抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶5在结直肠癌中的表达及 临床意义
2019-01-09虞佳音王振李鑫杨宏杰张琳汪静宇
虞佳音 王振 李鑫 杨宏杰 张琳 汪静宇

[摘要] 目的 研究抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶5(ACP5)在结直肠癌(CRC)中的表达,并探讨其临床意义。 方法 采用酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)检测2017年1月~2018年4月35例结直肠癌患者和46例正常健康人血清中ACP5的水平;采用免疫组织化学(IHC)技术检测160例CRC组织中ACP5蛋白的表达情况;采用统计学方法对ACP5蛋白水平及临床病理特征进行评估。 结果 与正常健康对照组相比,结直肠癌患者血清ACP5水平明显升高(P=0.0071);IHC结果显示,淋巴结转移组伴随ACP5高表达(P=0.003);统计分析结果显示,ACP5高表达的患者生存期较短(P=0.001),ACP5表达与淋巴结转移相关。 结论 ACP5有可能成为预测CRC淋巴转移的标志物,其在CRC组织中的表达是影响预后的不良因素。
[关键词] ACP5;结直肠癌;转移标志物;免疫组化;酶联免疫吸附试验
[中图分类号] R735.3 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2019)33-0131-05
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the expression of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase 5 (ACP5) in colorectal cancer (CRC) and to explore its clinical significance. Methods The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to detect the serum ACP5 levels of 35 patients with colorectal cancer and 46 normal healthy individuals from January 2017 to April 2018. The immunohistochemical method (IHC) was used to detect the expression of ACP5 protein in 160 cases of CRC tissues. Statistical methods were used to evaluate the ACP5 protein levels and clinicopathological features. Results It was found by ELISA that the serum ACP5 levels in the patients with colorectal cancer were significantly elevated compared to those in the normal healthy controls(P=0.0071). It was found by IHC that the lymph node metastasis group was associated with high expression of ACP5(P=0.003). It was found by statistical analysis that the survival time was shorter for the patients with higher expression of ACP5 (P=0.001) and that ACP5 expression was associated with lymph node metastasis. Conclusion ACP5 may serve as a marker for predicting CRC lymphatic metastasis and that its expression in CRC tissue is an adverse factor affecting prognosis.
[Key words] ACP5; Colorectal cancer; Metastatic marker; Immunohistochemistry; Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
根據《CA:临床医师癌症杂志》2019年最新癌症统计数据显示,大肠癌患者的新发病率和死亡率在男性和女性中均居第三位[1]。2017年中国一项研究报告显示,结直肠癌(colorectal cancer,CRC)的发病率和死亡率持续上升。在我国城镇化程度较高的地区,结直肠癌的发病率和死亡率甚至上升到第二位和第四位[2]。这些权威数据表明,结直肠癌仍是人类健康的主要威胁之一,结直肠癌的预防和控制问题十分严峻。结直肠癌的发生发展与多种信号通路及相关基因有关,然而,结直肠癌发生发展的分子机制还没有完全了解。因此,研究抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶5(tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase 5,ACP5)为结直肠癌的诊断、治疗和预后提供理论依据尤为重要。
近期研究表明,ACP5广泛参与了乳腺癌、卵巢癌、恶性黑色素瘤和肺腺癌的发生发展[3-5]。然而,关于ACP5与结直肠癌之间关系的报道却很少,ACP5在结直肠癌中的表达情况及其与结直肠癌发生发展的关系尚不明确。本研究中利用酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)检测了结直肠癌患者和正常健康人血清中ACP5的水平,并利用免疫组织化学(immunohistochemical me-thod,IHC)技术检测了结直肠癌组织中ACP5蛋白的表达情况,结合临床病理特征进行评估分析,探讨ACP5的表达在结直肠癌中的临床意义。现报道如下。
最近,ACP5在肝、胆、胃肠道恶性肿瘤中的作用开始受到越来越多的关注。Xia L等人[25]的研究表明,ACP5在肝癌组织中的表达明显高于癌旁组织,其过表达与微血管浸润、分化差、TNM分期高有关。此外,ACP5阳性HCC患者的预后较ACP5阴性HCC患者差。多因素生存分析显示ACP5是术后复发和低生存率的独立且显著的危险因素。ACP5可以直接调控FoxM1的转录,促进HCC的转移。因此,ACP5可能是HCC患者预后的候选靶点,并为其提供了新的治疗靶点。Mikio K等[26]人在胃癌(GC)中对ACP5的研究中发现,ACP5在胃癌组织中的mRNA表达明显高于癌旁配对组织。mRNA表达增加与淋巴结及腹膜转移相关,ACP5表达是腹膜转移的独立危险因素,预后较差。因此,ACP5是胃癌患者腹膜转移的预测因子,可能在胃癌腹膜转移中发挥重要作用。ACP5可能是胃癌腹膜转移及预后不良的标志物。
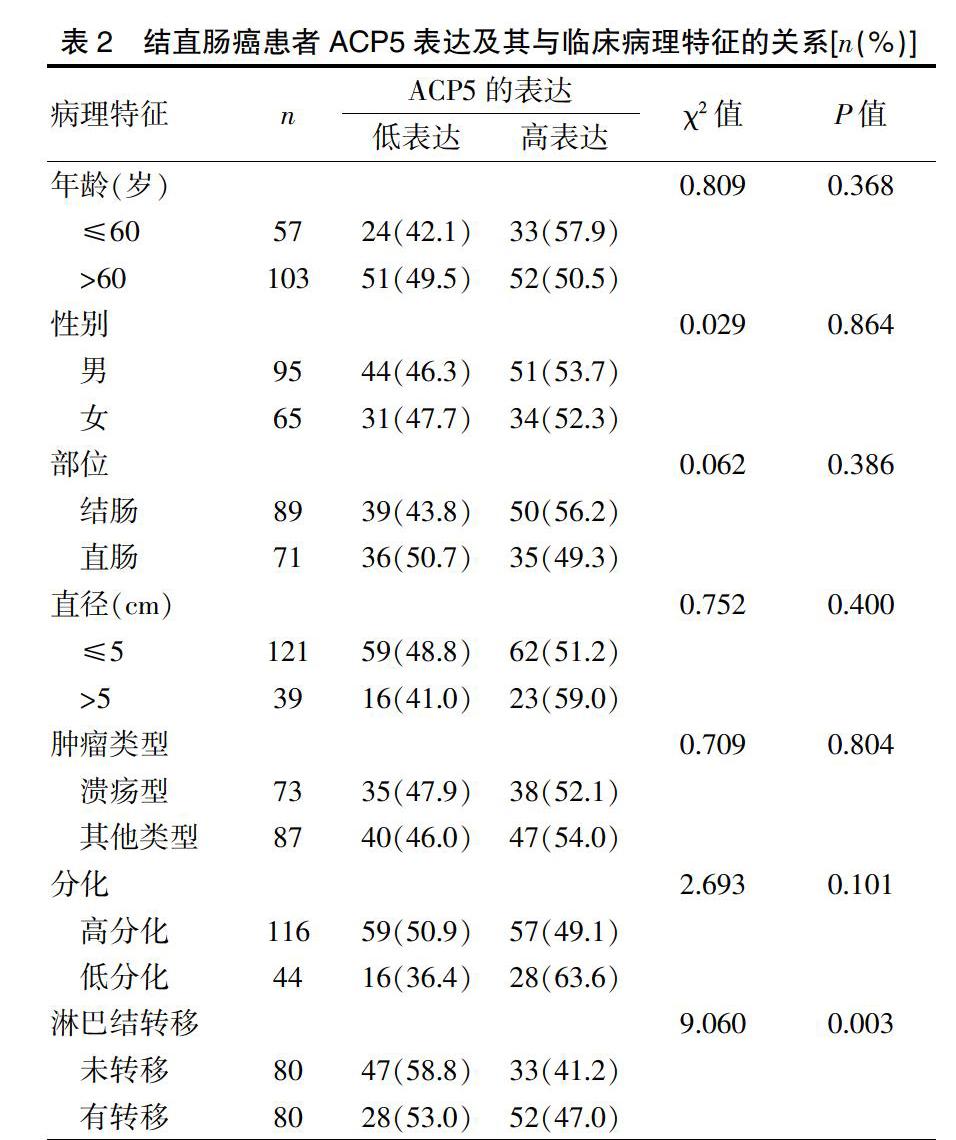
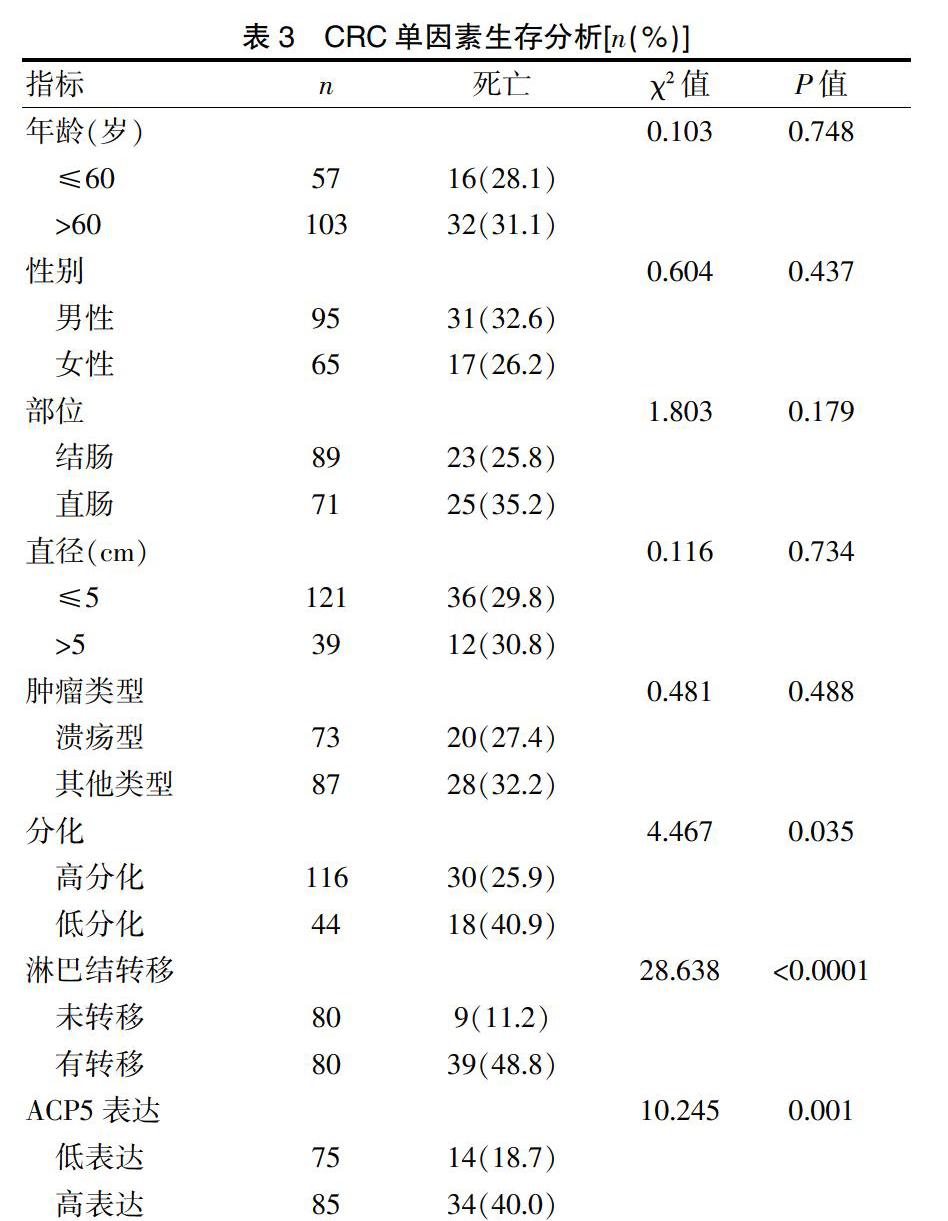
以上研究表明,ACP5在许多恶性肿瘤的发生发展过程中发挥着一定的作用。然而,ACP5在结直肠癌中的作用却鲜有报道。本研究采用免疫组织化学(IHC)方法探讨ACP5与结直肠癌临床病理特征的关系。结果表明,ACP5的表达与结直肠癌的直径、部位、肿瘤类型及分化程度无统计学意义。然而,ACP5的表达与淋巴结转移呈正相关,ACP5表达高的患者易引起淋巴结转移。此外,单因素生存分析显示,高表达水平ACP5的结直肠癌患者的生存时间要短于低表达水平ACP5的结直肠癌患者。这一结果与最近的一项研究一致,该研究[27]也表明ACP5的高表达与CRC淋巴结转移呈正相关。
考虑到ACP5是一种分泌蛋白,本研究也探讨了ACP5是否可以作为结直肠癌的血清学标志物。结果表明,结直肠癌患者血清ACP5水平明显高于正常对照组。提示血清ACP5水平可作为CRC的血清学指标。
本研究提示ACP5作為癌基因可能在结直肠癌的发生发展过程中发挥重要作用。ACP5的高表达可能会促进结直肠癌的转移,导致预后不良。血清中ACP5的检测也提示ACP5可作为结直肠癌的血清学标志物。本研究为进一步研究ACP5的功能和机制提供了良好的理论基础,并为结直肠癌的早期诊断和个体化靶向治疗提供新的可能。
综上所述,ACP5表达与淋巴结转移及预后不良呈正相关。ACP5可作为结直肠癌诊断、转移及预后的潜在预测因子,可能成为结直肠癌新的治疗靶点。
[参考文献]
[1] Siegel RL,Miller K D,Jemal A. Cancer statistics,2019[J].CA:A Cancer Journal for Clinicians,2019,69(1):7-34.
[2] Chen W,Zheng R,Zhang S,et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in China in 2013:An analysis based on urbanization level[J]. Journal of Clinical Immunology,2017,29(1):1-10.
[3] Scott KL,Nogueira C,Heffernan TP,et al. Proinvasion metastasis drivers in early-stage melanoma are oncogenes[J]. Cancer Cell,2011,20(1):92-103.
[4] Gao YL,Liu MR,Yang SX,et al. Prognostic significance of ACP5 expression in patients with lung adenocarcinoma[J]. The Clinical Respiratory Journal,2018,12(3):1100-1105.
[5] Honig A,Rieger L,Kapp M,et al. Increased tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase(TRAP) expression in malignant breast,ovarian and melanoma tissue:An investigational study[J]. BMC Cancer,2006,6(1):199.
[6] Wang Z,Ding M,Qian N,et al. Decreased expression of semaphorin 3D is associated with genesis and development in colorectal cancer[J]. World J Surg Oncol,2017, 15(1):67.
[7] Wu YY,Janckila AJ,Ku CH,et al. Serum tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase 5b activity as a prognostic marker of survival in breast cancer with bone metastasis[J]. BMC Cancer,2010,10(1):158.
[8] Zhang Q,Cao L,Miao XD,et al. Diagnostic value of TRACP5b expression in patients with bone tumors[J]. Journal of Biological Regulators and Homeostatic Agents,2019,33(2):557-562.
[9] Halleen JM,Alatalo SL,Janckila AJ,et al. Serum tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase 5b is a specific and sensitive marker of bone resorption[J]. Clinical Chemistry,2001,47(3):597-600.
[10] Briggs TA,Rice GI,DalyS,et al. Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase deficiency causes a bone dysplasia with autoimmunity and a type Ⅰ interferon expression signature[J].Nature Genetics,2011,43(2):127-131.
[11] Ren X,Shan WH,Wei LL,et al. ACP5:Its structure,distribution,regulation and novel functions[J]. Anti-cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry,2018,18(8):1082-1090.
[12] Briggs TA,Rice GI,Adib N,et al. Spondyloenchondrodysplasia due to mutations in ACP5:A comprehensive survey[J]. Journal of Clinical Immunology,2016,36(3):220-234.
[13] Girschick H,Wolf C,Morbach H,et al. Severe immune dysregulation with neurological impairment and minor bone changes in a child with spondyloenchondrodysplasia due to two novel mutations in the ACP5 gene[J]. Pediatric Rheumatology,2015,13(1):37.
[14] An J,Briggs TA,Dumax-Vorzet A,et al. Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase deficiency in the predisposition to systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Arthritis & Rheumatology,2016,69(1):131-142.
[15] Capeller B,Caffier H,S?觔1/4Tterlin MW,et al. Evaluation of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase(TRAP) 5b as serum marker of bone metastases in human breast cancer[J]. Anticancer Research,2003,23(2A):1011-1015.
[16] Halleen JM. Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase 5B is a specific and sensitive marker of bone resorption[J]. Anticancer Research,2002,23(2A):1027-1029.
[17] Lyubimova NV, Pashkov MV,Tyulyandin SA,et al. Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase as a marker of bone metastases in patients with breast cancer and prostate cancer[J]. Bull Exp Biol Med,2004,138(7):77-79.
[18] Tsu-Yi C,Jyh-Cherng Y,Chih-Hung K,et al. Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase 5b is a useful serum marker for extensive bone metastasis in breast cancer patients[J].Clinical Cancer Research,2005,11(2 Pt 1):544-550.
[19] Yao NS,Wu YY,Janckila AJ,et al. Serum tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase 5b(TRACP5b) activity as a biomarker for bone metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer patients[J]. Clinica Chimica Acta,2011,412(1):181-185.
[20] Zenger S,He W,Ek-Rylander B,et al. Differential expression of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase isoforms 5a and 5b by tumor and stromal cells in human metastatic bone disease[J]. Clin Exp Metastasis,2011,28(1):65-73.
[21] Windrichova J,Fuchsova R,Kucera R,et al. Testing of a novel cancer metastatic multiplex panel for the detection of bone-metastatic disease-a pilot study[J]. Anticancer Research,2016,36(4):1973-1978.
[22] Lumachi F,Basso SMM,Camozzi V,et al. Bone turnover markers in women with early stage breast cancer who developed bone metastases. A prospective study with multivariate logistic regression analysis of accuracy[J]. Clinica Chimica Acta,2016,460(1):227-230.
[23] Adams LM,Warburton MJ,Hayman AR. Human breast cancer cell lines and tissues express tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase(TRAP)[J]. Cell Biology International,2013,31(2):191-195.
[24] Reithmeier A,Panizza E,Krumpel M, et al. Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase(TRAP/ACP5)promotes metastasis-related properties via TGFβ2/TβR and CD44 in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells[J]. BMC Cancer,2017,17(1):650.
[25] Xia L,Huang W,Tian D,et al. ACP5,a direct transcriptional target of FoxM1,promotes tumor metastasis and indicates poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Oncogene,2013, 33(11):1395.
[26] Mikio K,Koji T,Yuji T,et al. Clinical significance of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase type-5 expression in human gastric cancer[J]. Anticancer Research,2014,34(7):3425-3429.
[27] Bian ZQ,Luo Y,Guo F,et al. Overexpressed ACP5 has prognostic value in colorectal cancer and promotes cell proliferation and tumorigenesis via FAK/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J]. American Journal of Cancer Research,2019,9(1): 22-35.
(收稿日期:2019-07-24)
