H∞Tracking Control for Switched LPV Systems With an Application to Aero-Engines
2018-08-11KongweiZhuJunZhaoSeniorMemberIEEEandGeorgiDimirovskiSeniorMemberIEEE
Kongwei Zhu,Jun Zhao,Senior Member,IEEE,and Georgi M.Dimirovski,Senior Member,IEEE
Abstract—This paper focuses on the H∞ model reference tracking control for a switched linear parameter-varying(LPV)model representing an aero-engine.The switched LPV aeroengine model is built based on a family of linearized models.Multiple parameter-dependent Lyapunov functions technique is used to design a tracking control law for the desirable H∞tracking performance.A control synthesis condition is formulated in terms of the solvability of a matrix optimization problem.Simulation result on the aero-engine model shows the feasibility and validity of the switching tracking control scheme.
I.INTRODUCTION
AERO-engines are fairly complex multi-variable nonlinear systems with a large variation in the system dynamics.Since an accurate analytical engine model is almost impossible to be obtained,the system analysis and synthesis have to be conducted using an approximate analytical model[1].Many techniques for aero-engine control have been presented in literatures(see,[2]−[5]and the references therein).Nonlinear approaches are often hard to apply to a multi-dimensional control system.Approximate linearization techniques of nonlinear systems only ensure the performance around specific operating points,while exact input-output feedback linearization methods lack robustness.Zhao et al.proposed an approximate nonlinear engine model and a feedback linearization control strategy for local linear input-output performance[3].A widely applied nonlinear control technique is the gain scheduling[6],[7],however it has no stability or performance guarantee for off-design points[8].Linear parameter varying(LPV)control methods can provide a systematic gainscheduling method with guaranteed stability performance[8].Analysis and synthesis of LPV systems for aero-engines have been studied widely[4],[9].A model matching problem in the H∞and LPV framework is also investigated for an LPV turbofan engine model[9].Polynomial LPV synthesis and fixed-order controller scheme was discussed for reduced complexity gain-scheduled control laws for a class of aircraft turbofan engines[4].
An alternative method is switching control where a family of controllers are designed at different operating points and the system performs controller switching based on the switching logic.The applications of this strategy are stimulated by the recent development of switched systems.A switched system consists of a finite number of subsystems and a switching law which usually depends on time,states,or both that determines switching between these subsystems[10].Stability analysis and synthesis methods for switched systems have been widely studied in many literatures[11]−[16].References[11],[13]studied the stability for linear and nonlinear switched systems in lower triangular form under an arbitrary switching law.As shown in[14],multiple Lyapunov functions technique was used to deal with a hybrid nonlinear control problem of switched systems.Besides that,the average dwell-time approach was also employed to investigate the stability and stabilization of switched systems[15].The global robust stabilization problem for a class of uncertain switched nonlinear systems in lower triangular form was considered by[16]under any switching signal with dwell time specifications.
An LPV system is characterized as a smooth linear system with time-varying parameters.Modern aero-engines usually work in a large parameter variation range.Similar to the control of aircraft,the control of aero-engines is different in different parameter sub-regions[17],nevertheless these are more complicated than the control of aircrafts.The aircraft systems have been constructed as switched LPV models in some papers,such as[18],[19],therefore a single LPV model may not give sufficient approximation to nonlinear engine dynamics over the entire operating range.A reasonable and natural idea is to adopt several LPV models and corresponding controllers,each suitable for a specific parameter sub-region,and switching among them[17],such LPV systems then become switched LPV systems.The switching LPV control approach can obtain a better approximation of the nonlinear dynamics and better performance than a single LPV control method[20].Switched LPV systems have received considerable attention in the recent literatures[19],[21].A complete overview of the stability results for LPV and switched LPV systems was given in[21].Based on multiple parameter dependent Lyapunov functions,a switching LPV control technique was presented for an F-16 aircraft via controller state reset using hysteresis and average dwell time switching law in[18].Switching control for LPV systems in aero-engines is still an open and interesting issue.
On the other hand,due to the emergence of switching control in robotic systems and many other manufacturing processes,tracking control research on switched systems has received increasing attention.Based on the state-dependent switching method,sufficient conditions for the solvability of the state tracking control problem were given in[22].l1-l∞output tracking control problem was researched resorting to the average dwell time approach[23].The abovementioned results on the tracking control problem are only about general switched systems.A few results on the tracking control problem for LPV systems are also available.In[24]a model reference controller was designed using singular value decomposition to obtain the coefficient matrices.Based on poly-topic LPV models an LPV switching tracking control scheme was proposed for a flexible air-breathing hypersonic vehicle[25].However,the switching LPV tracking control results for aero-engines are not found at present.
Motivated by the above discussions,this technical note studies the problem of switching H∞tracking control for an aero-engine model via multiple parameter-dependent Lyapunov functions technique.Compared with the existing results,the main contributions of our study can be summarized as follows:1)This paper generalizes model reference H∞tracking problem to the switched LPV systems.We present a control design scheme to solve the H∞tracking control problem,and simulation result shows the effectiveness of the proposed control design method.2)The LPV model does not fully exhibit the desired levels of reliability and flexibility with dramatic parameter variations and a large flight range.In order to overcome the aforesaid problem and to improve design accuracy,we introduce a switched LPV model for an aeroengine.The parameter region is divided into several subregions and LPV controllers are designed for each parameter sub-region to satisfy specified performance criterion.
The technical note is organized as follows.Section II gives the problem formulation and preliminaries.Section III gives a tracking control design technique.In Section IV we apply the designed method to a switched LPV aero-engine model.Finally,the conclusion is given in Section V.
The notations used in this paper are fairly standard.For a matrix X,XTdenotes its transpose.He{X}is a shorthand notation of X+XT.X>0(X≥0)and X<0(X≤0)denote positive definite(positive semi-definite)and negative definite(negative semi-definite),respectively.Rn,Rn×mand Snrespectively denote sets of n-dimensional real vectors,n×mdimensional real matrices and n×n-dimensional symmetric real matrices,∗denotes an abbreviated off-diagonal block in a symmetric matrix,and diag{X1,...,Xk}denotes a blockdiagonal matrix composed of X1,...,Xk.
II.PROBLEM FORMULATION AND PRELIMINARIES
In this section,the problem will be formulated,and some preliminaries about the switched LPV systems will be given.
A.Problem Formulation
Consider the following switched LPV system:
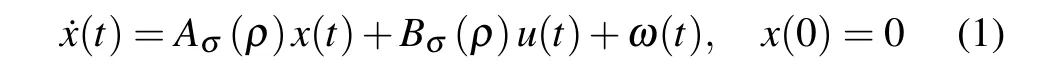
where x(t)∈Rn,u(t)∈Rnu,andω(t)∈Rnωare the state,the control input,and the disturbance input,respectively.
Suppose that the parameterρis in a compact set P⊂Rswith its parameter variation rate bounded by≤,k=1,2,...,s.The set P is partitioned into a finite number of closed subsets{Pi}i∈ZNby means of a family of switching surfaces SSSij(i,j∈ZN■),the adjacent parameter subsets are overlapped and P=Pi,where ZN={1,2,...,N}is the index set.The switching signal is defined asσ:R+=[0,∞)→ZNwhich is assumed to be a piecewise continuous(from the right)function depending on time or the parameter.The switching sequence is∑={x;(i0,t0),(i1,t1),...,(ij,tj),...|ij∈ZN,j=0,1,...}.σ(t)=i means the ith subsystem is activated at time instant t.The system matrices Ai(ρ),Bi(ρ),Ci(ρ)are of appropriate dimensions and all of the state-space data are continuous functions of the parameterρ.The parameterρ is exogenous variable and independent of the state x.
The reference state xr(t)is given by the reference model
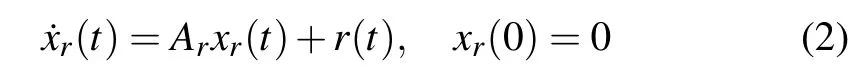
where xr(t)∈Rnris the reference state,r(t)∈Rnris the bounded reference input,Aris known Hurwitz matrix with compatible dimensions.
Remark 1:The reference signal can also be given by a parameter-dependent model.For this case we can replace(2)by˙xr(t)=A(ρ)rxr(t)+r(t),the designed process for the parameter-dependent model is similar to the model(2).Without loss of generality,we consider the reference model as(2).
Combining the system(1)with the system(2),one can get the augmented system
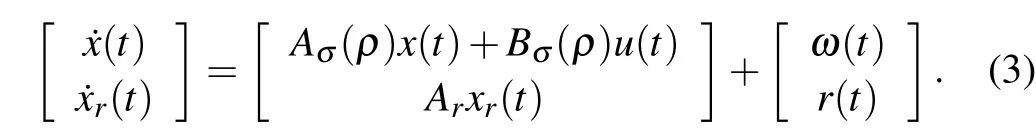
Give the following performance index:
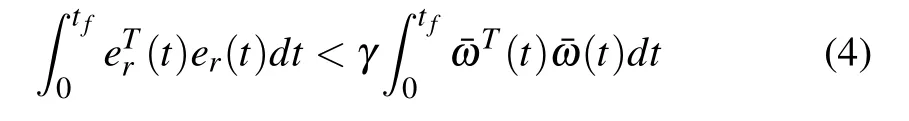
where er(t)=x(t)−xr(t)denotes the state error,tfis the control termination time,¯ω(t)=(ωT(t),rT(t))T,γ>0 is the disturbance attenuation level.
The H∞tracking control performance of the switched system(3)can be stated as follows:
1)the system(3)is asymptotically stable,when the¯ω(t)=0;
2)under the zero-initial condition,the inequality(4)holds for all¯ω(t)/=0,whereγis a constant number.
Our objective is to design both controller u(t)and a switching lawσto enforce x(t)of the system(1)to track the reference state xr(t)of the system(2).
B.Preliminaries
The following assumptions are adopted which are useful in our later development.
Assumption 1[17]:The matrix function triple(Ai(ρ),Bi(ρ),Ci(ρ))is parameter-dependent stabilizable and detectable for the parameterρ.
Assumption 2[12]:The switching signalσhas finite number of switchings occurring in any finite time interval.The subsystems and controllers are synchronously switching.
Lemma 1[26]:Let D,E be real matrices of appropriate dimensions with‖F‖≤1.Then for any scalarγ>0,the following inequality holds
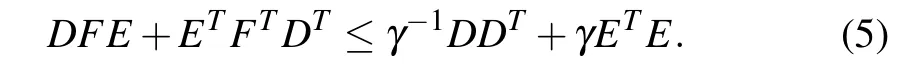
III.MAIN RESULTS
In this section,we will design the state feedback parameter dependent controller and a switching lawσ(t)to solve the H∞tracking control problem via multiple Lyapunov functions approach.
The state feedback controller is given as
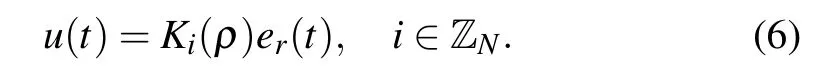
From augmented system(3)with controller(6)we have the following closed-loop system:
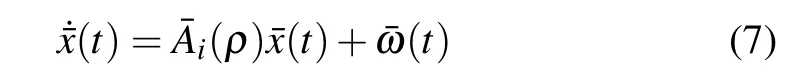
where

Now we deal with the issue of parameter-dependent switching lawσ(t)to achieve H∞tracking performance with the help of parameter-dependent state feedback controller given in(6).
Firstly,we choose multiple parameter-dependent Lyapunov function candidate for the system(1)with the system(2)as
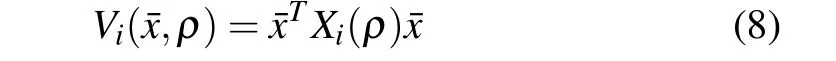
where Xi(ρ)> 0,i∈ ZN.
Hysteresis Switching Law:As previously mentioned,the set P is partitioned into number of subsets{Pi}i∈ZNby SSSij(i,j∈ZN).Suppose that SSSijdenotes the trajectory ofρmoving unidirectional from subset Pito Pj,and it is contrary to the switching surface SSSji.The switching signalσis described as When t=0, σ(0)=i, ifρ(0)∈Pi

For the switched closed-loop system(7),if on the switching surfacesij,the matrix Xi(ρ)of(8)is satisfying:Xi(ρ) ≥Xj(ρ),we have the Lyapunov function of(8)is non-increasing when switching from Pito Pj.For the switching surface SSSji,we have a similar result when switching from Pjto Pi,where i,j∈ZN.
Remark 2:The parameter subsets are partitioned by switching surfaces and the switching law is parameter-dependent in[17].In[27],[28]the switching law is not parameter dependent but rather is mode-dependent for dealing with the switching LPV control problem.In this paper,we studied the tracking problem for aero-engines,considering the character of practical problem,we choose the parameter-dependent switching law.
Remark 3:For the switching surface SSSij,when the partition way for P is decided,the specific valueρcorresponding to SSijis given such asρ∗.The matrix inequality Xi(ρ)≥Xj(ρ)holds only on the surface SSSijthat isρ=ρ∗.
For the closed-loop switched LPV system(7),we state the synthesis condition of switching LPV control in the following theorem.
Theorem 1:Consider the augmented closed-loop system(7)with the parameter set P and its overlapped covering{Pi}i∈ZN.If there exist positive definite matrix functions Xi(ρ):Rs→ S2n,and matrix functions Ki(ρ):Rs→ Rn×m,such that for∀ρ∈Pi,
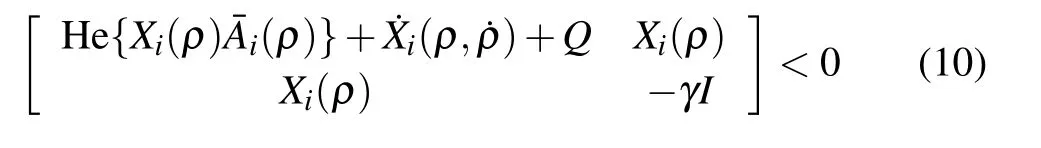
and

Proof:For the multiple parameter-dependent Lyapunov functions candidate(8),computing time derivative along the state variables trajectory of the system(7),we have

The matrix inequality(10)implies
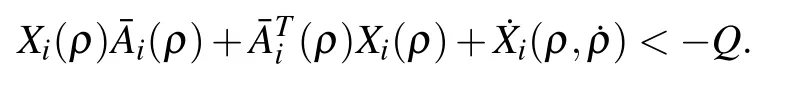
Because Q≥0,that is

Now we show the performance index(4)under the zero initial condition with(t)/=0.
From(12),applying Lemma 1,we have
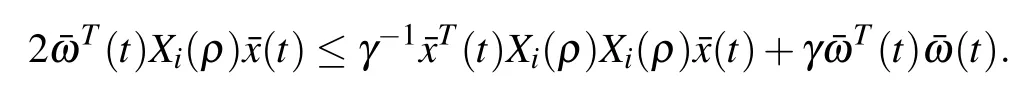
Then,
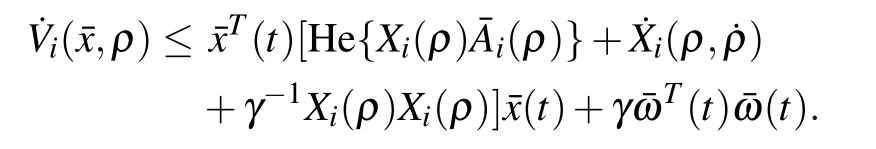
From the inequality(10)and with Schur complement,we have
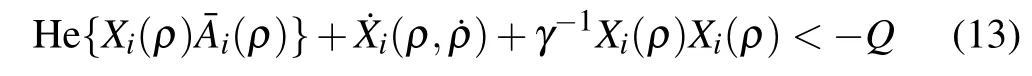
that is
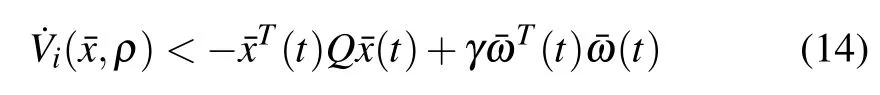
since

it follows from(14)that
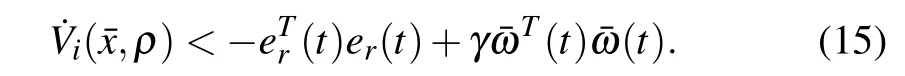
Integrating both sides of(15)from zero to tfwe get
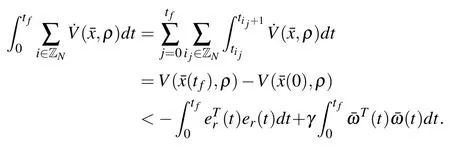
According to the zero initial condition and V((t),ρ)>0,it is easy to derive
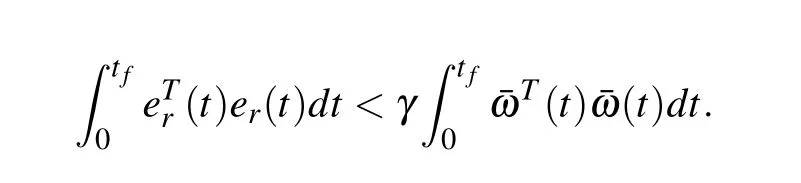
Therefore,under the switching law(9),the H∞tracking controller(6)solves the H∞tracking control problem for the switched LPV system(1). ■
Remark 4:The appearance of matrix Q in the inequality(10)is because of the er(t).To show the relation between er(t)and the states x(t),xr(t),we just rewrite eTr(t)er(t)into a compact form using matrix Q=[I,−I;−I,I]and connect them together,then we introduce er(t)into the inequality(10).
Since the matrix inequalities condition(10)of Theorem 1 are non-convex in Ki(ρ)and parameter matrix variable Xi(ρ),we convert these conditions into solvable linear matrix inequalities(LMIs).
Theorem 2:Consider the system(7)with the parameter set P and its overlapped covering{Pi}i∈ZN.If there exist positive definite matrix functions Yi(ρ):Rs→ Sn,matrix functions Wi(ρ):Rs→Rn×mand a constantγ> 0,such that for anyρ∈Pi,the following LMI holds

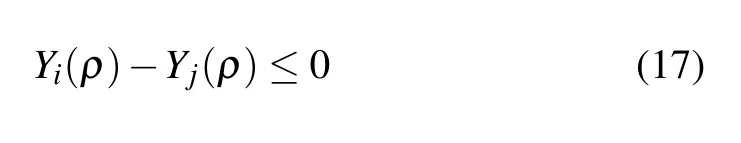
where

Then,under the switching law(9),the controller(6)with controller gain given bysolves the H∞tracking control problem for the system(1).

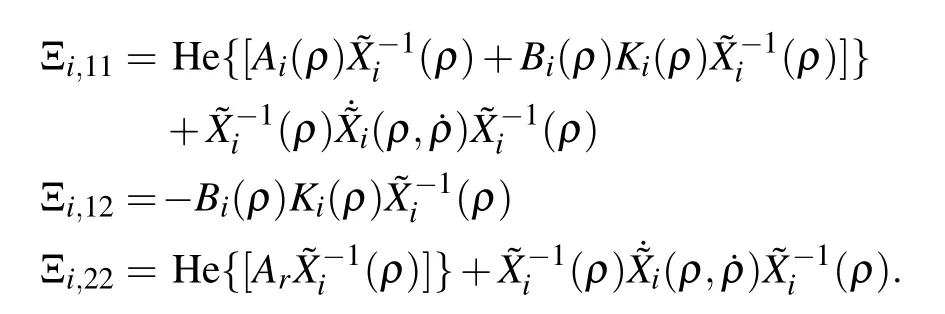
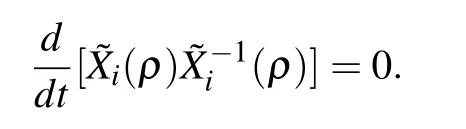
Then,we have
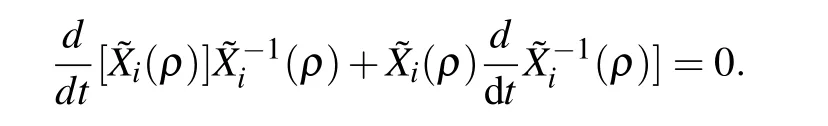
Finally we can obtain


With Schur complement,
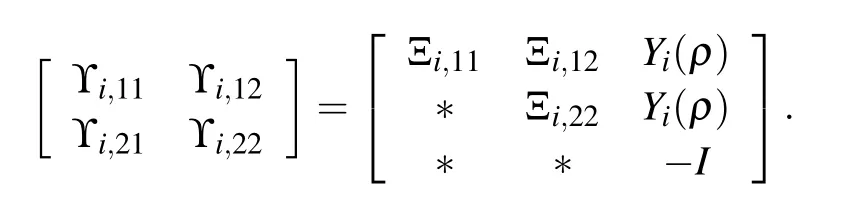
Defining Wi(ρ)=Ki(ρ)Yi(ρ)and using Schur complement,we have solved LMIs(16).For anyρ∈the switching condition(11)is equivalent to
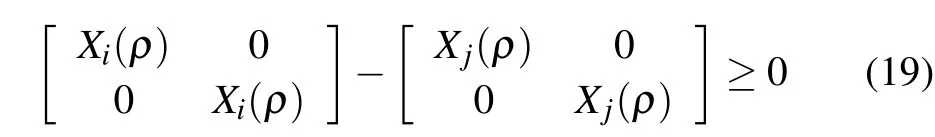

consequently,the matrix inequality(17)can be obtained.■
Remark 5:The diagonal structure of Xi(ρ)may bring about some conservativeness,but based on this form we can give the solvable parameter-dependent LMIs.For this kind of LMIs,we cannot directly solve them.By forming a grid method for parameter values,we can approximately convert(16)and(17)to a finite collection of solvable LMIs.Then the continuous matrix function(6)can be formed by interpolation[8].
IV.SIMULATION EXAMPLE
We will apply the designed method to a turbofan engine model to show the effectiveness of the designed scheme.
A.The Switched LPV Model of Aero-Engines
The turbofan engine model is corresponding to a large,high bypass ratio two-spool turbofan engine similar to the GE90.It is based on the data from GE-90K engine of commercial modular aero-propulsion system simulation(CMAPSS)[29].The input is WF(fuel flow rate),the states are Nf(fan speed)and Nc(core speed).The altitude means the distance of the engine from the sea-level,the Mach number means the number determining the relative speed between the air flow and the aero-engine divided by the sound velocity.
A switched LPV model is established with the method of curve- fitting and small deviation linearization.A turbofan model is modeled by two different scheduling parameter sets as a switched LPV system.The turbofan engine model data is from[29].The altitude and the fan speed are normalized by 10000 and 3000,respectively.Then according to the curveiftting method,based on a family of local linearized models,a switched LPV model of turbofan engine is given as
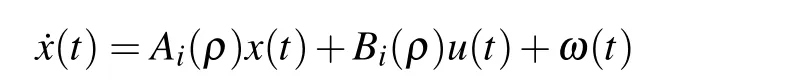
where x(t)=[∆Nf,∆Nc]T,u(t)= ∆WF. ∆Nf=Nf−Nfeis the fan speed increment,∆Nc=Nc−Nceis the core speed increment and∆WF=WF−WFeis the fuel flow rate increment,respectively.Here Nfe=2324/3000 and Nce=8719/3000.ω(t)is given by the health parameter input which can represent the disturbances or the effects of engine components aging[29].
For simplicity we only consider the Mach number as the gain scheduling parameter and let the altitude as 0.The variation range of the parameterρis[0.20,0.9].To divide the parameter P into two sub-regions of P1=[0.20,0.65]and P2=[0.55,0.9],where P1■P2=P and the overlapping region is[0.55,0.65].Here,we can divide the parameter set into smaller intervals and establish more subsystems for aeroengine to get better accuracy.Without loss of generality,we partition the parameter set into two subsets.Ai(ρ),Bi(ρ),i=1,2 are parameterized inρby means of curve fitting,which are given as
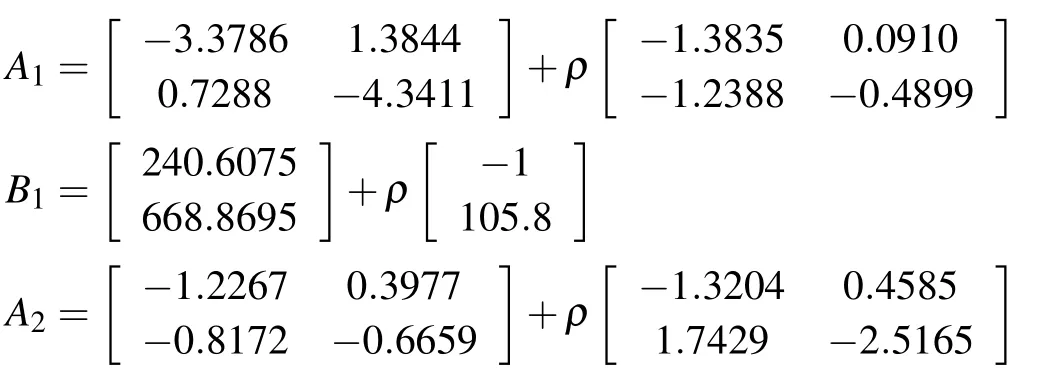

The reference model is given as
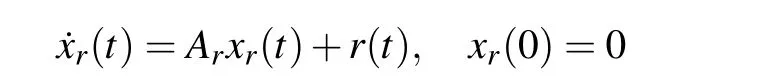
where xr(t)=[∆Nf,∆Nc]T,and the state space data of Aris
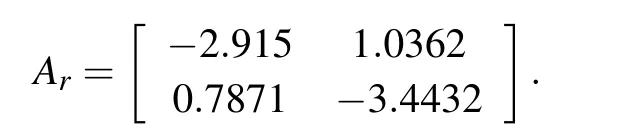
B.H∞Model Reference Tracking Control Problem of the Switched LPV Model
We conduct simulation for the turbofan engine model with a varying parameter.The time-varying Mach number trajectory is shown in Fig.1.Choosing disturbanceω(t)=[e−2t,e−2t]Tand the reference input r(t)=[0.01sin(0.01t),0.01sin(0.01t)]T.In addition,the initial value of the switched LPV system(1)is assumed to be x(t0)=[∆Nf,∆Nc]T=[0.2,0.25]T.
To solve the optimization problem(16)and(17)in Theorem 2,we obtain
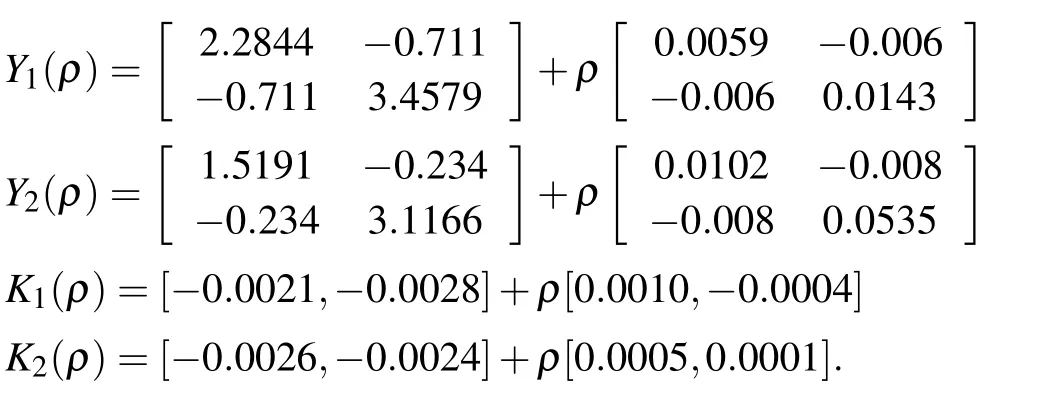
According to Theorem 2,we solve the H∞tracking control optimization problem for the switched system(1),and the H∞disturbance attenuation index isγ=0.4672 over the entire parameter set.Compared with the method of[9]for single LPV model,we getγ=0.4810.The switched LPV H∞tracking scheme has a smaller disturbance attenuation level and a better performance than general LPV control method.
The H∞tracking control problem for the switched system(1)is solved.The switching signal is shown in Fig.2.The tracking control error is depicted in Fig.3.The fan speed increment and fuel flow increment are shown in Figs.4 and 5,respectively.The simulation result shows the effectiveness of the designed scheme.
V.CONCLUSION
In this paper,we have studied the H∞model reference tracking control problem for the switched LPV systems.A switched LPV turbofan engine model for different parameter regions has been constructed from a family of linearized engine models.Sufficient conditions have been developed to guarantee the H∞model tracking performance using the multiple parameter dependent Lyapunov functions method.The desired tracking controller gain has been obtained by a set of LMIs.The tracking control under a hysteresis switching law was applied to the obtained switched LPV engine model,and promising simulation result is obtained.
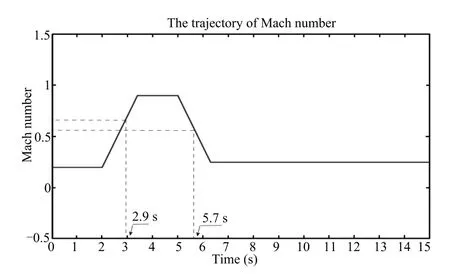
Fig.1.The gain scheduling parameter.

Fig.2. The switching signal.

Fig.3.The tracking control error.
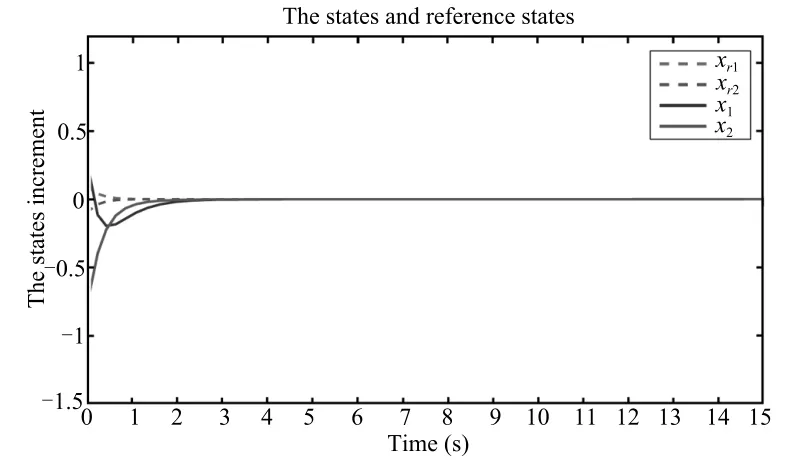
Fig.4. The fan speed increment.

Fig.5. The fuel flow increment.
杂志排行
IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica的其它文章
- Advances in Vision-Based Lane Detection:Algorithms,Integration,Assessment,and Perspectives on ACP-Based Parallel Vision
- Deep Scalogram Representations for Acoustic Scene Classification
- A Mode-Switching Motion Control System for Reactive Interaction and Surface Following Using Industrial Robots
- Adaptive Proportional-Derivative Sliding Mode Control Law With Improved Transient Performance for Underactuated Overhead Crane Systems
- On“Over-sized"High-Gain Practical Observers for Nonlienear Systems
- Neural-Network-Based Terminal Sliding Mode Control for Frequency Stabilization of Renewable Power Systems
