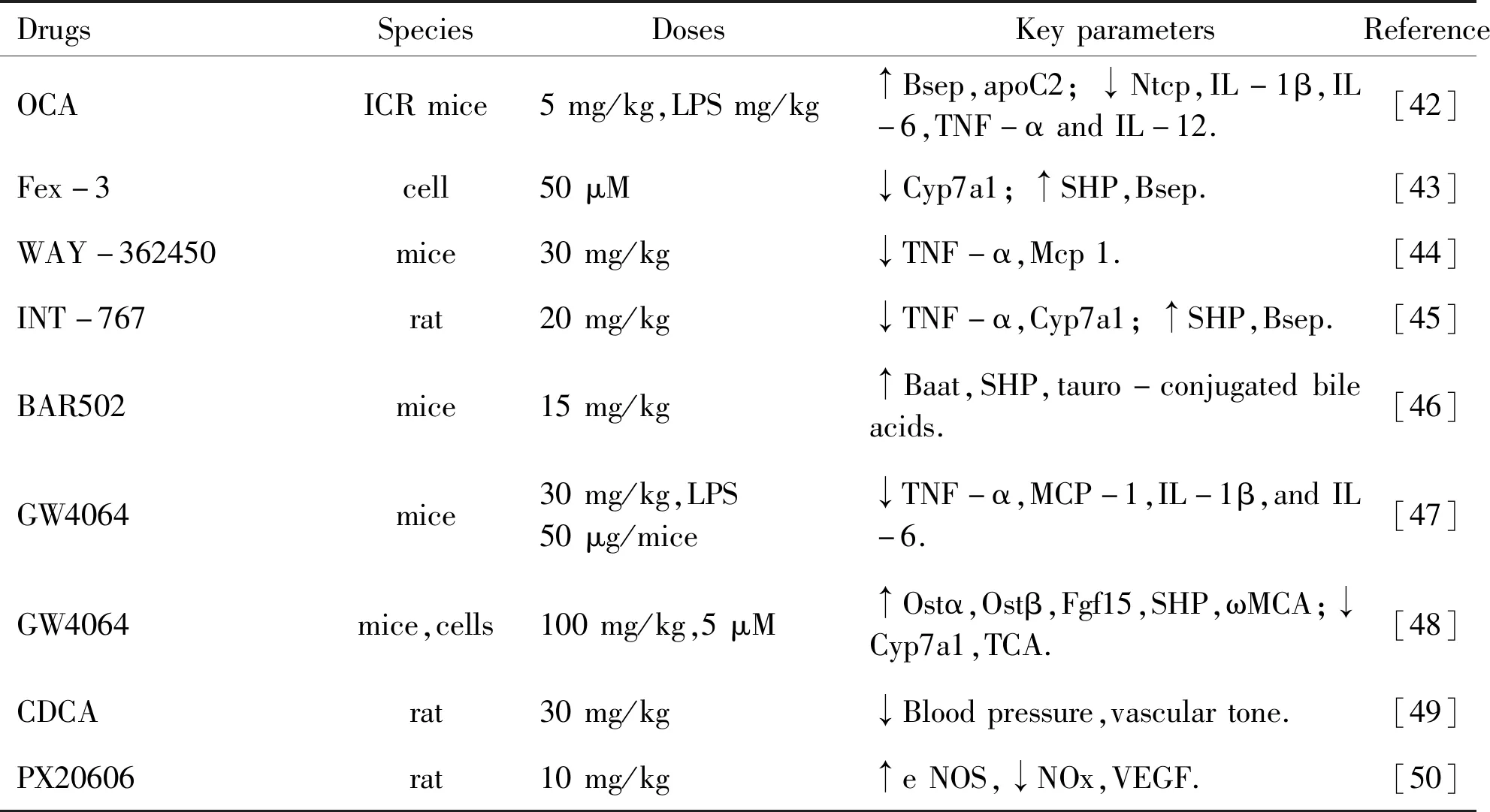
Table 2 FXR agonists and developed for treating in diseases
GW 4064,another FXR agonist,activates cAMP and subsequently regulates the FXR signaling pathway,improving bile acid and lipid metabolism.Also,studies revealed that GW 4064 reduced endotoxin-induced hepatic inflammation and drug induced-liver toxicity by reducing the levels of cytokines promoting inflammation[47-48].Furthermore,it provides the basis for a novel way to recover bile acid homeostasis.Bile acid is the natural ligands of FXR,particularly hydrophobic bile acid such as CDCA.CDCA can active FXR to inhibit bile acid synthetase through negative feedback,to upregulate FXR target genes,whereas,different bile acids have different effects on FXR activation,with the ability as CDCA>DCA>LCA>CA[49,53].Date palm fruit (Phoenix dactylifera) actives bile acid-bound FXR and reduces serum triglyceride levels in human,which is superior to bile acid alone[54].In addition to the above,the FXR agonist,PX 20606,ameliorates portal hypertension and fibrosis was investigated in CCl4-induced cirrhosis rats[50].
4 Conclusion and perspective
Rising evidences indicate a strong association between the FXR and DIC.Although there is no effective treatment for DIC,FXR may be a promising therapeutic target in DIC.FXR activation can relieve cholestasis via regulating FXR downstream genes,which results in increase output of bile acid and decrease synthesis.However,current knowledge of the relevance of FXR in DIC is still scarce.In the present review,we have discussed the protective effects of FXR for the treatment of drug cholestasis.But of note,studies display that FXR agonist OCA aggravated liver damage in piglet model and chronic activation FXR caused perinatal toxicity and increase neonatal mortality in mice[55-56].
Over all,it is clear that the benefit of FXR outweighs the side effects,although the side effects should still be considered.Additionally,most drugs may lead to cholestasis.More studies are needed to further understand the exact role of FXR and to develop efficient therapeutic drug for DIC by targeting FXR.
