Big-data analysis: A clinical pathway on endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography for common bile duct stones
2019-03-09WeiZhangBingYiWangXiaoYanDuWeiWeiFangHanWuLeiWangYuZhengZhugeXiaoPingZou
Wei Zhang, Bing-Yi Wang, Xiao-Yan Du, Wei-Wei Fang, Han Wu, Lei Wang, Yu-Zheng Zhuge, Xiao-Ping Zou
Abstract BACKGROUND A clinical pathway (CP) is a standardized approach for disease management.However, big data-based evidence is rarely involved in CP for related common bile duct (CBD) stones, let alone outcome comparisons before and after CP implementation.AIM To investigate the value of CP implementation in patients with CBD stones undergoing endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP).METHODS This retrospective study was conducted at Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital in patients with CBD stones undergoing ERCP from January 2007 to December 2017. The data and outcomes were compared by using univariate and multivariable regression/linear models between the patients who received conventional care (non-pathway group, n = 467) and CP care (pathway group, n= 2196).RESULTS At baseline, the main differences observed between the two groups were the percentage of patients with multiple stones (P < 0.001) and incidence of cholangitis complication (P < 0.05). The percentage of antibiotic use and complications in the CP group were significantly less than those in the nonpathway group [adjusted odds ratio (OR) = 0.72, 95% confidence interval (CI):0.55-0.93, P = 0.012, adjusted OR = 0.44, 95%CI: 0.33-0.59, P < 0.001, respectively].Patients spent lower costs on hospitalization, operation, nursing, medication, and medical consumable materials (P < 0.001 for all), and even experienced shorter length of hospital stay (LOHS) (P < 0.001) after the CP implementation. No significant differences in clinical outcomes, readmission rate, or secondary surgery rate were presented between the patients in the non-pathway and CP groups.CONCLUSION Implementing a CP for patients with CBD stones is a safe mode to reduce the LOHS, hospital costs, antibiotic use, and complication rate.
Key words: Common bile duct stones; Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography;Clinical pathway; Outcomes; Costs
INTRODUCTION
Gallstone disease is one of the most frequent biliary diseases leading to hospitalization and imposing a significant financial burden. The worldwide prevalence of gallstones presents a rising tendency due to the change of dietary structure and routine living customs in recent years[1,2]. Of the patients who suffered from gallstones,approximately 10%-15% were found to have synchronous common bile duct (CBD)stones[3,4]. The clinical manifestations of CBD stones are varied from biliary colic to a combination of complications, such as acute pancreatitis or cholangitis; sometimes,CBD stones even may be asymptomatic[5]. Treatment and management of CBD stones have changed considerably during the last three decades. With the popularization of minimally invasive surgery in clinical practice, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is currently recognized as a standard therapy for patients with CBD stones[6,7]. Despite this, a risk of complications after ERCP cannot be avoided, and it is even associated with increased morbidity and mortality[8]. In addition, there is evidence showing that in some patients with gallstones received ERCP and routine care at first admission, re-admission and longer preoperative stay were caused[9]. Due to the growing complexity of CBD stone treatments and care, it is crucial to develop a standardized multidisciplinary approach to avoid chaotic management of this disease.
A clinical pathway (CP) is an advanced medical diagnosis, treatment, and management mode, which may optimize medical treatment by facilitating clinical assessments, improving utilization efficiency of medical sources, and reducing economical expenses[10-12]. Nowadays, a CP is thought to be an effective tool to be explicit about the sequencing, timing and provision of interventions in clinical practice and can guide physicians and nursing staff in providing evidence-based results[13,14]. Moreover, analysis of evaluating indexes (including clinical outcome,efficiency indicators, financial indicators, and antibiotic use indicators) can guarantee the effectiveness of the CP implementation and optimization[15,16]. One study has demonstrated that a CP presents sustainable effects in gallstone-related care, resulting in shorter length of hospital stay (LOHS) and lower hospital expenses[9]. In addition,several studies conducted in other surgical domains also presented similar results[17-19].However, implementation of the CP in China is in its start-up stage, especially in the field of hepatobiliary surgery. The status and value of the CP in the management of patients with CBD stones after ERCP remain to be explored. Given this concern, a retrospective study based on a big-data, intelligence database platform was launched.The aim of the present study was to analyze the impact of a CP on LOHS,readmission, treatment outcomes, hospital costs, and postoperative complication rate in patients with CBD stones undergoing ERCP.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study patients and data collection
This is a retrospective study of patients with CBD stones who received ERCP at Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital (Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, China) between January 2007 and December 2017. This study was approved by Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Drum Tower Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School (201817001),and informed consent was obtained from all subjects.
All patients aged above 18 years old without previous ERCP history were included in this study. The exclusion criteria were: (1) Patients with previous or present hepatolithiasis; (2) patients with severe liver diseases, cardio-pulmonary or renal inadequacy; (3) patients with severe hematologic diseases and concomitant obvious coagulopathy; (4) patients with combined gallbladder, CBD, duodenal papillary neoplasm, or congenital choledochal cyst; (5) patients who underwent Billroth I and II gastrectomy or gastrojejunostomy; and (6) pregnant patients. Subjects who met criteria for this study were extracted automatically from a big-data, intelligence database platform (Yidu Cloud Technology Co. Ltd., Beijing, China) by setting the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The study population consisted of two groups which accepted conventional care (non-pathway group) and a CP (CP group), respectively.
Demographic and clinical characteristics of subjects were obtained from electronic medical records. Outcomes of pathway complementation were compared between the two groups in LOHS (total and preoperative LOHS), readmission rate (a second hospital admission within 30 d due to CBD stones and postoperative complications),treatment outcomes, hospital charges (also including medication, operation,perioperative examinations, nursing and medical consumable materials charges),antibiotic use, secondary surgery rate, and postoperative complications.
CP
A set of sophisticated CPs for patients with CBD stones was implemented at this hospital in 2012. Development and optimization of the CP involved a multidisciplinary team under the instruction of relevant guidelines, including attending surgeons and residents, an anesthesiologist, a head of pharmacy faculty,and representatives from nursing and rehabilitation department. The training of the CP was performed before implementation to relevant personnel. Pathway I was designed for patients with expected LOHS less than 5-10 d, while pathway II was used for LOHS of 7-10 d. These CPs were explicit about the sequence of strategies for diagnosis, treatment, medication, routine care, and assessment. The pathway I is shown as an example in Appendix 1.
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were conducted using SAS, version 9.4 (SAS Institute, Cary,NC, United States). Data following a normal distribution are presented by mean ±standard deviation (mean ± SD), and otherwise are presented as median (interquartile range). Differences between the two groups were compared using Wilcoxon signedrank test (continuous variables) or chi-squared test (categorical variables). In addition,univariable logistic regression models were used to determine whether odds of outcomes differed between the groups. We also utilized multivariable logistic (linear)regression models for evaluating the effect of pathway complementation on each outcome by controlling age, gender, smoking and drinking habits, the number of stones, and white blood cell (WBC) count at hospital admission. A P-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Two thousand six hundred and sixty-three eligible patients were included finally, of whom 467 were in the non-pathway group and 2196 in the clinical-pathway group(Figure 1). Table 1 shows the comparison of demographic and clinical characteristics between the patients who received routine care and CP care. There were no differences between the two groups in terms of age, gender, insured status, health behaviors, or maximum diameter of stones. The percentage of patients with multiple stones was found to be significantly different between the two groups (P < 0.001). The number of patients suffering from comorbidities was similar, although the percentage of patients with cholangitis was higher in the non-pathway group (P = 0.041).Although WBC counts in both groups were within the normal range, there was a significantly higher WBC count among the patients in the non-pathway group (P =0.005).
Table 2 presents the outcomes of efficiency, treatment, hospital costs, and antibiotic use following the CP implementation. The median total LOHS was 8 (range, 6-11) d in the non-pathway group, while it was one day shorter (7, 5-9) in the CP group (P <0.001). The pre-operative LOHS was found to be similar between the two groups.There were no significant changes with respect to the treatment outcomes (recovered,improved, not improved, and died) in both groups, and even no patients died in our study. Thirty-four (7.28%) patients in the non-pathway group required readmission to hospital, while readmission rate (173, 7.88%) was increased after pathway complementation, although this difference was not statistically significant (P = 0.661).A considerably decreasing trend in the costs was observed among patients with the CP implementation, including hospitalization, medication, operation, nursing,materials, and preoperative examination (P < 0.001). In addition, implementation of the CP was associated with a reduced proportion of antibiotic use (P < 0.001). The median time of antibiotic use [11 (7.0-17.0) d] in the CP group was one day shorter than that before the CP complementation [12 (8.0-18.5) d] (P = 0.004). For patients in the CP group, secondary procedure occurred more frequently, although this difference was not statistically significant (16.94 vs 14.78%, P=0.253).
The postoperative complication rates are compared in Table 3. About 26.77% of patients with routine care had at least one complication, while the incidence of complications dropped to 14.39% after the CP complementation (P < 0.001). The incidence rates of acute pancreatitis and liver abscess were considerably lower in patients after CP implementation, with significant differences between the two groups(P < 0.001).
The effect of the CP complementation on each outcome was also assessed by univariate and multivariate logistic regression through controlling age, gender,smoking and drinking habits, the number of stones, and WBC count at hospital admission (Tables 4 and 5). After adjusting for differences between the two groups,antibiotic use and postoperative complications were less in patients with the CP complementation [odds ratio (OR) = 0.72, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.55-0.93, P =0.012; and OR = 0.44, 95%CI 0.33-0.59, P < 0.001, respectively]. The costs of hospitalization, operation, nursing, medication, and materials (P < 0.001 for all) and LOHS (P < 0.001) decreased significantly after implementation of the CP.
DISCUSSION
Despite wide adoption of CPs throughout different departments currently, their evaluation and optimization remain doubtful[20]. The purpose of this study was to compare the indicators of CP implementation in five domains (clinical outcome,efficiency indicators, financial indicators, and antibiotic use indicators) for patients with CBD stones undergoing ERCP. Our results confirmed that pathway implementation in CBD stones was associated with reduced total LOHS, costs,antibiotic use, antibiotic use duration, and complication rate. More importantly, the decrease has not been achieved at the expense of increased readmission rate or mortality.
With the development of endoscopic technique, ERCP is considered a preferred therapeutic method in management of CBD stones. However, it can be still challenging in some cases, such as high total hospital expenses and high risk of post-ERCP complications[21,22]. CP, one of the main modes to standardize treatment and care, is increasingly adopted by hospitals to strive to better outcomes and lower costs.However, the definition of CP has not yet been fully elucidated in clinical practice,and the impact of pathway complementation is varied by different factors and conditions[23,24]. Findings of our study are consistent with those obtained by Kristin et al who demonstrated a considerable reduction in terms of costs and LOHS in patients with complicated gallstone disease after the CP implementation[9]. More recent studies showed similar improvements in other specialties of diseases, such as acute pancreatitis[25], breast cancer[15], and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[26].However, pre-operative length of stay showed no distinct disparity in our study, andthe implementation of pathway might have greater impact on postoperative hospital stay. Similar to our results in terms of antibiotic use, Dona et al[27]reported that there was a reduction of antibiotic prescriptions in patients with community-acquired pneumonia after introducing a CP. Our study provided further evidence that the CP implementation can also significantly reduce the duration of antibiotic use and threeline antibiotic prescriptions. Thus, it is possible to conclude that a marked reduction of costs appears to be associated with several factors, such as effective pre-operative examination and rational use of medications and materials. Moreover, CP seems to be one of key approaches to maximize cost-effectiveness, while without sacrificing good treatment outcomes[28]. The most common causes of dropout from CP were postoperative complications that needed additional treatment. The findings of the present study demonstrated that rates of complications were lower in patients operated upon admission who implemented the CP compared to patients receiving routine care. There have been multiple previous publications in various domains which have demonstrated the lower incidence of complications following critical pathways[29-31]. However, critical factors may have affected outcomes, such as patients’characteristics, living habits, disease features, and individual laboratory measurements. Thus, these factors did not affect the findings that CP use achieved a significantly shorter LOHS, lower costs, and reduced complications after adjustments.

Table 1 Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients
Large-scale populations with gallstones and data process and application platform utilization are the main strengths in the present study. Furthermore, the findings were demonstrated by adjusting the potential confounders. However, this study was limited by its single-center retrospective design, indicating that further multiplecenter trials with larger variable are in need to confirm the results.
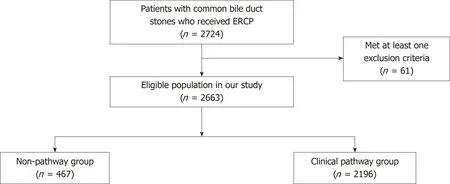
Figure 1 Flow diagram of study population.
In conclusion, findings of our study have demonstrated that patients with CBD stones who accepted the CP appear to be significantly lower in the LOHS, the costs,the rate of antibiotic use, and the incidence of complications. Our study provides further evidence of CP use in Chinese patients and also standardizes gallstone management and treatment.
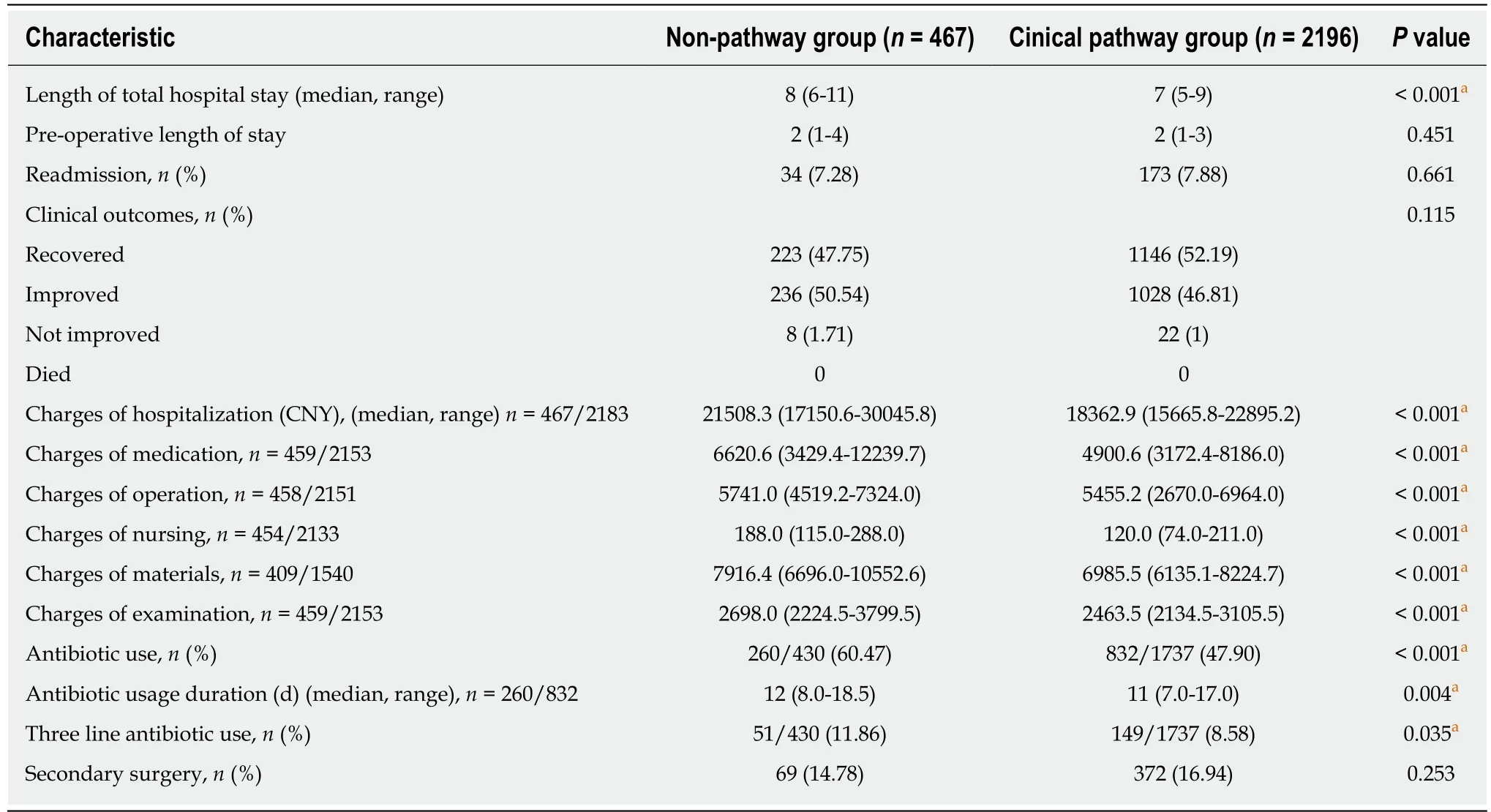
Table 2 Comparison of length of hospital stay, clinical outcomes, hospital charges, and drug use between the non-pathway and clinical pathway groups

Table 3 Comparison of postoperative complication rates between the non-pathway and clinical pathway groups
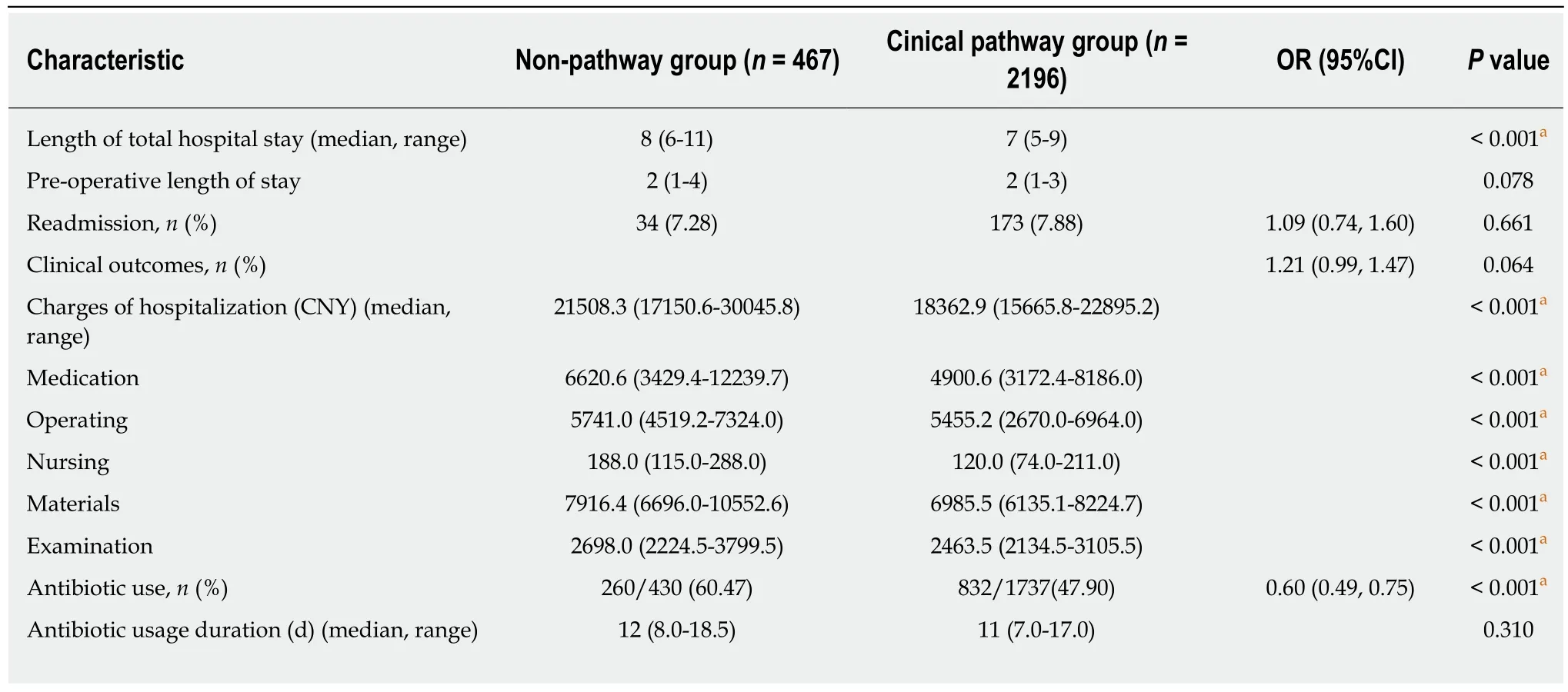
Table 4 Univariate logistic regression analysis of outcomes

aP < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. OR: Odds ratio; CI: Confidence interval.
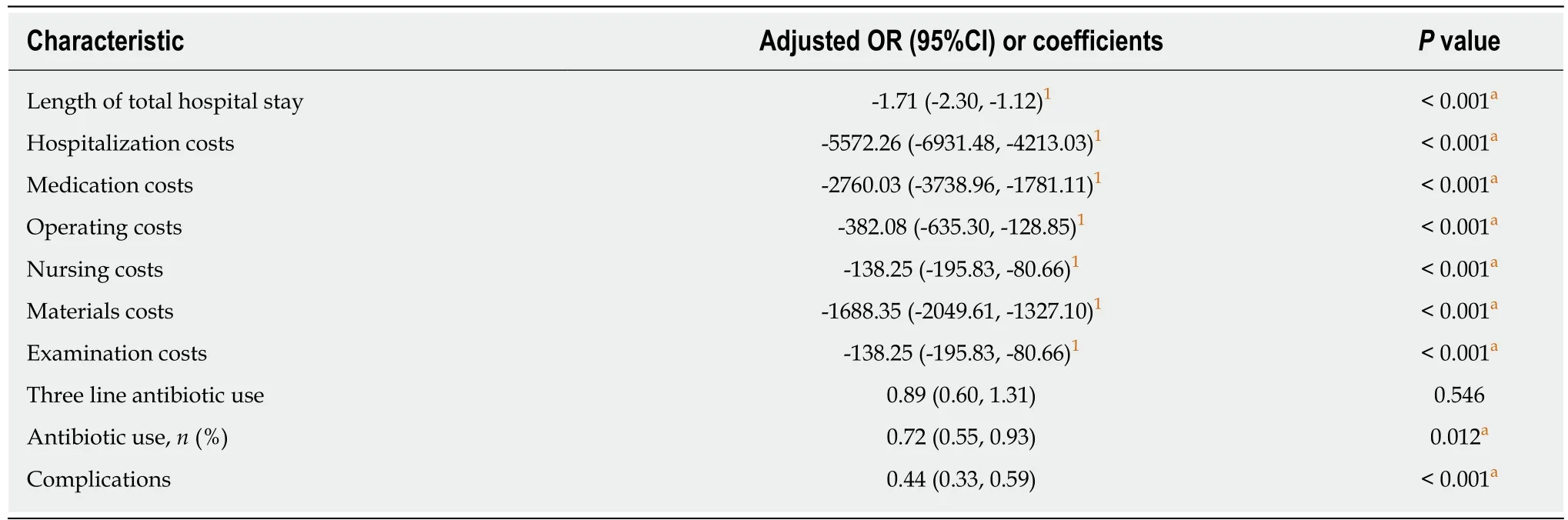
Table 5 Multivariate logistic and linear regression analysis of outcomes
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is widely recognized as a standard endoscopic technique for patients with common bile duct (CBD) stones. However, ERCP is associated with significant morbidity, mortality, and longer preoperative stay. A clinical pathway (CP) is an advanced methodology that provides a sequence of diagnosis, treatment, and management. Although CP implementation could optimize medical treatment and improve efficiency of medical sources utilization, CP implementation for CBD stones has not been fully promoted at present.
Research motivation
Current situation and value of the CP in management of CBD stones receiving ERCP still need to be explored. With the arrival of the era of big-data, we utilized a big-data process and application platform to provide a solid data base and scientific evidence for the establishment of the CP.
Research objectives
The objective of this study was to compare length of hospital stay (LOHS), costs, clinical outcomes, antibiotic use, and postoperative complication rate before and after implementing a CP for patients with CBD stones undergoing ERCP.
Research methods
Patients with CBD stones from Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital between January 2007 and December 2017 were identified from a big-data, intelligence database platform (Yidu Cloud Technology Ltd., Beijing, China). The enrolled population consisted of two groups which accepted conventional care (non-pathway group, n = 467) and the CP (CP group, n = 2196),respectively. Univariate and multivariable regression/linear models were utilized to compare the medical records and outcomes.
Research results
The percentage of antibiotic use and complications in the CP group were significantly less than those in the non-pathway group [adjusted odds ratio (OR) = 0.72, 95% confidence interval (CI)0.55-0.93, P = 0.012, adjusted OR = 0.44, 95%CI 0.33-0.59, P < 0.001, respectively]. Patients experienced lower costs in hospitalization, operation, nursing, medication, and materials (P <0.001 for all), and even shorter LOHS (P < 0.001) after implementation of the CP. No significant differences in clinical outcomes, readmission rate, or secondary surgery rate were presented between the patients in non-pathway and CP groups.
Research conclusion
In conclusion, implementation of the CP for patients with CBD stones undergoing ERCP significantly reduced LOHS, the costs, the rate of antibiotic use, and the incidence of complications without increasing readmission rates. A CP is confirmed to be an effective mode which is explicit about the sequencing, timing, and provision of interventions in the field of CBD stones. Meanwhile, our study provides further big-data evidence of a multidisciplinary CP in Chinese patients.
Research perspectives
Despite that this is the rare big-data evidence of a CP in Chinese patients with CBD stones,further multiple-center studies with larger variable are essential to strengthen the results.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We sincerely appreciate Yidu Cloud (Beijing) Technology Co. Ltd., China for providing technical support in extracting data by using the big-data intelligence platform.
杂志排行
World Journal of Gastroenterology的其它文章
- Current and future pharmacological therapies for managing cirrhosis and its complications
- Outcomes of per oral endoscopic pyloromyotomy in gastroparesis worldwide
- Dbx2 exhibits a tumor-promoting function in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines via regulating Shh-Gli1 signaling
- Dynamic changes of key metabolites during liver fibrosis in rats
- Procyanidin B2 protects against diet-induced obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via the modulation of the gut microbiota in rabbits
- Triggers of histologically suspected drug-induced colitis
