Analysis of Products and Synergetic Effect During Low Temperature Co-pyrolysis of Lignite and Rape Straw
2019-07-31FANGuipingHEXuanmingLIHaoZHAOLuhan
FAN Guiping HE Xuanming LI Hao ZHAO Luhan
ABSTRACT Indonesia lignite(IL)was co-pyrolyzed with different mass fractions of rape straw (RS)in a lowtemperature coal carbonization furnace.The results indicate that the yield of pyrolysis oil reaches a maximum of 14.03%and the productivity will be 57.59%higher than that of pure lignite pyrolysis as the mass fraction of RS is 30%.The morphology and structure of semi-coke surfaces were described quantitatively by SEM,and pyrolysis oils were detected by FTIR and GC-MS.Thermogravimetric analysis of samples shows that the pyrolysis temperature range overlaps.The DTG peak of rape straw partially overlaps with lignite's,and the pyrolysis process conformed to the second-order kinetic equation during co-pyrolysis.The activation energy Edecreases and the reactivity increases.Consequently,the TG curve moves to the low temperature region.By using the proposed method,the clean and efficient utilization of lignite and rape straw is realized,and the resources are turned into precious.
KEYWORDS lignite,rape straw,co-pyrolysis,synergetic effect
0 Introduction
The biomass energy is considered as one of the main energy sources for sustainable development in the future.It is coal that has been chronically in a very significant position in the world's primary energy consumption structure[1].By the middle of this century,fossil energy will still be the most primary form of energy,and coal energy will play a vital role[2].Indonesia's lignite (IL)resources are abundant.Lignite and other low-rank coals account for a large proportion of coal resources[3].However,lignite’s metamorphic degree is low,and its water content and volatile matter are high,making it difficult to be utilized[4].Lignite mainly has several kinds of utilization methods,such as combustion,gasification,liquefaction and pyrolysis.The approach of combustion is convenient and fast,but the utilization rate is low,and it wastes resources and yields pollutants[5].Coal gasification requires gasification agent,and coal liquefaction requires catalyst, making them undesirable[6-8].The low-temperature coal pyrolysis operation is perfect.Specifically,the hydrogen in the coal can be enriched in the tar and gas,and the carbon can be enriched in the semi-coke[9-11].Coal staged conversion cascade utilization is one of the most reasonable methods to utilize coal resource[2].
China is a big agricultural country,and annual crops will produce more than 10million t of agricultural waste[12],the total rape straw output alone is about 700million t[13],which will be a considerable resource.If IL is co-pyrolyzed with RS,RS will be used as an inexpensive hydrogen donor and it is rich in alkali/alkaline earth metal,which promotes the pyrolysis process of coal and improves the quality of pyrolysis oil[13-15].Based on the similar characteristics of coal and biomass,coal and biomass co-pyrolysis technologies have been studied in recent years[16].Many researchers have conducted extensive research on the co-pyrolysis process,synergy and mechanism of low-rank coal and biomass[17].KRRKKAIWAN et al[18]chowed that the synergetic effect can be explained by the transferring of active OH and H radicals from the biomass to the coal as well as the catalytic role of potassium (K)from the biomass.YUAN et al[19]reported that synergies occurrs during rapid copyrolysis of rice straw and Shenfu coal(m(rice)/m(coal)=1∶4),which results in decreasing char yields and increasing volatile yields.ZHANG et al[20]observed the volatiles-char interactions promoted the tar generation mainly at the char bed temperature range from 600 ℃ to 700 ℃,and in the optimum condition with the blending ratios of 0.50and char bed temperature of 700 ℃ under such condition,the tar yield increases up to 28.7%.However,there are few studies on pyrolysis and co-pyrolysis of rape straw.
The analysis of the co-pyrolysis of IL and RS with different mass fractions was carried out using a self-made coal carbonization furnace.Interaction between IL and RS were studied by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA),gas chromatography-mass spectrometer (GC-MS),infrared spectroscopy(FTIR), and scanning electron microscopy(SEM).This experiment provides positive effects to achieve a clean and efficient cascade utilization of lignite and rape straw.
1 Experiment
1.1 Material analysis
In the experiment,the IL and RS were used as raw materials.RS was soaked in pure water for 12 h and then filtered.And it was dried in a forced air drying oven at 60 ℃ for 12h.The coal samples were dried at 40℃for 4h.Then IL and RS were crushed by agrinder and filterted by an 80mesh sieve.The results of industrial analysis and elemental analysis are shown in Table 1.
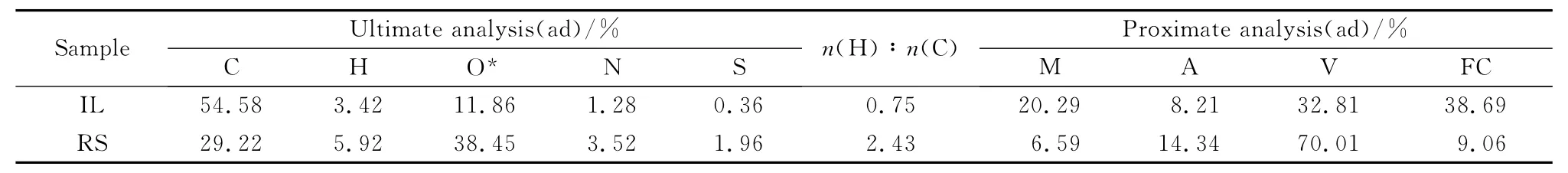
Table 1 Ultimate and proximate analysis of samples(mass fraction)
1.2 Experimental device
The pyrolysis experimental device was a selfdeveloped coal carbonization furnace (Fig.1),which mainly includes aluminum crucible,furnace body,thermowell,temperature controller,product condensation and collection devices.The threephase products were collected and analyzed when samples had been pyrolyzed in the furnace.The pyrolysis oils were analyzed by GC-MS which uses Agilent’s gas chromatograph/mass spectrometer and FTIR which uses BRUKER VERTEX 70Fourier infrared spectrometer.The morphology of the pyrolysis semi-coke was analyzed by SEM using a scanning electron microscope from FEI,Hong Kong.The metal content of the semi-coke was measured by ICP using an IRIS advantage radial plasma spectrometer thermo elemental instruments.The results are presented in Table 2.
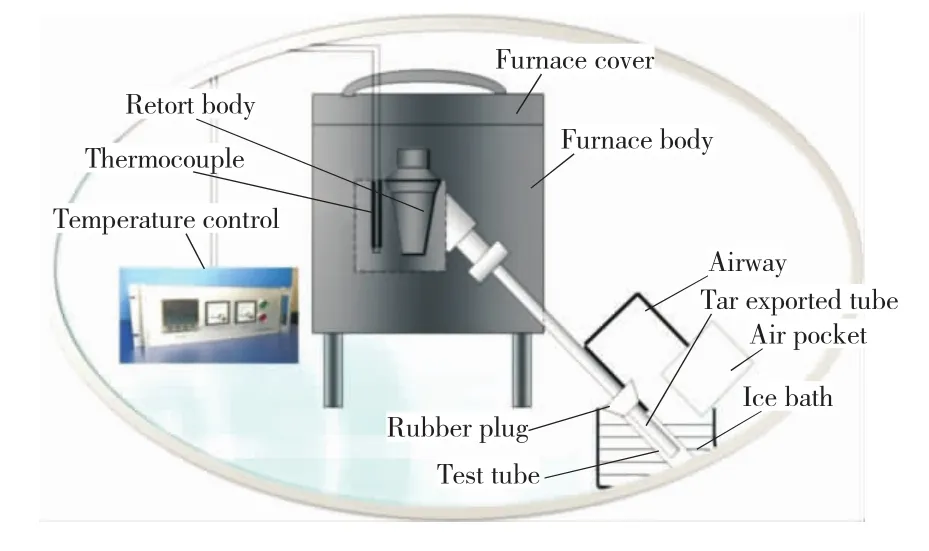
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of homemade prolysis apparatus
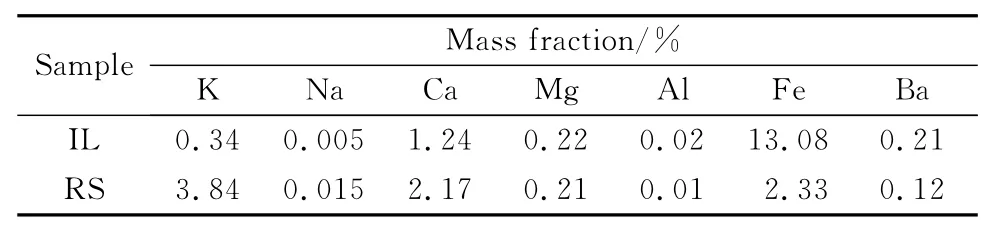
Table 2 Metal content of samples pyrolysis char
1.3 Experimental scheme
Weigh RS and IL after pretreatment on the tin foil paper.The mass ratio of RS to IL is 0g∶10 g,1g∶9g,2g∶8g,3g∶7g,4g∶6g,5g∶5 g,10g∶0g.The blended mass fraction of RS was 0%,1%,20%,30%,40%,50%,and 100%.The total mass of the blended samples were 10g(±5mg).The specific operation process was as follows:the mixture was put in the coal carbonization furnace,and the temperature should be controlled the rising range from room temperature to 510℃for 60min,and the heat was maintained for 30min.To ensure the reliability of the test results,each test was repeated for three times.Comparing the yield of each product from the low-temperature destructive distillation,the maximum pyrolysis oil yield was considered as the main evaluation index to select the best ratio from the blended samples.The pyrolysis mechanism was analyzed by using thermogravimetry,and the pyrolysis oil in the optimal blended ratio was subjected to FTIR,GCMS and semi-focus SEM detection.The pyrolysis oil and pyrolysis gas yields were calculated as follows:

2 Results and discussion
2.1 Effect of rape straw blending ratio on the yield
During the low-temperature co-pyrolysis experiments of RS and IL,RS was blended in 7different mass blending ratios.The yields of semicoke,pyrolysis gas and pyrolysis oil are shown in Fig.2.
Fig.2presents that the co-pyrolysis products of rape straw and lignite are water,semi-coke,pyrolysis gas and pyrolysis oil.The primary product is oil,which accounts for more than 40%.According to Table 1,the sum of RS fixed carbon content and ash content are significantly lower than that of IL,nevertheless the volatile content of RS was more than that of IL.Therefore,with the increase of rape straw blending ratio,the semi-coke yield of the solid product decreases constantly,while the pyrolysis gas and pyrolysis oil yield of the volatile products increases gradually.Specially,the semicoke yield decreases from 54.26%to 40.8%,the pyrolysis gas yield increases from 23.69%to 27.97%and the pyrolysis oil yield increases from 9.03%to 14.23%.
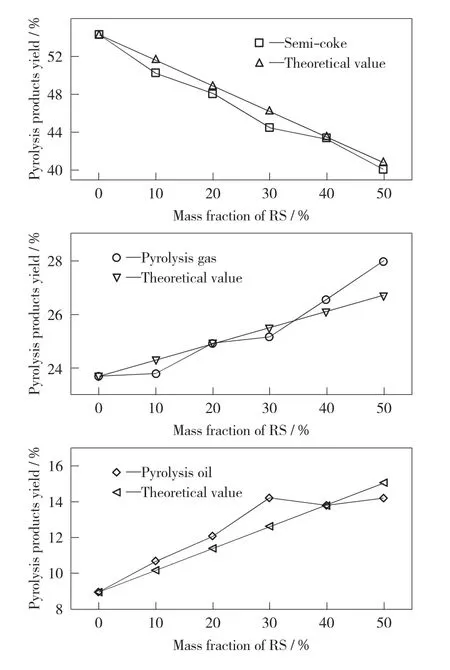
Fig.2 Yield of co-pyrolysis products
To verify the synergistic effect between RS and IL during the co-pyrolysis,the measured value of the co-pyrolysis product yield was compared with the theoretical values (mass weighted values).As can be seen from Fig.2,the measured value of the product yield has a large deviation from the theoretical value,and the measured value of the product yield doesn’t change linearly with the change of the blend ratio of RS.The pyrolysis oil yield was considered as the main evaluation index to consider the influence of the yield of co-pyrolysis products after RS was blended.The deviations between the measured and the theoretical values of the pyrolysis oil yields vary with the variation of the blending ratio of RS.When the blending ratio of the RS reaches 30%,the deviation be-tween them reaches a maximum,and the measured value increases by 12.43%compared to the theoretical value.
From Table 1it can be observed that RS has a higher n(C)∶n(H),which can reach 2.43,i.e.3.24times of size of lignite’s.During the process of co-pyrolysis,the hydrogen radicals produced by RS could be used as the hydrogen donor for the coal pyrolysis.The hydrogen radicals can combine with the free radical fragments produced by the pyrolysis of IL.The conjugation can generate oil with relatively low molecular weight.The occurrence of secondary reactions such as polycondensation and cross-linking will be inhibited,which can improve the pyrolysis oil yield and the pyrolysis oil quality simultaneously[21-22].In addition,the pyrolysis process of RS is earlier than that of coal pyrolysis during the co-pyrolysis of IL and RS.Volatile components which is produced by the early pyrolysis of RS such as H2,CH4,and CO2can react with IL,affecting the yield and quality of pyrolysis products.Table 2shows that RS contains high levels of alkali/alkaline-earth metals.Alkaline/alkaline-earth metals have certain catalytic effects on the pyrolysis reaction of coal.The K element in the pyrolysis semi-coke of RS is 11times higher than that in the IL pyrolysis semi-coke.The K element can catalyze the gasification of the semi-coke with water vapor and.
When the mass fraction of RS is more than 30%,the yield of pyrolysis oil is no longer increased or even decreased. When the blending amount of RS is too large,it causes the production carbon black and some volatile substances that were pyrolyzed in advance and covers the surface of IL.In this regard,those substances block the gap and then affect the precipitation of volatiles,reducing coal pyrolysis conversion and pyrolysis oil yield[22,24].Therefore,the co-pyrolysis process of RS and IL has synergistic effects and inhibitory effects.In this experiment,the co-pyrolysis process shows the best synergistic effect when the RS mass fraction is 30%.
2.2 SEM analysis of pyrolysis semi-coke
The samples of RS,IL,lignite semi-coke and co-pyrolysis semi-coke were analyzed with SEM to study the effect of co-pyrolysis on the morphology and structure of semi-coke surfaces.The results are depicted in Fig.3.The figures depict that there are some wrinkles on the RS surface;the surface of the IL is relatively smooth,and there are no obvious voids or cracks on the surfaces.Comparing Fig.3cand Fig.3d,as the same as the results of thermogravimetric analyses,the co-pyrolysis semicoke with 30%RS has a rougher surface and a more abundant lamellar structure than IL semicoke,leading to increased reactivity.The combined effects of releasing of volatiles in the pyrolysis process,and the inhomogeneous shrinkage between the semi-coke particles during pyrolysis after the addition of rape straw,result in the co-pyrolysis semi-coke in a more abundant pore structure[25].The changes in surface morphology and structure of the co-pyrolysis semi-coke make it potentially useful for the wastewater treatment industry and increase its reactivity to further widen its application in the metallurgical industry.
2.3 Analysis of pyrolysis oil characteristics
2.3.1 FTIR analysis of pyrolysis oil
To study the influence of co-pyrolysis on the pyrolysis oil functional groups,Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR)analyses were performed on the pyrolysis oil of IL and the co-pyrolysis of 30%RS addition.The FTIR spectra are presented in Fig.4.
As shown in Fig.4,a strong absorption peak is around 3 404.80cm-1,which was produced by hydrogen bonded (—OH)stretching vibration of alcohols and phenols.Two prominent absorption peaks are seen at 2 922.57cm-1and 2 854.79 cm-1,due to the C—H stretching vibrations of the straight chain aliphatic compounds or aliphatic side chains.Thearomaticskeletalvibrationgen eratesstrongabsorptionpeaksat1691.67cm-1and 1 602.86cm-1.A well-defined absorption peak is at 1 456.39cm-1,which is caused by bending vibration of methyl and methylene groups[26].There are many absorption peaks in the fingerprint region between 1 300cm-1and 600cm-1.Among them,absorption peaks from 1 000cm-1to 1 300 cm-1are generated by C—O stretching vibration and C—C skeleton vibration.The absorption peak between 600cm-1and 950cm-1is generated by bending vibration of benzene ring C—H.Absorption peaks are absent from 2 000cm-1to 2 500 cm-1,indicating that no alkyne hydrocarbons are produced in the pyrolysis oil.The absorption peaks of co-pyrolysis tar and lignite tar are roughly similar,indicatiing that the components are almost the same,and both of them contain aliphatic,aromatic,alcoholic,phenolic,aldehyde and other chemicals.At 3 404.80cm-1,the peak of co-pyrolysis tar is stronger than that of lignite tar,indicating that the content of phenols and alcohols in co-pyrolysis tar is higher than that of lignite tar,which is consistent with the results of GC-MS detection.
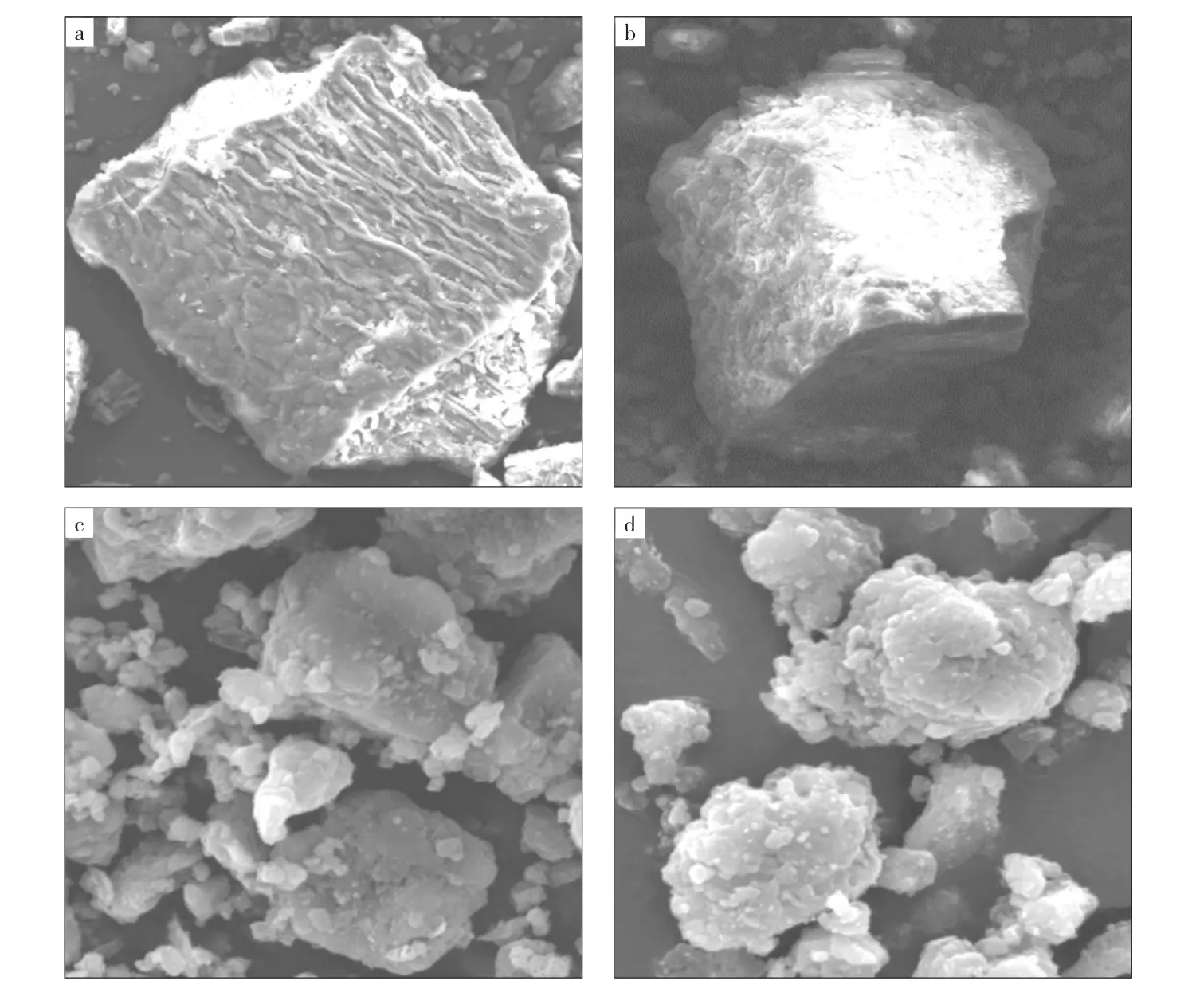

Fig.3 SEM images of samples
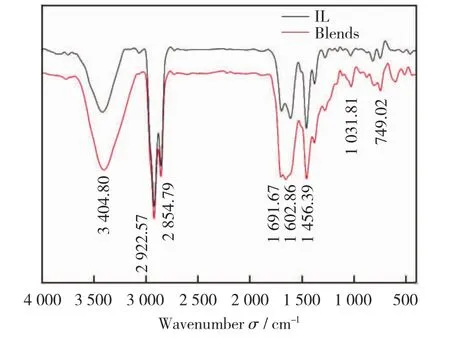
Fig.4 Infrared spectrogram of pyrolysis oils
2.3.2 GC-MS analysis of pyrolysis oil
The co-pyrolysis oil with the best blended mass fractions of 30%and pure lignite pyrolysis oil were detected with GC-MS.The content of their components and distribution are illustrated in Fig.5.The pyrolysis oil composition is complex,and it mainly contains straight chain aliphatic compounds,benzene ring aromatic compounds,phenols,esters,ketones,organic acids,alcohols,and other heteroatom compounds containing nitrogen and sulfur.The content of aliphatic hydrocarbons and alcohols in pyrolysis oil is relatively high,with the content of aliphatic chemicals approximately up to 30%,and the content of alcohols up to 28%.The contents of aromatic chemicals,esters,heteroatoms,and phenols are the second highest,and each content is about 10%.The lowest leve of ketones and acids are about 2%.The content of aliphatic co-pyrolysis oil is 32.12%,which is 32.34%higher than that of lignite oil.The aromatic content drops from 14.76%to 6.47%,and the rate of declination reaches 128.13%,attesting the addition of RS promotes the breaking of C aromatic-C alkane and C alkane-C alkane bonds.The phenol content of co-pyrolysis oil is 12.27%.The mass fraction increases by more than 4.5times,and the high-value-added products of pyrolysis oil are also greatly increased.The acids of the co-pyrolysis oil decrease from 2.30%to 1.68%,and the acidity of pyrolysis oil is deeply reduced to facilitate the subsequent processing of tar.
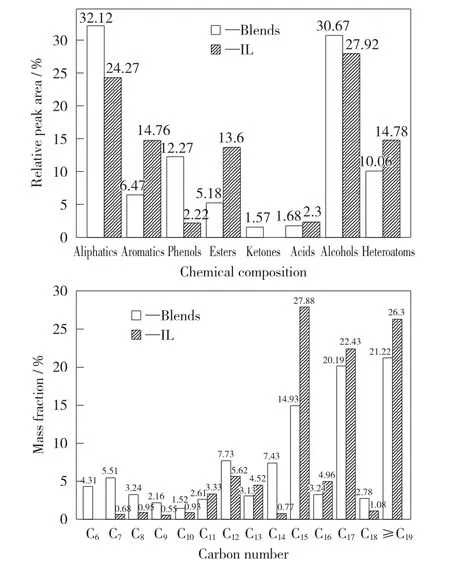
Fig.5 Contents of organics in different oils
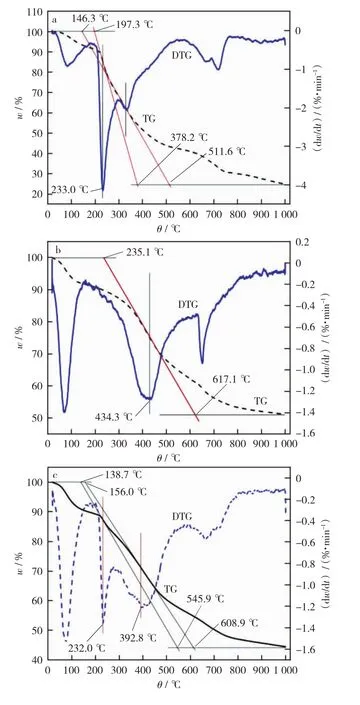
Fig.6 TG-DTG curves of samples
According to the number of carbon atoms,pyrolysis oils were classified into three parts that include light oils with 5-10carbon atoms,medium oils with carbon number of 11-18,and heavy oil with carbon atoms greater than 18.The mass fraction of medium-quality oil was the highest one,with the contents of co-pyrolysis oil and pure lignite tar both more than 60%.The heavy oil of co-pyrolysis oil accounts for 21.22%,which is 26.30%lower than that of lignite tar.The light oil content of co-pyrolysis tar is 16.74%,which is 438.3%higher than that of pure lignite tar.The co-pyrolysis tar has been lightened to a great extent.
2.4 Thermogravimetric analysis of co-pyrolysis characteristics
2.4.1 Individual pyrolysis characteristics of IL and RS
From Fig.6,it can be observed that the pyrolysis process of IL and RS can be divided into three stages roughly.The first stage is the dehydration.That is,the sample is dehydrated at about 100 ℃and generates the dehydration peak.It clearly shows that the DTG peak of IL is more evident than that of RS at this temperature.As the result of industrial analysis in Table 1,IL air dry basis water content is greater than that of RS.The second stage is rapid pyrolysis.That is,the sample is decomposed by heat from 200 ℃to 600 ℃.There were two DTG peaks at this stage:the RS’s corresponding hemicellulose weight loss peak at 233.0 ℃,and the RS’s corresponding weight loss peak at 332.4 ℃,while IL only has a weight loss peak at 434.3 ℃ during this phase.The third stage was the carbonization.That is,the sample undergoes a thermal condensation reaction after reaching 600 ℃,resulting in the formation of semi-coke(coke)[16-17,27].
The TG-DTG tangent method was used to obtain the pyrolysis characteristic parameters of the two samples,including the initial pyrolysis temperature T1,the termination pyrolysis temperature T2,the maximum weight loss rate(dw/dt)maxand the corresponding temperatureθmax,the maximum weight loss rate(dm/dt)max.The results are summarized in Table 3that the pyrolysis temperature range of IL is 235.1 ℃-617.1 ℃,while the pyrolysis temperature range of RS is 146.3 ℃-511.6 ℃.The pyrolysis temperature range of IL and RS partly overlaps in range of 235.1℃-511.6℃.The maximum temperature of IL and RS overlap 510℃is chosen as the final temperature of co-pyrolysis,which provides the best synergistic process conditions for the co-pyrolysis process.The initial temperature of RS’s pyrolysis is about 90 ℃ lower than that of IL’s,and the maximum weight loss rate of RS is three times more than that of lignite,which provides favorable conditions for co-pyrolysis.
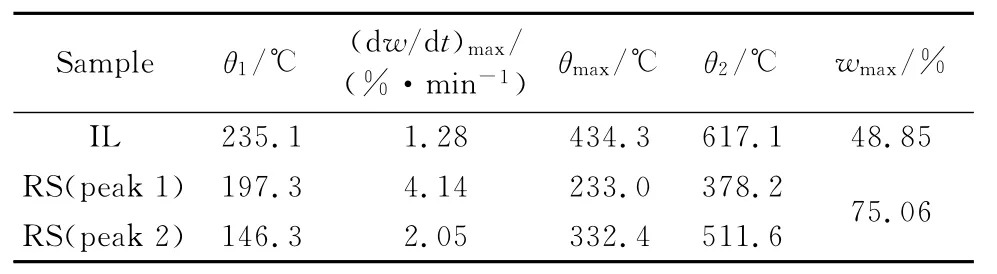
Table 3 Pyrolysis characteristic parameters of individual samples
2.4.2 Co-pyrolysis characteristics of lignite and rape straw
Table 4shows that the co-pyrolysis temperature range of IL and RS is 138.7℃-608.9℃,and the maximum weight loss was 55.51%,which was lower than the sum of IL’s weighted values and RS’s.This testifies that there is the synergy in the co-pyrolysis process.As can be seen in Fig.5,there are only two distinct DTG peaks(232.0 ℃,392.8 ℃)in the co-pyrolysis of IL and RS in the pyrolysis temperature range.The two peaks are less than the sum of individual DTG peak of IL and RS.The reduction of DTG peaks’sum is due to the weight loss peaks of the RS cellulose pyrolysis and the IL pyrolysis appears partial overlap,resulting in only one distinct characteristic peak around 400℃.In the co-pyrolysis,IL’sθ1(156.0 ℃),θmax(392.8 ℃)andθ2(608.9℃)are lower than the corresponding characteristic temperature of the individual IL pyrolysis,which proves that the blending of RS promotes the IL’s pyrolysis process and makes the pyrolysis process of the lignite move to the low temperature zone.

Table 4 Pyrolysis characteristic parameters of blends
2.4.3 Co-pyrolysis kinetics analysis
In this experiment,the Coat-Redfern method was used to analyze the thermogravimetric data of IL,RS and the blends of 30%RS-IL[28].
The Coats-Redfern equation is given by Equation(3)and(4):
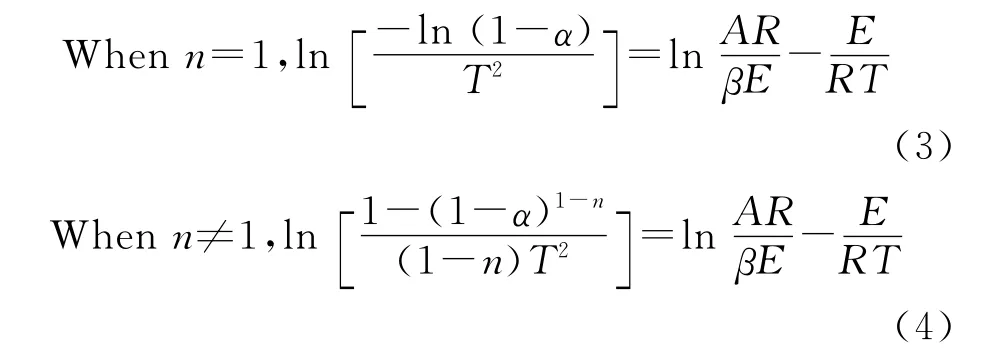
In the formula,the conversion ratewt(%)is the residual mass fraction of the sample at a certain temperature,ω∞(%)is the final sample residual mass fraction;R=8.314J/(mol·K),E(J/mol)is the apparent activation energy;A(min-1)is the pre-exponential factor;T(K)is the reaction temperature;n is the reaction progres-sion,the heating rateβis 10K/min.
It can be seen from Table.5and Fig.7that the pyrolysis processes of all samples conform to both the first-order and the second-order kinetic models.The second-order kinetic model has better fitting results than the first-order kinetic model,and both of them have a relatively high correlation coefficient in a wide temperature range.The smaller the apparent activation energy E,the higher the reactivity is.The larger the pre-exponential factor Ais,the faster the reaction rate is.In the main pyrolysis interval,the two kinetic models show that the pre-exponential factor of RS is greater than that of IL and blend.This reveals that the pyrolysis reaction rate of RS is the fastest.The activation energy of co-pyrolysis of blends is lower than that of individual pyrolysis of IL and RS,which validates that there is a synergistic effect in the co-pyrolysis process,and the effect is mainly reflected in the increase of reactivity due to co-pyrolysis.

Fig.7 Kinetic curves of samples
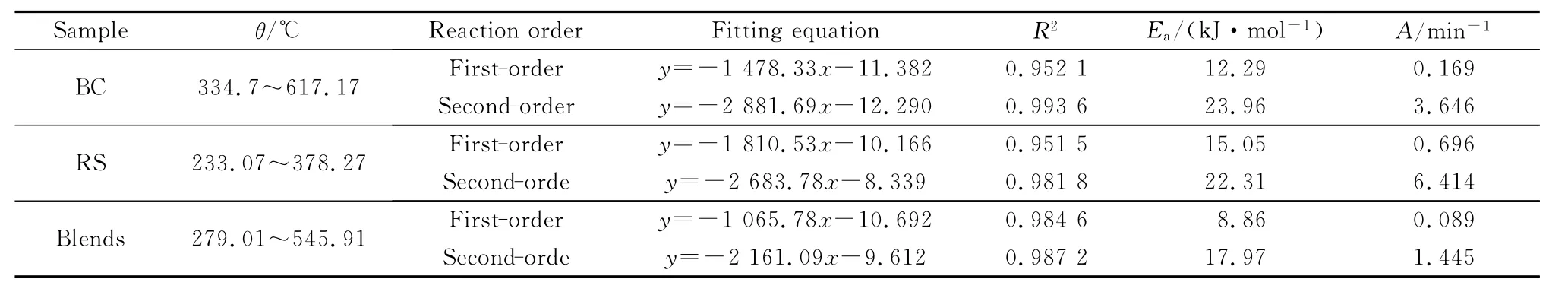
Table 5 Pyrolysis kinetic parameters of samples
3 Conclusions
The co-pyrolysis process shows the best synergistic effect when the RS mass fraction is 30%,and the yield of pyrolysis oil is 57.59%higher than that of pure lignite pyrolysis.SEM and FTIR of samples indicate that co-pyrolysis semi-coke and co-pyrolysis oil are both upgraded.The contents of aliphatic hydrocarbons and phenolic of co-pyrolysis oil increase with the reducing co-pyrolysis oil’s content of aromatic chemicals and acids.TG analyzer shows that the DTG peak of rape straw overlaps partially with the DTG peak of lignite.The TG curve moves to the low temperature region,and the pyrolysis process conformes to the secondorder kinetic equation of Coat-Redfern method.The change of pyrolysis product yield,analysis of product characteristics, analysis of pyrolysis process characteristics,etc.indicate that there are synergetic effects in the co-pyrolysis process.
