高效液相色谱法与常见免疫法监测环孢素血药浓度效果比较的系统评价Δ
2018-04-17蒋志美张伶俐杨春松
蒋志美,张伶俐,罗 婷,詹 琳,陈 卓,刘 丹,杨春松
(1.四川大学华西第二医院药学部,四川 成都 610041; 2.四川大学华西第二医院循证药学中心,四川 成都 610041; 3.出生缺陷与相关妇儿疾病教育部重点实验室,四川 成都 610041; 4.四川大学华西第二医院药物临床试验机构,四川 成都 610041)
环孢素(cyclosporin A,CsA)是从真菌代谢物中提取分离而得到的一种亲脂性环状多肽,为强效免疫抑制剂,被广泛用于减轻或防止肝、肾及骨髓等器官移植的排斥反应和治疗其他自身免疫性疾病。但其口服吸收不完全,存在明显的肠肝循环和个体差异,治疗窗较窄[1];且其血药浓度受药物相互作用、胃肠功能、红细胞含量、性别、年龄、食物及术后时间等因素的影响[2-3]。CsA血药浓度过高容易引起肝肾及中枢神经系统毒性,其血药浓度过低则易引起排斥反应或诱发自身免疫性疾病[4]。因此,临床需定期监测CsA血药浓度,以提高疗效、减少不良反应。目前,CsA血药浓度监测的方法主要有色谱法和免疫法,前者主要为高效液相色谱法(high performance liquid chromatography,HPLC),后者包括放射免疫法(radioimmunoassay,RIA)、荧光偏振免疫法(fluorescent polarization immunoassay,FPIA)、酶放大免疫分析法(enzyme multiplied immunoassay technique,EMIT)、微粒子酶联免疫分析法、化学发光微粒子免疫分析法、抗体修饰的磁性免疫分析法和克隆酶供体免疫分析法(cloned enzyme donor immunoassay,CEDIA)等[5-8]。由于HPLC测定周期较长、前处理复杂,因此,临床批量检测时,免疫法已成为首选方法。但免疫法也存在一定的局限性,由于与代谢物及异嗜性抗体的交叉反应,其测定值一般比色谱法偏高。近年来,有关HPLC和免疫法比较的研究较多,但结论不统一,现系统评价HPLC与免疫法分别监测CsA血药浓度的效果,为CsA血药浓度监测提供可靠方法。
1 资料与方法
1.1 纳入与排除标准
1.1.1研究类型:有关HPLC与免疫法监测CsA血药浓度相关性的二次研究、队列研究、基础研究及综述;。
1.1.2研究对象:术后使用CsA且进行CsA血药浓度监测的肝、肾、心及骨髓等器官移植患者。
1.1.3干预措施:观察组采用HPLC监测CsA血药浓度,对照组则采用免疫法。
1.1.4结局指标:HPLC与免疫法的方法学指标,包括线性范围,日内、日间精密度,提取回收率,最低定量限及所需血样体积;HPLC与免疫法相关性方程及相关系数;HPLC与免疫法测定值的差异。
1.1.5排除标准:CsA用于器官移植以外其他用途的研究;非中英文文献。
1.2 文献检索策略
计算机检索PubMed、EMbase、the Cochrane Library、中国生物医学文献数据库、中国知网、维普数据库和万方数据库,收集HPLC与免疫法监测CsA血药浓度的相关文献。中文检索词包括“环孢素”“治疗药物监测”;英文检索词包括“cyclosporin A”“therapeutic drug monitoring”;检索时限均为建库至2017年4月。同时,检索各免疫法试剂盒的说明书。
1.3 资料提取
由2名研究者独立提取资料,交叉核对结果。提取内容主要包括:纳入文献基本信息,如作者、发表时间、研究设计类型、样本量、样本来源及样本类型等;研究对象类型;干预措施;结局指标。
2 结果
2.1 纳入文献的基本特征
初步检索出相关文献3 033篇,根据纳入与排除标准,最终纳入22篇[5,9-29],皆为基础研究,其基本特征见表1。
2.2 HPLC与免疫法的方法学比较
10篇 文献[5,11,16,21-25,27,29]报告了HPLC与免疫法的比较,其中5篇[11,22-25]比较了HPLC与FPIA,4篇[5,24,27,29]比较了HPLC与RIA,2篇[11,21]比较了HPLC与CEDIA,1篇[11]比较了HPLC与EMIT。结果显示,HPLC所需样本体积大于FPIA、RIA、CEDIA及EMIT;HPLC线性范围比FPIA宽,比CEDIA、EMIT窄;HPLC最低定量限低于FPIA、RIA、CEDIA及EMIT,见表2—4。

表1 纳入文献的基本特征Tab 1 Basic information of involved studies
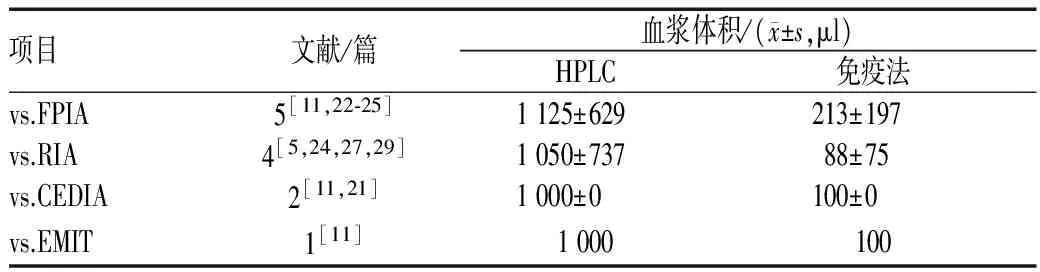
表2 HPLC与FPIA、RIA、CEDIA及EMIT所需血浆样本体积比较Tab 2 Comparison of required plasma volumes between HPLC and FPIA, RIA, CEDIA, EMIT
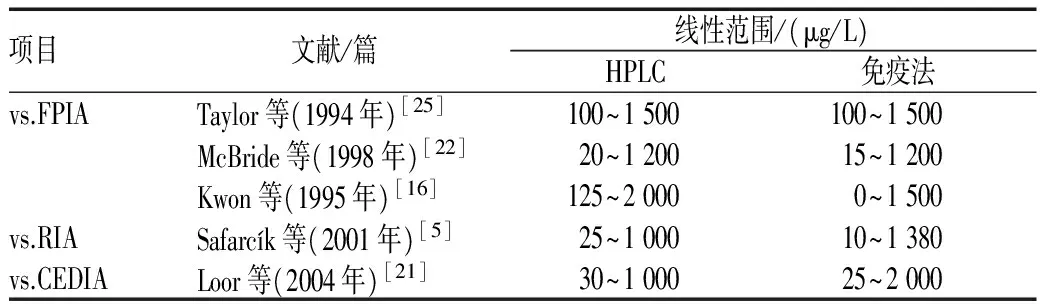
表3 HPLC与FPIA、RIA及CEDIA的线性范围比较Tab 3 Comparison of linearity ranges between HPLC and FPIA, RIA, CEDIA
2.3 HPLC与免疫法的CsA血药浓度测定值的相关性
14篇文献[5,9,11,13,16,18-22,26-29]报告了HPLC与免疫法的相关性,其中7篇[11,13,16,19,22,26,28]报告了HPLC与FPIA的相关性,5篇[5,18,20,27,29]报告了HPLC与RIA的相关性,3篇[11,21,26]报告了HPLC与CEDIA的相关性,4篇[9,11,13,26]报告了HPLC与EMIT的相关性。结果显示,HPLC与FPIA、RIA、CEDIA及EMIT的相关性方程和相关系数分别为CFPIA=1.54CHPLC+2.31(r=0.941)、CRIA=1.26CHPLC+55.92(r=0.908)、CCEDIA=1.19CHPLC-12.10(r=0.961)及CEMIT=1.04CHPLC+16.10(r=0.936),表明HPLC与FPIA、RIA、CEDIA及EMIT的相关性较强(r>0.9),见表5。

表4 HPLC与FPIA、RIA、CEDIA及EMIT的最低定量限比较Tab 4 Comparison of lowest limit of quantification between HPLC and FPIA, RIA, CEDIA, EMIT

表5 HPLC与FPIA、RIA、CEDIA及EMIT的相关性Tab 5 Correlation between HPLC and FPIA, RIA, CEDIA, EMIT
2.4 HPLC与免疫法的CsA血药浓度测定值的差异
16篇[5,10-15,17-19,22,24-28]文献报告了HPLC与免疫法的CsA血药浓度测定值的差异,其中10篇[11,13-14,17,19,22,24-26,28]报告了HPLC与FPIA的差异,9篇[5,10,12,15,17-19,24,27]报告了HPLC与RIA的差异,2篇[11,26]报告了HPLC与CEDIA的差异,3篇[11,13,26]报告了HPLC与EMIT的差异。结果显示,FPIA、RIA、CEDIA及EMIT的CsA血药浓度测定值分别比HPLC高(44.14±38.95)%、(50.91±72.05)%、(15.40±4.90)%及(14.28±5.74)%,CsA血药浓度测定值由高至低依次为RIA>FPIA>CEDIA>EMIT>HPLC,见表6—7。本研究表明HPLC与FPIA、RIA的CsA血药浓度测定值的差异与样本来源有关,对各方法不同样本来源CsA血药浓度测定值比较的结果显示,CsA血药浓度测定值差异由高至低依次为心移植>肾移植>肝移植,见表8。

表6 HPLC与FPIA、RIA、CEDIA及EMIT的CsA血药浓度测定值的差异Tab 6 Differences of determined values between HPLC and FPIA, RIA, CEDIA, EMIT

表7 HPLC与FPIA、RIA、CEDIA及EMIT的CsA血药浓度测定值的差异度Tab 7 Diversity factors of determined values of CsA plasma concentrations between HPLC and FPIA, RIA, CEDIA, EMIT
续表7

项目文献试剂盒种类样本来源[(C免疫法-CHPLC)/CHPLC]/%平均值SDVemlllet等(1989年)[27]SandozpolyclonalSandimmunekit骨髓移植者300心移植者200肝移植者-400Safarcík等(2001年)[5]Cyclo⁃Trac肾移植者800Lensmeyer等(1985年)[18]未提及未提及1141911843Klíma等(1987年)[15]SandozpolyclonalSandimmunekit心移植者27865Hirvisalo等(1990年)[12]SandozmonoclonalSandimmunekit心移植者5000肝移植者2000肾移植者3000骨髓移植者3000骨髓移植儿童2000肾移植儿童1000Grundmann等(2010年)[10]Cyclo⁃Trac肾移植者4063Lindholm等(1992年)[19]未提及肾移植者700vs.CEDIAHamwi等(1999年)[11]未提及肾移植者14101540490骨髓移植者2220心⁃肺移植者1340肝移植者930Steimer(1999年)[26]未提及肾移植者1800vs.EMITHamwi等(1999年)[11]未提及肾移植者18801428574骨髓移植者1150心⁃肺移植者1520肝移植者2460Steimer(1999年)[26]EMIT⁃MeOH肾移植者900EMIT⁃NPT1200Jebabli等(2007年)[13]未提及未提及888

表8 HPLC与FPIA、RIA、CEDIA及EMIT测定不同来源样本CsA血药浓度差异度的比较Tab 8 Comparison of diversity factors of CsA plasma concentrations in different sources between HPLC and FPIA, RIA, CEDIA, EMIT
3 讨论
本研究结果显示,CsA血药浓度因检测方法不同所得结果存在很大差别,HPLC的测定值比其他4种免疫法低。这是由于免疫法测定的CsA血药浓度除CsA原型药浓度外,还包括代谢产物的浓度、其他药物浓度及内源性杂质的浓度等,即免疫法存在严重的交叉反应。检索各试剂盒的说明书,FPIA、RIA、CEDIA及EMIT的交叉反应率见表9。而HPLC能排除各种干扰因素,其所测定的CsA浓度为原型药的浓度。本研究结果表明,FPIA、RIA、CEDIA及EMIT等4种免疫法的测定值与HPLC的相关性较强,可将上述4种免疫法的测定值统一转化为HPLC的测定值,有助于临床医师分析CsA血药浓度监测结果,以便准确调整患者用药方案。此外,进行CsA血药浓度监测时,建议尽量选择同一家医院的同一种仪器,以保证结果的可比性。
本研究结果还显示,HPLC与FPIA、RIA、CEDIA及EMIT的CsA血药浓度测定值的差异与样本来源有关,主要原因可能是移植患者类型影响了CsA的代谢程度。CsA主要经肝脏代谢,不同移植类型的患者,肝脏代谢能力不同,CsA的代谢产物种类及比例不同,对各免疫法测定值的干扰程度不同,因此导致HPLC与各免疫法测定值的差异不同。HPLC所需样本体积远大于4种免疫法,因此,建议采用免疫法对儿童患者进行CsA治疗药物监测,以减少对患儿的损伤,增加患儿顺应性,更符合医学伦理。HPLC的线性范围比FPIA宽,比CEDIA、EMIT法窄,且其最低定量限低于FPIA、RIA、CEDIA及EMIT,但相差不大,均可满足日常CsA的治疗药物监测。

表9 FPIA、RIA、EMIT及CEDIA的CsA代谢物交叉反应率(%)Tab 9 Cross-reactivity rates of metabolin between FPIA, RIA, CEDIA and EMIT(%)
本研究存在一定的不足,一是纳入的绝大多数文献只描述了HPLC与免疫法的CsA血药浓度测定值的差异,但未进行统计学分析,无法得知差异是否有统计学意义;二是只检索到HPLC与FPIA、RIA、CEDIA及EMIT等4种免疫法的比较,未检索到HPLC与其他免疫法的比较;三是有关HPLC与免疫法方法学比较的文献数量较少,且比较的方法学指标不全,无法对这两类技术进行全面比较;四是本研究未检索到HPLC和免疫法检测成本、检测效率的比较文献,无法评价HPLC与免疫法的经济性。
[1]Potter JM.Pharmacoeconomics of therapeutic drug monitoring in transplantation[J].Ther Drug Monit,2000,22(1):36-39.
[2]Gupta SK,Manfro RC,Tomlanovich SG,et al.Effect of food on the pharmacokinetics of cyclosporine in health subjects following oral and intravenous administration[J].J Clin Pharmacol,1990,30(7):643-653.
[3]孙成春,郝俊文,王景祥,等.环孢素A血药浓度的影响因素探讨[J].中国药房,1998,9(6):272-273.
[4]郑军华,闵志廉,朱有华,等.肾移植患者长期服用环孢素A后发生肝毒性的临床研究[J].中华器官移植杂志,2001,22(4):250.
[5]Safarcík K,Brozmanová H,Bartos V,et al.Evaluation and com-parison of therapeutic monitoring ofwhole-blood levels of cyclosporin A and its metabolites in renaltransplantation by HPLC and RIA methods[J].Clin Chim Acta,2001,310(2):165-171.
[6]Baldelli S,Zenoni S,Merlini S,et al.Simultaneous determination of everolimus and cyclosporine concentrations by HPLC withultraviolet detection[J].Clin Chim Acta,2006,364(1-2):54-58.
[7]Andrews DJ,Cramb R.Cyclosporin: revisions in monitoring guide-lines and review of current analytical methods[J].Ann Clin Biochem,2002,39(Pt 5):424-435.
[8]Wallemacq PE.Therapeutic monitoring ofimmunosuppressant drugs.Where are we?[J].Clin Chern Lab Med,2004,42(11):1204-1211.
[9]Dias VC,LeGatt DF,Yatscoff RW.The EMIT cyclosporine assay:development of application protocols for the boehringer Mannheim hitachi 911 and 917 analyzers[J].Clin Biochem,1997,30(2):155-162.
[10]Grundmann M,Perinova I,Brozmanova H,et al.Significant discr-epancy in cyclosporin A post-dose concentrations when analyzed with specific RIA and HPLC method[J].Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther,2010,48(2):87-92.
[11]Hamwi A,Veitl M,Männer G,et al.Evaluation of four automated methods for determination of whole blood cyclosporine concentrations[J].Am J Clin Pathol,1999,112(3):358-365.
[12]Hirvisalo EL,Kivistö KT,Neuvonen PJ.Therapeutic cyclosporine monitoring: comparison of radioimmunoassay and high-performance liquid chromatography methods in organ transplant recipients[J].Ther Drug Monit,1990,12(4):353-358.
[13]Jebabli N,Klouz A,Bahlous A,et al.Comparison of three methods for cyclosporine therapeutic monitoring[J].Transplant Proc,2007,39(8):2557-2559.
[14]Kaplan B,Wang Z,Keilani T,et al.The specificity of monoclonal fluorescence polarization immunoassay for cyclosporine in recipients of simultaneous pancreas-kindeny transplants[J].Ther Drug Monit,1995,17(5):499-503.
[15]Klíma J,Petrásek R,Kocandrle V.Simple and specific isocratic liquid chromatographic procedure for cyclosporine A determination in whole blood,compared with radioimmunoassay[J].J Chromatogr,1987,385:357-361.
[16]Kwon K,Kim MH,Park JW,et al.Pharmcokinetics of two cyclos-porine formulations using FPIA and HPLC assay in volunteers[J].Arch Pharm Res,1995,18(6):385-390.
[17]LeGatt DF,Coates JE,Simpson AI,et al.A comparison of cyclo-sporine assays using sequential samples from selected transplant patients[J].Clin Biochem,1994,27(1):43-48.
[18]Lensmeyer GL,Fields BL.Improved liquid-chromatographic deter-mination of cyclosporine,with concomitant detetion of a cell-bound metabolite[J].Clin Chem,1985,31(2):196-201.
[19]Lindholm A,Napoli K,Rutzky L,et al.Specific monoclonal radio-immunoassay and fluorescence polarization immunoassay for through concentration and area-under-the-curve monitoring of cyclosporine in renal transplantation[J].Ther Drug Monit,1992,14(4):292-300.
[20]Loo JCK,Gallicano KD,McGilveray IJ,et al.Monitoring of blood levels of cyclosporine in renal and cardiac transplant recipients-comparison of HPLC to Incstar CYCLO-Trac SP RIA[J].Clin Biochem,1991,24(1):49-53.
[21]Loor R,Pope L,Boyd R,et al.Monitoring cyclosporine of pre-dose and post-dose samples using nonextraction homogeneous immunoa-ssay[J].Ther Drug Monit,2004,26(1):58-67.
[22]McBride JH,Kim S,Rodgerson DO,et al.Conversion of cardiac and liver transplant recipients from HPLC and FPIA(polyclonal)to an FPIA(monoclonal)technique for measurement of blood cyclosporine A[J].J Clin Lab Anal,1998,12(6):337-342.
[23]Regazzi MB,Rondanelli R,Gastaldi L,et al.Optimization of sam-pling time for cyclosporine monitoring in transplant patients[J].J Clin Pharmacol,1992,32(11):978-981.
[24]Schroeder TJ,Brunson ME,Pesce AJ,et al.A comparison of the cli-nical utility of the radioimmunoassay,high-performance liquid chro-matography,and TDx cyclosporine assays in outpatient renal transplant recipients[J].Transplantation,1989,47(2):262-266.
[25]Taylor PJ,Salm P,Norris RL,et al.Comparison of high-performance liquid chromatography and monoclonal fluorescence polarization im-munoassay for the determination of whole-blood cyclosporin A in liver and heart transplant patients[J].Ther Drug Monit,1994,16(5):526-530.
[26]Steimer W.Performance and specificity of monoclonal immunoassays for cyclosporine monitoring: how specific is specific?[J].Clin Chem,1999,45(3):371-381.
[27]Vemillet L,Keller HP,Le Bigot JF,et al.Determination of cyclo-sporine in plasma:specific radioimmunoassay with a monoclonal ant-ibody and liquid chromatography compared[J].Clin Chem,1989,35(4):608-611.
[28]Winkler M,Schumann G,Petersen D,et al.Monoclonal fluorescence polarization immunoassay evaluated for monitoring cyclosporine in whole blood after kidney,heart,and liver transplantation[J].Clin Chem,1992,38(1):123-126.
[29]Wolf BA,Daft MC,Koenig JW,et al.Measurement of cyclosporine concentrations in whole blood: HPLC and radioimmunoassay with a specific monoclonal antibody and 3H- or 125I-labeled ligand com-pared[J].Clin Chem,1989,35(1):120-124.
