妊娠梅毒母婴阻断治疗效果及护理分析
2019-09-27刁明芳
刁明芳
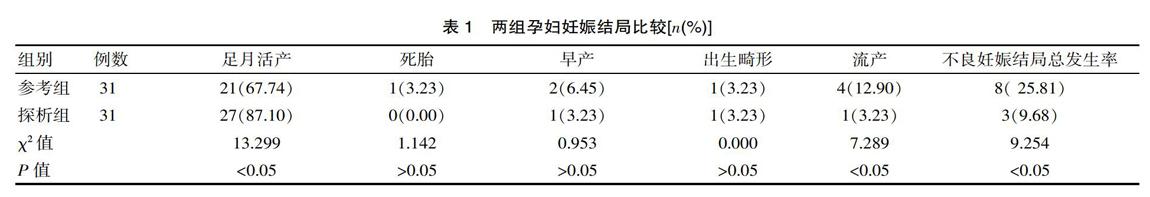
[摘要] 目的 分析妊娠梅毒孕婦接受母婴阻断治疗以及护理干预的效果。 方法 回顾性分析2016年2月—2018年10月在该院接受妊娠梅毒母婴阻断治疗的孕妇,该研究方便选取62例并经随机抽签法分为两组,探析组(n=31)和参考组(n=31)孕妇均接受母婴阻断治疗以及病情观察等常规护理,同时给予探析组孕妇综合性护理干预措施。 结果 探析组足月活产率明显高于参考组,两组孕妇足月活产率差异有统计学意义(χ2=13.299,P<0.05),探析组孕妇不良妊娠结局总发生率为9.68%,参考组孕妇为25.81%,两组不良妊娠结局总发生率差异有统计学意义(χ2=9.254,P<0.05)。参考组25例孕妇依从性较好,6例孕妇依从性不佳,治疗依从性为80.65%,探析组30例孕妇依从性较好,1例孕妇依从性不佳,治疗依从性为96.77%,探析组孕妇治疗依从性明显更高,两组差异有统计学意义(χ2=7.812,P<0.05)。 结论 妊娠梅毒孕妇接受母婴阻断治疗以及综合性护理干预有助于提高孕妇治疗依从性并改善母婴结局以及新生儿预后,可提升人口素质。
[关键词] 妊娠;梅毒;母婴阻断;治疗与护理效果
[中图分类号] R473.71 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1674-0742(2019)07(c)-0130-03
Therapeutic Effect and Nursing Analysis of Maternal and Child Blockade of Syphilis in Pregnancy
DIAO Ming-fang
Department of Preventive Health, Xuyi Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Huai'an, Jiangsu Province, 211700 China
[Abstract] Objective To analyze the effect of maternal and child blockade treatment and nursing intervention on pregnant women with syphilis. Methods A retrospective analysis of pregnant women who received maternal and fetal meiosis in pregnant women from February 2016 to October 2018 was conveniently selected in this study. A total of 62 patients were enrolled in this study and divided into 2 groups by random sampling. The probing group (n=31) and the reference group (n=31) received routine care such as maternal and child blockade treatment and condition observation, and comprehensive nursing intervention measures were given to the pregnant women in the probing group. Results The full-term live birth rate of the probing group was significantly higher than that of the reference group. There was a statistically significant difference in the live birth rate between the two groups (χ2=13.299, P<0.05). The total incidence of adverse pregnancy outcomes in the prognosis group was 9.68%. The reference group of pregnant women was 25.81%, and the total incidence of adverse pregnancy outcomes in the two groups was statistically significant (χ2=9.254, P<0.05). In the reference group, 25 pregnant women had better compliance, 6 pregnant women had poor compliance, and the treatment compliance was 80.65%. In the probing group, 30 pregnant women had good compliance, and 1 pregnant woman had poor compliance. The treatment compliance was 96.77%. The treatment compliance of the pregnant women in the analysis group was significantly higher, and the difference between the two groups was statistically significant (χ2=7.812, P<0.05). Conclusion Maternal and child blockade treatment and comprehensive nursing intervention for pregnant women with syphilis can improve the treatment compliance of pregnant women and improve maternal and child outcomes and neonatal prognosis, which can improve the quality of the population.
