动态神经肌肉稳定技术胸腹联合呼吸控制在功能性便秘治疗中的疗效研究
2019-06-20杨宽女胡金娜李建华吴方超郝彦张凯王达
杨宽女 胡金娜 李建华 吴方超 郝彦 张凯 王达
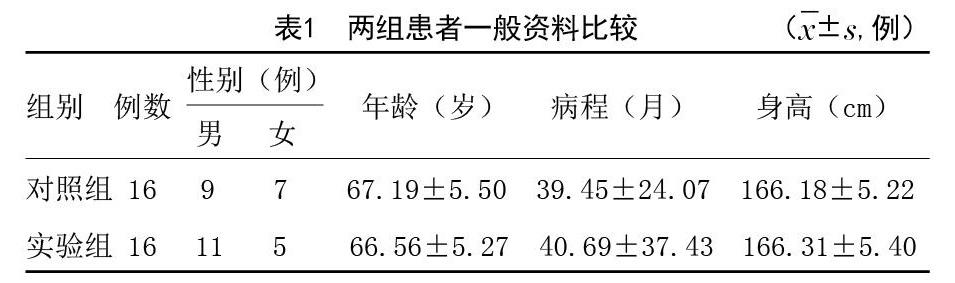
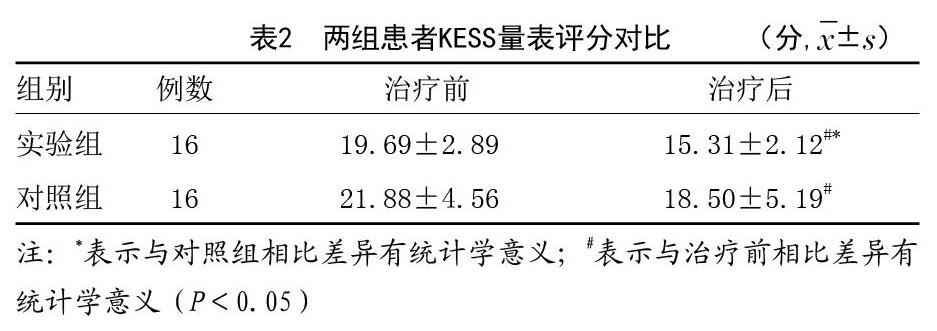
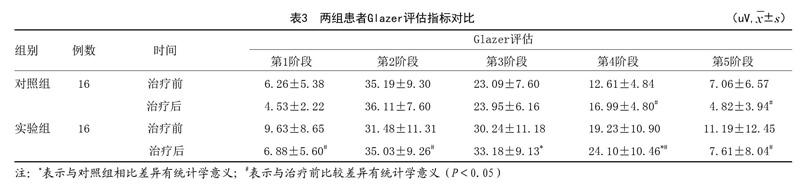
[摘要]目的:探索動态神经肌肉稳定技术(DNS)胸腹联合呼吸控制在功能性便秘治疗中的疗效。方法:本试验采取前瞻性研究,选取2018年7月-2019年2月笔者科室门诊行康复治疗的功能性便秘患者40例,按照电脑随机化方法将所有患者分为实验组和对照组,每组各20例,由于试验过程中两组中各有4例患者终止了治疗,故样本脱落后实际参与实验的样本量为每组各16例。对照组患者采用常规盆底肌电刺激治疗,实验组在对照组基础上进行DNS胸腹联合呼吸训练,每周5次,连续2周。对两组分别进行Knowles-Eccersley-Scott症状评分(KESS)、Glazer法评估盆底表面肌电指标。结果:两组排便功能均有改善,实验组治疗后KESS量表评分较治疗前改善,且较对照组明显降低,症状改善明显,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。通过Glazer指标对比,实验组第3、4阶段的平均肌电值均较对照组改善,盆底肌耐力较对照组增加,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论:DNS胸腹联合呼吸控制训练有助于改善功能性便秘患者的排便功能,进一步完善了功能性便患者的保守治疗方案以及提供了该类患者自我管理有效性的证据,也为DNS呼吸技术用于治疗功能性便秘奠定了研究基础。
[关键词]功能性便秘;动态神经肌肉稳定技术(DNS);胸腹联合呼吸;低频电刺激
[中图分类号]R57 [文献标志码]A [文章编号]1008-6455(2019)06-0012-05
Abstract: Objective To explore the efficacy of dynamic neuromuscular stabilization technique (DNS) combined with thoracic and abdominal breathing control in the treatment of functional constipation. Methods In this prospective study, 40 patients with functional constipation who received rehabilitation treatment in our department from July 2018 to February 2019 were selected, and all patients were assigned to the experimental group and the control group with 20 cases each according to the computer randomization method, and 4 patients in the control group and the experimental group were separated during the experiment. Patients in the control group received conventional pelvic floor electrical stimulation therapy, and patients in the experimental group received DNS combined thoracic and abdominal breathing training on the basis of the experimental group. Practice five times a week for two weeks. The two groups were evaluated by Glazer method in terms of pelvic floor surface electromyography, knowles-eccersley-scott symptom score (KESS), depression and anxiety scale, etc. Results The defecation function of the two groups was improved. After treatment, the score of KESS scale in the experimental group was significantly lower than that in the control group, and the symptoms were significantly improved, the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). According to Glazer index comparison, the average emg of the experimental group at the third and fourth stages was improved compared with that of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). The pelvic floor muscle endurance of the experimental group was increased compared with that of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion DNS thoracic and abdominal combined breathing control training is helpful to improve the defecation function of patients with functional constipation, further improve the conservative treatment program for functional constipation patients and provide evidence for the effectiveness of self-management of such patients, and also lay a research foundation for the application of DNS breathing technology in the treatment of functional constipation.
