原发性干燥综合征的自身抗体研究进展①
2018-03-07喻晓雯白殊同刘金坤高洪燕
喻晓雯 王 琴 冯 婧 白殊同 刘金坤 高洪燕 吴 斌
(重庆市中医院中医药基础研究室,重庆 400021)
原发性干燥综合征(primary Sjögren′s syndrome,pSS)是一种病因未明的慢性自身免疫性疾病,以淋巴细胞浸润和外分泌腺功能损伤为特征。pSS好发于女性,多于40~60岁发病,口干、眼干是常见的临床表现。成人患病率为0.5%~1%,是风湿病科第二大疾病[1,2]。由于非专科医生对本病认识不足,同时pSS的诊断常需完善唾液腺功能、眼科检查、唇腺活检等,在基层医院往往无法完成诊断,有研究提示超过一半的pSS患者出现漏诊或误诊,平均需要3.9年才能确诊[3,4 ]。基于上述原因,自身抗体在pSS诊断中的作用就尤为突出。在pSS患者血清中可检测出多种自身抗体,抗Ro/SSA和抗La/SSB抗体是pSS的标志性抗体,但其特异性较低[5]。近年来,抗M3毒蕈碱乙酰胆碱受体(anti-M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor,抗M3R)抗体和抗α-胞衬蛋白抗体(anti-α-Fodrin antibody,AFA)逐渐运用于临床诊断,且特异性有所提高[6]。此外,其他自身抗体也引起研究者的重视,如抗着丝点抗体、抗环瓜氨酸抗体、抗线粒体抗体和抗平滑肌抗体等[7],其检出率和临床意义具体见表1。
1 抗Ro/SSA 和抗La/SSB抗体
抗Ro/SSA和抗La/SSB抗体是pSS的标志性抗体,已经被列入诊断标准[5]。抗Ro/SSA和抗La/SSB抗体在pSS的病程中比较稳定,即使是生物制剂利妥昔单抗治疗后亦很难改变[10]。研究发现抗La/SSB与抗Ro/SSA抗体与pSS疾病活动度有一定的相关性,其中抗Ro/SSA抗体具有更高的相关性[11]。抗Ro/SSA抗体包括抗Ro52和抗Ro60两种自身抗体,抗Ro52抗体是pSS患者中最常被检出的自身抗体[7]。研究还发现12%的抗Ro/SSA抗体阴性的pSS患者可检测到抗Ro52抗体阳性,提示抗Ro52抗体提高了pSS的检出率[5]。在临床上,检测抗Ro/SSA和抗La/SSB抗体的常用方法为ELISA,其敏感性偏低且易出现假阳性。Volchenkov等[12]发现液相荧光素酶免疫沉淀系统技术能提高抗Ro/SSA和抗La/SSB抗体的检出率,抗La/SSB抗体可提高11%,抗Ro60抗体可提高4%,可见新的实验方法可以提高pSS的诊断率。
抗Ro/SSA和抗La/SSB对pSS疾病有预测作用,早在1982年,Isenberg等[2]发现15例关节炎伴抗La/SSB抗体阳性的患者,其中有11例患者2年后发展为pSS。最近亦发现抗Ro/SSA和抗La/SSB抗体在确诊pSS前20年就已经存在[13]。此外,Tandander等[14]也发现ANAs在pSS患者中最早出现,其次是类风湿因子(Rheumatoid factor,RF)、抗Ro60/SSA、抗Ro52/SSA和抗La/SSB,表明早期检测对pSS的早期筛查意义重大。
抗Ro/SSA和抗La/SSB抗体参与了pSS的发病机制。研究发现抗Ro/SSA抗体阳性的pSS患者的唾液流率明显低于抗Ro/SSA抗体阴性的患者,提示抗Ro/SSA抗体可能介导唾液腺的机能障碍[4]。其机制可能是自身抗体沉积于唾液腺,促炎的细胞因子KC、IL-1α、MIG、MIP2和PDGF-β的上调协助自身抗体介导唾液腺的损伤,进而诱发口干症状[15]。此外,抗Ro/SSA和抗La/SSB抗体还介导了pSS患者的腺外损伤。有报道pSS患者中抗Ro/SSA和抗La/SSB抗体与腺外症状(脾肿大,淋巴结病,脉管炎和雷诺现象)呈正相关[10]。高滴度的抗-Ro52抗体与唇腺活检阳性,腮腺肿胀、贫血、白细胞减少和RF显著相关[5]。韩国的一项研究也发现抗-Ro52与肝脏和肌肉的受累高度相关,而抗-Ro60与肝脏的受累呈负相关[16]。可见抗Ro/SSA、抗La/SSB参与了pSS腺体及腺体外损伤的发病机理,将近年研究发现的一些参与了pSS的发病机制自身抗体总结于表2。
2 抗M3R抗体
抗M3R抗体是可以作为pSS诊断的另一个的血清学标志物。M3R是一个膜结合蛋白,表达于外分泌腺,在腺体分泌中发挥着关键作用。血清中的抗M3R抗体检出率较低,约为50%[19]。采用唾液样本可提高抗M3R抗体的检出率,且特异性可达到88.16%。研究还发现唾液抗M3R IgG抗体与年龄、病程和球蛋白水平相关[17]。国内报道69%的pSS患者在唾液中能检测到抗M3R抗体[18]。从方便临床诊断角度看,唾液中抗M3R抗体检测可能更贴近临床。
越来越多的证据表明抗M3R抗体可能是引起唾液腺分泌功能丧失的重要因素,其可能的机制如下:首先pSS患者血清中纯化的抗胆碱自身抗体以肌醇磷脂、半胱天冬酶-3和MMP-3依赖的方式介导了A253细胞系的凋亡,抗M3R抗体通过与磷脂酶C、钙通信激活半胱天冬酶-3和MMP-3,从而诱导上皮细胞凋亡,进而导致唾液腺的破坏性损伤[22]。其次,抗M3R抗体能抑制人类颌下腺、唾液腺细胞的分泌功能[23]。如Iwabuchi等[24]发现在小鼠唾液腺中M3R的活化引起唾液的产生,M3R对唾液分泌的副交感神经有非常重要的调控作用[25],因此抗M3R抗体可能直接通过阻断神经传输导致干燥症状的显现。最后,抗M3R抗体介导的氧化压力与唾液腺的损伤有关。在正常情况下,泪腺和唾液腺的眼睛和口腔表面存在ROS/抗氧化剂的平衡,一旦这种平衡被打破,眼睛和口腔会受到损伤[26]。ROS的水平和抗氧化物酶系统的不平衡在唾液腺的致病性中发挥着关键的作用[27]。抗M3R抗体刺激pSS唾液腺中超氧化物歧化酶(Superoxide dismutase,SOD)和过氧化氢酶(Catalase,CAT)的活性增加,并且上调NO和前列腺素E2的表达。因此,我们推断SOD和CAT在pSS患者中活性的增加可能是机体对ROS增加的一个防御反应,但这种防御反应一旦过度就会引起唾液腺细胞和组织不可逆的损伤[28]。
表1pSS疾病相关自身抗体
Tab.1AssociatedautoantibodiesdetectedinpSS
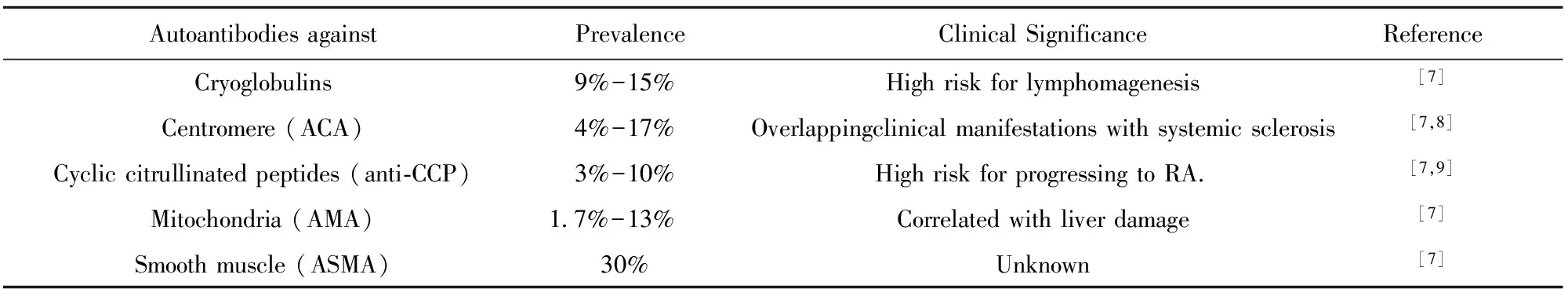
Autoantibodiesagainst PrevalenceClinicalSignificanceReferenceCryoglobulins 9%-15%Highriskforlymphomagenesis[7]Centromere(ACA) 4%-17%Overlappingclinicalmanifestationswithsystemicsclerosis[7,8]Cycliccitrullinatedpeptides(anti⁃CCP) 3%-10%HighriskforprogressingtoRA [7,9]Mitochondria(AMA)1 7%-13%Correlatedwithliverdamage[7]Smoothmuscle(ASMA) 30%Unknown[7]
表2参与pSS发病机理的相关自身抗体
Tab.2AssociationofautoantibodieswithpSSpathogenesis

AutoantibodiesPrevalenceSpecificityClinicalSignificanceReferenceAnti⁃Ro/SSAantibody 33%-74%52 1%Associatedwithlongerdiseaseduration,extensivelymphocyticinfiltrationofMSG,severeexocrineglanddamage,parotidenlargement[5,7,10,14,16]Anti⁃La/SSBantibody 23%-52%49%Associatedwithhypergammaglobulinemia,cryoglobulinemia,glandulardamageandorganinvolvement[5,7,14,16]Anti⁃M3Rantibody44 19%-69%88 1%-95 1%Associatedwithsalivaryglanddamage,gastrointestinalandbloodsystemabnormalities[17-19]Anti⁃α⁃fodrinantibody(AFA)39 3%-41 9%82 8%-83 1%Correlatedwithlymphocytesinfiltrationofsalivaryglandandinvolvinginearlypathogenesis[20,21]
抗M3R抗体也介导了pSS患者的腺外系统的损伤。pSS患者普遍存在胃肠道的损伤,但具体原因未知。Park等[29]发现在pSS患者中,抗M3R抗体有介导胃肠道多重机能不良的潜在风险,包括食道蠕动减弱和结肠动力改变等,因此推测pSS患者胃肠道动力的改变可能部分是由抗M3R抗体介导的功能障碍。另外在pSS患者中,抗M3R抗体还介导了神经免疫的相互作用,这种相互作用可能与pSS复杂的病理生理相关。换言之自身抗体的产生直接靶向自发的神经递质受体抗M3R抗体,从而抑制了唾液的分泌[30]。此外,最近发现pSS患者的抗M3R抗体可诱导存在于质膜的M3R和MHCⅠ类分子的下调和随后的NK细胞介导的细胞死亡,这可能是pSS患者易发生白细胞减少的原因[31]。上述研究表明抗M3R抗体介导了腺外系统损伤,其机理是复杂的。
3 抗α-胞衬蛋白抗体
AFA是pSS早期诊断的标志物[32]。AFA在唾液腺炎和组织凋亡时形成,是一个器官特异性自身抗原,与自身免疫损伤和组织破坏存在相关[10]。早在1997年,在pSS小鼠模型中发现了AFA[32]。通常AFA的出现早于抗Ro/SSA或抗La/SSB抗体[10]。有研究者检测了64例pSS患者和108例非pSS患者血清中的AFA IgA和IgG抗体,通过ROC分析以评估其对pSS诊断的准确性,结果发现敏感性分别为59%和55%,特异性为75%和73%,证明了其在pSS中的诊断潜能[33]。由于不同研究对AFA抗体在pSS诊断中的准确性相差较大,Hu等[20]选取23个研究,通过meta分析系统评价了AFA对pSS诊断的准确性,结果发现AFA的敏感性和特异性分别为39.3%和83%,IgG亚型、IgA亚型的敏感性分别为38%和41.9%,特异性分别为82.8%和83.1%,因此认为AFA在pSS诊断中具有可靠性。最近发现在抗SSA/SSB抗体阴性的pSS患者中,AFA与RF和/或ANA联合可把诊断的敏感性从56.9%提高到70.7%,提示可作为pSS诊断的替代免疫学标准[21]。此外,AFA的浓度与唾液腺中淋巴细胞的浸润程度呈正相关,AFA可能参与了早期的致病过程,因为AFA IgG抗体阳性的pSS患者往往有更短的疾病病程[10]。
4 其他自身抗体
在pSS患者中,一些抗体的出现可能提示发生相关疾病的风险,如aβ2GP Ⅰ 和p-ANCA抗体可能预示pSS患者有发生神经病变的可能[34]。ADAMTS13抗体阳性提示可能有并发血液系统疾病的风险[35]。IFN-γ的过度表达与肺间质病变有紧密的联系[36]。PAX6的下调与眼睛损伤高度相关,可作为预测pSS早期眼睛并发症的指标之一[37]。而且一些自身抗体具有一定的预测作用,如抗NA-14抗体阳性提示pSS病程短[38]。抗MDM2阳性提示pSS病程长,同时常伴有贫血、血小板减少和抗-SSB抗体阳性,且与疾病活动度和IgG的水平正相关[39]。
表3近年发现与pSS相关的自身抗体
Tab.3AutoantibodiesnewlyfoundinpSS
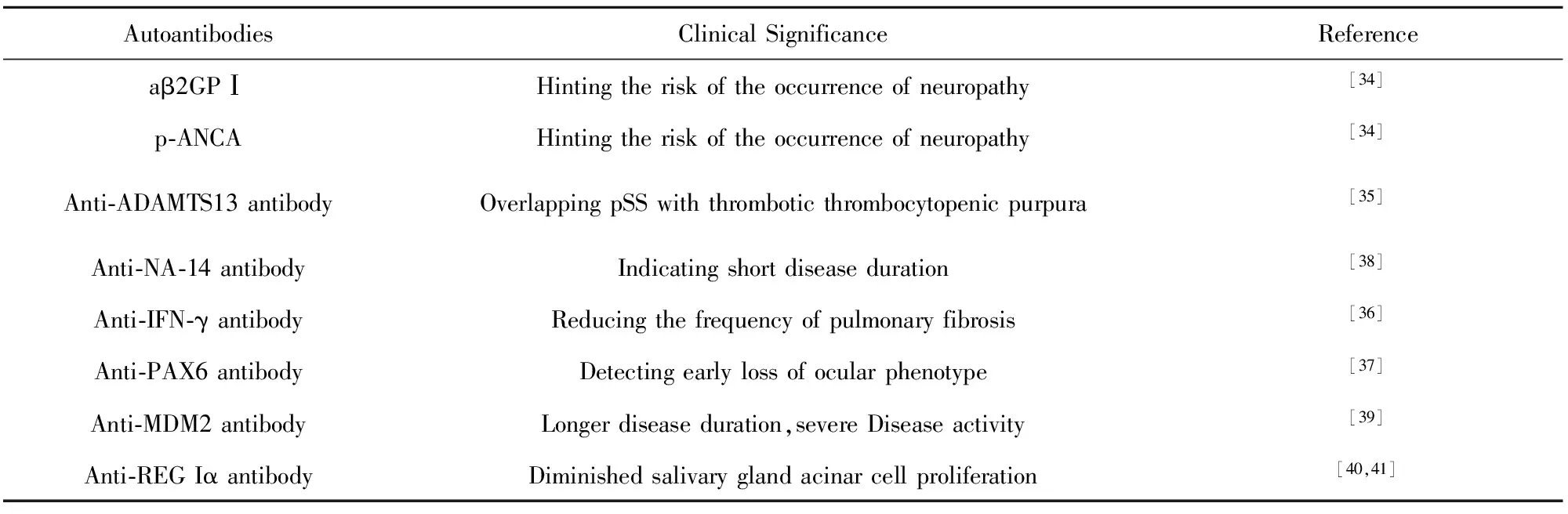
AutoantibodiesClinicalSignificanceReferenceaβ2GPⅠHintingtheriskoftheoccurrenceofneuropathy[34]p⁃ANCAHintingtheriskoftheoccurrenceofneuropathy[34]Anti⁃ADAMTS13antibodyOverlappingpSSwiththromboticthrombocytopenicpurpura[35]Anti⁃NA⁃14antibodyIndicatingshortdiseaseduration[38]Anti⁃IFN⁃γantibodyReducingthefrequencyofpulmonaryfibrosis[36]Anti⁃PAX6antibodyDetectingearlylossofocularphenotype[37]Anti⁃MDM2antibodyLongerdiseaseduration,severeDiseaseactivity[39]Anti⁃REGIαantibodyDiminishedsalivaryglandacinarcellproliferation[40,41]
Reg家族基因产物作为生长因子,可促进细胞增殖和再生,与各种炎症疾病关系密切。研究发现REG Iα在pSS患者的唾液腺导管上皮细胞中过表达,并且在血清中可检测到抗REG Iα自身抗体[40]。Fujimura等[41]发现抗REG Iα抗体阳性的患者唾液分泌功能低下,其机理与IL-6诱导REG Iα破坏唾液腺管状上皮细胞的再生有关。各种近年发现自身抗体的临床意义,见表3。
5 自身抗体与疾病预后
自身抗体与风湿病预后往往存在一定的联系,如在系统性硬化症,抗ACA阳性的患者预后多良好,而抗topo I抗体与不良预后相关[42]。高滴度的RF(IgM和/或IgA)、抗CCP抗体和抗核周因子等多提示类风湿性关节炎疾病活动度高,难以控制[43,44]。目前自身抗体与pSS预后相关的研究明显不足,以后应加强这方面的研究。
6 结语
自身抗体及其在疾病pSS的预测、诊断和发病机制中都发挥着重要的作用。当前用于实验室诊断的自身抗体-抗Ro/SSA、抗La/SSB、抗M3R和AFA普遍存在着特异性或者敏感性较低的缺陷,致使pSS患者易出现漏诊或误诊。探索提高诊断准确性的方法就迫在眉睫,是否可以考虑多种自身抗体的联合应用?如AFA与RF和/或ANA联合敏感性从56.9%提高到70.7%。另外新技术也是提高传统自身抗体敏感性的有效途径。此外,研究发现许多自身抗体与pSS相关,寻找特异性和敏感性较高的新的自身抗体或者通过整合生物标志物体系,或许对提高诊断的准确性和深入阐述致病机理具有重要意义。
[1] Hauk V,Calafat M,Larocca L,etal.Vasoactive intestinal peptide/vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor relative expression in salivary glands as one endogenous modulator of acinar cell apoptosis in a murine model of Sjogren′s syndrome[J].Clin Exp Immunol,2011,166(3):309-316.
[2] Henriksson G.Presymptomatic autoantibodies in Sjogren′s syndrome:what significance do they hold for the clinic?[J].Exp Rev Clin Immunol,2014,10(7):815-817.
[3] Beckman KA,Luchs J,Milner MS.Making the diagnosis of Sjögren′s syndrome in patients with dry eye[J].Clin Ophthalmol,2016,10:43-53.
[4] Wei P,Li CL,Qiang L,etal.Role of salivary anti-SSA/B antibodies for diagnosing primary Sjögren′s syndrome[J].Med Oral Patologia Oral Y Cirugia Bucal,2015,20(2):E156-E160.
[5] Retamozo S,Akasbi M,Brito-Zeron P,etal.Anti-Ro52 antibody testing influences the classification and clinical characterisation of primary Sjogren′s syndrome[J].Clin Exp Rheumatol,2012,30(5):686-692.
[6] Chen Y,Zheng JF,Huang QN,etal.Autoantibodies against the second extracellular loop of M3R do neither induce nor indicate primary sjogren′s syndrome[J].PLoS One,2016,11(2):e0149485.
[7] Kyriakidis NC,Kapsogeorgou EK,Tzioufas AG.A comprehensive review of autoantibodies in primary Sjogren′s syndrome:Clinical phenotypes and regulatory mechanisms[J].J Autoimmunity,2014,51:67-74.
[8] Kitagawa T,Shibasaki K,Toya S.Clinical significance and diagnostic usefulness of anti-centromere antibody in Sjogren′s syndrome[J].Clin Rheumatol,2012,31(1):105-112.
[9] Ryu YS,Park SH,Lee J,etal.Follow-up of primary Sjogren′s syndrome patients presenting positive anti-cyclic citrullinated peptides antibody[J].Rheumatol Int,2013,33(6):1443-1446.
[10] Shen L,Suresh L.Autoantibodies,detection methods and panels for diagnosis of Sjogren′s syndrome[J].Clin Immunol,2017,182:24-29.
[11] Maslinska M,Manczak M,Wojciechowska B,etal.The prevalence of ANA antibodies,anticentromere antibodies,and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies in patients with primary Sjogren′s syndrome compared to patients with dryness symptoms without primary Sjogren′s syndrome confirmation[J].Reumatologia,2017,55(3):113-119.
[12] Volchenkov R,Jonsson R,Appel S.Anti-Ro and anti-La autoantibody profiling in Norwegian patients with primary Sjogren′s syndrome using luciferase immunoprecipitation systems(LIPS)[J].Scand J Rheumatol,2012,41(4):314-315.
[13] Trier NH,Nielsen IO,Friis T,etal.Comparison of antibody assays for detection of autoantibodies to Ro 52,Ro 60 and La associated with primary Sjogren′s syndrome[J].J Immunological Methods,2016,433:44-50.
[14] Theander E,Jonsson R,Sjostrom B,etal.Prediction of Sjogren′s syndrome years before diagnosis and identification of patients with early onset and severe disease course by autoantibody profiling[J].Arthritis Rheumatol,2015,67(9):2427-2436.
[15] Szczerba B,Kaplonek M,Wolska N,etal.Interaction between innate immunity and Ro52-induced antibody causes Sjogren′s syndrome-like disorder in mice[J].Ann Rheum Dis,2016,75(3):617-622.
[16] Song JS,Do JH,Lee SW.The prevalence and the clinical relevance of anti-Ro52 in Korean patients with primary Sjogren′s syndrome[J].Rheumatol Int,2012,32(2):491-495.
[17] Jayakanthan K,Ramya J,Mandal SK,etal.Younger patients with primary Sjogren′s syndrome are more likely to have salivary IgG anti-muscarinic acetylcholine receptor type 3 antibodies[J].Clin Rheumatol,2016,35(3):657-662.
[18] He J,Guo J,Ding Y,etal.Diagnostic significance of measuring antibodies to cyclic type 3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor peptides in primary Sjogren′s syndrome[J].Rheumatology,2011,50(5):879-884.
[19] Sumida T,Iizuka M,Asashima H,etal.Pathogenic role of anti-M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor immune response in Sjogren′s syndrome[J].Presse Med,2012,41(9 Pt 2):e461-e466.
[20] Hu Q,Wang D,Chen W.The accuracy of the anti-alpha-fodrin antibody test for diagnosis of Sjogren′s syndrome:a meta-analysis[J].Clin Biochem,2013,46(15):1372-1376.
[21] Hernandez-Molina G,Nunez-Alvarez C,Avila-Casado C,etal.Usefulness of IgA anti-alpha-fodrin antibodies in combination with rheumatoid factor and/or antinuclear antibodies as substitute immunological criterion in sjogren syndrome with negative anti-SSA/SSB antibodies[J].J Rheumatol,2016,43(10):1852-1857.
[22] Reina S,Sterin-Borda L,Borda E.Anti-M(3)peptide IgG from Sjogren′s syndrome triggers apoptosis in A253 cells[J].Cell Immunol,2012,275(1-2):33-41.
[23] Dawson LJ,Stanbury J,Venn N,etal.Antimuscarinic antibodies in primary Sjogren′s syndrome reversibly inhibit the mechanism of fluid secretion by human submandibular salivary acinar cells[J].Arthritis Rheum,2006,54(4):1165-1173.
[24] Iwabuchi Y,Masuhara T.Sialogogic activities of SNI-2011 compared with those of pilocarpine and McN-A-343 in rat salivary glands:identification of a potential therapeutic agent for treatment of Sjorgen′s syndrome[J].Gen Pharmacol,1994,25(1):123-129.
[25] Nakamura T,Matsui M,Uchida K,etal.M(3)muscarinic acetylcholine receptor plays a critical role in parasympathetic control of salivation in mice[J].J Physiol,2004,558(Pt 2):561-575.
[26] Brik R,Rosen I,Savulescu D,etal.Salivary antioxidants and metalloproteinases in juvenile idiopathic arthritis[J].Mol Med,2010,16(3-4):122-128.
[27] Zalewska A,Knas M,Gindzienska-Sieskiewicz E,etal.Salivary antioxidants in patients with systemic sclerosis[J].J Oral Pathol Med,2014,43(1):61-68.
[28] Reina S,Rodriguez M,Stranieri G,etal.Action of anti-M(3)muscarinic acetylcholine receptor IgG of primary Sjogren′s syndrome on the enzymatic antioxidant system in rat submandibular gland[J].J Oral Pathol Med,2015,44(10):876-883.
[29] Park K,Haberberger RV,Gordon T,etal.Antibodies interfering with the type 3 muscarinic receptor pathway inhibit gastrointestinal motility and cholinergic neurotransmission in Sjogren′s syndrome[J].Arthritis Rheum,2011,63(5):1426-1434.
[30] Deak M,Szvetnik A,Balog A,etal.Neuroimmune interactions in Sjogren′s syndrome:relationship of exocrine gland dysfunction with autoantibodies to muscarinic acetylcholine receptor-3 and mental health status parameters[J]Neuro Immunomodulation,2013,20(2):79-86.
[31] Namkoong E,Lee SW,Kim N,etal.Effect of anti-muscarinic autoantibodies on leukocyte function in Sjogren′s syndrome[J]Mol Immunol,2017,90:136-142.
[32] Haneji N,Nakamura T,Takio K,etal.Identification of alpha-fodrin as a candidate autoantigen in primary Sjogren′s syndrome[J]Science,1997,276(5312):604-607.
[33] Qin Q,Wang H,Wang HZ,etal.Diagnostic accuracy of anti-alpha-fodrin antibodies for primary Sjogren′s syndrome[J]Modern Rheumatol,2014,24(5):793-797.
[34] Hsu CW,Su YJ,Chang WN,etal.The association between serological biomarkers and primary Sjogren′s syndrome associated with peripheral polyneuropathy[J].Biomed Res Int,2014,2014:902492.
[35] Yamashita H,Takahashi Y,Kaneko H,etal.Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura with an autoantibody to ADAMTS13 complicating Sjogren′s syndrome:two cases and a literature review[J].Mod Rheumatol,2013,23(2):365-373.
[36] Yang L,Bai L,Wei F,etal.Autoantibodies against interferon-gamma reduce the frequency of pulmonary fibrosis and concentration of C-reactive protein in patients with primary Sjogren′s syndrome[J].Mod Rheumatol,2015,25(2):325-327.
[37] McNamara NA,Gallup M,Porco TC.Establishing PAX6 as a biomarker to detect early loss of ocular phenotype in human patients with Sjogren′s syndrome[J].Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci,2014,55(11):7079-7084.
[38] Uomori K,Nozawa K,Ikeda K,etal.A re-evaluation of anti-NA-14 antibodies in patients with primary Sjogren′s syndrome:Significant role of interferon-gamma in the production of autoantibodies against NA-14[J].Autoimmunity,2016,49(5):347-356.
[39] Liu Y,Liao X,Wang Y,etal.Autoantibody to MDM2:A potential serological marker of primary Sjogren′s syndrome[J].Oncotarget,2017,8(9):14306-14313.
[40] Yoshimoto K,Fujimoto T,Itaya-Hironaka A,etal.Involvement of autoimmunity to REG,a regeneration factor,in patients with primary Sjogren′s syndrome[J].Clin Exp Immunol,2013,174(1):1-9.
[41] Fujimura T,Fujimoto T,Itaya-Hironaka A,etal.Significance of interleukin-6/STAT pathway for the gene expression of reg ialpha,a new autoantigen in sjogren′s syndrome patients,in salivary duct epithelial cells[J].Clin Rev Allergy Immunol,2017,52(3):351-363.
[42] Hamaguchi Y.Autoantibody profiles in systemic sclerosis:predictive value for clinical evaluation and prognosis[J].J Dermatol,2010,37(1):42-53.
[43] Mota LM,Santos Neto LL,Burlingame RW,etal.Disability and quality-of-life are not influenced by the prevalence of autoantibodies in early rheumatoid arthritis patients-results of the Brasilia Cohort[J].Rev Bras Reumatol,2012,52(6):824-829.
[44] Nell-Duxneuner V,Machold K,Stamm T,etal.Autoantibody profiling in patients with very early rheumatoid arthritis:a follow-up study[J].Ann Rheum Dis,2010,69(1):169-174.
