采用K均值聚类和环形结构的狭叶锦鸡儿木质部提取算法
2020-03-03王海超宗哲英张文霞殷晓飞王晓蓉张海军刘艳秋王春光
王海超,宗哲英,张文霞,殷晓飞,王晓蓉,张海军,刘艳秋,石 鑫,王春光
采用均值聚类和环形结构的狭叶锦鸡儿木质部提取算法
王海超,宗哲英,张文霞,殷晓飞,王晓蓉,张海军,刘艳秋,石 鑫,王春光※
(内蒙古农业大学能源与交通工程学院,呼和浩特 010018)
针对木质部交互统计误差大、效率低、重现性差、劳动强度高和传统图像处理算法精度不理想等问题,该文以狭叶锦鸡儿木质部切片图像为研究对象,根据木质部特点提出基于均值聚类算法和环形结构提取算法相结合,实现木质部准确提取的方法。首先通过动态巴特沃斯同态滤波法对30幅供试图像进行光照不均校正,然后采用均值聚类法对光照补偿后图像初分割,最后采用环形结构提取算法实现木质部提取计数。试验结果表明:采用均值聚类算法对光照补偿后的木质部图像初分割分割误差(section error,)、过分割误差OR(over-segmentation error, OR)和欠分割误差UR(under-segmentation error, UR)均值分别为5.15%、1.48%和6.46%,优于未光照补偿和3R-G-B算法;该文提出的环形结构提取算法对初分割后木质部图像检测的平均相对误差为2.26%,比分水岭法低11.69个百分点,比凹点匹配法低4.93个百分点。从速度上看,该算法平均耗时3.17 s,比分水岭法快1.40 s,比凹点匹配法快4.88 s。该算法检测的均方根误差RMSE(root mean squared error, RMSE)为0.52%,约相当于分水岭法的1/3,约相当于凹点匹配法的1/2,该算法优于其他2种分割算法;在图像结构复杂、光照不均匀、内部分布不均等缺陷条件下,该文算法也能很好地实现木质部的分割和提取。该方法不仅能对狭叶锦鸡儿木质部自动分割和提取,也可为其他植物木质部分割提取提供参考。
提取;算法;木质部;均值聚类;环形结构提取;狭叶锦鸡儿
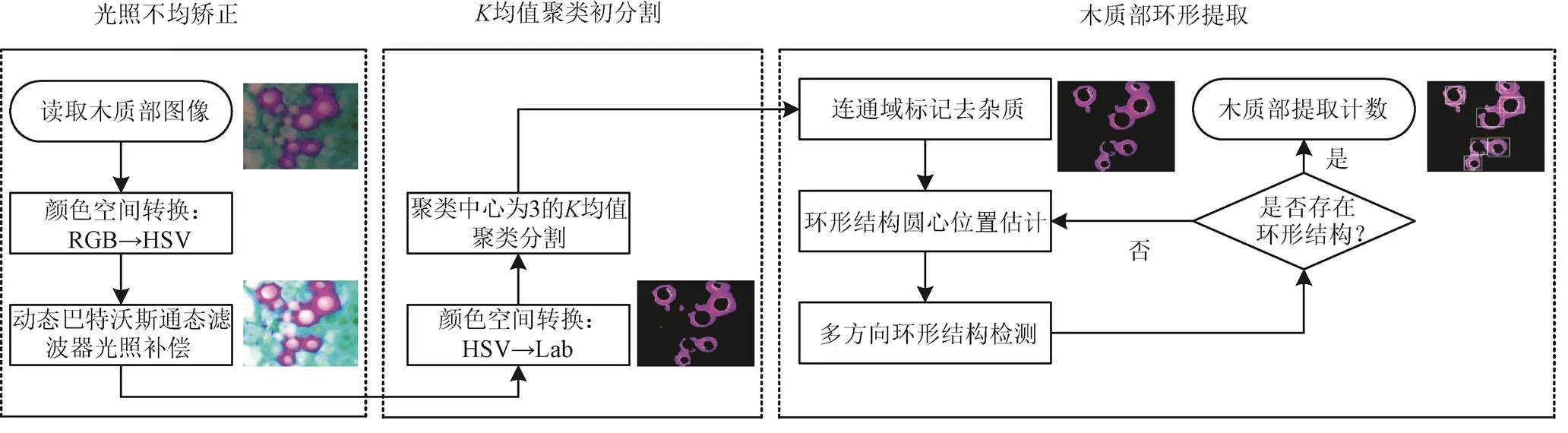
0 引 言
木质部是维管植物体内重要的复合组织,负责水分及水分中离子运输和支撑作用[1-2],其深入研究对揭示维管植物抗旱机制和不同条件下耐旱植物的选育具有重要意义。目前木质部统计常通过离析、切片等手段制成样本,采用显微镜人工交互方式进行计数,该方式存在人为误差大、效率低、重现性差和劳动强度大等缺点,制约了该领域的深入研究[3-5]。
木质部多存在黏连情况,黏连细胞分割和统计是图像处理领域一项基本而又十分关键的技术,一直是细胞统计学中研究难点和热点问题。常用的黏连细胞分割方法有分水岭算法、凹点匹配法、形态学法、椭圆建模法、水平集法和机器学习法[6-11],其中分水岭算法、凹点匹配法因其实现简单、高效,得到的应用最多,目前以这2种算法为框架,并出现了各种改进算法。Salim等[12]提出基于距离地形图分水岭变换分离黏连细胞,提高了正常白细胞和致密白血细胞病簇的分割精度;Miao等[13]提出一种标记控制分水岭算法自动分割和统计血液中白细胞和红细胞数量,该算法基于距离变换和边缘梯度信息来获取血细胞轮廓,通过分类获得分段的白细胞和红细胞,此法相较传统分水领算法精度较高,但对先验标记精度要求较高;Hasan等[14]提出2步验证分水岭匹配算法对脑肿瘤进行分割,其使用伪影去除、中值滤波和三边滤波对图像进行预处理,首先从MR图像中分割出肿瘤区域,然后使将分割后的部分与验证图像进行匹配,从而准确分割脑肿瘤;Albayrak等[15]采用两级超像素分割算法对肾癌细胞进行提取,该算法首先利用简单线性迭代聚类法(simple linear iterative clustering,SLIC)将图像分割为超像素图像,然后采用基于密度的聚类算法(density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise,DBSCAN)对获得的超像素进行聚类,找到组成细胞核的相似超像素,从而实现肾癌细胞准确分割;闫沫[16]结合梯度修正和区域归并策略对传统分水岭算法进行改进,改善了分水岭算法过分割现象;赵红英等[17]采用基于水平集主动轮廓(active contour model,ACM)算法对宫颈癌细胞初分割,然后将归一化后图像与感兴趣区域(region of interest,ROI)梯度图像点乘来抑制无用梯度信息,最后运用标记分水岭算法对感兴趣区域细胞进行分割;廖慧司等[18]提出一种结合距离变换利用边缘梯度的分水岭血细胞显微图像分割算法,该算法由距离图提取前景标记,将距离分水岭变换所得的脊线作为梯度分水岭变换的背景标记,能有效地分离黏连目标,但该方法鲁棒性较差,对切片质量要求较高;张建华等[19]在H-minima分水岭分割基础上,结合最小二乘圆法误差理论,提出了自适应H-minima分水岭分割方法,实现了棉花叶部黏连病斑的准确分割,但当病斑黏连较紧密和大小病斑重叠在一起时会存在欠分割情况。Yao等[20]采用边缘中心模态比例(edge center mode proportion,ECMP)法对水稻粒进行凹点匹配,在协同约束条件下进行分割,然后再用最小外接矩形计算其长度,从而精确识别出稻米粒,但该算法容易出现过分割情况;Zhang等[21]采用canny边缘检测和改进的凹点匹配算法对接触种子进行分离,有效地提取了种子的位置和方向信息,有效地实现了种子自动挑选,Zhang等[22]利用凹点检测和线性分组技术对重叠细胞进行自动分割,该算法主要包括轮廓提取、凹点检测、轮廓段分组好椭圆拟合四个步骤,但模糊图像凹点和边界的准确定位仍是难点;杨辉华等[23]提出一种结合水平集轮廓提取的凹点区域检测的黏连细胞分割方法,准确地分割了黏连细胞,但对于黏连严重情况分割精度不高,常出现过分割;王晓鹏等[24]提出一种基于形态学多尺度重建结合凹点匹配的枸杞图像分割方法,结合枸杞颗粒的大小和形状特点,实现黏连枸杞颗粒的分割和计数;李毅念等[25]通过颜色空间转换、去除细窄黏连、黏连判断、凹点检测等算法过程,实现了图像中黏连麦穗的有效分割,依据麦穗和麦粒间关系,构建了产量预测模型,进一步得到了单位面积内的小麦麦穗数量、总籽粒数及产量信息,但对于黏连麦穗存在部分过分割。
木质部存在多个不黏连和黏连形式,其显微图像具有纹理多、结构复杂、形状不规则等特征,常存在低对比度、边界模糊、内部分布不均等缺陷,限制了细胞分割和统计的准确性,也对算法鲁棒性提出了挑战,目前国内外对其分割提取的研究鲜有报道。因此,本文以狭叶锦鸡儿木质部图像为研究对象,在分析总结前人算法和木质部图像特点基础上,首先对采集的木质部图像采用动态巴特沃斯滤波器进行滤波,消除显微图像光照不均现象;然后采用均值聚类算法将木质部从原图像中分离出来;最后采用本文提出的环形结构提取算法实现木质部提取和计数。
1 材料与方法
1.1 图像获取

a. 第一组木质部图像a. First set of xylem imageb. 第二组木质部图像b. Second set of xylem imagec. 第三组木质部图像c. Third set of xylem image
1.2 木质部初分割方法
1.2.1 光照不均校正
显微图像常存在光照不均和光照不足现象,这会对后续图像分割和特征提取准性造成较大影响,改善图像分辨率和视觉效果是图像处理中不可缺少的环节。本文采用HSV变换和动态巴特沃斯同态滤波算法对木质部图像进行光线补偿,该算法在不改变原图色调和饱和度不变的前提下对亮度分量进行增强,图像细节增强同时削弱低频分量,改善图像质量[27-29]。
1.2.2均值聚类
均值聚类算法是典型的无监督硬聚类算法,其以欧式距离、汉明距离、闵可夫斯基距离和街区距离等作为相似度度量(默认采用欧式距离),以误差平方和作为聚类准则,可实现类间相似度最低和类内相似度最高,且局部最优,十分适合彩色图像分割[30]。采用均值聚类算法对彩色图像进行分割时,往往选用Lab颜色空间,Lab模型可近似使用球体结构表示,颜色空间是均匀的,过球心的笛卡尔三坐标对应各颜色分量,各任意色彩均可由以上亮度()、色度(,+表示红色,-表示绿色)和色度(,+表示黄色,-表示蓝色)3个分量叠加而成[31]。由于木质部图像主要由红色的木质部、白色液体膜和绿色韧皮部部分构成,故聚类中心数目为3,聚类后红色区域为分割的目标区域。
1.2.3 初分割质量评价
为定量评价算法分割效果,本文在总结分析已有图像分割评价法基础上,选用分割误差R(section error,R)、过分割误差OR(over-segmentation error,OR)和欠分割误差UR(under-segmentation error,UR)对分割结果进行评价。这3种评价指标值越低,表明图像分割效果越好,目标提取精度越高。这3种评价指标均需要分割目标真实面积作为基准,目标真实面积采用Photoshop进行手动分割,擦除背景区域后剩余像素数作为目标真实尺寸。3种评价指标计算公式为
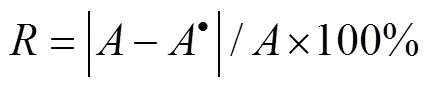
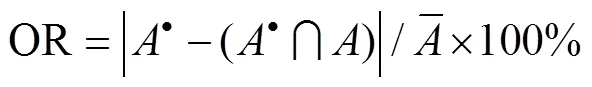

1.3 木质部提取算法
由木质部结构特点可知,其经初分割后存在独立、黏连和不闭合现象,且木质部呈环状。从分割目标考虑,对木质部个数统计时,不必保证木质部结构完整性,只需保证个数准确即可。故本文在充分分析木质部细胞结构特点和前人算法基础上,提出一种环形结构提取算法,从而实现木质部准确提取计数。该算法首先确定木质部图像连通域,并对联通域进行标记,剔除较小的杂质区域;然后采用定步长窗口扫描方式粗略估计出环形结构中心位置;最后通过圆心位置对其对应上、下、左、右4个进行检测,若检测出不少于2个方向上存在环形部分结构,则该圆心对应的环形结构即为1个木质部,具体过程如下:
1)连通域标记
2)环形结构圆心位置估计

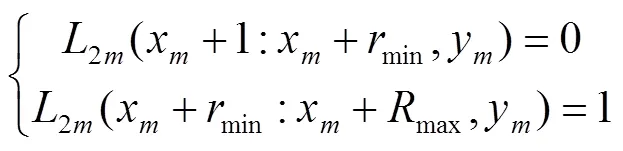

注:图中各个变量为点的坐标,1m为组数,为图像宽度。
Note: Variables in the graph are the coordinates of points,1mis the number of group,is the width of image.
图2 环形结构圆心位置示意图
Fig.2 Schematic diagram of circular structure’s center position
3)环形结构判定
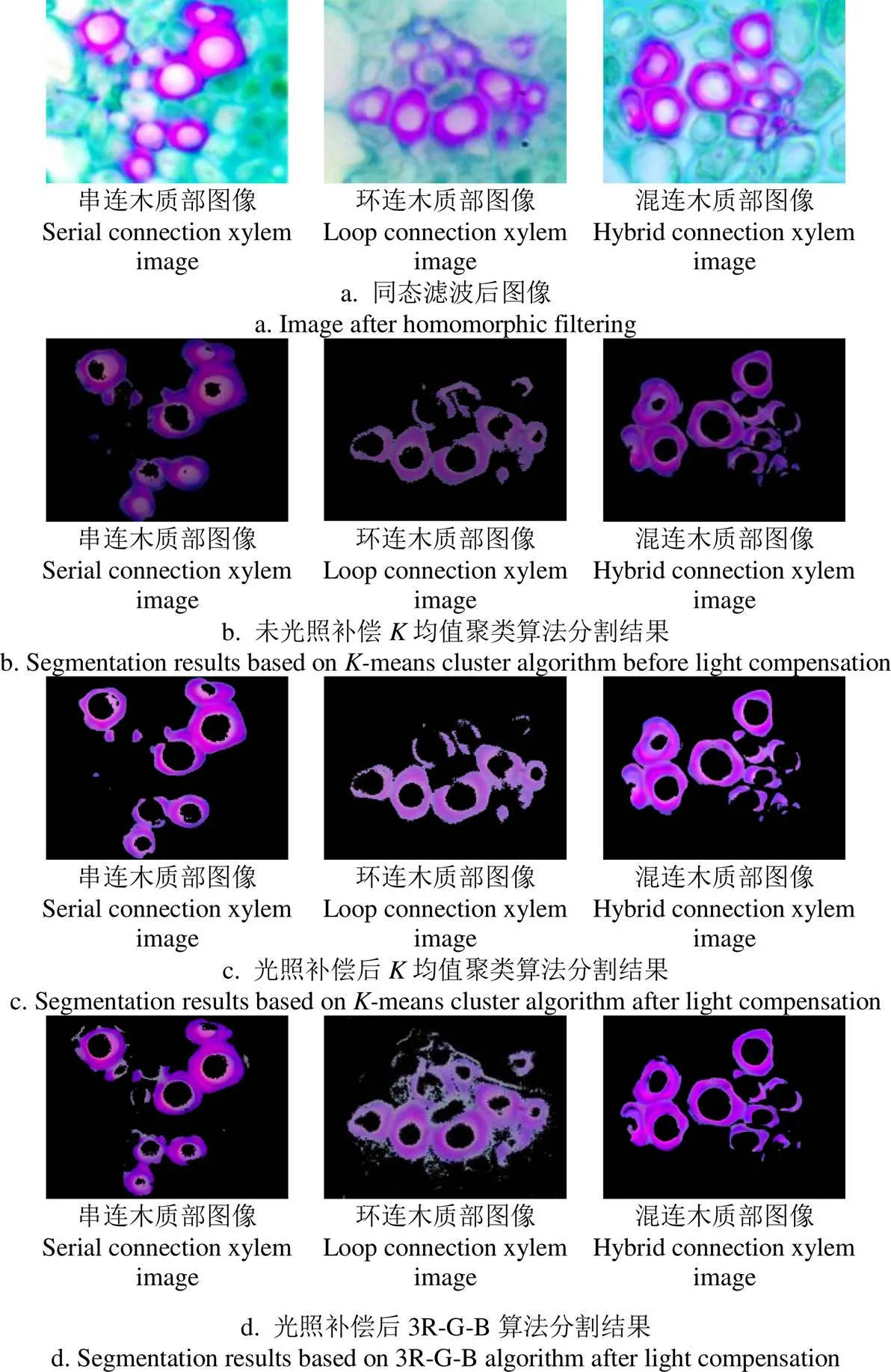
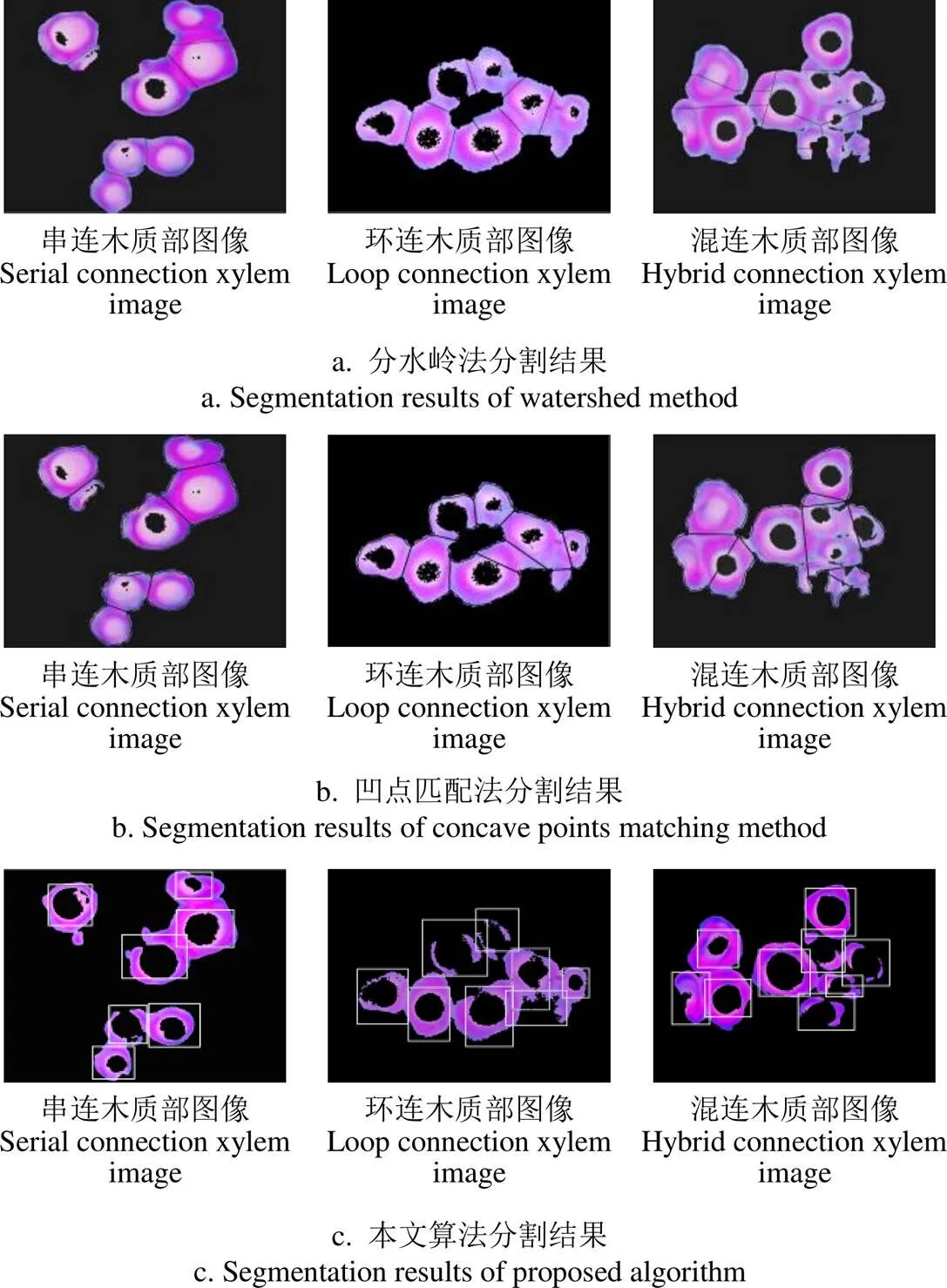
①采用Sobel算子提取木质部边缘,对木质部上、下、左、右4个方向进行检测,若距圆心(,)>min和 ②当上、下、左、右4个方向上无法检测出2个及以上环形结构时,可能木质部存在缺口,此时需将原检测方向左右偏移45°,若有2个以上方向上存在环形结构,则认为存在1个木质部,如图3b所示。 注:Rmax为最大外径,rmin为最小内径,(a,b)为圆心,r为实际检测半径。 4)环形结构提取 以(,)为中心,用矩形框将环形结构标出并计数,实现环形结构提取。 上述木质部提取流程如图4所示。 图4 算法流程 为验证算法精度、稳定性和速度等有效性,从已拍摄的木质部图像中随机选取木质部黏连程度各异的图像30幅进行木质部分割提取。试验采用Window7旗舰版64位系统、主频2.40 GHz、8 G内存Asus笔记本电脑,软件采用MatlabR2014a,具体试验分为4部分: 1)为验证光照补偿的有效性,从已拍摄的木质部图像中选取木质部黏连程度各异的图像30幅进行试验,采用均值聚类算法分别对原始图像和同态滤波后图像ab分量进行聚类,分别采用分割误差、过分割误差OR和欠分割误差UR对算法进行定量评价; 2)为验证分割算法有效性,采用均值聚类算法和3R-G-B阈值分割算法[32]对同态滤波后木质部图像进行分割,并对分割效果进行比较; 3)为检验本文环形提取算法性能,对初分割后的30幅木质部图像进行提取,试验软件和硬件与木质部初分割使用相同。分别采用分水岭法[33]、凹点匹配法[34]和本文算法对木质部进行提取,最后将各算法提取结果与实际木质部数量进行对比,从而对各算法性能进行评价。 1)采用聚类中心数目为3的均值聚类算法对30幅供试图像处理,结果如图5所示,聚类后红色区域为目标区域,分割效果如表1所示。其中,图5a为动态巴特沃斯同态滤波后图像,可以看出,滤波后木质部图像细节、纹理、对比度和视觉效果得到明显改善,光照均匀度增强;图5b是未进行光照补偿直接采用均值聚类算法分割后效果,由于受光照不足和不均影响,存在较严重的过分割现象;图5c为同态滤波光照补偿后均值聚类算法分割后效果,可以发现分割效果得到明显改善,木质部分割的更为完整。由表1知,采用均值聚类算法对未进行光照补偿处理的木质部图像分割误差、过分割误差OR和欠分割误差UR均值分别为28.75%、9.23%和19.47%,同态滤波光照补偿后,均值聚类算法分割误差、过分割误差OR和欠分割误差UR均值分别为5.15%、1.48%和6.46%,较未进行光照补偿分别降低了23.60、7.75和13.01个百分点。由此可以发现,采用动态巴特沃斯同态滤波算法对木质部图像光照补偿后,不但能改善图像质量和分割效果,而且还能够提高分割算法分割精度; 图5 光照补偿前后不同分割算法分割结果示例 2)采用3R-G-B阈值分割算法对光照补偿木质部细胞图像分割结果如图5d所示,分割效果客观评价如表1所示。可以发现,虽然部分分割效果优于均值聚类算法,但大部分分割存在较大误分割,整体分割效果不如均值聚类算法。由表1知,3R-G-B阈值分割算法对光照补偿后木质部细胞分割误差、过分割误差OR和欠分割误差UR均值分别为15.58、6.06和11.42个百分点,较光照补偿后均值聚类算法分别增加了10.43、4.58和4.96个百分点。由上述结果可以发现,针对木质部细胞图像,均值聚类算法分割效果优于3R-G-B阈值分割算法,分割误差、过分割误差OR和欠分割误差UR更低。 表1 本文算法与3R-G-B算法对测试图像分割效果 注:、OR、UR分别为分割误差、过分割误差和欠分割误差。 Note:stands for segmentation error; OR stands for over-segmentation error; UR stands for under-segmentation error. 图6 本文算法与其他算法对测试图像木质部分割结果 表2 不同算法对测试图像木质部检测结果对比 由图6a和6b可以看出,当木质部黏连较简单时,分水岭法和凹点匹配法分割较准确,但当木质部黏连程度复杂时,分割效果较差,出现了较多误分割。由图6c可知,相较上述2种算法,本文提出的环形结构提取算法分割较准确。由表2可以看出,本文算法检测木质部数目平均相对误差为2.26%,比分水岭法低11.69个百分点,比凹点匹配法低4.93个百分点;从速度上看,本文算法平均耗时3.17 s,比分水岭法快1.40 s,比凹点匹配法快4.88 s,但本文算法与凹点匹配法耗时均随木质部数目增多、黏连复杂度增高呈上升趋势,分水岭法耗时相对稳定;本文算法检测的均方根误差RMSE(root mean squared error,RMSE)为0.52%,约相当于分水岭法的1/3,约相当于凹点匹配法的1/2。综合衡量,本文算法较好。 本文以狭叶锦鸡儿木质部图像为研究对象,针对黏连细胞分割问题,通过光照不均校正、K均值聚类初分割和木质部环形提取等算法,实现了图像中木质部的有效分割和提取。通过试验得出以下结论: 1)采用均值聚类算法对光照补偿后的木质部图像初分割误差(section error,)、过分割误差OR(over-segmentation error,OR)和欠分割误差UR(under-segmentation error,UR)均值分别为5.15%、1.48%和6.46%,优于3R-G-B阈值分割算法; 2)本文提出的环形结构提取算法能够实现木质部准确提取计数,对初分割后木质部图像检测的平均相对误差为2.26%,比分水岭法低11.69个百分点,比凹点匹配法低4.93个百分点。从速度上看,本文算法平均耗时3.17 s,比分水岭法快1.40 s,比凹点匹配法快4.88 s,但本文算法与凹点匹配法耗时均随着木质部数目增多、黏连复杂度增高呈上升趋势,分水岭法耗时相对稳定。本文算法检测的均方根误差RMSE(root mean squared error,RMSE)为0.52,约相当于分水岭法的1/3,约相当于凹点匹配法的1/2。综合衡量,本文算法优于上述2种算法。 当木质部黏连特别紧密和缺失严重时,本文方法存在部分欠分割现象,在今后进一步研究中,将结合深度学习中的语义分割和实例分割,提高黏连木质部分割精度,改善本文算法不足。 [1]董星光,曹玉芬,王昆,等. 中国3个主要梨砧木资源木质部导管分子结构及分布比较[J]. 植物学报,2015,50(2):227-233. Dong Xingguang, Cao Yufen, Wang Kun, et al. Comparison of the characters and distribution of vessel elements in xylem among three main pear rootstocks in China[J]. Bulletin of Botany, 2015, 50(2): 227-233. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2]Tombesi S, Johnson R S, Day K R, et al. Relationships between xylem vessel characteristics, calculated axial hydraulic conductance and size-controlling capacity of peach rootstocks[J]. Annals of Botany, 2010, 105(2): 327-331. [3]王明浩,张晓玮,王婧如,等. 一种简易准确测定木质部导水率的新方法[J]. 植物生理学报,2013,49(3):297-300. Wang Minghao, Zhang Xiaowei, Wang Jingru, et al. A simple and accurate method for measuring hydraulic conductivity in xylem[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2013, 49(3): 297-300. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4]Morris H, Plavcová L, Gorai M, et al. Vessel-associated cells in angiosperm xylem: Highly specialized living cells at the symplast-apoplast boundary[J]. American Journal of Botany, 2018, 105(2): 151-160. [5]Savi T, Petruzzellis F, Martellos S, et al. Vineyard water relations in a karstic area: deep roots and irrigation management[J]. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 2018, 263(5): 53-59. [6]李叶舟,胡静,朱少彰,等. 基于光照方向不一致的图像盲取证技术[J]. 北京邮电大学学报,2011,34(3):26-30. Li Yezhou, Hu Jing, Zhu Shaozhang, et al. Exposing digital image forgeries by detecting inconsistence in light source direction[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2011, 34(3): 26-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) [7]Felix B, Carsten M, Michael S, et al. An automatic method for robust and fast cell detection in bright field images from high-throughput microscopy[J]. BMC Bioinformatic, 2013, 14(1): 297-310. [8]Chitade A Z, Katiyar S K. Colour based image segmentation using-means clustering[J]. International Journal of Engineering Science and Technology, 2010, 2(10): 5319-5325. [9]Dzyubachyk O, Van Cappellen W, Essers J, et al. Advanced level set-based cell tracking in time-lapse fluorescence microscopy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2010, 29(3): 852-867. [10]Duartea M, Alvarenga A, Azevedo C, et al. Evaluating geodesic active contours in microcalcifications segmentation on mammograms[J]. Computer Methods Programs Biomedical, 2015, 122(3): 304-315. [11]宋怀波,张传栋,潘景朋,等. 基于凸壳的重叠苹果目标分割与重建算法[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(3):163-168. Song Huaibo, Zhang Chuandong, Pan Jingpeng, et al. Segmentation and reconstruction of overlapped apple images based on convex hull[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(3): 163-168. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12]Salim A, Emel O, Cigdem G D. A color and shape based algorithm for segmentation of white blood cells in peripheral blood and bone marrow images[J]. International Society for Advancement of Cytometry, 2014, 85(1): 480-490. [13]Miao H, Xiao C. Simultaneous segmentation of leukocyte and erythrocyte in microscopic images using a marker-controlled watershed algorithm [J]. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2018, 2018(9): 1-9. [14]Hasan S M K, Ahmad M. Two-step verification of brain tumor segmentation using watershed-matching algorithm[J]. Brain Informatics, 2018, 5(2): 1-11. [15]Albayrak A, Bilgin G. Automatic cell segmentation in histopathological images via two-staged superpixel-based algorithms[J]. Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing, 2019, 57(3): 653-665. [16]闫沫. 基于组件树滤波及快速区域合并的分水岭分割算法[J]. 计算机科学,2013,40(1):282-285. Yan Mo. Watershed algorithm based on image filtering by using component tree and fast region merging[J]. Computer Science, 2013, 40(1): 282-285. (in Chinese with English abstract) [17]赵红英,周中顺,孙存杰,等. 一种新的用于宫颈癌粘连细胞图像分割的分水岭算法[J]. 军事医学,2014,32(12):972-975. Zhao Hongying, Zhou Zhongshun, Sun Cunjie, et al. A new modified watershed algorithm for image segmentation in cervical cancer cell adhesion[J]. Military Medical Sciences, 2014, 32(12): 972-975. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18]缪慧司,梁光明,刘任任,等. 结合距离变换与边缘梯度的分水岭血细胞分割[J]. 中国图象图形学报,2016,21(2):192-198. Liao Huisi, Liang Guangming, Liu Renren, et al. Watershed algorithm using edge gradient combined with distance transformation for segmentation of blood cells[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2016, 21(2): 192-198. (in Chinese with English abstract) [19]张建华,韩书庆,翟治芬,等. 改进自适应分水岭方法分割棉花叶部粘连病斑[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(24):165-174. Zhang Jianhua, Han Shuqing, Zhai Zhifen, et al. Improved adaptive watershed method for segmentation of cotton leaf adhesion lesions[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(24): 165-174. (in Chinese with English abstract) [20]Yao Y, Wu W, Yang T, et al. Head rice rate measurement based on concave point matching[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 41353. [21]Zhang G, Sun Q, Jiang S, et al. Automatic seed picking for brachytherapy postimplant validation with 3D CT images[J]. International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, 2017, 12(4): 1-9. [22]Zhang W, Li H. Automated segmentation of overlapped nuclei using concave point detection and segment grouping[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 71: 349-360. [23]杨辉华,赵玲玲,潘细朋,等. 基于水平集和凹点区域检测的粘连细胞分割方法[J]. 北京邮电大学学报,2016,39(6):11-16. Yang Huihua, Zhao Lingling, Pan Xipeng, et al. Overlapping cell segmentation based on level set and concave area detection[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2016, 39(6): 11-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) [24]王小鹏,姚丽娟,文昊天,等. 形态学多尺度重建结合凹点匹配分割枸杞图像[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(2):212-218. Wang Xiaopeng, Yao Lijuan, Wen Haotian, et al. Wolfberry image segmentation based on morphological multi-scale reconstruction and concave points matching[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(2): 212-218. (in Chinese with English abstract) [25]李毅念,杜世伟,姚敏,等. 基于小麦群体图像的田间麦穗计数及产量预测方法[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(21):185-194. Li Yinian, Du Shiwei, Yao Min, et al. Method for wheatear counting and yield predicting based on image of wheatear population in field[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(21): 185-194. (in Chinese with English abstract) [26]王海超,王春光,宗哲英,等. 基于噪声类型及强度估计的狭叶锦鸡儿叶切片图像盲去噪[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(10):229-238. Wang Haichao, Wang Chunguang, Zong Zheying, et al. Blind image denoising of microscopic slices image of Caragana stenophylla Pojark based on noise type and intensity estimation[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(10): 229-238. (in Chinese with English abstract) [27]焦竹青,徐保国. HSV变换和同态滤波的彩色图像光照补偿[J]. 计算机工程与应用,2010,46(30):142-144. Jiao Zhuqing, Xu Baoguo. Color image illumination compensation based on HSV transform and homomorphic filtering[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2010, 46(30): 142-144. (in Chinese with English abstract) [28]张亚飞,谢明鸿. 基于HSI和局部同态滤波的彩色图像增强算法[J]. 计算机应用与软件,2013,30(12):303-307. Zhang Yafei, Xie Minghong. Colour image enhancement algorithm based on HIS and local homomorphic filtering[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2013, 30(12): 303-307. (in Chinese with English abstract) [29]焦竹青,徐保国. 基于同态滤波的彩色图像光照补偿方法[J]. 光电子,激光,2010,21(4):602-605. Jiao Zhuqing, Xu Baoguo. Color image illumination compensation based on homomorphic filtering[J]. Journal of Optoelectronics. Laser, 2010, 21(4): 602-605. (in Chinese with English abstract) [30]徐黎明,吕继东. 基于同态滤波和均值聚类算法的杨梅图像分割[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(14):202-208. Xu Liming, Lü Jidong. Bayberry image segmentation based on homomorphic filtering and-means clustering algorithm[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(14): 202-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) [31]Azetsu T, Suetake N. Hue-preserving image enhancement in CIELAB color space considering color gamut[J]. Optical Review, 2019, 26(12): 1-12. [32]宋怀波,屈卫锋,王丹丹,等. 基于光照无关图理论的苹果表面阴影去除方法[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(24):168-176. Song Huaibo, Qu Weifeng, Wang Dandan, et al. Shadow removal method of apples based on illumination invariant image[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(24): 168-176. (in Chinese with English abstract) [33]张红民,王一博. 一种改进的细胞图像分水岭分割方法[J]. 重庆理工大学学报,2012,26(11):59-62. Zhang Hongmin, Wang Yibo. An improved method of cell images segmentation based on watershed[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology, 2012, 26(11): 59-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) [34]陶德威. 基于凹点匹配和分水岭变换的车辆图像分割算法研究[D]. 南昌:南昌大学,2016. Tao Dewei. Research on the Vehicle Image Segmentation Algorithm Based on Concave Points Matching and Watershed Transformation[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract) An extraction xylem images ofPojark based on-means clustering and circle structure extraction algorithm Wang Haichao, Zong Zheying, Zhang Wenxia, Yin Xiaofei, Wang Xiaorong, Zhang Haijun, Liu Yanqiu, Shi Xin, Wang Chunguang※ (,010018,) In the slice images of the xylem ofPojarkthis paper proposed a novel algorithm that combined the-means clustering and circle structure extraction algorithm, to achieve much more accurate information data of the xylem than that from the traditional image processing algorithms. Firstly, the dynamic Butterworth homomorphic filtering can be used to compensate for illumination variations on V components in the 30 imagesofPojark xylem in a HSV color space; then the-means clustering can be used to initially segment theandcomponents of the pre-processed xylem images under the Lab color space with a cluster of 3,finally, the circle structure extraction algorithm can be used to accurately cluster and extract the specific feature of the xylem images. The processing results showed that the Butterworth homomorphic filtering have a good effect on the illumination compensation for the various illumination variations in a series of different images, indicating some high resolution information in detail, texture, contrast and visual effect of the images. After being initially segmented by-means clustering, the illumination compensated xylem images had an average section error () of 5.15%, over-segmentation error (OR) of 1.48% and under-segmentation error (UR) of 6.46%, respectively, which decreased by 23.60, 7.75 and 13.01 percentage points, respectively compared to the xylem images before the illumination compensation. The segmentation accuracy was enhanced significantly, which decreased 10.43 percentage points in, 4.58 percentage points in OR and 4.96 percentage points in UR to 3R-G-B threshold value clustering algorithm after the illumination compensation. The average mean error of the circle structure extraction for the xylem images after the initial segment reached 2.26%, which was 11.69 percentage points lower than that of the watershed method, and 4.93 percentage points lower than that of pit matching method. The average duration of the algorithm in this case was 3.66 s on each image, saving 0.95 and 4.78 s compared to that of the watershed and pit matching method, respectively. The root mean squared error (RMSE) of the algorithm was 0.52%, one third of that from the watershed and half of that from the pit matching. The proposed combined algorithm can automatically segment and extract the xylem information data fromPojark, particularly on some images with the complex xylem structure, uneven illumination and uneven internal distribution, indicating better than the other two types of segmentation algorithms. These findings can provide fundamental reference for the promising extraction algorithm and the image processing of the xylem from other plants. extract; algorithm; xylem;-means clustering; circle structure extraction;Pojark 王海超,宗哲英,张文霞,殷晓飞,王晓蓉,张海军,刘艳秋,石 鑫,王春光. 采用均值聚类和环形结构的狭叶锦鸡儿木质部提取算法[J]. 农业工程学报,2020,36(1):193-199.doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.01.022 http://www.tcsae.org Wang Haichao, Zong Zheying, Zhang Wenxia, Yin Xiaofei, Wang Xiaorong, Zhang Haijun, Liu Yanqiu, Shi Xin, Wang Chunguang. An extraction xylem images ofPojark based on-means clustering and circle structure extraction algorithm[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2020, 36(1): 193-199. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.01.022 http://www.tcsae.org 2019-08-22 2019-12-26 内蒙古农业大学高层次人才科研启动项目(NDYB201857);内蒙古自治区自然科学基金项目(2019BS06003,2017MS0514,2017MS0361);教育部“云数融合科教创新”基金项目(2017A10019);内蒙古自治区博士研究生科研创新项目(B20151012902Z);实验室开放项目(20180104) 王海超,博士,讲师,研究方向:荒漠草原典型植物切片图像特征与草原早期退化相关性研究。Email:wanghaichao1129@163.com 王春光,教授,博士生导师,研究方向:图像与数字化研究。Email:jdwcg@imau.edu.cn 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.01.022 TP391.41 A 1002-6819(2020)-01-0193-07
2 试验与结果分析
2.1 试验方法
2.2 结果与分析


3 结 论
