基于3种方法对河道底泥重金属污染评价
2018-04-14高阳俊
舒 伟,陈, 高阳俊
(1.上海环科环境认证有限公司,上海200233;2.荷兰瓦格宁根大学,荷兰瓦格宁根6700AA;3.上海市环境科学研究院,上海200233)
0 引言
近年来,随着社会和经济的发展,生活和生产中的污染物产生量逐年增加,大量未经处理的污染物直接排入河道中,大多数重金属等污染物在河道中沉积,被河道底泥吸附和积累,进而被鱼类吸收或贝类体表吸附,进入食物链,从而造成公害[1]。另外,当化学、动力等外部条件发生变化时,底泥中的重金属会被重新释放出来,可能会造成水体的二次污染,引起更多环境问题[2]。
重金属原是指密度大于5 g/cm3的金属,但从环境污染角度来说,重金属主要是指汞、镉、铅及砷(类金属)等生物毒性显著的金属[3]。这些重金属在水中不能被溶解,且能与水中的其他有害物质结合生成毒性更大的有机物。当人体直接或间接地摄取重金属元素且在人体中累积到一定程度,就会造成人体的慢性中毒。例如,日本发生的水俣病(汞污染)和骨痛病(镉污染)等公害病,都是由重金属污染引起的[4]。
根据国家环保部公布的2015年中国环境状况公报[5],我国的水污染情况依旧处于比较严峻的形势。水体的严重污染势必密切关联河道底泥的污染状况,但目前尚未开展全国统一的河道底泥重金属污染调查,对于各大中小河道底泥重金属污染的现状尚不清楚。因此,本文查阅了大量已经发表的有关河道底泥重金属含量的国内外文献,通过对各重金属的研究频次、含量分析、污染评估,以期能对河道底泥的重金属污染现状有详细了解,同时也为科学合理评估重金属污染提供依据。
1 河道底泥重金属污染的现状
本文查阅了97篇国内外对于河道底泥重金属研究的文献,并对这97篇的研究数据进行了整体分析。得到了现阶段国内外对河道底泥重金属研究的情况以及国内外河道底泥重金属污染的现状。
1.1 河道底泥重金属研究频次
在97篇文献中,国内外文献各占50%,共对14种重金属进行了研究,本文对河道底泥重金属的研究频次进行了统计,得到表1、图1和图2。
从中可以看出,研究最频繁的依次是Cu、Pb、Zn,研究频率均达到90%以上。研究频次最低的是Ti、Sr、Sn、V,研究频率均在6%以下,且仅在国外的研究中出现。国内研究最多的Cr、Cu、Pb、Zn,研究频次均在40以上,研究最少的是Mn和Co,研究频次均少于5次。在国外的文献中,研究最多的是Zn和Cu,研究频次分别达到了42和41次。研究频次最少的是Ti、Sr、Sn、V,研究频次均在5次以下。
1.2 河道底泥重金属含量
本文用SPSS对97篇文献中的重金属污染数据进行了统计,计算出了平均值、中位数和变异系数,并根据背景值计算出了这些重金属在土壤中的富集系数,具体的数据分为国内和国外,分别列于表2和表3。

表1 河道底泥重金属研究频次Tab.1 Research frequency of heavy metals in river sediment

图1 河道底泥重金属研究频次总计Fig.1 Summary of research frequency of heavy metals in river sediment

图2 国内外重金属研究频次对比Fig.2 The comparison of heavy metals research frequency from home and abroad

表2 国内河道底泥重金属含量统计Tab.2 Contents of heavy metals in thesediment from domestic river channel

表3 国外河道底泥重金属含量统计Tab.3 Contentsof heavy metalsin river sediment from abroad
国内的文献共对10种重金属进行了研究,从富集系数可以看出,国内河道底泥中Cd的污染是最严重的,富集系数达到109.78,Hg的污染也十分严重,富集系数达到了94.00。污染较为轻微的是Co和Ni,其富集系数分别为1.26和1.28。
国外的文献对全部14种重金属进行了研究,从富集系数的值来看,污染最严重的是Sn,富集系数达到了86.29。Ti、Sr、V的值均低于土壤背景值。
2 河道底泥重金属评价
河道底泥重金属污染的评价方法有很多,本文选取了生态风险指数法、地积累指数法和富集因子法3种常用的评价方法对国内外土壤重金属污染情况进行了评价。
2.1 潜在生态风险指数法
潜在生态风险指数法[95]是由瑞典科学家Hakanson在1980年提出的,该方法是用Risk Index(RI)来评价重金属的污染情况,RI的计算公式如下:
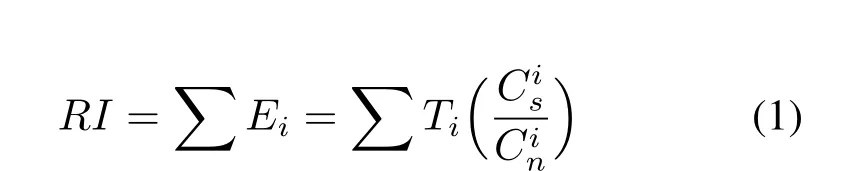
其中,RI为生态危害指数,用于描述某一点多个污染物潜在生态危害系数的综合值;Ei为重金属i的生态危害系数,用于描述某一污染物(元素)的污染程度;Ti为重金属i的毒性系数;Cis为底泥表层重金属i的测定值;Cin为重金属i的参比值(本文使用重金属在土壤中的背景值作为参比值),见表4。
生态风险指数法的重点在于重金属元素的毒性系数。通过查找文献[96],根据12个重金属的毒性系数,计算出了这12种重金属的Ei值,见表5。
表5中显示的是根据生态风险指数法计算出的12种重金属在国内、国外及整体平均中的Ei值,根据Ei值可以判断重金属的污染程度。对国内的数据分析显示,除Cd和Hg属于极强污染外,其他重金属均为轻微污染。经过对国外研究的数据分析,可以看到 Cu、Zn、Cr、Mn、Ti、Co、V、Ni属于轻微污染,Pb属于中等污染,As属于强污染,Cd和Hg属于极强污染。

表4 生态危害系数和风险指数分级Tab.4 Ecological hazard coeffi cient and classifi cation of risk index

表5 国内外各重金属生态危害系数Tab.5 Ecological hazard coeffi cient of heavy metals from home and abroad
根据生态风险指数法对国内外重金属污染情况的分析发现,无论国内还是国外,Cd和Hg都属于极强污染的程度,Cu、Zn、Cr、Mn、Ni均为轻微污染,As和Pb在国外的污染情况比国内的污染情况严重。
2.2 地积累指数法
地积累指数法[97]是德国海德堡大学的Muller提出的一种研究水环境沉积物中重金属污染的方法。地积累指数的计算公式如下:

式中:Ci为元素在小于2µm沉积物中的实测值;Bi为普通页岩中该元素的地球化学背景值;常数K取值为1.5,主要是考虑到成岩作用可能会引起的背景值的变动。根据地积累指数值的大小,重金属的污染程度可分为7级,具体分级情况见表6。
根据地积累指数法的计算公式,计算出了研究中14种重金属的Igeo值(见表7),根据Igeo值的范围,可以判定出各个重金属的污染程度。就我国国内情况而言,Mn、Co、Ni属于无污染,As、Cr属于轻微污染,Cu、Pb、Zn属于中等污染,Cd和Hg为极强污染。从国外文献的分析情况来看,Sr、V属于无污染,Cr和Mn属于轻微污染,Co、Ni为中等污染,Cu、Pb、Zn和Hg为中等到强污染,Cd、As为强污染,Ti为强到极强污染,Sn为极强污染。

表6 地积累指数I geo值分级Tab.6 Classifi cation of geo-accumulation index value

表7 国内外重金属I geo值Tab.7 I geo valueof heavy metalsfrom homeand abroad
对比国内外重金属的污染情况可以发现,Co、Ni在国内可认为是无污染的,而在国外属于中等污染,As在国内仅属于轻微污染的情况,而在国外属于强污染,Hg在国内属于极强污染,而在国外仅属于中等到强污染。Cu、Pb、Zn在国内外的污染情况差别不大,均属于中等污染。
2.3 富集因子法
富集因子[97]是评价人类活动对土壤中重金属富集程度影响的参数,为了减少采样和制样过程中的人为影响以及保证各指标间的可比性与等效性,以参比元素为参考标准,对测试样品中元素进行归一化处理。本文选择Fe作为参比元素,主要考虑到Fe在地壳中丰度高,占地壳元素总量的4.75%,在中性和碱性环境中铁的溶解度低,不易淋溶迁移,生物利用度也低,性质较为稳定。从实地测试结果看,Fe含量是所有测试指标中最稳定的。富集因子的数学表达式为:式中:EF为重金属在土壤中的富集系数,Cn(sample)、Bn(background)是某元素的实测浓度和背景浓度,Cref(sample),Bref(background)是参比元素的实测浓度和背景浓度。富集因子将重金属的污染分为5个等级,具体分级见表8。

根据富集因子法的计算公式,计算出了14种富集系数EF值(见表9),根据EF值的范围,可以判定出各个重金属的污染程度。就我国国内情况而言,As、Cr、Mn、Co和Ni属于无污染或轻度污染,Cu、Pb、Zn属于中等污染,Cd和Hg为极重污染。从国外文献的分析情况来看,Cr、Mn、Sr、Co、V、Ni属于无污染或轻微污染,Cd、Cu、Pb、Zn、Hg为中度污染,As、Ti为重度污染,Sn属于严重污染。As在国内属于无污染或轻微污染,在国外属于重度污染。Cd和Hg在国内已属于极重污染,而在国外分别属于重度污染和中度污染。

表8 富集系数分级Tab.8 Classifi cation of enrichment factors

表9 国内外各种金属富集系数Tab.9 Enrichment Factors of heavy metals from home and abroad
2.4 不同评价方法的比较
本文运用了3种评价方法,根据已有的数据评价了国内外重金属的污染情况,从结果可以看出,不同的评价方法会得到不同的结果。例如,当利用生态风险指数法进行评估时,Ti仅为轻微污染,而地积累指数法的评估结果显示Ti为强到极强污染;当利用富集因子法评估时,Ti也属于重度污染。这可能是由于不同的评价方法的原理及侧重点不同。
生态风险指数法是运用毒性系数计算重金属的潜在生态风险,并根据计算结果对污染程度进行分级评价,评价结果不仅与沉积物中的重金属含量有关,同时还与重金属的毒性系数有关。毒性系数是由Hakanson提出的根据“元素丰度原则”和“元素释放度”经过一系列方法计算所得的,即某一重金属元素的潜在生态毒性与其丰度成反比,且易于释放的元素对生物的潜在毒性更大。
地积累指数法是对数形式的表达,并考虑到成岩作用对背景值的影响引入了常数K,运用地积累指数法进行评价时还需要考虑沉积物颗粒大小的因素,该评价方法中指明沉积物颗粒需小于2µm,而本研究是采用各研究数据的平均值进行计算,不同研究中的沉积物颗粒大小不尽相同,因此计算结果存在一定程度的误差。
富集因子法则是引用了参比元素,本文选用Fe作为参比元素,除Fe以外,Sc、Cs、Li、Mn、Ti、Al、Ca也因其性质较稳定、不易受所在环境与分析测试过程的影响而被选为常用的参比元素。用不同的参比元素进行计算得到的结果也有可能存在一些差异。
3 结 论
(1)国内和国外发表的文献对于重金属污染情况的研究有较大的差别。国内文献对10种重金属进行了研究,而国外文献对14种重金属进行了研究;国内外对一些金属的研究频次存在较大的差别,国内对于Cd、As和Hg的研究频次远高于国外,而国外文献中Mn、Co、Ni的数据明显多于国内;除了Cu和Cr以外,国内外不同重金属的富集系数存在极大的差别。
(2)不同的环境评价方法对不同的重金属评价结果不完全相同。生态风险指数法主要侧重于重金属毒性造成的环境危害,Cd和Hg由于毒性系数很高属于极强污染;地积累指数法是通过对比重金属的含量与背景值计算地积累指数来表示重金属对水环境沉积物的污染情况;富集因子法是选用参比元素进行计算,主要反映人类活动对于重金属富集情况的影响。
(3)3种评价方法对于Cd的评价结果都较为一致,Cd在国内外研究的河道中都属于重度或极重污染的情况。
参考文献:
[1] 王倩,杨丽阎,牛韧,等.从环境公害解决方案到重金属污染对策制度建立——日本“痛痛病”事件启示[J].环境保护,2013,41(21):71-72.
[2] 黄廷林.水体沉积物中重金属释放动力学及试验研究[J].环境科学学报,1995,15(4):440-446.
[3] 施周,贺维鹏.饮用水水源中重金属污染防控技术与对策[J].给水排水,2012,38(8):1-3.
[4] 刘丽,邓时铭,黄向荣,等.浅谈水产动物中的重金属污染[J].河北渔业,2011(7):51-54.
[5] 环境保护部.2015年中国环境状况公报[EB/OL].[2016-06-02].http://www.zhb.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/qt/201606/t20160602353078.htm.
[6] 杨卓,李贵宝,王殿武,等.白洋淀底泥重金属的污染及其潜在生态危害评价[J].农业环境科学学报,2005,24(5):945-951.
[7] 吕文英,汪玉娟,刘国光.北江底泥中重金属污染特征及生态危害评价[J].中国环境监测,2009,25(3):69-72.
[8] ZHANG Z,LIJ,MAMAT Z,et al.Sources identifi cation and pollution evaluation of heavy metalsin thesurfacesediments of Bortala River,Northwest China[J].Ecotoxicology&Environmental Safety,2016,126:94-101.
[9] ZHENGN,WANGQ,LIANGZ,et al.Characterization of heavy metal concentrationsin thesedimentsof threefreshwater riversin Huludao City,Northeast China[J].Environmental Pollution,2008,154(1):135-42.
[10]ZHAO G,YES,YUAN H,et al.Distribution and contamination of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Daya Bay and adjacent shelf,China[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2016,112(1):420-426.
[11]LIN Q,LIU E,ZHANG E,et al.Spatial distribution,contamination and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Erhai Lake,a large eutrophic plateau lake in southwest China[J].Catena,2016,145:193-203.
[12]王雪,樊贵盛.汾河河道及滩地铅镉汞分布特征研究[J].人民黄河,2015,37(10):74-77.
[13]宋宪强,雷恒毅,余光伟,等.重污染感潮河道底泥重金属污染评价及释放规律研究[J].环境科学学报,2008,28(11):2258-2268.
[14]余世清,许文锋,王泉源.杭州城区河道底泥重金属污染及潜在生态风险评价[J].四川环境,2011,30(4):36-43.
[15]丁涛,田英杰,刘进宝,等.杭州市河道底泥重金属污染评价与环保疏浚深度研究[J].环境科学学报,2015,35(3):911-917.
[16]梅明,刘庆,廖金阳.湖北省某矿山河道底泥重金属污染调查与评价[J].武汉工程大学学报,2014,36(1):33-37.
[17]黄宏,郁亚娟,王晓栋,等.淮河沉积物中重金属污染及潜在生态危害评价[J].环境污染与防治,2004,26(3):207-208.
[18]YUAN H,SONG J,LI X,et al.Distribution and contamination of heavy metals in surface sediments of the South Yellow Sea[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2012,64(10):2151-2159.
[19]王晓,韩宝平,张显龙,等.徐州市北郊工业区河流底泥重金属污染特征[J].污染防治技术,2003,16(S1):54-57.
[20]ZHANG J,GAO X.Heavy metals in surface sediments of the intertidal Laizhou Bay,Bohai Sea,China:Distributions,sources and contamination assessment[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2015,98(1):320-327.
[21]YANG X,WU P,YIN A,et al.Distribution and source analysisof heavy metals in soils and sediments of Yueqing Bay basin,East China Sea[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2017,115(1):489-497.
[22]ZHENGN,WANGQ,LIANGZ,et al.Characterization of heavy metal concentrationsin thesedimentsof threefreshwater riversin Huludao City,Northeast China[J].Environmental Pollution,2008,154(1):135-144.
[23]刘志彦,孙丽娜,郑冬梅,等.河道底泥重金属污染及农用潜在风险评价[J].安徽农业科学,2010,38(21):11436-11438.
[24]朱嵬,李志刚,李健,等.宁夏黄河流域湖泊湿地底泥重金属污染特征及生态风险评价[J].中国农学通报,2013,29(35):281-288.
[25]卓丽玲,杜凡,尹玉亭,等.沂河表层底泥重金属污染及其风险性评价[J].枣庄学院学报,2016,33(2):82-86.
[26]张中文,李光德,张世远,等.泮河底泥中重金属污染及潜在生态危害评价[J].环境科学与技术,2008,31(11):134-136.
[27]贾英,方明,吴友军,等.上海河流沉积物重金属的污染特征与潜在生态风险[J].中国环境科学,2013,33(1):147-153.
[28]王越兴,尹魁浩,彭盛华,等.深圳市河流底泥重金属的污染现状及生态风险评价[J].环境与健康杂志,2011,28(10):918-919.
[29]王秋莲.水源水输水河道洪泥河的水环境质量现状调查[J].环境卫生工程,2005,13(5):62-64.
[30]赵健,郑祥民.苏州河市郊段底泥重金属污染特征及对河道疏浚的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2001,20(1):27-30.
[31]CHEN CW,KAOCM,CHENCF,et al.Distribution and accumulation of heavy metals in the sediments of Kaohsiung Harbor,Taiwan[J].Chemosphere,2007,66(8):1431-1440.
[32]向勇,缪启龙,丰江帆.太湖底泥中重金属污染及潜在生态危害评价[J].大气科学学报,2006,29(5):700-705.
[33]孟宪禹.天津市入海排污河重金属污染的解析与控制[D].天津:天津大学,2008,21-25.
[34]吴纪南.苕溪流域典型工业、农业、城镇区河道沉积物重金属污染研究[D].合肥:合肥工业大学,2015,22-24.
[35]罗蔚华,南旭阳.温州市区部分河道重金属污染的调查研究[J].陕西农业科学,2007,(3):48-52.
[36]吴迪,陈浒,李存雄,等.乌江流域沉积物重金属污染特征及生态危害评价[J].土壤通报,2010,41(5):1180-1183.
[37]顾征帆,吴蔚.太湖底泥中重金属污染现状调查及评价[J].甘肃科技,2005,21(12):21-22.
[38]ZHENGN,WANGQ,LIANGZ,et al.Characterization of heavy metal concentrationsin thesedimentsof threefreshwater riversin Huludao City,Northeast China[J].Environmental Pollution,2008,154(1):135-142.
[39]邵学新,吴明,蒋科毅,等.西溪国家湿地公园底泥重金属污染风险评价[J].林业科学研究,2009,22(6):801-806.
[40]SIN S N,CHUA H,LO W,et al.Assessment of heavy metal cationsinsedimentsof Shing Mun River,Hong Kong[J].Environment International,2001,26(5):297-301.
[41]唐晓燕,彭渤,余昌训,等.湘江沉积物重金属元素环境地球化学特征[J].云南地理环境研究,2008,20(3):26-32.
[42]漆燕,成应向,刘湛,等.河流底泥重金属污染及潜在生态风险评价——以湘江株洲段为例[J].四川环境,2011,30(6):104-107.
[43]王蓓,余洋,鲁冬梅,等.云南玉溪城市河道底泥重金属污染特征与潜在生态风险评价[J].生态学杂志,2016,35(2):463-469.
[44]SONG Y,JI J,YANG Z,et al.Geochemical behavior assessment and apportionment of heavy metal contaminants in the bottom sediments of lower reach of Changjiang River[J].Catena,2011,85(1):73-81.
[45]解清杰,何锋.大东沟底泥重金属污染及潜在生态危害评价[J].工业安全与环保,2011,37(10):24-26.
[46]刘芳文,颜文,王文质,等.珠江口沉积物重金属污染及其潜在生态危害评价[J].海洋环境科学,2002,21(3):34-38.
[47]WANG C,LIU S,ZHAO Q,et al.Spatial variation and contamination assessment of heavy metals in sediments in the Manwan Reservoir,Lancang River[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2012,82:32-39.
[48]MALI M,DELL ANNA M M,MASTRORILLI P,et al.Assessment and source identifi cation of pollution risk for touristic ports:Heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments of 4 marinas of the Apulia region(Italy)[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2017,114(2):768-777.
[49]BOTSOU F,KARAGEORGIS A P,DASSENAKIS E,et al.Assessment of heavy metal contamination and mineral magnetic characterization of the Asopos River sediments(Central Greece)[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2011,62(3):547-563.
[50]PALANQUES A,LOPEZ L,GUILEN J,et al.Decline of trace metal pollution in the bottom sediments of the Barcelona City continental shelf(NW Mediterranean)[J].Scienceof the Total Environment,2017,579:755-767.
[51]WIJAYA A R,OUCHIA K,TANAKA K,et al.Evaluation of heavy metal contents and Pb isotopic compositions in the Chao Phraya River sediments:Implication for anthropogenic inputsfrom urbanized areas,Bangkok[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration,2013,126:45-54.
[52]SALASPM,SUJATHA CH,KUMARCSR,etal.Heavy metal distribution and contamination statusin thesedimentary environment of Cochin estuary[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2017,119(2):191.
[53]SINGH K P,MALIK A,SINHA S,et al.Estimation of source of heavy metal contamination in sediments of Gomti River(India)using principal component analysis[J].Water Air&Soil Pollution,2005,166(1):321-341.
[54]HOHH,SWENNENR,CAPPUYNSV,etal.Necessity of normalization to aluminum to assessthecontamination by heavy metalsand arsenic in sedimentsnear Haiphong Harbor,Vietnam[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2012,56:229-239.
[55]AUDRY S,SCHAFERJ,BLANCG,et al.Fifty-year sedimentary record of heavy metal pollution(Cd,Zn,Cu,Pb)in the Lot River reservoirs(France)[J].Environmental Pollution,2004,132(3):413-26.
[56]M¨ULLERJ,RUPPERT H,MURAMATSUY,et al.Reservoir sediments–a witness of mining and industrial development(Malter Reservoir,eastern Erzgebirge,Germany)[J].Environmental Geology,2000,39(12):1341-1351.
[57]DUNGTTT,CAPPUYNSV,SWENNEN R,etal.Leachability of arsenic and heavy metals from blasted copper slag and contamination of marinesedimentand soil in Ninh Hoa district,south central of Vietnam[J].Applied Geochemistry,2014,44:80-92.
[58]MORILLOJ,USEROJ,GRACIA I.Partitioning of metals insedimentsfromthe Odiel River(Spain)[J].Environment International,2002,28(4):263-71.
[59]DAUVALTER V,ROGNERUD S.Heavy metal pollution in sediments of the Pasvik River drainage[J].Chemosphere,2001,42(1)9-18.
[60]NGUYEN T T H,ZHANG W,LI Z,et al.Assessment of heavy metal pollution in Red River surface sediments,Vietnam[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2016,113(1):513-519.
[61]MILENKOVIC N,DAMJANOVIC M,RISTIC M.Study of heavy metal pollution in sediments from the Iron Gate(Danuae River),Serbia and Montenegro[J].Polish Journal of Environmental Studies,2005,14(6):781-787.
[62]FARKASA,ERRATICO C,VIGAN`O L.Assessment of the environmental signifi cance of heavy metal pollution in surfi cial sedimentsof the River Po[J].Chemosphere,2007,68(4):761-768.
[63]LOSKA K,WIECHU D.Application of principal component analysisfor theestimation of sourceof heavy metal contamination in surfacesedimentsfrom the Rybnik Reservoir[J].Chemosphere,2003,51(8):723-733.
[64]CHERNOVA E N,POTIKHA E V,NESTERENKO O E.The Content of heavy metals in bottom sediments of the streams of the Sikhote-Alin biosphere reserve and the streams draining mines of the transit zone of the reserve[J].Achievements in the Life Sciences,2015,9(1):9-14.
[65]VAROL M.Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River(Turkey)using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2011,195:355-364.
[66]GALˇAN E,GˇOMEZ-ARIZA J L,GONZ´ALEZ I,et al.Heavy metal partitioning in river sediments severely polluted by acid mine drainage in the Iberian Pyrite Belt[J].Applied Geochemistry,2003,18(3):409-421.
[67]VAROL M,S¸EN B.Assessment of nutrient and heavy metal contamination in surface water and sediments of the upper Tigris River,Turkey[J].Catena,2012,92:1-10.
[68]PARAMASIVAM K,RAMASAMY V,Suresh G.Impact of sediment characteristics on the heavy metal concentration and their ecological risk level of surface sediments of Vaigai river,Tamilnadu,India[J].Spectrochimica Acta Part A:Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy,2015,137:397-407.
[69]ALI M M,ALI M L,ISLAM M S,et al.Preliminary assessment of heavy metals in water and sediment of Karnaphuli River,Bangladesh[J].Environmental Nanotechnology,Monitoring&Management,2016,5:27-35.
[70]DUODU G O,GOONETILLEKEA,AYOKOG A.Comparison of pollution indices for the assessment of heavy metal in Brisbane River sediment[J].Environmental Pollution,2016,219:1077-1091.
[71]CONCASA,ARDAU C,CRISTINIA,et al.Mobility of heavy metals from tailings to stream waters in a mining activity contaminated site[J].Chemosphere,2006,63(2):244-53.
[72]KILUNGA PI,SIVALINGAM P,LAFFITE A,et al.Accumulation of toxic metals and organic micro-pollutants in sediments from tropical urban rivers,Kinshasa,Democratic Republic of the Congo[J].Chemosphere,2017,179:37-39.
[73]EI-AMIERY A,EINAGGARA A,EI-ALFY M A.Evaluation and mapping spatial distribution of bottom sediment heavy metal contamination in Burullus Lake,Egypt[J].Egyptian Journal of Basic&Applied Sciences,2017,4(1):55-56.
[74]AHMED M M,DOUMENQP,AWALEH M O,et al.Levels and sources of heavy metals and PAHs in sediment of Djibouti-city(Republic of Djibouti)[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2017,120(1-2):340-346.
[75]KADHUM SA,ISHAK M Y,ZULKIFLISZ,et al.Evaluation of the status and distributions of heavy metal pollution in surface sediments of the Langat River Basin in Selangor Malaysia[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2015,101(1):391-396.
[76]LEE PK,KANG M J,YU S,et al.Enrichment and geochemical mobility of heavy metals in bottom sediment of the Hoedong reservoir,Korea and their source apportionment[J].Chemosphere,2017,184:74-85.
[77]马锐,杨长明,李建华.崇明岛典型河道底泥重金属污染及农用潜在风险评价[J].净水技术,2009,28(4):1-5.[78]王晓,韩宝平,丁毅,等.京杭大运河徐州段底泥重金属污染评价[J].能源环境保护,2004,18(3):47-49.
[79]王立明,林超,刘德文.南水北调东线一期工程黄河以北段底泥重金属污染及其潜在生态危害评价[J].南水北调与水利科技,2008,6(3):5-8.
[80]TAMIM U,KHAN R,JOLLY Y N,et al.Elemental distribution of metalsin urban river sedimentsnear an industrial effl uent source[J].Chemosphere,2016,155:509-518.
[81]NETHAJIS,KALAIVANAN R,VISWAM A,et al.Geochemical assessment of heavy metals pollution in surface sedimentsof Vellar and Coleroon estuaries,southeastcoast of India[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2017,115(1):469-480.
[82]SURESH G,RAMASAMY V,MEENAKSHISUNDARAM V,et al.Infl uence of mineralogical and heavy metal composition on natural radionuclide concentrations in theriver sediments[J].Applied Radiation and Isotopes,2011,69(10):1466-1474.
[83]BINNINGK,DAN B.Survey of heavy metals in the sedimentsof the Swartkops River Estuary,Port Elizabeth South Africa[J].Water SA,2001,27(4):461-466.
[84]SKORBI WICZ E,SKORBI WICZ M.Metals in grain fractionsof bottomsedimentsfromselected riversin northeastern Poland[J].Physics and Chemistry of the Earth,Parts A/B/C,2011,36(12):567-578.
[85]NETHAJIS,KALAIVANAN R,VISWAM A,et al.Geochemical assessment of heavy metals pollution in surface sedimentsof Vellar and Coleroon estuaries,southeastcoast of India[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2017,115(1):469-479.
[86]POURKERMAN M,AMJADI S,BENI A N,et al.Evaluation of metal contamination in the Mand River delta,Persian Gulf[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2017,119(2):261-267.
[87]EL HACHIMIM L,EL HANBALIM,FEKHAOUIM,et al.Impactd’un siteminier abandonn´esur l’environnement:Casdelaminede Ze¨ıda(Haute Moulouya,Maroc)[J].Bulletin del’institut Scientifi que,Rabat,section Sciencesdela Terre,2005(27):93-100.
[88]TAYLOR M P.Distribution and storage of sedimentassociated heavy metals downstream of the remediated Rum Jungle Mine on the East Branch of the Finniss River,Northern Territory,Australia[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration,2007,92(1):55-72.
[89]TEIXEIRA E,ORTIZ L,ALVESM,et al.Distribution of selected heavy metals in fl uvial sediments of the coal mining region of Baixo Jacu´ı,RS,Brazil[J].Environmental Geology,2001,41(1):145-154.
[90]DE PAULA FILHO F J,MARINSRV,DELACERDA L D,et al.Background values for evaluation of heavy metal contamination in sediments in the Parna´ıba River Delta estuary,NE/Brazil[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2015,91(2):424-428.
[91]OKOROH K,IGEJO,IYIOLA OA,et al.Fractionation profi le,mobility patterns and correlations of heavy metals in estuary sediments from Olonkoro river,in tede catchment of western region,Nigeria[J].Environmental Nanotechnology,Monitoring&Management,2017,8:53-62.[92]MALVANDI H.Preliminary evaluation of heavy metal contamination in the Zarrin-Gol River sediments,Iran.[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2017,117(1-2):547-553.
[93]中国环境监测总站.中国土壤元素背景值[M].北京:中国环境科学出版社,1990.
[94]Toxic Substances Portal. Agency for toxic substances and disease registry [DB/OL].[2017-8-8].https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofi les/index.asp.
[95]许丁丁,朱宇翔.城市表层土壤重金属污染综合评价方法[J].资源节约与环保,2016(2):106.
[96]徐争启,倪师军,庹先国,等.潜在生态危害指数法评价中重金属毒性系数计算[J].环境科学与技术,2008,31(2):112-115.
[97]胡恭任,于瑞莲.应用地积累指数法和富集因子法评价324国道塘头段两侧土壤的重金属污染[J].中国矿业,2008,17(4):47-51.
