基于最小切块应力的西兰花切块加工刀具参数优化研究
2018-11-23陈建能陈礼群喻陈楠蔡双雷夏旭东
陈建能,陈礼群,喻陈楠,蔡双雷,夏旭东
基于最小切块应力的西兰花切块加工刀具参数优化研究
陈建能1,2,陈礼群1,喻陈楠1,蔡双雷1,夏旭东1,2
(1. 浙江理工大学机械与自动控制学院,杭州 310018;2. 浙江省种植装备技术重点实验室,杭州 310018)
为了给西兰花切块机的设计提供理论依据,获得最佳切块效果,该文以收获期的西兰花作为切块对象,选择西兰花切块位置、刀具刃角、刀具结构以及入切角为影响因素,在万能材料试验机上进行了单因素与多因素的切应力试验,单因素试验结果表明:切块位置为距离花蕾顶端40 mm、光刀、入切角为60°、刀具刃角为5°~10°之间时切应力最小。多因素试验结果表明:影响切应力的因素主次次序依次是切块位置、刀具结构、刀具刃角、入切角;切块位置为距离花蕾顶端40 mm、刀具结构为球形刀、刀具刃角为8°、入切角为90°时切块效果最佳。根据试验优化结果设计了西兰花切块刀具,并在自制的切块样机上进行了切块试验,切块效果良好,切块成功率达到91%,验证了刀具参数优化的合理性。研究结果可为后续西兰花切块机切块刀具的设计提供参考。
刀具;应力;西兰花;切块;优化
0 引 言
随着日本和欧洲从中国进口西兰花的不断增加,激发了中国农户生产西兰花的积极性,在沿海一带,逐步形成了一些出口导向型的西兰花产地[1-3]。目前中国西兰花对外出口量还在日益增加,出口的西兰花也从之前的整棵转变为西兰花小块,但中国现阶段还是采用人工切块,机械化加工程度低,制约了中国西兰花产业发展。
为了提高西兰花加工机械化水平,国内外对西兰花切块技术及装备进行了研究。目前中国对西兰花切块技术研究主要集中在结构设计方面,武传宇等提出了一种旋转式花椰菜切削装置[4],采用了圆筒形削刀,压杆将西兰花压至圆筒形削刀内,利用螺旋式刀片进行切割,但此种刀具一般适合切片或削皮上的应用,不适合用于西兰花切块场合。贺磊盈等提出了一种茎花分离式西兰花自动切削装置[5],采用了横纵交替切块方法对西兰花进行切块,切块刀具为光刀。上述两种方案目前仅止步于理论结构设计,市场上未见相关机械成品。国外有关西兰花切块技术研究比中国早,早在上世纪九十年代初,就出现了西兰花切块机的相关研究,现已有西兰花切块机的产品,如SMJ系列的青花菜切块机[6],采用锥形刀具对西兰花进行切块;美国Charlie公司研发一种气动西兰花切块机[7],采用球形刀具对西兰花进行切块。这两种切块机均只是在网上做产品的介绍,没有详细的技术研究报道。
为了提高西兰花的切块效率,西兰花切块时的刀具参数至关重要,而刀具参数的选择和西兰花的机械物理特性密切相关本文拟借鉴国内外对农作物茎秆切割时刀具参数优选的方法进行研究[8-21],选择西兰花切块位置、刀具刃角、刀具结构以及入切角为影响因素,在万能材料试验机上进行了单因素与多因素的切应力试验,优化西兰花切块刀具的结构参数与工作参数,以期为降低切块机械功耗,设计高效、低耗、切块效果好的西兰花切块装置及切块刀具提供理论依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
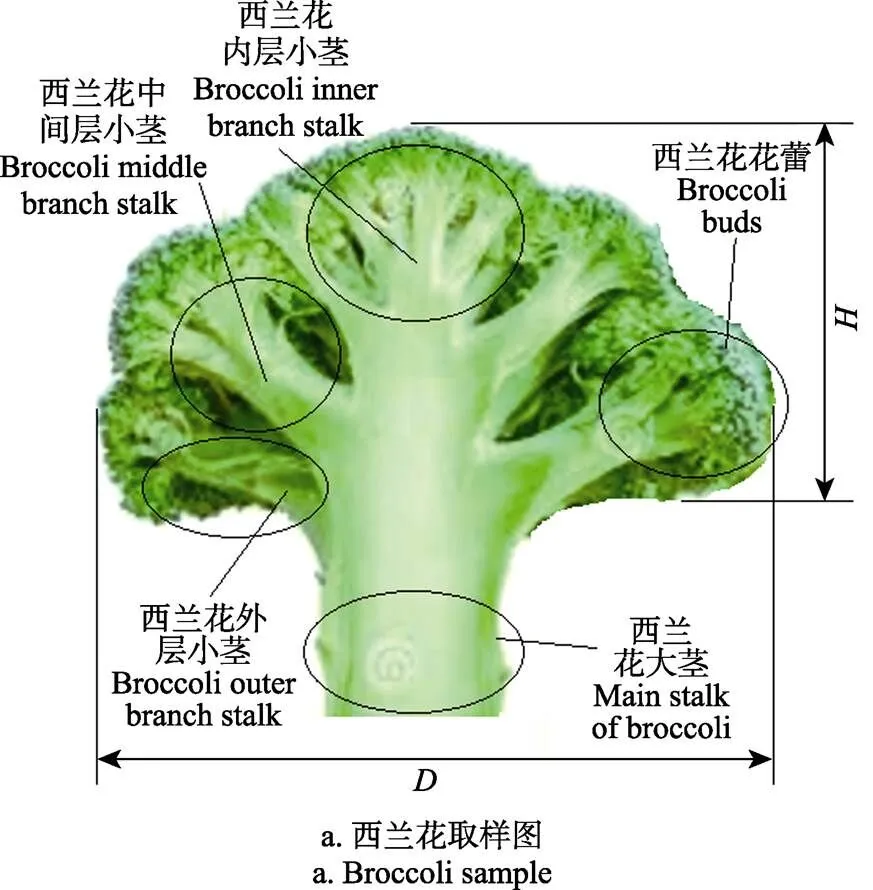
试验西兰花品种为由浙江省农科院选育的“浙青95号”,种植于浙江省温岭、台州、宁波等地,对自然生长条件下并处于3月份收获期西兰花整朵进行取样,试验得到“浙青95号”花苞直径介于140~160 mm之间,花苞高度介于70~90 mm之间,西兰花小茎分3个不同的部位,分别为西兰花外层,中间层和内层的小茎,如图1a所示。由于切块加工过程为先外层再中间层最后内层,并且外层小茎纤维层较厚,硬度较高。故本文将取西兰花外层小茎作为试验样品如图1b所示,并对小茎距花蕾顶端的30、40和50 mm处做上标记,以备后续试验用。
b. 西兰花小茎样品
b. Broccoli branch stalk sample
注:为西兰花苞高,mm;为西兰花苞径,mm;
Note:is broccoli height, mm;is broccoli diameter, mm;
图1 西兰花试验样品图
Fig.1 Broccoli test sample
1.2 试验仪器与设备
本试验仪器和设备有如图2a的微机控制电子万能材料试验机(型号:LDW-1;最大载荷:50 kg;功率:12 kW;制造商:上海松顿机械设备有限公司)、球形刀(刀具为1/4球面,刀刃为半圆弧,直径为100 mm);光刀(刀刃为直线,长度为100 mm);锥形刀(刀具为1/4圆锥面,圆锥底面直径100 mm,高80 mm);刀片厚度均为2 mm。切台与刀具如图2b~2e所示,均利用夹具固定于试验台上。试验用仪器还包括数码相机及其图像处理分析软件ImageJ、镊子、米尺、游标卡尺、量角器、记号笔等。
1.3 试验方法及方案设计
由于西兰花切块机在进行切块时大多采用正切,故此试验不考虑往复式切块形式。西兰花切块示意图如图2f所示。通过移动块上下移动实现入切角的调整。试验时万能材料试验机的测控系统会自动将其压力传感器测得的数据转化为刀具的切割力记录下来,并显示切割力与时间的关系曲线图(图3),将切西兰花小茎过程中得到的峰值作为西兰花小茎最大切割力MS。有研究学者指出采用单位切割力作为研究目标更加合理,因此,消除西兰花小茎切割部位直径差异对实验结果的影响,本文采用单位面积最大切割力即最大切应力作为目标值,研究西兰花切块刀具工作参数刀具结构、刀具刃角、入切角、切块位置对西兰花小茎切应力的影响。
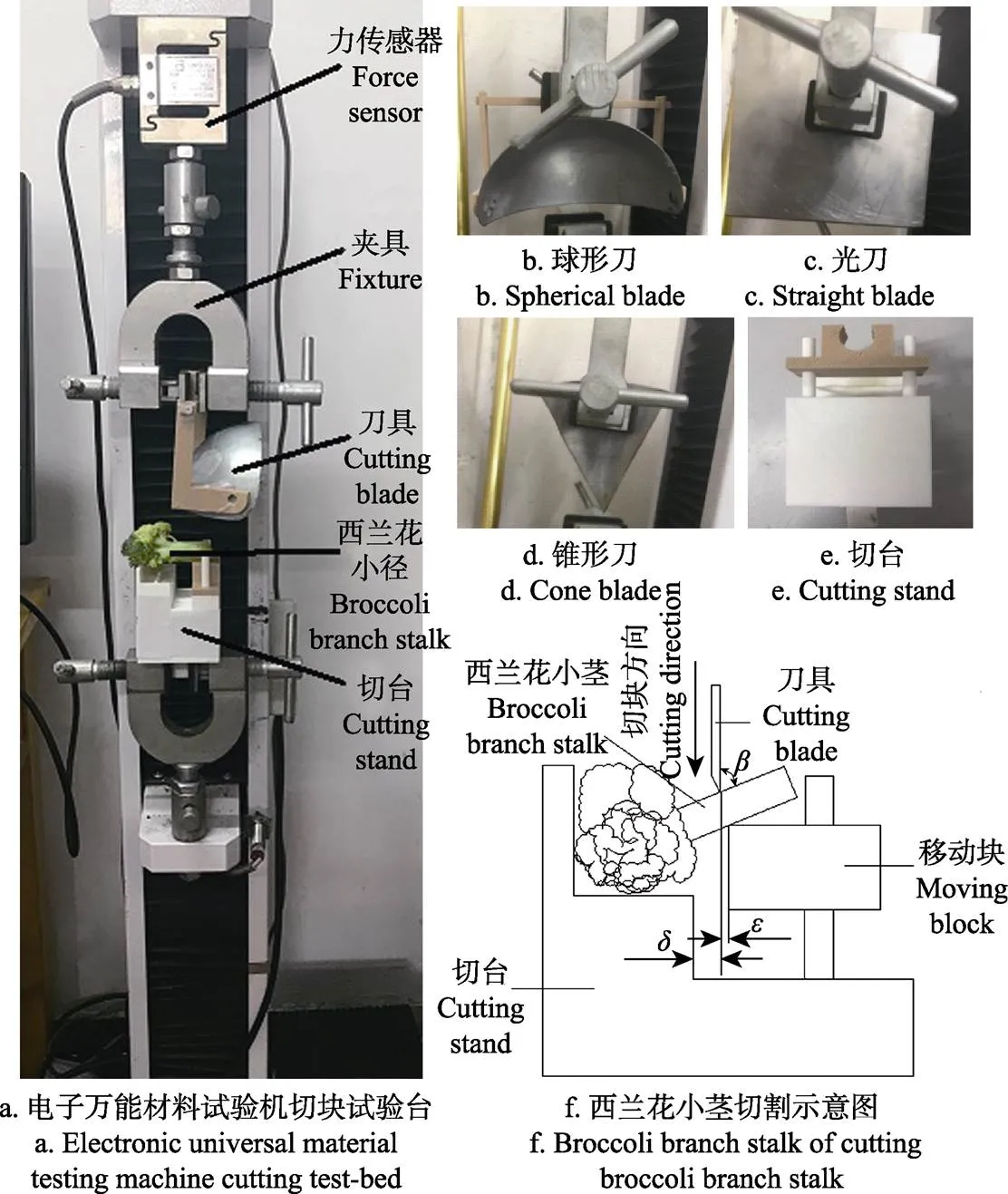
注:β为入切角,(°);刀具与移动块的间隙ε为1 mm、刀具与切台的间隙d为3 mm。
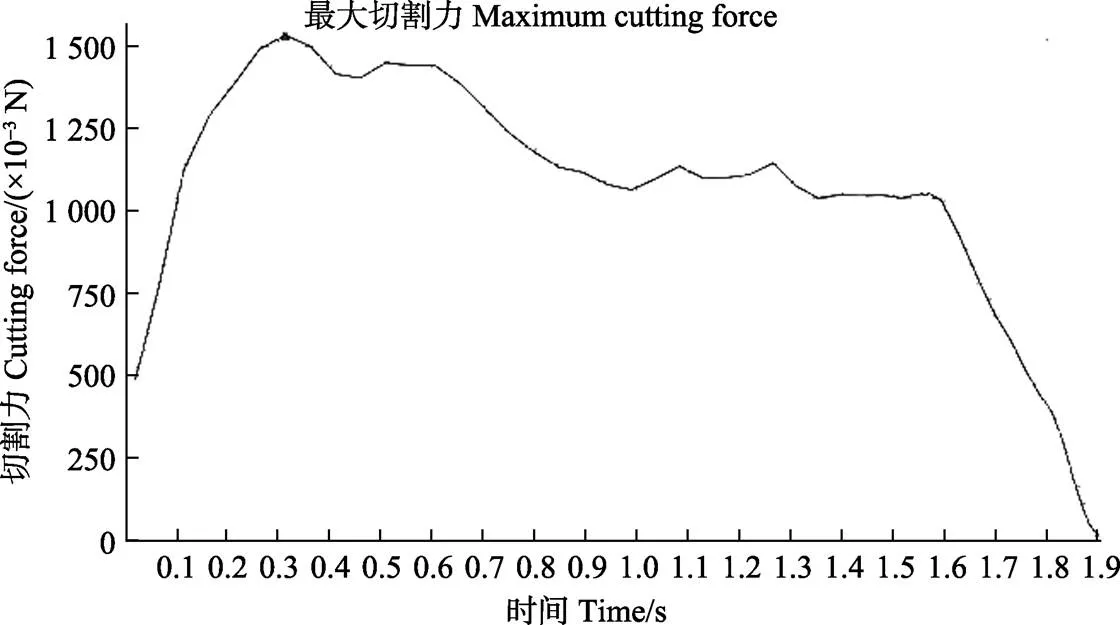
图3 切割力-时间变化曲线图
西兰花小茎最大切应力按式(1)计算。
=MS/(1)
式中MS为最大切割力,10-3N;为小茎切块面积,mm2;为最大切应力,kPa。小茎的切块面积通过以下方法获得:选取粗细一致的小茎为试验对象,然后在切块试验台上进行切块,将切后的小茎切面涂上颜色制作拓本,按1:1比例印到纸面上,进行拍照,然后用ImageJ软件计算拓图面积即得到小茎切块面积,如图4所示。
图4 西兰花小径切面拓本图
Fig.4 Extension map of broccoli branch stalk cutting surface
1.3.1 单因素试验
参考文献[22-27],选定西兰花切块力单因素试验参数:刀具结构单因素试验时,刀具刃角为8°、入切角为90°、切块位置为40 mm;刀具刃角单因素试验时,刀具结构为光刀、入切角为90°、切块位置为40 mm;入切角单因素试验时,刀具结构为光刀、刀具刃角为8°、切块位置为40 mm;切块位置单因素试验时,刀具结构为光刀、刀具刃角为8°、入切角90°;每一水平下重复10次,在=0.05水平进行检验。
1.3.2 多因素试验
为了进一步研究西兰花切块刀具主要工作参数(刀具结构、刀具刃角、入切角、切块位置)对西兰花切应力的影响,寻求最佳组合,在单因素试验的基础上,以刀具结构、刀具刃角、入切角、切块位置为因素,采用水平正交法设计正交试验[28-32],每组重复10次,结果取平均值。
2 结果与分析
2.1 单因素试验结果与分析
2.1.1 刀具刃角对西兰花小茎切应力的影响
为了考查刀具不同刃角对西兰花小茎切应力的影响,以光刀为例,分别用刃角为5°、8°、11°、14°、17°的刀片对直径为8±0.5 mm的小茎进行切块试验,测得各个小茎受到的最大切应力,结果如表1所示。
通过调用Matlab中的Anova1函数对表1中数据在=0.05水平下进行-检验(本文中所涉及显著性检验的值均采用此方法计算),结果如表2所示。由表2中=3.92´10–5<0.05可知5种不同刀具刃角之间对切应力的影响存在显著差异。

表1 不同刀具刃角的西兰花小径最大切应力值
注:刀具结构为光刀、入切角为90°、切块位置为40 mm。±SD表示平均值±标准差。
Note:Cutting blade is light blade.Cutting angle is 90°. The cutting position is 40 mm.±SD means average value ± standard deviation.
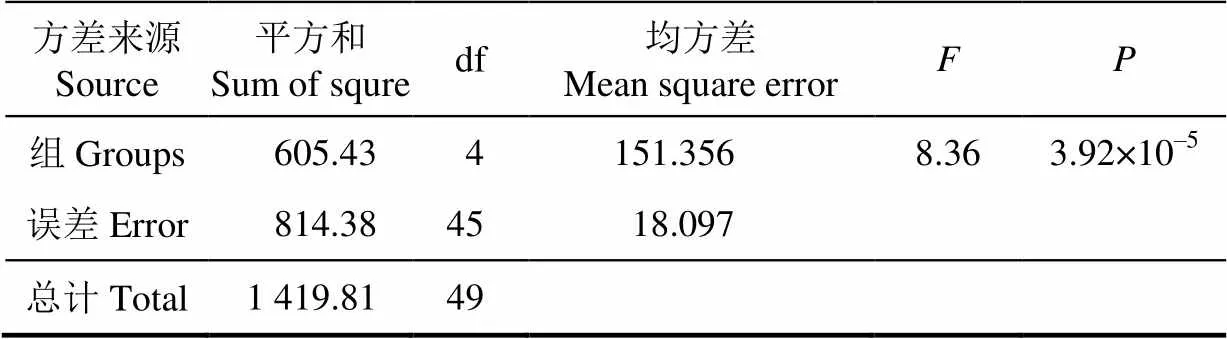
表2 不同刀具刃角显著性检验结果
由表1可知,刀具刃角从5°增加到17°时,西兰花小茎的最大切应力随刀具刃角增加而增加,刀具刃角为5°的时候切块力最小。刃角10°~30°的刀具一般适用于高速、被切割材料木质化程度较高的场合,而西兰花花茎是蔬菜纤维层,故选择刀具刃角为5°~10°之间适合。
2.1.2 刀具结构对西兰花小茎切应力的影响
为了考查不同结构的刀具对西兰花小茎切应力的影响,分别用球形刀、光刀和锥形刀对直径为8±0.5 mm的小茎进行切块试验,并记录下小茎受到的最大切应力,结果见表3。对表3中的数据进行显著性检验计算出= 1.4´10–9<0.05,因此不同刀具对切应力的影响存在显著差异。由表3可知,光刀产生的最大切应力最小,其次为球形刀,锥形刀产生的最大切应力最大。
2.1.3 切块位置对西兰花小茎切应力的影响
为了考察不同切块位置对西兰花小茎的切应力的影响,分别对西兰花小茎的不同位置进行切块试验,并记录下最大切应力值,结果见表4。对表4中的数据进行显著性检验计算出=1.0776´10–16<0.05,因此不同切块位置对切应力的影响存在显著差异。由表4可知,西兰花小茎切块时受到的最大切应力值随切块位置增加先降低再增加。在切块位置为40 mm处最大切应力值最小。这主要是因为西兰花小茎距花蕾顶端30 mm处比较接近花蕾,会存在分节点或形状不规则,切块时所需切割力较大,从而导致最大切应力较大,西兰花小茎距花蕾顶端50 mm处比较接近西兰花大茎,茎秆较成熟,纤维层较厚,所需切割力大,因此最大切应力也较大。
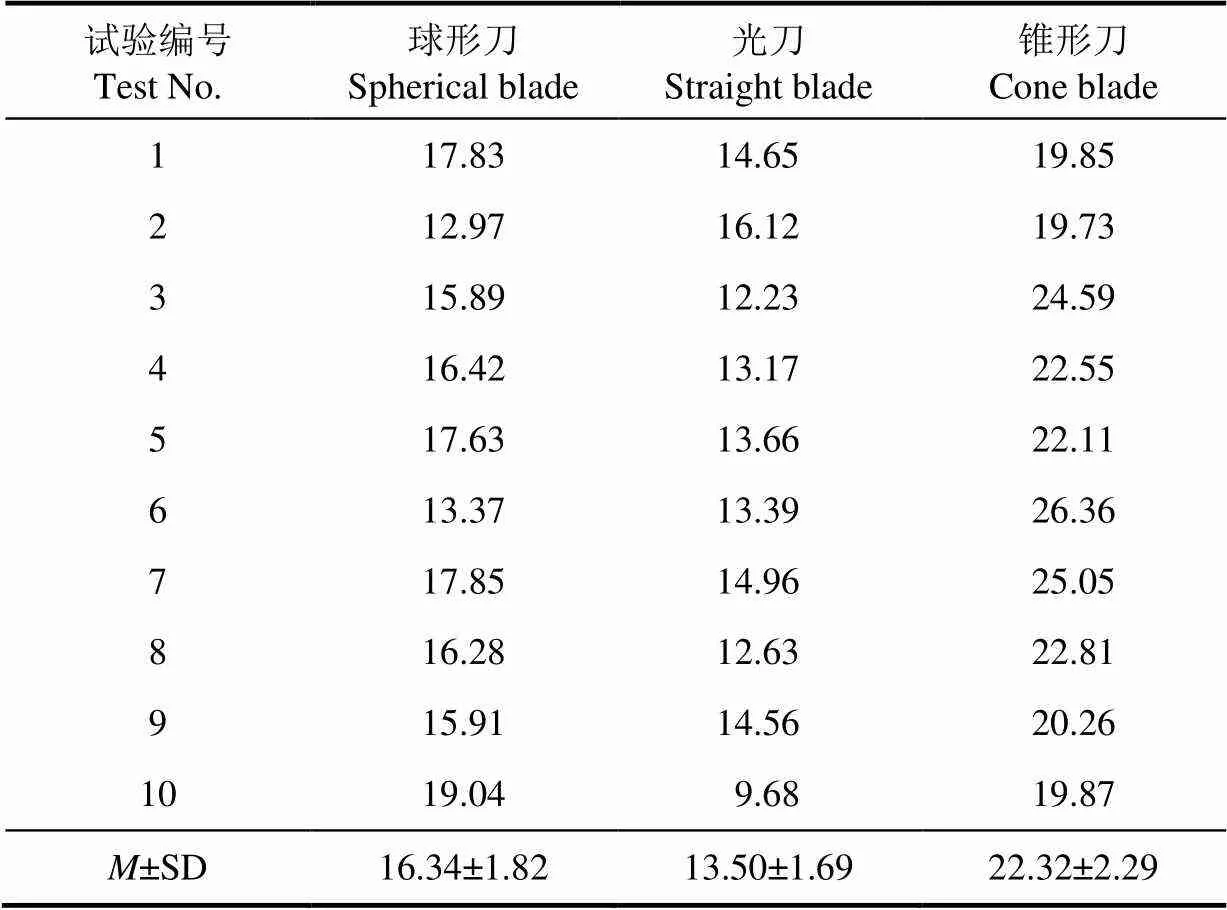
表3 不同结构刀具的最大切应力值
注:刀具刃角为8°、入切角为90°、切块位置为40 mm。
Note:Blade angle is 8°, cutting angle is 90°, cutting position is 40 mm.
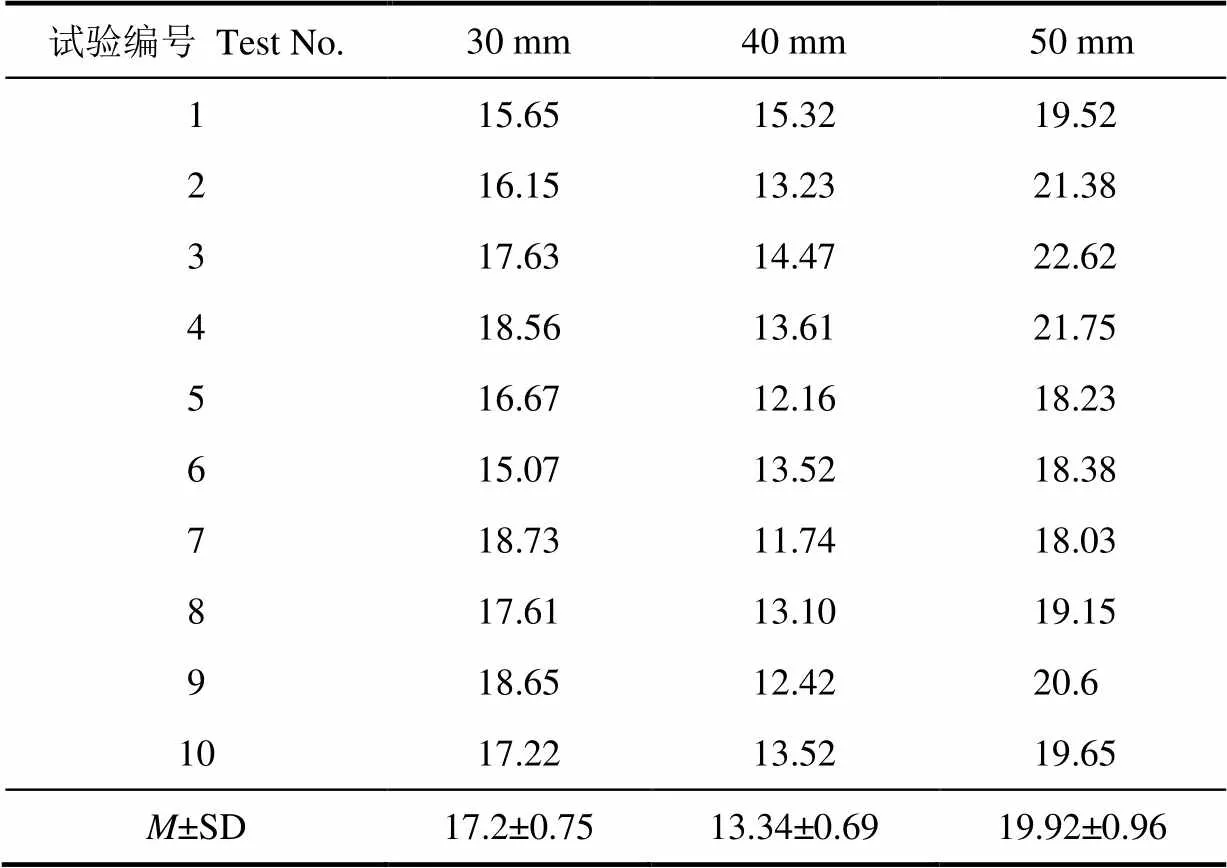
表4 不同切块位置的最大切应力值
注:刀具结构为光刀、刀具刃角为8°、入切角为90°。
Note:Cutting blade is light blade, blade angle is 8°, cutting angle is 90°.
2.1.4 入切角对西兰花小茎切应力的影响
为了考查不同入切角对西兰花小茎切应力的影响,分别设定入切角为90°、60°、45°对直径为8±0.5 mm的小茎进行切块试验,并记录下小茎受到的最大切应力,结果见表5。对表5中数据进行显著性检验,计算得出= 0.046 1<0.05,因此不同入切角对切应力的影响存在显著差异。由表5可知,入切角为60°时最大切应力最小。
2.2 多因素试验结果与分析
由上述单因素试验发现,西兰花小茎的最大切应力大小主要与刀具结构、刀具刃角、切块位置以及入切角度有关。由于涉及因素较多,故采用水平正交法来设计正交试验,其因素水平编码表如表6所示。对试验结果进行分析计算,计算参数为各因素在水平所对应的的总切块力K=(1,2,3),其中i=∑各因素在水平所对应的切块力;各因素在水平下的平均切块力k=K/3;各因素的极差为,计算结果见表7。
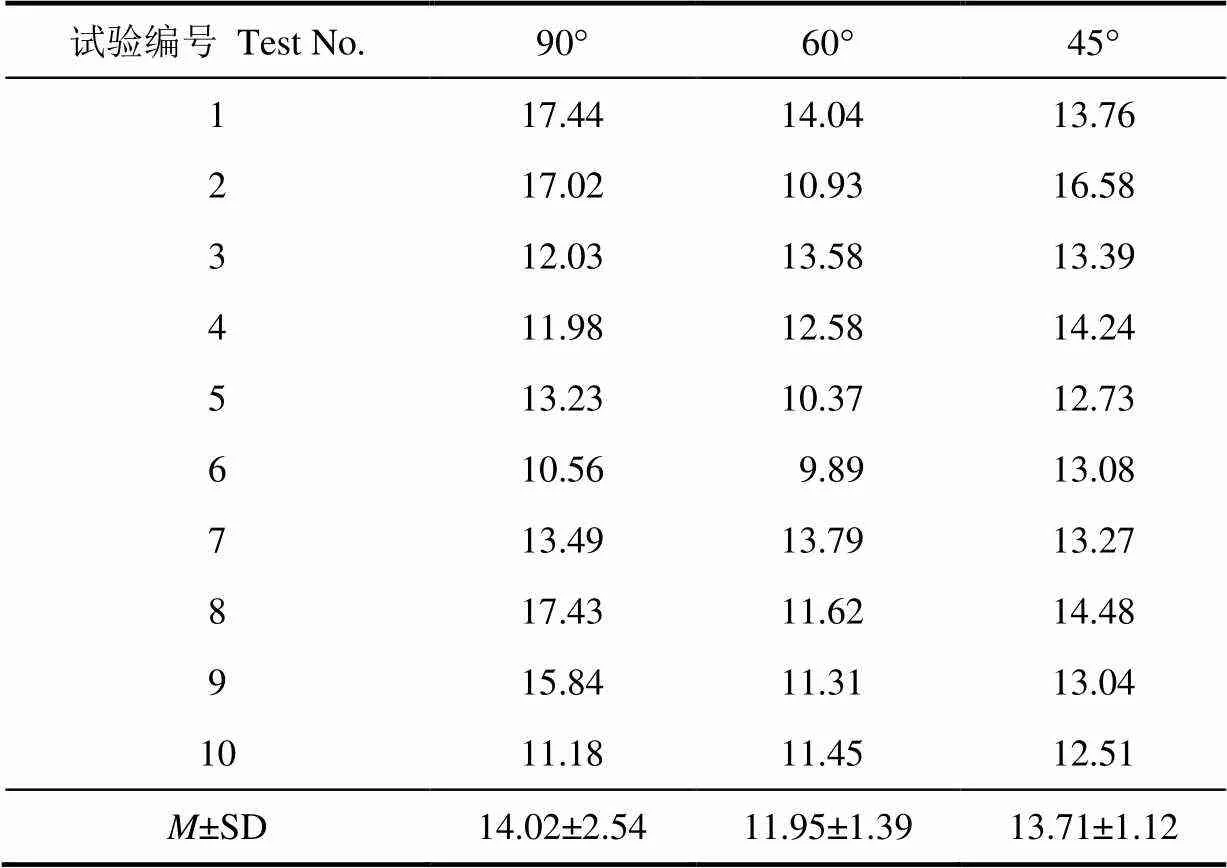
表5 不同入切角的最大切应力值
注:刀具刃角为8°、刀具结构为光刀、切块位置为40 mm。
Note: Blade angle is 8°, cutting blade is light blade, cutting position is 40 mm.
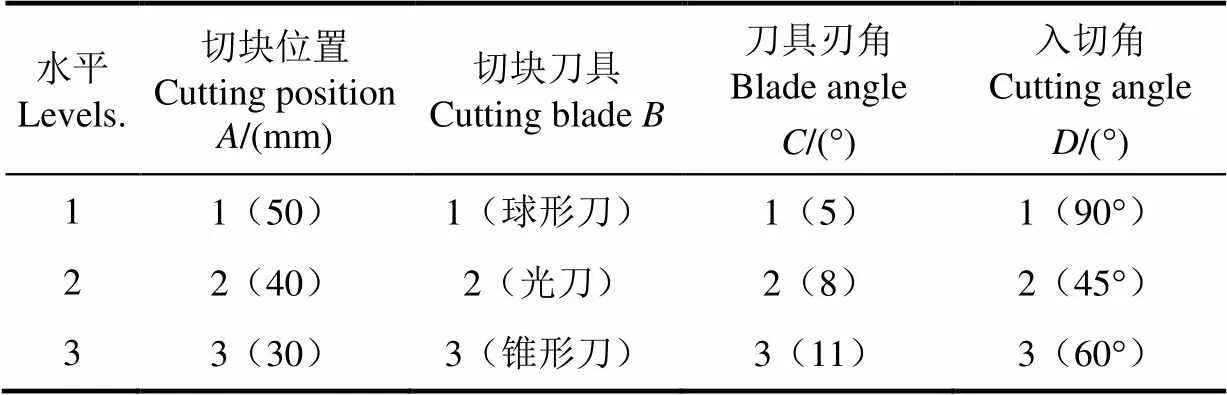
表6 试验因素水平表
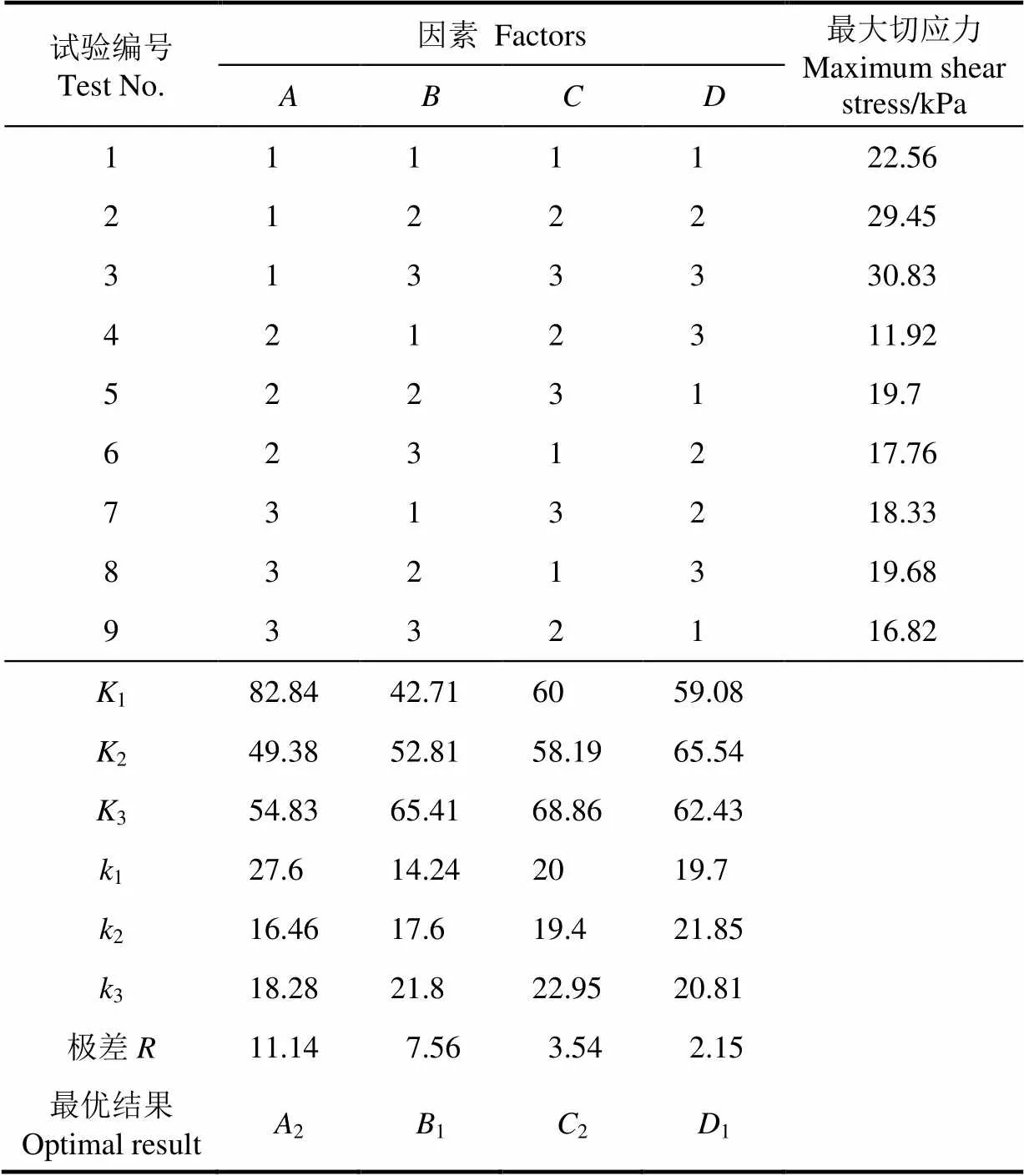
表7 最大切应力正交试验结果
由表7可知,极差最大的因素是切块位置,故切块位置对于切应力的影响力最大;其次是切块刀具类型,在正交试验中出现的结果是球形刀所需切块力最小;再次是刀具刃角,取第2水平最好;最后是入切角,对切块试验的影响最小,取第1水平最好。故该试验的最优方案为2121即西兰花小茎切块位置离花蕾顶端40 mm,刀具结构为球形刀,刀具刃角为8°,入切角为90°时切块应力最小,切应力平均值为17.45 kPa。
2.3 验证试验
利用正交试验结果得到西兰花切块刀具的最佳工作参数,设计了刃角为8°的球形刀具,刀具直径为90 mm,入切角90°,研制了西兰花切块试验台[33],并在自制的试验台(如图5)上进行了切块试验,参考现有西兰花切块机[6-7]的切块速度,设西兰花切块样机工作转速为60 r/min,试验中刀具切块姿态如图6所示;样机中电机转动1周完成1次切块。
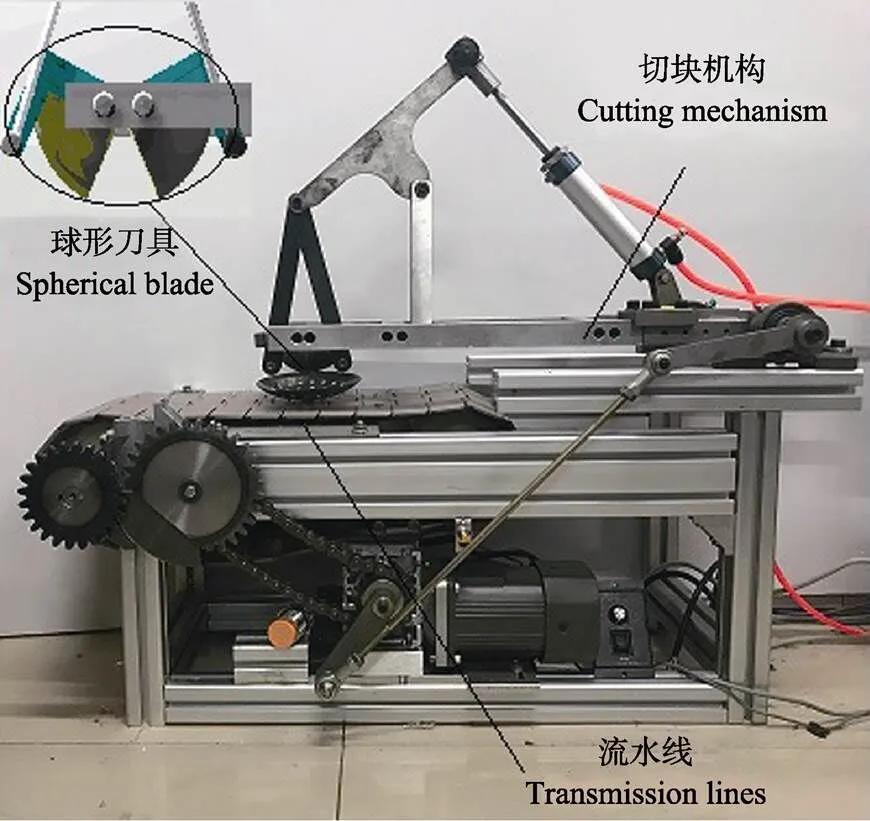
图5 西兰花切块试验样机

a. 开始切块 a. Start cuttingb. 切块结束 b. End of cutting c. 西兰花小块 c. Small piece of broccolid. 西兰花茎 d. Broccoli stalk
在样机转速为60 r/min情况下进行100朵切块试验,成功切块91朵,成功去芯100朵,切块成功率91%。工作效率达50~60个/min。切块应力平均值为18.32 kPa,与理论值17.45 kPa基本接近,验证了刀具参数设置的合理性。
2.4 讨 论
本文采用单位面积最大切割力作为目标值,利用单因素试验与多因素试验对西兰花切块刀具工作参数进行了优化,从定性与定量2个方面研究了切块刀具工作参数对西兰花切应力的影响,确定切块位置、刀具结构、刀具刃角与入切角依次是影响切应力的主要因素;结果表明最佳的切块组合是切块位置为40 mm、球形刀、刀具刃角为8°、入切角为90°。根据最佳切块位置为刀具尺寸设计提供依据。同时入切角为90°的切面最小,有利于西兰花保存。
3 结 论
1)通过对西兰花切应力的单因素试验得到:切块位置为距离花蕾顶端40 mm处最大切应力值最小;刀具刃角为5°~10°之间适合;光刀产生的最大切应力最小。
2)多因素试验得到各个影响因素对切应力的影响:西兰花的切块位置对切应力影响最大,入切角对切应力影响最小,各个因素交互的作用下的最佳切块因素组合是切块位置为距离花蕾顶端40 mm处、刀具结构为球形刀、刀具刃角为8°、切块时入切角为90°。
3)根据优化结果设计了切块刀具,并在自制切块样机上进行了切块试验,样机在转速为60 r/min情况下进行100朵切块试验,切块成功率91%,工作效率达50~60个/min,切块应力平均值为18.32 kPa,验证了西兰花切块刀具参数优化结果的合理性。
[1] 何玉池,李云,焦颜成,等. 西兰花出口的现状及产业化安全生产研究初探[J]. 现代农业科技,2007(14):12-13. He Yuchi, Li Yun, Jiao Yancheng, et al. Present situation of the export of broccoli and preliminary study on industrialized safe production[J]. Journal of Modern Agriculture and Technology, 2007(14): 12-13. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 屈为栋,何道根,苏英京. 台州市西兰花产业现状、存在问题及发展对策[J]. 浙江农业科学,2009(6):1062-1065. Qu Weidong, He Daogen, Su Yingjing. Current status, existing problems and development countermeasures of broccoli industry in Taizhou City[J]. Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2009(6): 1062-1065. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 肖体琼,何春霞,陈巧敏,等. 基于机械化生产视角的中国蔬菜成本收益分析[J]. 农业机械学报,2015,46(5): 75-82. Xiao Tiqiong, He Chunxia, Chen Qiaomin, et al. Analysis of chinese vegetable cost and income based on mechanized production perspective[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society forAgricultural Machinery, 2015, 46(5): 75-82. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 武传宇,杨太玮,童俊华,等. 旋转式花椰菜切削装置:中国专利,CN106863444A[P].2017-06-20.
[5] 贺磊盈,刘晓晨,童俊华. 茎花分离式西兰花自动切削装置:中国专利,CN106863443A[P]. 2017-06-20.
[6] Brussel sprout trimming machines[Z]. http://www. mhmelincolnshire.com/index.htm, 2018-10-26.
[7] Air-driven broccoli floret machine[Z]. http:// charliesmachineandsupply.com/catalog/broccolifloret.shtml, 2018-10-26.
[8] 王洪明,王芳,杨铮,等. 向日葵茎秆切割阻力影响因素试验研究[J]. 中国农业大学学报,2018,23(5):102-107. Wang Hongming, Wang Fang, Yang Zheng, et al. Experimental study on influencing factors of cutting resistance of sunflower stem[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2018, 23(5): 102-107. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 杨静,李晓莲,郭楠. 啤酒花茎秆力学性能与微观结构的试验研究[J]. 农业机械,2017,42(3):93-94,96. Yang Jing, Li Xiaolian, Guo Nan. Experimental study on mechanical properties and microstructure of hops stalks[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Machinery, 2017, 42(3): 93-94, 96. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 袁巧霞,胡凌. 莲藕切割阻力影响因素试验分析[J]. 农业机械学报,2008,36(2):208-211. Yuan Qiaoxia, Hu Ling. Experimental analysis of influence factors on cutting resistance of lotus root[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2008, 36(2): 208-211. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 吴良军,杨洲,段洁利,等. 龙眼树枝修剪机具刀片切割力的影响因素试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(24):8-14. Wu Liangjun, Yang Zhou, Duan Jieli, et al. Influencing factors of cutting force of longan branch tree trimmer blade[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(24): 8-14. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 宋占华,宋华鲁,耿爱军,等. 棉花秸秆双支撑切割性能试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(16):37-45. Song Zhanhua, Song Hualu, Geng Aijun, et al. Experimental study on double-support cutting performance of cotton straw[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(16): 37-45. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 杜冬冬,王俊,裘姗姗. 甘蓝根茎部切割部位及方式优化试验研究[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(12):34-40. Du Dongdong, Wang Jun, Qiu Shanshan. Optimization of cutting position and mode for cabbage harvesting [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(12): 34-40. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 张世福,宋占华,闫银发,等. 农作物秸秆切割试验台测控系统的研制与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(增刊1):10-17. Zhang Shifu, Song Zhanhua, Yan Yinfa, et al. Development and experiment of the measure and control system for stalk cutting test bench[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(Supp.1): 10-17. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 滕绍民,王泽群,李洋,等. 切割方式与切割阻力的理论研究[J]. 农机化研究, 2009,31(5):89-90,96. Teng Shaomin, Wang Zequn, Li Yang, et al. Theoretical study on cutting method and cutting resistance[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2009, 31(5): 89-90,96
[16] 刘庆庭,区颖刚,卿上乐,等. 甘蔗茎秆切割力试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2007,33(7):90-94. Liu Qingting, Ou Yinggang, Qing Shangle, et al. The cutting force test of sugarcane stalk[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2007, 33(7): 90-94. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 靳瑞生. 玉米收获机茎秆切割刀体设计与改进[J]. 农业机械,2009,18(13):74-75. Jin Ruisheng. Design and improvement of stem cutter body for corn harvester[J]. Agricultural Machinery, 2009,18(13): 74-75. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 吴明亮,官春云,汤楚宙,等. 油菜茎秆切割力影响因素试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2009,25(6):141-144. Wu Mingliang, Guan Chunyun, Tang Chuzhou, et al. Experimental study on influencing factors of cutting power of rapeseed stalk[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2009, 25(6): 141-144. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] A. Ince; S. Uğurluay; E. Güzel; et al. Bending and shearing characteristics of sunflower stalk residue[J].Biosystems Engineering, 2005, 92(2): 175-181.
[20] Chen Ying, Jean Louis Gratton, Liu Jude. Power requirements of hemp cutting and conditioning[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2003, 87(4): 417-424.
[21] C.Igathinathane, A.R.Womac, S.Sokhansanj. Corn stalk orientation effect on mechanical cutting[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2010, 107(2) : 97-106.
[22] 闫鹏,崔红梅,赵满全,等. 9R-60型揉碎机试验台设计及单因素试验研究[J]. 农机化研究,2019,41(6):67-71. Yan Peng, Cui Hongmei, Zhao Manquan, et al. Design and single factor test study of 9 R-60 type crusher test bench[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2019, 41(6): 67-71. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 丁素明,薛新宇,蔡晨,等. 梨树枝条切割装置刀片参数优化与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(增刊2):75-82. Ding Suming, Xue Xinyu, Cai Chen, et al. Optimization and experiment of blade parameters of pear twig cutting device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(Supp.2): 75-82. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 董东营,王涛,廖宇兰,等. 木薯杆多角度切割力学特性测试仪的设计与试验[J]. 中国农机化学报,2015,36(3):59-62. Dong Dongying, Wang Tao, Liao Yulan, et al. Design and experiment of multi-angle cutting mechanical property tester for cassava rod[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Mechanization, 2015, 36(03): 59-62. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 尹秋,王涛,张喜瑞,等. 香蕉果梗切割力学特性试验[J]. 中国农机化学报,2013,34(04):75-77. Yin Qiu, Wang Tao, Zhang Xirui, et al. Experimental study on mechanical properties of banana fruit stem cutting[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Mechanization, 2013, 34(4): 75-77. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 沈成,陈巧敏,周杨,等. 苎麻单茎秆切割试验与分析[J]. 中国农机化学报,2015,36(6):40-43,63. Shen Cheng, Chen Qiaomin, Zhou Yang, et al. Test and analysis of single stem cutting of ramie[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Mechanization, 2015, 36(6): 40-43, 63. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 张园,李明福,李玉林,等. 胡椒鲜果力学性能测试与试验分析[J]. 农机化研究,2015,37(11):157-160. Zhang Yuan, Li Mingfu, Li Yulin, et al. Test and experimental analysis of mechanical properties of fresh pepper fruit[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2015, 37(11): 157-160. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 于昭洋,胡志超,杨柯,等. 大蒜联合收获切根试验台设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(22):77-85. Yu Zhaoyang, Hu Zhichao, Yang Ke, et al. Design and experiment of garlic combined harvesting root cutting test bench[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(22): 77-85. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 高国华,王天宝,周增产,等. 设施蔬菜收获切割影响因素优化试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(19):15-21. Gao Guohua, Wang Tianbao, Zhou ZengChan, et al. Optimization experiment on factors affecting harvesting and cutting of facility vegetables[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(19): 15-21. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 陈燕,蒋志林,李嘉威,等. 基于机器人采摘的柑橘果柄切割力学特性研究[J]. 河南农业科学,2017,46(4): 147-150. Chen Yan, Jiang Zhilin, Li Jiawei, et al. Study on mechanical characteristics of citrus fruit handle cutting based on robot picking[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 46(4): 147-150. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 李小强,王芬娥,郭维俊,等. 甘蓝根茎切割力影响因素分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(10):42-48. Li Xiaoqiang, Wang Fene, Guo Weijun, et al. Analysis of factors influencing cutting power of cabbage roots[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(10): 42-48. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 曹少波,李鑫,杨欣,等. 麻山药根茎力学特性测试研究[J]. 农机化研究,2018,40(4):200-205. Cao Shaobo, Li Xin, Yang Xin, et al. Study on the mechanical properties of the roots and stalks of Mashan medicine[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2018, 40(4): 200-205. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 宋占华,肖静,张世福,等. 曲柄连杆式棉秆切割试验台设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2011,42(增刊1):162-167. Song Zhanhua, Xiao Jing, Zhang Shifu, et al. Design and experiment of crank link cotton stalk cutting test bench[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2011, 42(Supp.1): 162-167. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Study on blade parameter optimization analysis of broccoli cuts based on minimum slice stress
Chen Jianneng1,2, Chen Liqun1, Yu Chennan1, Cai Shuanglei1, Xia Xudong1,2
(1.310018,; 2.310018,)
In order to explore the effect of the broccoli cutter working parameters on cutting characteristics of broccoli branch stalk as well as to optimize the working parameters of the cutting blade, the cutting tests of broccoli branch stalk were performed with electronic universal material testing machine cutting test-bed. The samples were the outer branch stalk of broccoli with same diameter. The main test equipment included the electronic universal material testing machine, blades and cutting stand, a digital camera and its image processing and analysis software ImageJ, scorpion, meter ruler, vernier caliper, protractor and marker pen. The test method and scheme were designed based on the measurement and control system of the universal material testing machine, the data measured by the pressure sensor on the universal material testing machine automatically displayed, relation curve of cutting force and time of cutting blade could be get. The maximum cutting force obtained during the cutting process was taken as the maximum cutting forceFof broccoli branch stalk. Some researchers considered that it is more reasonable to use unit cutting force as the research target. therefore, in order to eliminate the influence of the diameter difference of broccoli branch stalk on the experimental results, the maximum cutting force per unit area was taken as the target value. The influence of the cutting blade working parameters on the maximum cutting force were studied, the cutting blade working parameters include blade structure, blade angle, cutting angle and cutting position on the branch stalk. The cutting tests were grouped into the single factor tests, multi-factor orthogonal test. The testing factors were cutting position(ranging from 30-50 mm), cutting blades (cone blade、straight blade、spherical blade), blade angle (5°-17°), cutting angle (45°-90°). Multi-factor orthogonal method was a three-factor three-level testing scheme. The multi-factor orthogonal method used to optimize the working parameters of broccoli cutter. The multi-factor test results showed that the change trends of the objective values (the maximum cutting force per unit cutting area) with the changes of the testing factors were basically consistent with the results of the single factor tests. Single factor test results show that the dicing performance is best when the cutting position is 40 mm, the straight blade, the cutting angle is 60°, and the blade edge angle is 5°-10°. The results of multi-factor test showed that the position of the cutting, the structure of the blade, the blade angle and the cutting angle of the cutting tests were the primary and secondary factors that affect the cutting performance, the cutting position was 40 mm, the blade structure was spherical blade, blade edge angle was 8°and the cutting angle is 90°. According to the experimental optimization results, the broccoli cutter was designed, and the cutting test was carried out on the prototype. The cutting effect was good and the cutting success rate reached 91%, the mean value of cutting force was 18.32kPa, which is basically close to the theoretical value of 17.45kPa, it verified the rationality of tool parameter setting. The study results provided theoretical support for the development of subsequent broccoli cutting machine and cutting blade parameters.
tools; stresses; broccoli; cuts; optimization
陈建能,陈礼群,喻陈楠,蔡双雷,夏旭东. 基于最小切块应力的西兰花切块加工刀具参数优化研究[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(23):42-48.doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.23.005 http://www.tcsae.org
Chen Jianneng, Chen Liqun, Yu Chennan, Cai Shuanglei, Xia Xudong. Study on blade parameter optimization analysis of broccoli cuts based on minimum slice stress[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(23): 42-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.23.005 http://www.tcsae.org
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.23.005
S226.9
A
1002-6819(2018)-23-0042-07
2018-06-08
2018-10-17
国家自然科学基金(51675486)
陈建能,教授,博士,主要从事农业机械装备与技术方面的研究。Email:jiannengchen@zstu.edu.cn
中国农业工程学会会员:陈建能(E041200166S)
