大型枢纽机场航站楼发展趋势探讨
2020-07-14邱小勇谭奔潘磊
邱小勇,谭奔,潘磊
Abstract:With the rapid economic and technological development in China, the airport terminal, as a building type sensitive to economic and technological situations, has undergone a trend of rapid change and evolution in recent years. This paper analyses the changes in the airport terminal design from the macro urban planning level, the middle airport planning level and the micro terminal designing level, and puts forward demonstrations and imaginations on the terminal design by combining the cases such as Tianfu International Airport of Chengdu and Jiaodong International Airport of Qingdao.
Keywords:development of urban agglomeration, airport terminal core area development, passengers walking distance, technological development, efficiency matching, flexibility
1 宏观层面:城市群之间以及城市内的协调发展
1.1 城市群之间协调发展
十八大以来,在以习近平同志为核心的党中央坚强领导下,我国深入实施区域协调发展战略,如京津冀协同发展、粤港澳大湾区建设、长三角一体化发展等。这类区域城市群的协调发展,会极大地带动该区域的经济增长。将轨道交通引入机场,提升综合集疏运能力,建设协同共享的城市机场群,是各个区域协调发展的重要内容之一,机场航站楼在城市群发展中将扮演越来越重要的角色。
以成都天府国际机场为例,在选址上,成都天府国际机场就选在了成都市龙泉山以东,其目的之一便是更好地把机场影响力辐射到东面的各级县市。天府国际机场楼前引入蓉昆高铁线,并在GTC 设站停靠。该线路建成后将很便捷地联系起成都与川东南城市,如资阳、内江、自贡等,也能和重庆、昆明形成良性联动,促进西南城市群之间的快速融合。
从目前的发展趋势来看,大型机场与轨道交通形成多层次的交通系统是宏观层面的一个快速变化点。可以畅想,在不远的未来,轨道交通与机场航站楼之间的关系将从短距离的二元并置到一体化的以机场功能为主的空铁联运综合体。一体化的综合体设计是机场航站楼可能的发展方向。
1.2 城市内的协调发展
机场航站楼在城市新区发展过程中往往能起到提振经济的作用。成都市设立的天府新区,它的新区起搏器就是天府国际机场。待未来机场落成后,依托天府国际机场庞大的人流、物流,天府新区将构建起层层外放的开发圈层,形成富有航空特点的活力经济圈。机场土地的合理开发和规划就显得格外重要。合理的开发与规划不仅能使得机场运行更有效率,还能让周边土地价值最大化,实现新区的快速发展。
城市内其他区域和以航空为核心发展出来的新区之间也会产生紧密联系。城市轨道系统、城市公路网,都会受到牵引,在新区形成复合密集的交通体系,更好地刺激城市基础设施建设,拉动周边区域协调发展。
2 中观层面:机场规划中的变化趋势
2.1 机场大系统的高效运转
从目前几大核心城市的枢纽机场发展来看,随着该区域经济水平的快速发展,机场年旅客吞吐量和货邮吞吐量逐年上升:北京首都机场2019 年旅客吞吐量再破1 亿,上海浦东机场年旅客吞吐量7600 万人次,广州白云机场年旅客吞吐量7350 万人次。从增速来看,一座机场/多条跑道/多座航站楼的发展方式不可避免。因此在中观规划层面来看,需要将多航站楼的机场大系统进行统筹研究。如何把这个系统塑造成一个高标准、全融合、一体化的综合交通枢纽是规划中必须考量的问题。
航站楼之间的陆侧联系可以选择地铁或航站楼穿梭巴士进行联系,航站楼之间的空侧联系一般来说,选择空侧捷运系统是比较好的一个选项。由于捷运系统产品的国产化,使得投资总造价和运维成本下降,大型枢纽航站楼内引入捷运系统是不可避免的一个趋势。

2
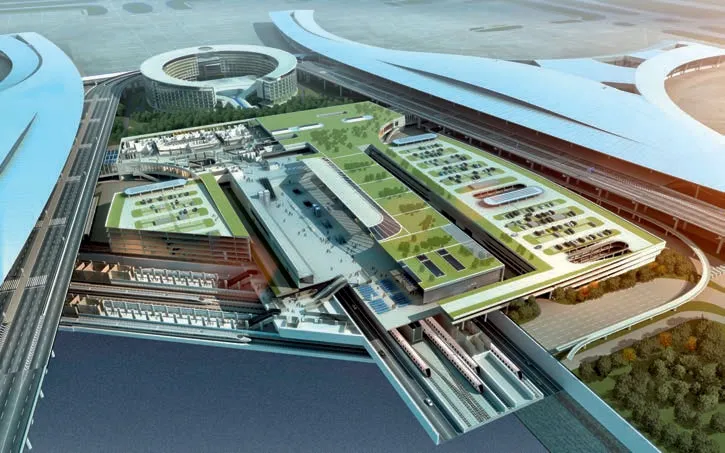
1 成都天府国际机场鸟瞰效果/Aerial view rendering of Chengdu Tianfu International Airport
2 成都天府国际机场楼前多种交通形式汇聚/Multi-level transportation system of Chengdu Tianfu International Airport

3
2.2 机场规划中的弹性预留
大型枢纽机场航站楼的规划要注重空间使用的弹性和运营的灵活性,用来应对机场航站楼发展中的快速变化。特别是在机场用地规模没有条件扩展的情况下,空陆侧的规划都应留有余量。
首先在土地利用上应该留有余量,使得空侧能根据远期需求的变化进行不同方式的拓展,陆侧航站楼核心区土地能根据旅客吞吐量变化进行功能调配。其次,陆侧道路系统的容量要有富余,特别是出发/到达车道边,应在设计中考虑设计一定的余量。这一点从近期出现的分层出发车道边设计中可以看到变化趋势。
国内国际可转换机位的设置能够很好地实现国内国际量的调配,也能为虚拟航班提供近楼靠桥使用的可能性;组合机位的设计可以提高登机廊桥的使用效率和适用性;楼内预留设施设备的可扩展空间,也能为远期容量的发展留有余地。
2.3 城市功能高度综合的发展趋势
大型枢纽机场航站楼和GTC 形成以机场为主的一体化交通综合体后,还会根据城市发展需求,增加其他城市功能进去(如公园、会展、大型购物中心、体育场、植物园、酒店、会议中心等)。航站楼前1km 内的核心区将成为重要的城市综合体,吸引城市内外的旅客和市民前来活动。这些功能的实现得益于机场航站楼强大的交通枢纽能力,能够更便捷的组织人流货流在该区域的流动。虹桥核心商务区就是该理念的国内先行者,从现在的情况来看取得了良好的社会反响。
3 微观层面:航站楼建筑设计
3.1 集中式航站楼与旅客步行距离之间的关系
由于我国机场建设主要由政府出资,为了避免建设不久的航站楼就需要扩建的尴尬场面,现在各地方在修建大型枢纽机场的时候都会一次性修大一点,因此形成我国大型枢纽航站楼以集中式航站楼构型为主的局面。集中式航站楼有很多优点,比如调配灵活,应对远期发展有空间余量,但是会带来旅客步行距离过远等问题。
在最近的设计竞赛中,往往机场运营方又会追求高近机位率,导致空侧岸线长度变长,进一步加大了楼内旅客步行距离。国内好几座大型航站楼都因为过长的旅客步行距离(近1km),引来旅客的诟病。因此,怎样做到既有高近机位率,又能很好地进行楼内调配,并能兼顾较舒适的旅客步行距离是设计中很重要的思考点。故成都天府机场一期选择两个单元式航站楼的构型,就是希望可以探讨出能兼顾多方效益的设计思路。
此外,多个航站楼之间需要捷运系统进行联系,捷运系统的建设会变得不可或缺。那么通过楼内捷运来减少旅客步行距离也应该是一个值得关注的设计点,楼内捷运的使用将很好地对国内大型集中式航站楼进行补充,从而形成楼内高效的旅客流程。
3.2 体验式航站楼
当代航站楼在设计中越来越强调体验感。航站楼需要在形象、空间、选材、色彩等内容上围绕当地特点进行设计。此外楼内的各式增值服务,比如展览、观演、互动活动等,既服务了旅客又提升了服务的品质,还起到了良好的宣传作用。
3.3 智慧航站楼
航站楼内的应用技术发展也是非常值得关注的一个设计点。从整体趋势来看,随着大数据、人工智能、5G 万物互联等技术的发展,航站楼的智慧性将体现在智慧运行、智慧安全和智慧服务3 个方面。通过搭建生产运行智能管理系统,实现空地运管信息动态联动,实现机场的智慧运行;以人证识别、指纹识别、人脸识别、虹膜识别技术为基础,结合自助值机、自助行李托运等设备,可以实现安全的旅客无接触通关,提高旅客满意度;利用微信小程序或手机APP 实现旅客楼内的全方位线上服务,提供室内定位、智能客服、楼内商品网购、订车订票等多种精准服务。
3.4 对非航收入的重视
非航收入的提高越来越受到机场运营方的重视。它不仅能带来更好的旅客服务体验,还能为机场赚取不菲的收入。纵观全球的优秀机场航站楼,许多都在“怎样营造更好的机场商业”上下足了功夫,比如樟宜机场、史基辅机场、成田机场等。它们也通过良好商业的打造赢得了旅客的青睐,许多机场都渐渐成为了旅客们的旅游目的地,实现了机场功能角色的综合性跃升。
3.5 建筑形象空间对地域特点的反映
建筑形象和空间应该反映地域化特点,特别是气候特点,比如全年温差较大的北方就不建议在航站楼内设置大型庭院,因为这不仅不节能,也起不到太多庭院该有的景观效果;而全年温热,过渡季节较长的南方就可以考虑在楼内设置大型庭院,既能起到通风换气调节小区域气候的作用,还能在楼内呈现常年绿意盎然的景观效果。
另外,建筑形象和楼内空间应该对城市精神有一定的反映,通过形到、意到和形意结合的设计创意,创造城市新名片,为城市刻画新的精神内涵。
4 案例分析:青岛机场
4.1 项目概况
青岛胶东国际机场定位于“面向日韩具有门户功能的区域性枢纽机场,环渤海地区国际航空货运枢纽”,新机场设计目标年为2025 年,满足年旅客吞吐量3500 万人次,远期目标2045 年,满足年旅客吞吐量5500 万人次。

4
3 成都天府国际机场出发大厅/Departure hall of Chengdu Tianfu International Airport
4 成都天府国际机场T2商业中心/T2 commercial centre of Chengdu Tianfu International Airport t

5
青岛新机场选址青岛市胶州东北,距离青岛市中心约 40km。近期征地约 15.63km2,全场规划机位总数为 178 个,近期建设T1 航站楼,建筑面积约478,000m2,楼前设置交通中心208,000m2,包含济青高铁、两条城市轨道线的机场站,以及停车楼、长途车站和商业中心等功能。远期在陆侧继续扩建航站楼,在空侧东西两侧陆续扩建第三、四跑道。
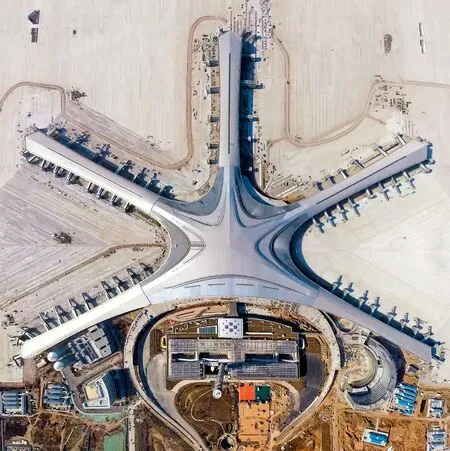
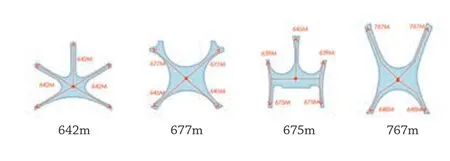
新机场航站楼概念设计按照“规划导引、安全第一、功能齐备、便捷舒适、环保节能、协调美观、质优价公”的原则,确定以“齐”字状为总体布局,以富有张力的连续曲面将极具向心力的5 个指廊与大厅融为整体,实现大集中与单元式的合理平衡,造型融合仿生学设计理念,一期工程犹如岸边的一颗海星。
4.2 机场跑道间距的变化趋势对航站楼构型的影响
机场的设计容量与跑道的布局密切相关,单跑道起降容量在40 架次左右,近距跑道在60 架次左右,而远距跑道可以达到80 架次。国内机场近年一直经历着高速的增长,随着航空业务量的持续增长,新建的大型机场在规划中选择采用远距跑道的模式。
按照民航总局令第123 号的相关规定,当两条平行跑道中心线的间距分别不小于 1035m、915m、760m等时,相应的允许航空器分别按照独立平行仪表进近、相关平行仪表进近、独立平行离场、隔离平行运行等4 种模式运行。
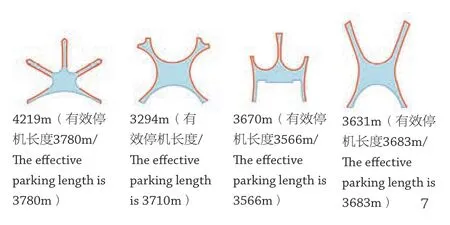
远距跑道距离的选择又进一步影响航站楼的构型设计,从表1 中,我们可以看到国内机场普遍采用大间距的远距跑道。
航站楼在满足航空器安全运行的前提下,可以通过增加指廊数量来增长停机岸线,获得更多的近机位数,青岛新机场和北京大兴机场,在跑道间距达到 2200~2400m 的情况下,均选择了单楼集中五指廊的布局,把近机位数量做到了极致。
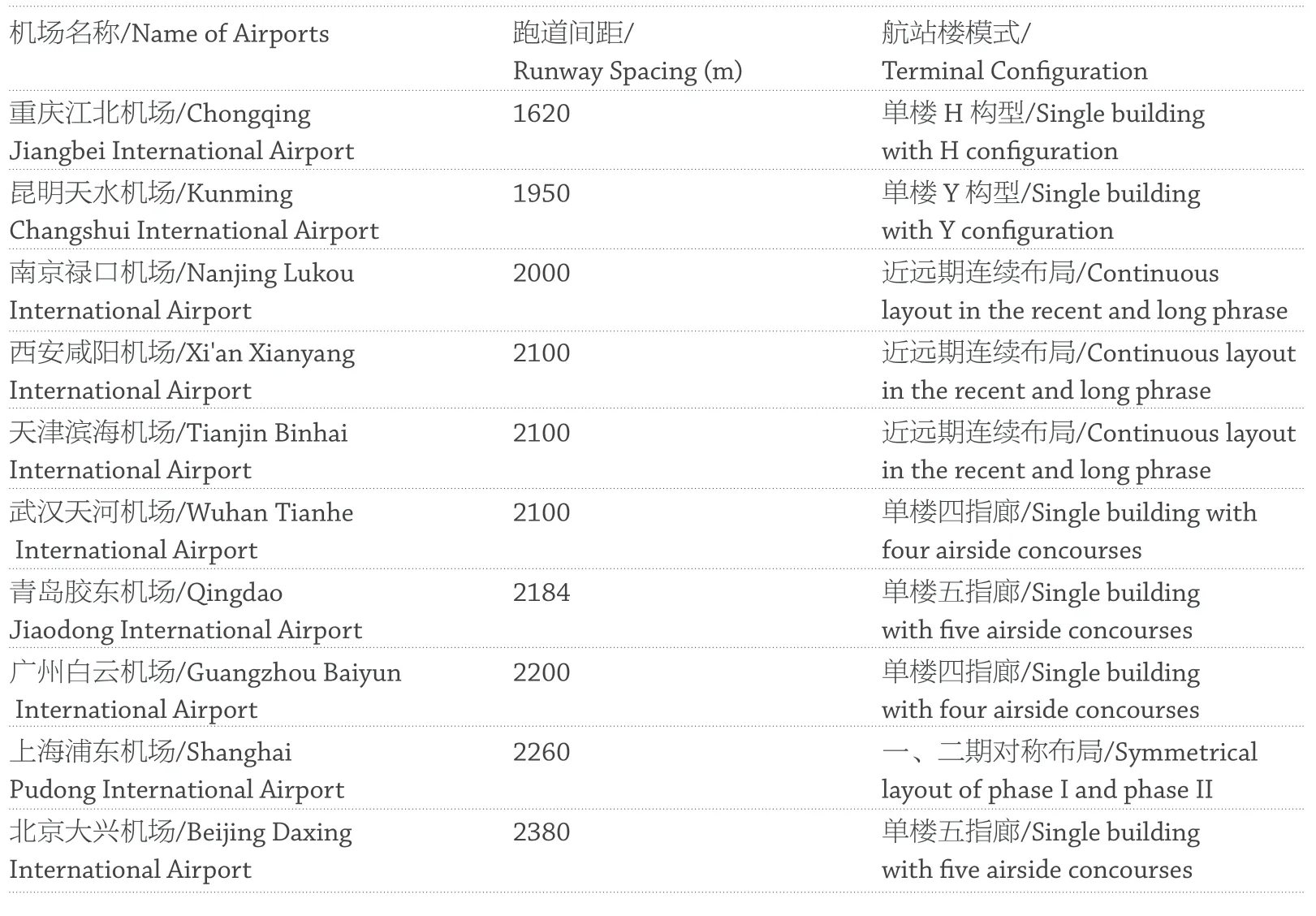
表 1 机场远距跑道距离与航站楼构型/Table 1 Spacing of the airport long-distance runway and the terminal conf iguration
5 青岛新机场雪景/Snow scene of Qingdao New Airport
6 旅客步行距离比较/Comparison of passenger walking distance
4.3 青岛新机场对旅客流程的关注
对旅客的关怀是快速变化的机场设计中不变的主题,青岛新机场方案设计之初就确定了空陆侧整体平衡的设计原则。
航站楼方案比选中,我们对比了不同方案对旅客步行距离及停机岸线的影响,采用五指廊向心布局,航站楼值机大厅更靠近航站楼的中心,旅客安检后前往候机区最远距离控制在650m 以内。是3000 万~4000 万级别航站楼中,步行距离最短的航站楼之一。
同时,五指廊构型提供了优越的停机长度,近机位数量比例相对需求值,达到80%的比例,可以停放47C22E2F 或者69C13E(按组合机位计算)。从机场服务质量要求和未来发展趋势来看,原来按照70%的近机位比例进行设计,已经不能满足新时代机场对人文机场的要求(表2)。
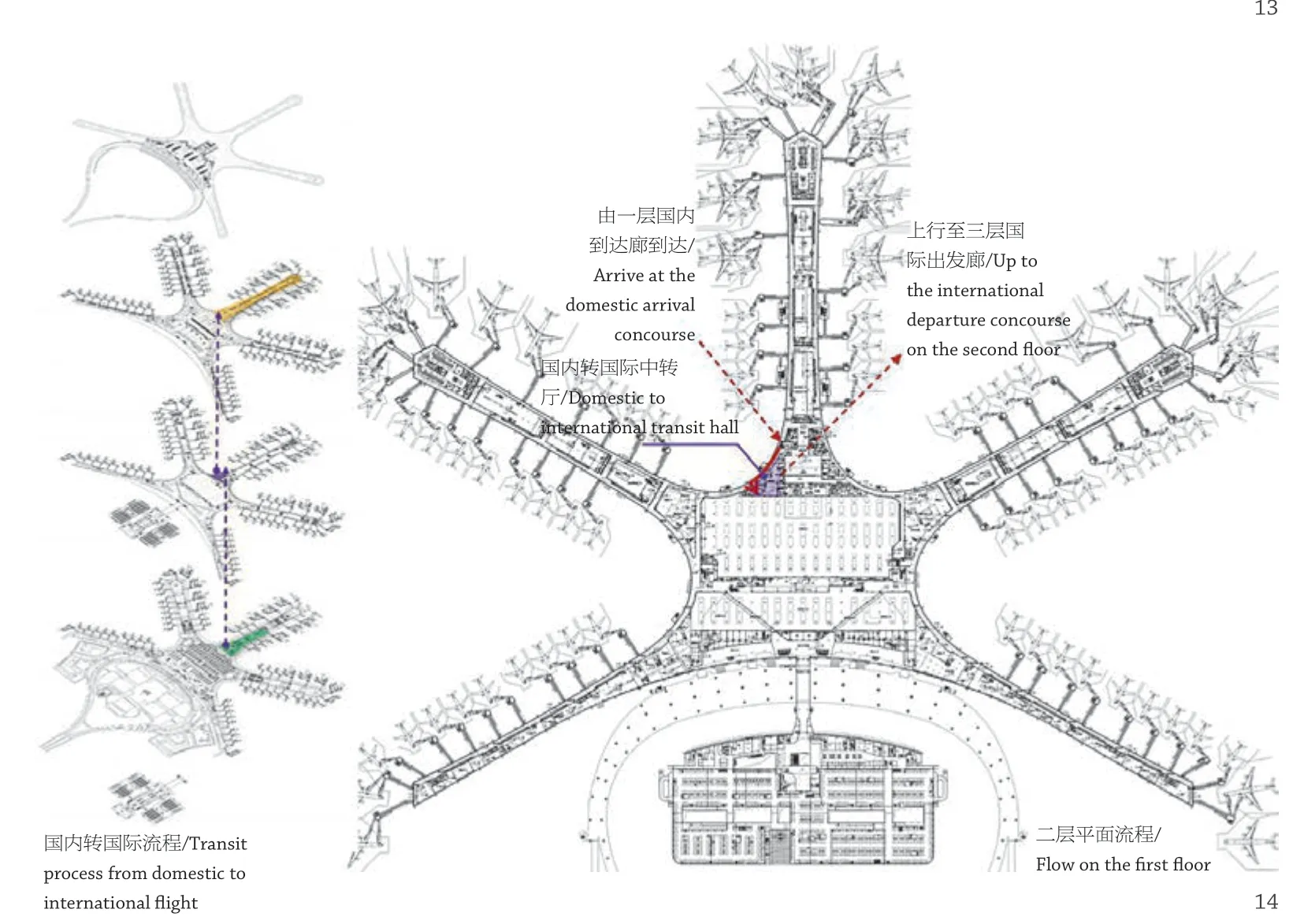
机场设计需要充分考虑不同机场旅客流程的特点,青岛机场作为国内地缘东部的机场,和其他中部机场不同,国内中转的需求低于国际中转的需求。同时,基地航空公司山航和东航,分属于星空联盟和天合联盟,且航班比例接近。青岛机场设计充分发挥向心构型的特点,将国际指廊设置在中间,不同联盟的国内部分分置在两侧,这样形成非常便捷的国内、国际流线。
我们还在国际指廊区域设置了6 个可转换机位,这几个机位均可以独立实现顺畅的国内、国际机位身份转换,并和中转流程结合,实现楼内快速国内、国际中转。
4.4 智慧机场的应用
青岛新机场设计过程正好经历了智慧机场快速发展的时期,自助设备、无纸化通关、智慧大通关等设施和政策纷纷落地,国内硬件和软件的开发也逐步完善。青岛机场在设计和实施过程中不断完善和修订智慧机场策略。
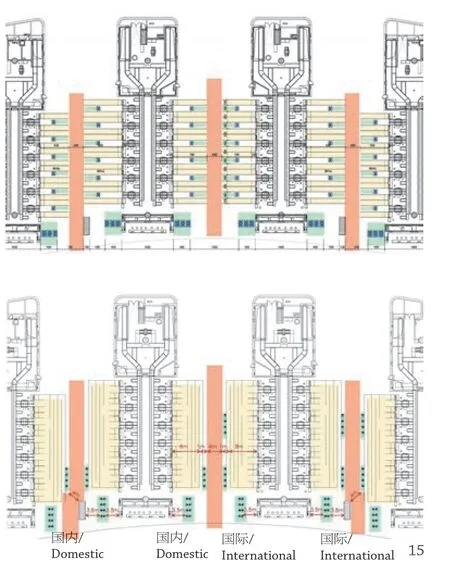
(1)在值机区,比选多种方案,采用两段式自助值机布局方案。每个值机岛配有自动回框系统,并在值机岛之间形成一个完整的自助行李托运区。
(2)在安检排队区,采用自助安检验证通道和安检通道自助回框设施。
(3)候机区 3 登机口设置自助登机设备,加快登机效率,节约人力。
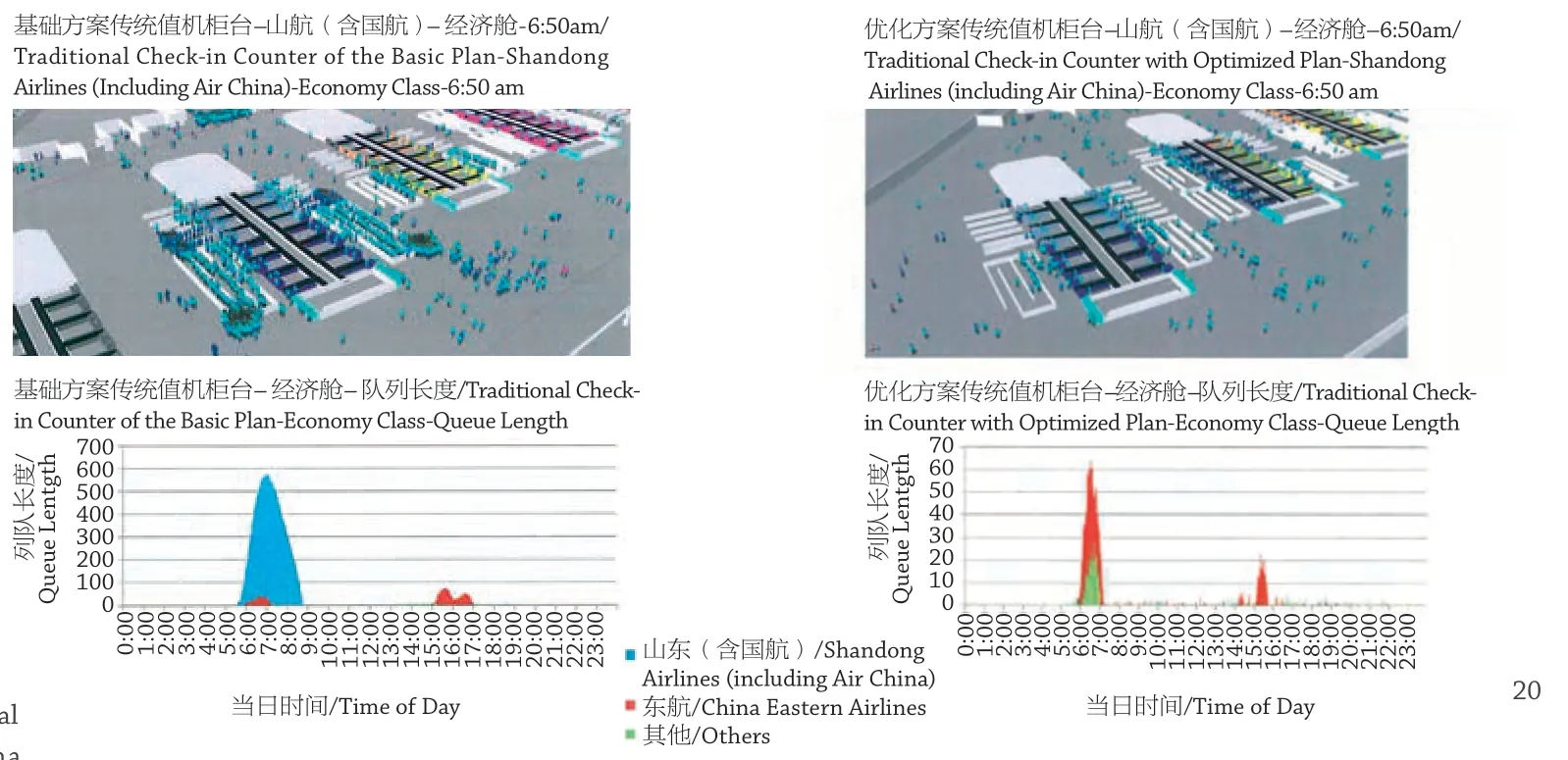
(4)在航站楼设计中采用仿真模拟进行辅助验证,同时对空侧运行效率和楼内通道设施进行仿真评估,并反复验证,优化设计。仿真模拟随着软件的完善和硬件性能的提高,对于投资大、建设周期长及人流量大的建筑设计起到良好的指导分析作用,正在逐步成为我们设计的优选工具。
通过仿真模拟,我们直观地看到了小角度空侧港湾的运行情况。结果显示,小角度港湾在间距足够大的情况下运行是顺畅的,拥堵仅出现在跑道起飞等候区。
通过导入高峰月航班时刻,结合设计年预测数据,形成非常真实的模拟结果,通过设施模拟,我们优化了值机岛布局,机组、员工安检通道数量,边检排队空间等原设计不足的地方。
4.5 青岛新机场在新材料方面的尝试
航站楼屋面采用不锈钢焊接屋面,经过时间的检验,极大的减少了漏雨和风揭的风险,特有的金属质感,在阳光下更突显出航站楼优美的造型曲线。
另外,能源采用三联供形式,利用余热发电;交通中心屋面使用了5500m2的光伏发电,充分利用青岛良好的日照条件;航站楼楼内采用室内可控制的电动百叶窗,解决早晚东、西晒不利时段影响……青岛胶东国际机场遵循中国民航四型机场建设行动纲要的相关要求,在全生命周期内实现资源集约节约、 低碳运行、 环境友好的机场,并顺利通过了国家绿色三星标准的设计评审。

13
14
15
13 青岛胶东机场构型/Conf iguration of Qingdao Jiaodong International Airport
14 青岛机场空侧快捷中转/Quick transfer on the airside of Qingdao Airport
15 不同值机方案比选/Comparison and selection of different check-in options
16自助行李托运系统和回框系统/Self-baggage-check-in system and box return system
17 空侧仿真模拟/Airside simulation
1 Macro-Level: the Coordinated Development Among Cities and Inside the City
1.1 The Coordinated Development Among Cities
Since the 18th National Congress, under the strong leadership of the CPC central committee, China has implemented the strategy of regional coordinated development, such as the coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region, the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Great Bay Area, the Yangtze River Delta Region. The coordinated development of such regional city clusters will greatly promote the economic growth of the region. It is one of the most important contents of the regional coordinated development to introduce the rail transit into the airport, improve the comprehensive collection and distribution capacity, and build a collaborative and shared urban airport cluster. Airport terminals will play an increasingly important role in the development of urban clusters.
Take Chengdu Tianfu International Airport as an example. In terms of site selection, Chengdu Tianfu International Airport is located in the east of Longquan Mountain. One of its purposes is to have a better influence on all towns and cities in the east. Chengdu-Kunming high-speed rail line is introduced in front of Tianfu International Airport and set up a station in the GTC of the airport. Once this high-speed rail line is completed, it will be very convenient to connect Chengdu with the southeast cities of Sichuan, such as Ziyang, Neijiang and Zigong. It will also connect in a benign way with Chongqing and Kunming and promote the rapid integration of southwestern urban clusters.
Knowing the current development tendency, at the macro level, the formation of a multi-level transportation system between large airports and rail transit changes rapidly. It can be imagined that in the near future, the relationship between rail transit and airport terminals will transform from the short distance juxtaposition to the integration of air-rail transport complexity with airport functions as the main function. In this sense, the integrated complex design of the airport terminal would be a possible development direction.
1.2 The Coordinated Development Inside the City
Airport terminals often boost the economy during the development of new urban areas. International Airport is the development engine of Tianfu New District, an urban area set by Chengdu. When the airport is completed in the future, relying on the huge flow of people and logistics, Tianfu New District will build development circles layer by layer, forming a dynamic economic circular zone featured with aviation. To achieve this purpose, rational planning and development of airport land would be particularly important. Reasonable development and planning can not only make the operation of the airport more efficient, but also maximise the value of the surrounding land and realise the rapid development of the new district.
There will also be close links between the new area developed around aviation and other areas of the city. Urban railway system and urban road network will be pulled, forming a complex and dense traffic system in the new area, stimulating the construction of urban infrastructure, and pulling the coordinated development of surrounding areas.
2 Medium-Level: the Trend in Airport Planning
2.1 The Efficiency of Airport System
Analyzing the development of several airports in core hub cities, the throughput of passengers and goods in airports is increasing year by year with the rapid development of the regional economic level. 2019, the passenger throughput of Beijing Capital Airport has reached one hundred million, the passenger throughput of Shanghai Pudong Airport has reached 76 million, the passenger throughput of Guangzhou Baiyun airport passenger throughput has reached 73.5 million. In terms of growth, the development mod, one airport multiple runways and multiple terminals, is inevitable. Therefore, from the perspective of airport planning, it is necessary to study the multi-terminal airport system as a whole. How to shape the system into that of high standards, and fully integrated transport hub is a problem that must be considered in the future.
Landside connections between terminals can be made by subway of terminal shuttle bus. While airside connections be-tween terminals would be harder. Generally speaking, it is a good choice to use the airside APM (Auto Passenger Mover) system. Due to the localisation of APM system products, the total cost of investment and operation costs are reduced, consequently, the introduction of the APM system in large hub terminals is an inevitable trend.
2.2 The Flexibility of Airport Planning
The planning of large hub airport terminals should focus on the flexibility of space use and operation to cope with the rapid changes in the development of airport terminals. Especially in the case that the scale of airport land cannot be extended, the planning of the airside and landside should have design margins.
First of all, there should be design margins in land use, so that the airside can be expanded in different ways according to the change of longterm demands, and the land in the core area of the landside terminal can be allocated according to the change of passenger footfall. Secondly, the capacity of the landside road system should have design margins, especially the departure/arrival lane side. This trend could be seen from the recent emergence of the stratif ied departure lane.
It is necessary to set up swinging aircraft stands, which could realise the allocation of domestic and international sectors and provide the possibility for virtual flights to use boarding bridge. The design of the flexible aircraft stands can improve the efficiency and applicability of the boarding bridge. The building reserves expandable space for facilities and equipment, as well as room for future capacity development.
2.3 The Development of Highly Integrated Urban Functions
After the large hub airport terminal and GTC form an integrated transportation complex, other urban functions will be added (such as parks, exhibitions, shopping malls, stadiums, botanical gardens, hotels, conference centres, etc.) according to the needs of urban development. The core area, less than one kilometre from the terminal, will become an important urban complex, attracting tourists and citizens from inside and outside the city. These functions are realised thanks to the strong transportation capacity of the airport terminals, which can organise the flow of people and goods more conveniently in the region. The core business district at Hongqiao pioneers this concept in China, which has gained a good social response by now.
3 Micro-Level: Architectural Design of Terminals
3.1 The Relationship between Centralised Terminal and Passenger Walking Distance
Since China's airport construction is mainly funded by the government, in order to avoid the awkward situation that the airport needs to be expanded after the previous construction, all the constructions of large hub airports will be built a little larger, so the main formation of Chinese large hub terminals is centralised terminal conf iguration. Centralised terminal configuration has many advantages, such as flexible deployment, space margins to deal with the long-term development, but is also bring problems such as long passengers walking distance, etc.
In the recent design competition, the airport operators often pursue a high proximity rate, resulting in the increases of the airside shoreline length, further increasing the passenger walking distance in the building. Several large terminals in China have been criticised for their long walking distance (about 1 kilometre). Therefore, how to achieve the goal which could have a high proximity rate, a good in-building deployment, a comfortable passenger walking distance is important to be considered in the design. Therefore, in the first phase of Chengdu Tianfu International Airport the selection of two unit terminals aims to explore the design ideas that can balance the multi benef its.
Besides, multiple terminals need to be connected with the APM system, the construction of the APM system will be-come indispensable. Therefore, it would be worthy to consider in-building APM to reduce the walking distance. The use of inbuilding APM would well supply the domestic largescale centralised terminal, to form an efficient passenger flow in the building.
3.2 Experiential Terminal
Contemporary terminals are being designed with an increasing emphasis on experience. The terminal needs to be de-signed around local characteristics in terms of images, spaces, material selection, and colours. In addition, various valueadded services in the building, such as exhibitions, performances, and interactive activities, not only serve visitors well and improve the quality of service, but also play a good role in publicity.
3.3 Intelligence Terminal
The development of application technology in the terminal is another point that is worth paying attention to. From the overall trend, with the development of technologies such as big data, artificial intelligence, 5G, and the Internet of everything, the intelligence of the terminal is manifested in three aspects: intelligent transport management, intelligent security and intelligent service. Through the establishment of intelligent management system, realise the dynamic linkage of air and land transportation management information, realise the intelligent operations of the airport. Based on the technology of human identity recognition, fingerprint recognition, face recognition, iris recognition, combined with selfservice check-in machine, self-service luggage consignment and other equipment, realise the safe passenger non-contact customs clearance and improve the passenger satisfaction. Use WeChat small programme or mobile apps to realise the comprehensive online service in the passenger building provides a variety of precise services, such as indoor positioning, intelligent customer service, online shopping of goods in the building, car booking and ticket booking.
3.4 The Emphasis on Non-Airline Revenue
The increase in non-airline revenue has been paid more and more attention from airport operators. It can not only bring a better passenger service experience, but also make a lot of profit for the airport. Looking at the world's best airport terminals, many of them have put a lot of effort into "how to build a better airport business", such as Changi Airport, Shikiev Airport, Narita Airport and so on. They have also won the favour of passengers through good business, and many airports have gradually become tourist destinations for passengers, realising the comprehensive leap of airport functions and roles.
3.5 The Ref lection of Regional Characteristics
The architectural image and space should reflect the regional characteristics, especially the characteristics of the climate. For example, in the north China, where the annual temperature difference is large, it is not recommended to set up a large courtyard in the terminal, because it not only wastes energy but also precules have the image of a green landscape; In South China, a large courtyard can be considered to be set up in the building, which cannot only play the role of ventilation and ventilation to adjust the climate of the small area but also needs to present the perennial green landscape in the building.
In addition, the architectural image and the space inside the building should ref lect the spirit of the city. Through the creative design, the shapes, meanings, and forms are combined, and a new name card of the city can be created to depict the spiritual connotation of the city.
4 Case Study: Qingdao New Airport
4.1 Project Prof ile
Qingdao Jiaodong International Airport is positioned as "a regional hub airport as a gateway for Japan and South Korea and an international air cargo hub around the Bohai Sea Rim Region." The new airport is designed to meet the annual passenger throughput of 35 million by 2025, and meet the passenger throughput of 55 million by 2045.
The new airport is located in the northeast of Jiaozhou of Qingdao City, about 40 km from the centre of Qingdao City. The recently acquired land area is about 15.63 km2, and the total number of planned aircraft stand is 178. The Terminal 1 is to be constructed recently with floor area of about 478,000 m2. A traffic centre of 208,000 m2is also to be set up recently in front of the building, including the Jinan-Qingdao High-Speed Railway, the airport station of two urban rails, as well as parking buildings, coach stations and commercial centres. In the long term, the terminals will continue to be expanded on the landside, and the third and fourth runways will be gradually constructed on the east and west sides of the airside.
The conceptual design of the terminal of the new airport follows the principles of "planning guided, safety first, complete functions, convenience and comfort, environmental protection and energy saving, coordination and beauty, high quality and reasonable price". The overall layout of the new airport is designed to be as the shape of Chinese character "齐", and the five extremely centripetal airside concourses are integrated with the hall, displaying a continuous curved surface full of tension to achieve a reasonable balance between large concentration and separated sections. The design has incorporated bionics design concept, and the phase I of the project is like a starfish on the shore.
4.2 Impact of the Changing Trend of Airport Runway Spacing on Terminal Conf iguration
The design capacity of the airport is closely related to the layout of the runway. The taking-off and landing capacity of a single runway is about 40 sorties, that of the closely spaced runway is about 60 sorties, and that of the long-distance runway can reach 80 sorties. Domestic airports have been experiencing high-speed growth in recent years. With the continuous growth of aviation business, for the large newly-built airport, the model of longdistance runway has been chosen and adopted.
According to the relevant provisions of Ordinance No. 123 issued by Civil Aviation Administration of China, when the distance between the central lines of two parallel runways is not less than 1035 m, 915 m or 760 m, the corresponding allowable aircrafts shall operate in four modes respectively, namely independent parallel approach, dependent parallel approach, independent parallel departure and segregated parallel operation.
The distance choosing of long-distance runway further affects the configuration design of the terminal. From Table 1, it can be seen that domestic airports generally employ the long-distance runways with large spacing:
Under the premise of satisfying the safe operation of the aircraft, the length of the parking line can be increased by an addition of the number of airside concourses in the terminal layout to obtain more contact stands. Both Qingdao New Airport and Beijing Daxing International Airport have been set with the layout of a single building with centralised five airside con-courses when the runway spacing reaches 2200 m to 2400 m, which maximises the number of contact stands.
4.3 Attention to Passenger Flow of Qingdao New Airport
Caring for passengers is a constant theme in airport design of rapid change. The design principle of achieving the overall balance of the air and land sides has been determined at the beginning of the schematic design of Qingdao New Airport.
When comparing the options of terminal, the impact of different options on passengers' walking distances and parking lines has been compared. The five-airside-concourse centripetal layout has been used for that the check-in hall of the terminal is closer to the centre of the terminal in the layout. After the security check, the farthest distance to the terminal area is within 650 m, making it be one of the terminals with the shortest walking distance among those with 30 to 40 million throughout.
At the same time, the configuration of five airside concourses has provided superior parking length. Compared with the required number, the proportion of the contact stand number reaches 80%, where 47C22E2F or 69C13E is suited (calculated according to the combined stands). From the perspective of requirements on airport service quality and future development trends, the original design based on the contact stand ratio of 70% can no longer meet the requirements on the airport in the new era for humanistic airports (Table 2).
The characteristics of passenger flow in different airports need to be fully considered in airport design. Qingdao Air-port, as an airport in eastern China and different from other central airports, its domestic transit demand is lower than the international transit one. At the same time, the base airlines Shandong Airlines and China Eastern Airlines belong to the Star Alliance and the SkyTeam respectively and have similar flight ratios. The design of Qingdao Airport gives full rise to the characteristics of the centripetal configuration, setting the international airside concourse in the middle, and the domestic parts of different alliances are set on both sides, thus forming a very convenient domestic and international circulation.
6
7

8

9

10

11

12
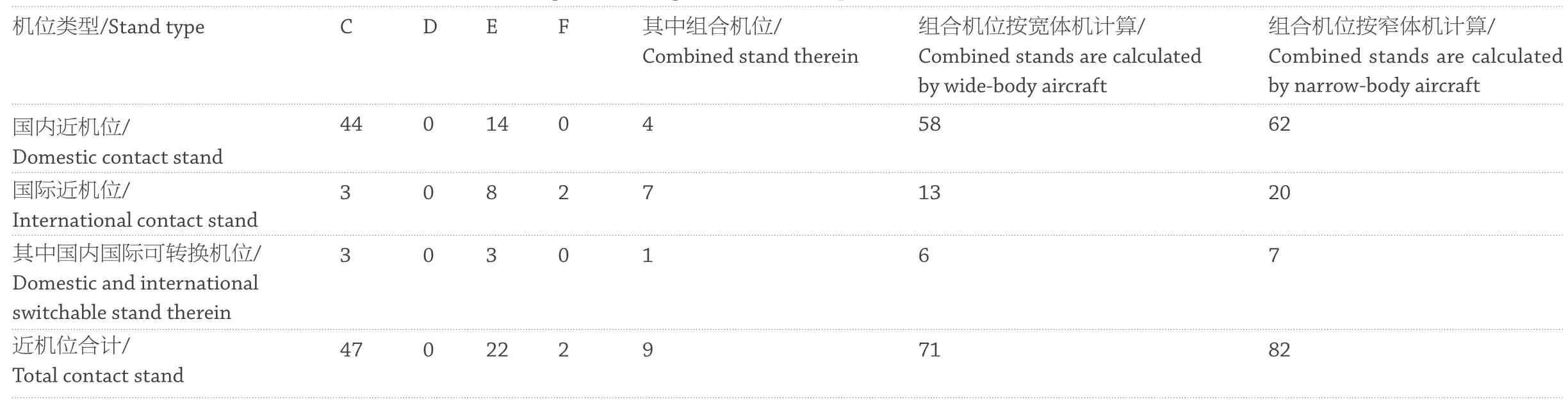
表 2 青岛胶东机场机位统计/Table 2 Stand statistics of Qingdao Jiaodong International Airport
7构型停机长度比较/Comparison of parking lengths of different conf igurations
8 西安咸阳机场构型/Configuration of Xi'an Xianyang International Airport
9上海浦东机场构型/Configuration of Shanghai Pudong International Airport
10 重庆江北机场构型/Configuration of Chongqing Jiangbei International Airport
11广州白云机场构型/Configuration of Guangzhou Baiyun International Airport
12 北京大兴机场构型/Configuration of Beijing Daxing International Airport
There are also 6 switchable stands in the international airside concourse area, which can realise the smooth domestic and international flight switch independently, and combined with the transfer process, the rapid domestic and international transfer can be achieved in the building.
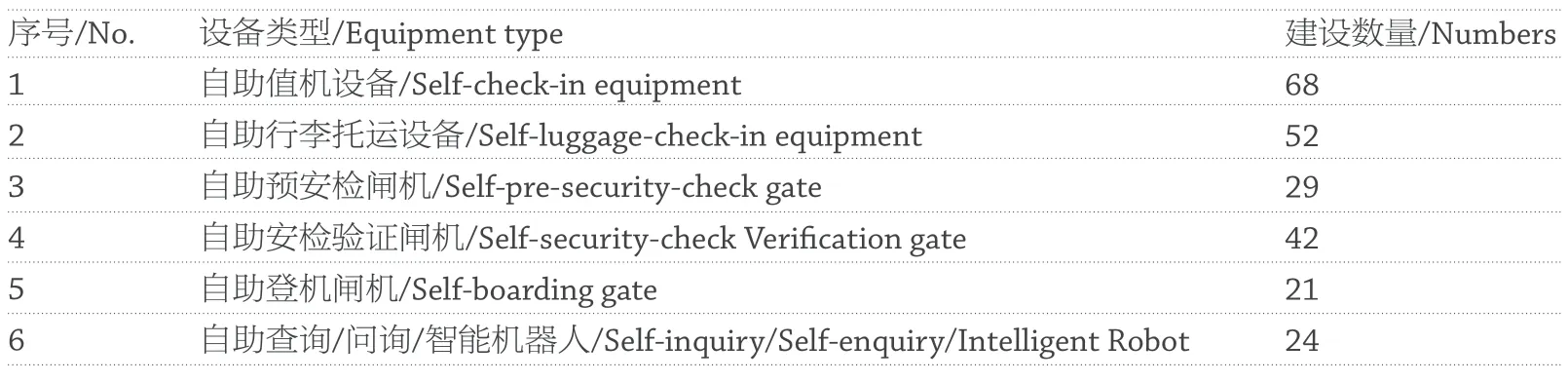
表 3 自助设备类型及数量/Table 3 Self-service equipment type and numbers
4.4 Application of Smart Airport
Qingdao New Airport has just been designed in a period of rapid development of smart airports. Selfservice equipment, paperless customs clearance, smart customs clearance and other facilities and policies have been implemented one after another, and the development of domestic hardware and software has gradually improved. In the design and construction process, the smart airport strategy of Qingdao Airport has been constantly improved and revised.
(1) In the check-in area, after comparing multiple options, a two-stage self-check-in layout plan was adopted. Each check-in counter is equipped with an automatic box-return system and forms a complete self-check-in area between normal counters.
(2) In the queuing area of security check, selfsecurity-check verification channel and self-boxreturn facility in the security channel are adopted.
(3) Self-boarding equipment is set up at the boarding gate of the waiting area 3 and etc. to speed up boarding efficiency and save manpower.
(4) In the terminal design, simulation has been used to assist verification. At the same time, the operational efficiency of the air side and the passage facilities in the building have been simulated and evaluated, and repeatedly verified to optimise the design. With the improvement of software and the improvement of hardware performance, for building design with large investment, long construction period and visitor's flow rate, simulation is gradually becoming the preferred tool for the design.
Through simulation, the operation of the smallangle airside harbour can be seen intuitively. The results show that the small-angle harbours operate smoothly as the intervals are large enough, and congestion only appears in the departure waiting area of the runway.
By importing the flight time of the peak month, combined with the predicted data of the design year, a very real simulation result is formed, and through the facility simulation, the original design def iciency like the layout of check-in counters, number of safety check channels for crew and employees, and queue space for frontier inspection has been optimised.
4.5 Attempts of New Materials by Qingdao New Airport
The roof of the terminal is welded by stainless steel. It proves that after a period of time, the risk of rain leakage and wind exposure is greatly reduced. The unique metal texture highlights the beautiful shape of the terminal in the sun.
In addition, the form of triple supply is used to provide energy and the waste heat is used to generate electricity; 5500 m2of photovoltaic power generation is used on the roof of the transportation centre to make full use of the good sunshine in Qingdao; indoor controllable electric shutters are used in the terminal to minimum the impact of the unfavourable period of the morning and evening. Qingdao Jiaodong International Airport complies with the relevant requirements of Outline of Action for the Construction of China's Civil Aviation Type IV Airport, and has been built with resource intensive and saving, low-carbon operation, and environmentally friendly throughout the life cycle, and has successfully passed the design review of the Chinese three-star green building standard.

16

18

19
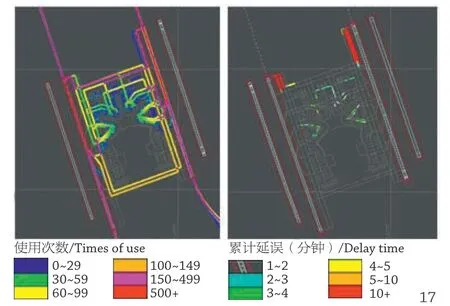
17
20
18 自助安检验证柜台/Self-security check verif ication counter
19 自助登机通道/Self-boarding channel
20 航站楼仿真模拟及优化/Simulation and optimisation of the terminal
(1-20图片来源/Sources: 中国建筑西南设计研究院有限公司/China Southwest Architectural Design & Research Institute Co., Ltd.)
