二维码建筑—印度昌迪加尔知识博物馆设计方案
2018-03-11朱文一
朱文一
2015年,印度Archasm举办了“未建成的昌迪加尔:知识博物馆设计竞赛”,以纪念建筑大师勒·柯布西耶逝世50周年。大师在印度留下了堪称经典的一座城和一组建筑。这就是著名的昌迪加尔城及其行政建筑群。其中,位于行政建筑群东北部的省长官邸就是竞赛标题提到的未建成建筑。大师对这幢建筑倾注了大量心血。这是柯布西耶设计的整座昌迪加尔城东北端的建筑,其背景是延绵不断的喜马拉雅山脉。竞赛主办方以这幢未建成建筑为场地,功能设定为知识博物馆公共建筑类型。
朱文一工作室提交的“二维码建筑”(QR Code Architecture)方案探索了数字时代新建筑类型的可能性,方案有以下特点。
第一是关于大师遗产。方案尊重建筑大师勒·柯布西耶针对行政办公区的总体设计,延续其空间肌理,在原址布置知识博物馆的主体建筑(图1)。此外,通过对整个行政办公区规划的分析和研究,方案在主体建筑底层和前面布置大面积水池,增加整个行政办公区的水景,同时创造视线贯通的宽阔视野,将主入口设置在东南面,与勒·柯布西耶著名的“手”雕塑广场连接,整合为对市民和游客开放的公共空间片区(图2)。
第二是关于知识博物馆的功能。它不仅是收藏知识的地方,还是一个探索未来的地方。在建筑物二层,设计了宗教、科学、文学、历史、社会、技术、艺术和建筑8个灵活的、多功能的、友好的知识单元(图3)。每一个单元本身就是一个知识的容器,供城市居民和游客体验。单元之间是半室外的、相互交融的公共交流空间,人们在这里可以体验不同知识碰撞出的灵感火花。建筑表皮则由若干读书小方体构成。这是为一个人或几个人读书研讨而专门设计的安静空间(图4—图6)。
第三是关于建筑创新。勒·柯布西耶是现代建筑大师,他大胆而富有激情的创新所开创的建筑新时代影响至今。如何通过建筑设计纪念这位伟大的建筑大师?方案“二维码建筑”以二维码为介质来设计建筑,创造性地实现了现实和虚拟建筑的连接和互动。建筑表皮的读书小方体是现实的读书空间。其中,建筑屋顶的小方体组成的二维码图案代表昌迪加尔知识博物馆(Chandigarh Museum of Knowledge),也可以设置为其网站的网址。
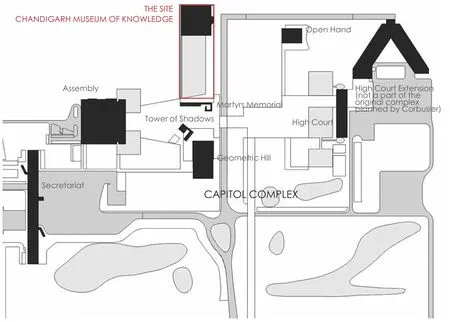
图1 / Figure 1勒·柯布西耶的首都行政区建筑群中的设计场地The Site in the Capitol Complex Designed by Le Corbusier
第四是关于万能视角。在数字时代,人们已经习惯于在卫星地图上查找建筑。这种万能视角优先的体验建筑方式,将建筑物的屋顶或第五立面提升到建筑主立面的地位。在卫星地图上,方案“二维码建筑”屋顶的二维码图案提供了虚拟和现实连接的可能性。只需用手机上的二维码读码APP扫描建筑屋顶,即可获得建筑的虚拟信息(图7)。
近100年前,勒·柯布西耶倡导“走向新建筑”。今天,何谓数字时代的新建筑?这是当代建筑师面临的挑战。方案“二维码建筑”在这方面探索了一种可能性。
图片来源
Figure Sources
文中图片均为朱文一工作室提供
All figures are provided by ZHU Wenyi Atelier
FULL TEXTS TRANSLATED FROM CHINESE
In 2015, Archasm of India hosted the “Chandigarh Unbuilt: Knowledge Museum Design Competition” to commemorate the 50th anniversary of the death of great architect Le Corbusier. The master created a classic city and architecture, Chandigarh City and it's the Capitol complex. Among them, the governor‘s house is the unbuilt building mentioned in the title of the competition. The program takes this unbuilt building area as the site and functions as the public building of the Knowledge Museum.
The “QR Code Architecture” proposal submitted by ZHU Wenyi Atelier explores a new typology of architecture in the digital age.
First, Respecting the existing Capitol complex and continuing its fabric, the main building of the Knowledge Museum is arranged at the original site (Figure 1). In addition, the large-scale pool is arranged on the ground floor and front of the main building to increase the waterscape of the entire Capitol complex. The main entrance is located in the southeast and is connected to Le Corbusier‘s famous “Open Hand” sculpture square, which is integrated into a public space area (Figure 2).
Second, It is not only a place to collect knowledge,but also a place to explore the future. On the second floor of the building, eight flexible, versatile and friendly knowledge units (Figure 3). The in-between units is semi-outdoor space where you can experience the spark of inspiration from different knowledge. The building skin is made up of many reading cubes (Figure 4—6).
Third, The scheme shows a smart way to make the real building connecting the virtual one through QR code as the medium. The QR code pattern consisting of the reading cube on the building roof represents the Chandigarh Museum of Knowledge,and of course it can be set as the website address.
Fourth, On the satellite map, the QR code pattern provides the possibility of virtual and realistic connections. It would be very easily to get the virtual information of the building through scanning the building roof with the QR code reading app on your smart phone (Figure 7).
Nearly 100 years ago, Le Corbusier advocated“Towards a New Architecture”. Today, what is the new architecture in the digital age? This is a challenge for contemporary architects. The scheme “QR Code Architecture” explores a possibility in this regard.
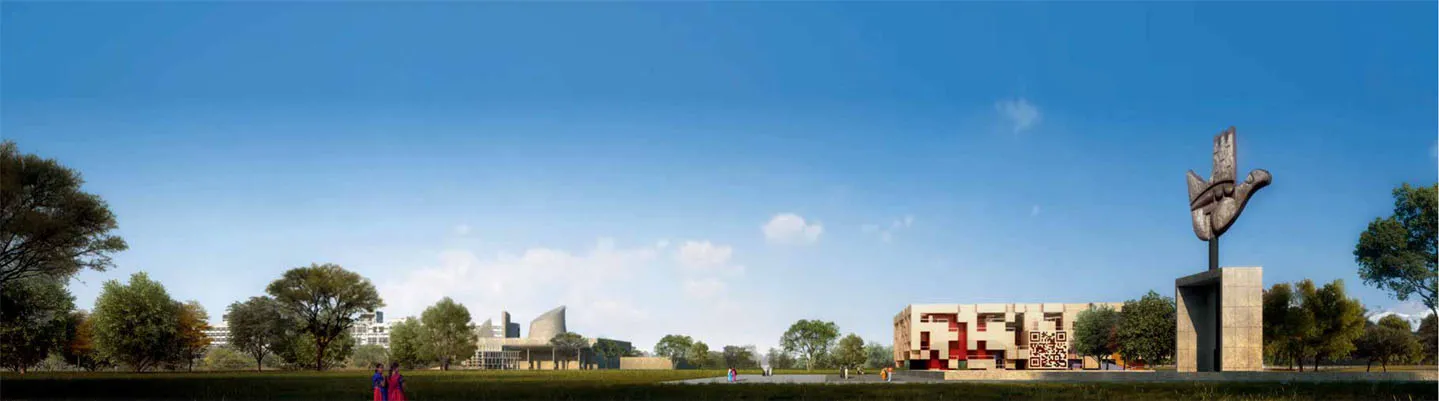

图2 / Figure 2二维码建筑与自由手雕塑QR Code Architecture and Open Hand Sculpture

图3 / Figure 3二维码建筑各层平面图Plans of QR Code Architecture

图4 / Figure 4二维码建筑立面Facade of QR Code Architecture

图5 / Figure 5二维码建筑入口立面Entrance Facade of QR Code Architecture
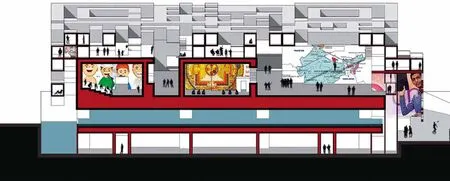
图6 / Figure 6二维码建筑剖面图Section of QR Code Architecture
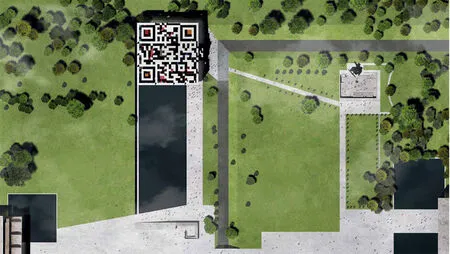
图7 / Figure 7二维码建筑总图Master Plan of QR Code Architecture
