基于支持向量机的滴灌灌水器流量预测模型建立与验证
2018-02-28王新端
郭 霖,白 丹,王新端,王 程,周 文,程 鹏
基于支持向量机的滴灌灌水器流量预测模型建立与验证
郭 霖1,白 丹1※,王新端1,王 程1,周 文2,程 鹏2
(1. 西安理工大学水利水电学院,西安 710048;2. 华北水利水电大学水利学院,郑州 450011)
为了直接、准确预测灌水器流量,引入支持向量机预测方法,取灌水器6个工作压力和8个几何参数作为因素,正交设计安排300组灌水器训练样本和30组检测样本,并采用精度较高的SST-模型模拟计算灌水器流量,同时利用遗传算法对支持向量机参数进行优化计算,得到与模拟流量误差最小的流量预测值。结果表明,惩罚参数为100、核函数参数为20时检测样本的流量预测值与模拟值的误差最小,平均相对误差为1.91%,决定系数为0.98,而回归拟合方法计算得到的平均相对误差为6.45%,决定系数为0.93,表明支持向量机预测流量的优越性,且30组试验验证样本的平均相对误差为2.25%,证明支持向量机预测的准确性和可靠性。预测模型建立可有效地提高灌水器研发效率,对水力性能评估和流道结构设计与优化提供依据。
流量;数值分析;模型;滴灌灌水器;工作压力;几何参数;支持向量机;优化
0 引 言
灌水器的消能方式主要是在流道内部产生局部水头损失,其原理是借助水力学中的圆角弯管、折角弯管、以及流道断面的突扩、突缩作用[1-2]通过流道结构[3]与形式[4]的变化,消除进口处的多余压力[5],将有压水流变成滴水状[6-7],从而使出流均匀与稳定,是保证灌溉质量最为重要的部件[8-9]。灌水器流道的不同几何参数[10-13]和工作压力[14-17]对应不同的流量,进而影响灌水器的水力性能,设计不同额定流量的灌水器产品可满足不同作物的灌水需求[18-19]。因此,流量测定对于灌水器性能研究和产品研发至关重要。
流道的几何参数和工作压力影响灌水器的流量[20-21],如何高效和准确地计算灌水器的流量是有待解决的问题[22-23]。刘春景等[24-25]采用响应曲面法对流态指数、流量系数与流道关键参数进行了二次多项式拟合,确定关键参数的最佳组合;Li等[26]采用SPSS软件对流量与流道几何参数进行多元线性回归,建立二者的经验公式;Li等[27]、Celik等[28]通过多元回归分析了灌水器压力与流量之间的关系,并建立流量计算的经验公式;Vekariya等[29]建立了流量与几何参数的多元回归模型,并利用量纲分析法[30]探究了几何参数对流量以及水力性能的影响。
综合目前计算灌水器流量的方法,鲜有对于灌水器流量直接预测的研究,一般根据流量与压力的经验公式先回归计算流态指数和流量系数,再建立二者与流道几何参数的线性或非线性回归方程,间接计算流量,统称为回归拟合方法,其原理为经验风险最小化(empirical risk minimization,ERM)[31]。但回归拟合方法存在一定的不足,其一,回归拟合方法的前提是样本数趋于无穷大时的渐进理论,即对于大样本数据可得到较为可信的预测结果,但在研究过程中所能提供的样本数有限,回归方程的泛化能力较弱[32];其二,通过流态指数和流量系数间接预测流量的方法,实质上是双变量回归计算问题,计算流量多有不便,同时多次回归计算存在较大的拟合误差。
因此,寻求更为合理、简便和直接的灌水器流量预测方法、弥补计算流量的不足、提高预测模型的泛化能力对于灌水器的深入研究是必要的。近年来,很多学者借鉴了具有较强泛化能力和广泛适用性的支持向量机(support vector machine,SVM)在气象、水文预测等领域的突出表现[33-34],对土壤的水力学参数[35]、湿度[36]、水分入渗[37]以及10 m压力下迷宫式滴头水力性能[31]等进行预测,并取得了较为理想的结果,同时由于SVM是在统计学习和结构风险最小化原理基础上建立的一种预测方法,对于预测对象具有一定的普适性,因此,本文采用SVM预测方法构建预测灌水器流量的SVM响应面,直接预测不同工作压力、不同几何参数的双向对冲流灌水器流量,即给定1组输入(不同工作压力、不同几何参数)如何求得所需的输出(流量)是本文研究的重点,解决这一问题对增加预测灌水器流量的可信度、提高灌水器研发效率、降低研发成本具有重要意义。
1 理论基础
1.1 Fluent数值模拟计算理论
连续性方程

动量方程为

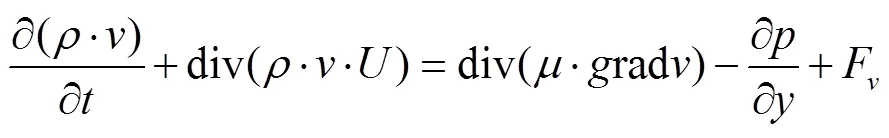

式中为流体速度,m/s;、、分别为流速在、、坐标轴上的分量,m/s;为水的密度,kg/m3;为动力黏度系数,N·s/m2;为流体的压力,Pa;div为散度;grad为梯度;F、F、F为微元体在、、坐标轴上的体力,N/m3,当体力只有重力,且轴竖直向上,则F=0,F=0,F=-。
由于在前期的研究中对Fluent模拟精度进行了综合对比[38],因此不再赘述,本文采用模拟精度较好的SST-模型对训练样本和检测样本中的灌水器流量进行模拟,以获得与流量真实值更为吻合的结果。
1.2 SVM计算理论
假设存在样本集为
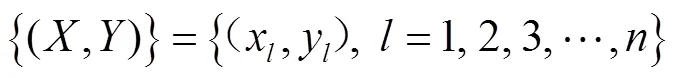
其中x∈n是第个训练样本的输入值,且为维列向量,对应的目标值为
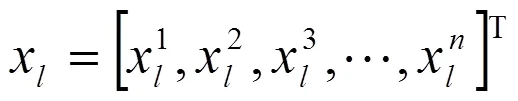
∈且y是第个训练样本的输出值,根据个训练样本值导出对的依存关系,同时引入核函数[32],核变换后,决策函数为
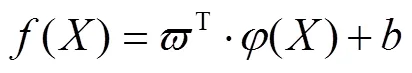
通常情况下最小化置信范围,决策函数可转换为最优化方程组求解
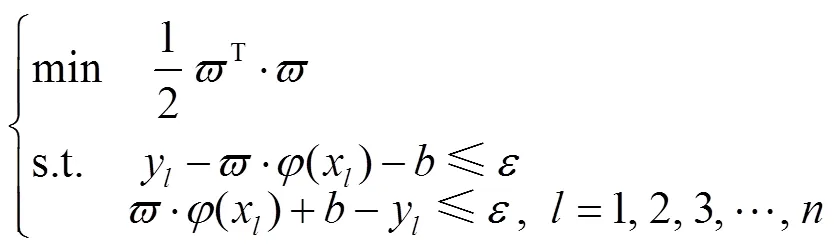
引入松弛变量ξ和ξ,可得到
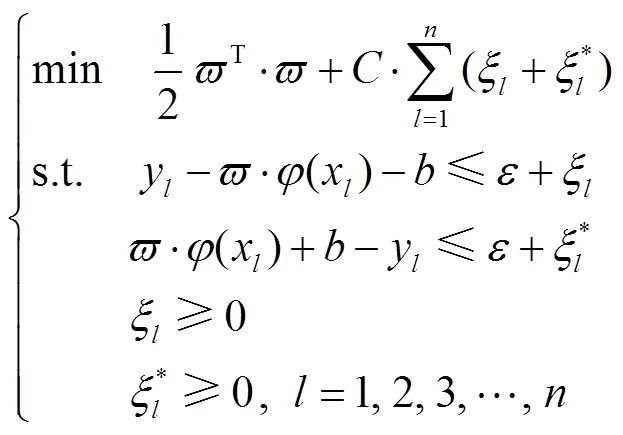
引入Lagrange函数,最优化函数可变换为

式中为不敏感损失参数;为惩罚参数,>0;ξ和ξ为松弛变量;α、α为与第个样本对应的Lagrange乘子;α和α为与第个样本对应的Lagrange乘子;(x,x)为核函数。
本文核函数采用径向基核函数进行计算,可表示为
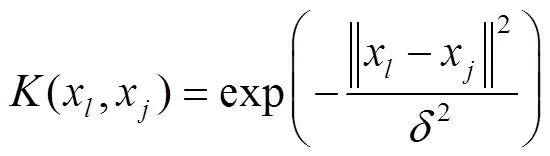
式中为核函数参数。
2 灌水器流量预测模型
2.1 灌水器三维模型
灌水器三维模型如图1所示。

1.流道进口 2.流道出口 3.外壁面 4.分水件 5.挡水件
2.2 灌水器流道几何参数
在文献[15-16]灌水器流道关键几何参数的取值基础上,增加相邻流道单元距离、流道深度、流道单元数,共设置8个灌水器流道几何参数,流道几何参数如图2所示。

注:S表示外壁面到分水件之间的流道距离,mm;T表示分水件与挡水件之间的齿尖距离,mm;W表示外壁面到挡水件之间的流道距离,mm;Z表示分水件到挡水件之间的最大流道距离,mm;d表示挡水件的垂直底柱高度,mm;e表示相邻流道单元距离,mm;D表示流道深度,mm;N表示流道单元数。下同。
流道几何参数取值范围包括:、、分别取0.6、0.7、0.8、0.9、1.0 mm,和分别取1.0、1.1、1.2、1.3、1.4 mm,取0、0.3、0.6、0.9、1.2 mm,取0.5、0.6、0.7、0.8、0.9 mm,取18、20、22、24、26。
2.3 流量预测模型样本集建立
2.3.1 训练样本集
流道几何参数和工作压力是影响灌水器流量的因素,且影响因素与流量之间存在复杂的数学关系,则因素与流量的SVM训练样本集表示为
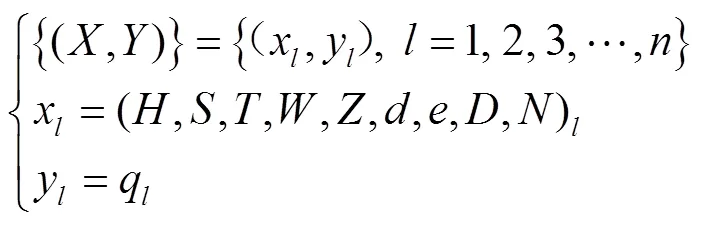
式中和分别为输入和输出的训练样本集;x为第个训练样本的输入值,为多维空间向量,包含9个变量;y为第个训练样本的输出值;为灌水器的工作压力,kPa;、、、、、、、均为灌水器的流道几何参数,mm;q为第个训练样本对应的灌水器流量,L/h。
2.3.2 检测样本集
影响因素与流量的SVM检测样本集可表示为
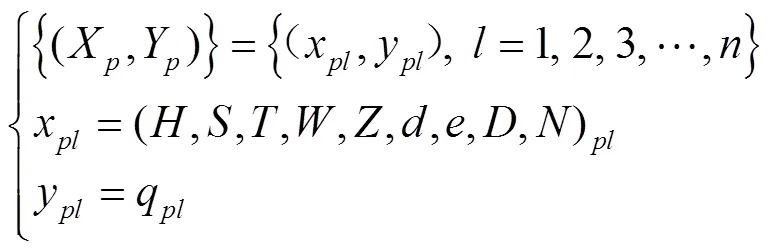
式中X和Y分别为输入和输出的检测样本集;x为第个检测样本的输入值;y为第个检测样本的预测值;q为第个检测样本对应灌水器的预测流量,L/h。
3 材料与方法
3.1 SVM训练样本集设计
为了从全面设计方案的样本点中挑选出部分具有代表性的样本点作为训练样本集,依据正交设计的“均匀分散”和“整齐可比”的“正交性”特征,按照正交设计表L50(511)安排训练样本方案,如表1所示,每个灌水器方案分别在50~250 kPa工作压力下采用数值模拟进行流量计算,每隔40 kPa计算一次,共计算6次,总共需要计算50×6=300组流量,并将300组流量模拟值作为SVM预测流量的训练样本集,即训练样本集中9个因素各有300组输入,对应训练样本集有300组输出。
3.2 SVM检测样本集设计
从全面设计方案的样本点中随机挑选5个灌水器几何参数组合作为检测样本方案,如表2所示,每个方案采用数值模拟计算6个工作压力的流量,总共需要计算5×6=30组流量,并将30组流量模拟值作为SVM预测流量的检测样本集,即通过SVM的训练学习可计算出检测样本集X中的30组输入所对应的30组灌水器流量的Y预测值。
3.3 SVM样本集数据归一化
为了消除SVM样本集中的输入、输出项对预测结果的影响,在对灌水器流量预测时应对训练样本和检测样本中各项分别进行归一化处理,其归一化公式为
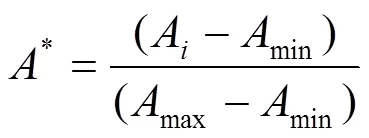
式中A和A分别为归一化处理前和处理后的各方案的变量;min和max分别为每个样本对应各项的最小值和最大值。
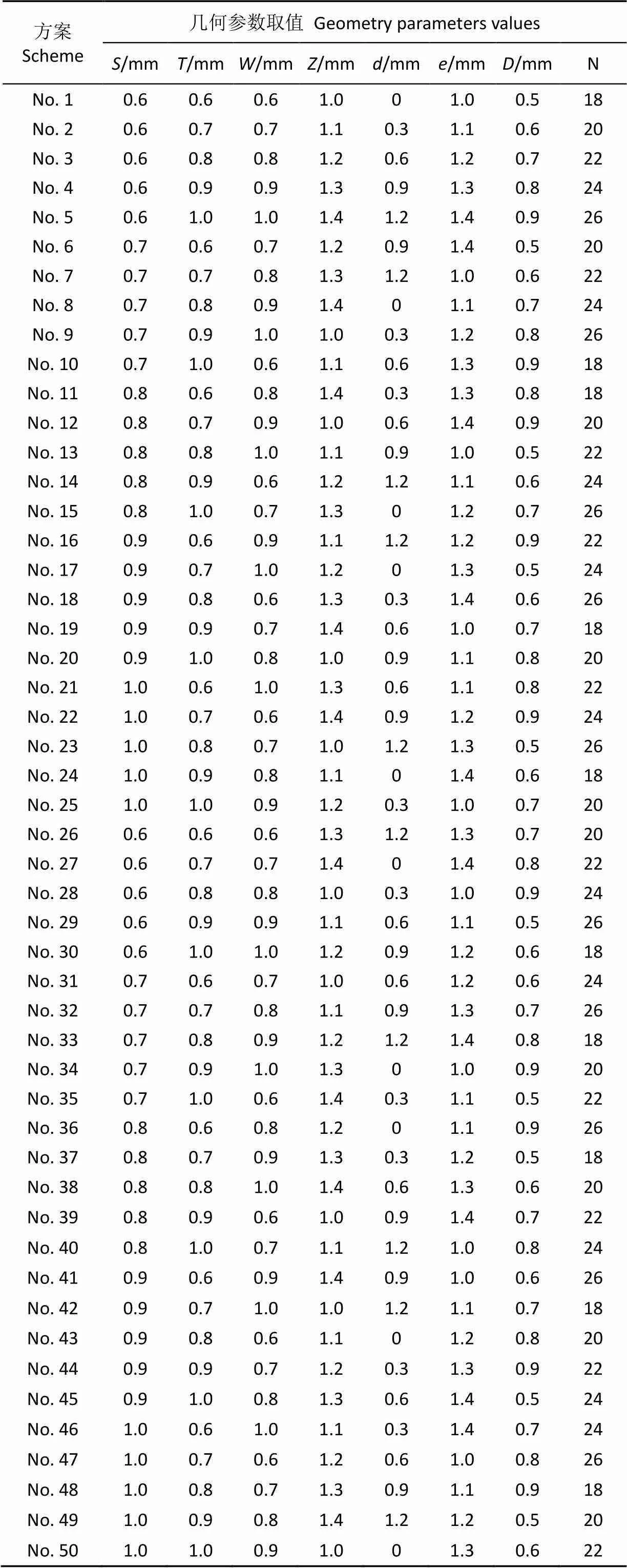
表1 训练样本方案

表2 检测样本方案
3.4 SVM参数
在SVM中对训练和学习效果影响最大的2个参数为和,其中参数直接影响模型的稳定性,避免模型在学习和推广过程中产生欠学习和过学习问题,决定了适应误差的最小化和平滑程度;参数反映了支持向量之间的相关程度,直接影响支持向量之间联系的松弛度,避免产生欠拟合和过拟合问题,决定模型预测的推广能力和泛化性,因此,在对灌水器流量预测时需要对参数和进行调节和优化,得到较为理想的预测结果。
3.5 SVM参数调节与优化
采用遗传算法对SVM参数各种群个体进行选择、交叉、变异,逐代产生新的近似最优结果,最终计算得到参数个体的最优解。
3.5.1 目标函数
本文对SVM预测流量准确性的评价通过流量预测值与流量模拟值进行相对误差对比,以相对误差最小为目标选择最优参数,目标函数可表示为
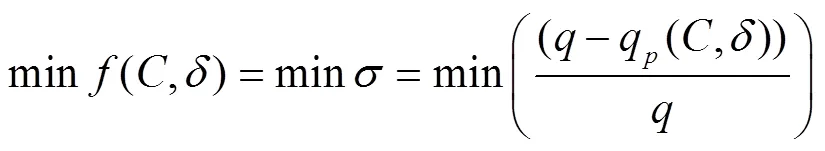
式中为惩罚参数;为核函数参数;为流量的相对误差,%;为流量模拟值,L/h;q为流量预测值,L/h。
3.5.2 约束条件
结合相关文献[39-40]中SVM参数的取值范围,将取值范围作为上下限约束,可表示为
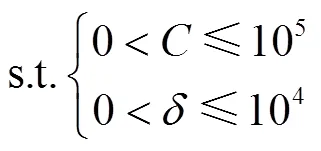
3.5.3 参数优化模型求解
采用Matlab遗传算法工具箱对目标函数进行求解,其中遗传算法适应度反映遗传算法优化计算中对应解的优劣程度,根据目标函数类型建立适应度函数,可表示为

式中为目标函数界限的保守估计值。
遗传算法程序中求解的主要变量分别设置为:群体中个体的数目NIND为100,每个变量使用20位表示,即PRECI为20,最大遗传代数MAXGEN为200,交叉概率XOVR为1,代沟GGAP为0.9。
4 结果与分析
4.1 SVM训练样本流量模拟结果
对训练样本中的300组灌水器进行流量模拟计算(样本编号为1~300),由于样本量较大,且篇幅有限,列出部分模拟结果仅供参考,训练样本结果如表3所示,并分别对各项进行归一化处理。
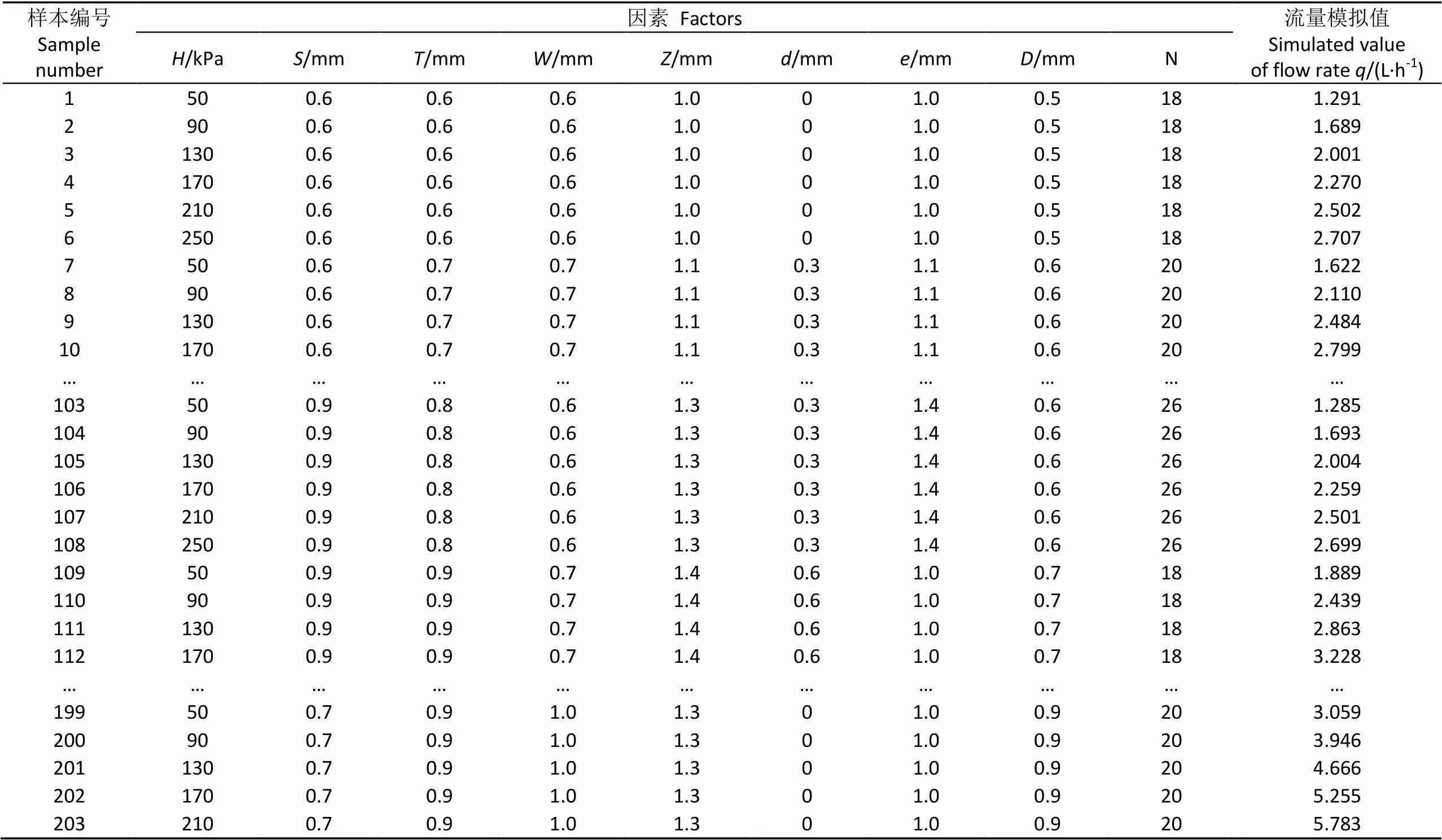
表3 训练样本结果
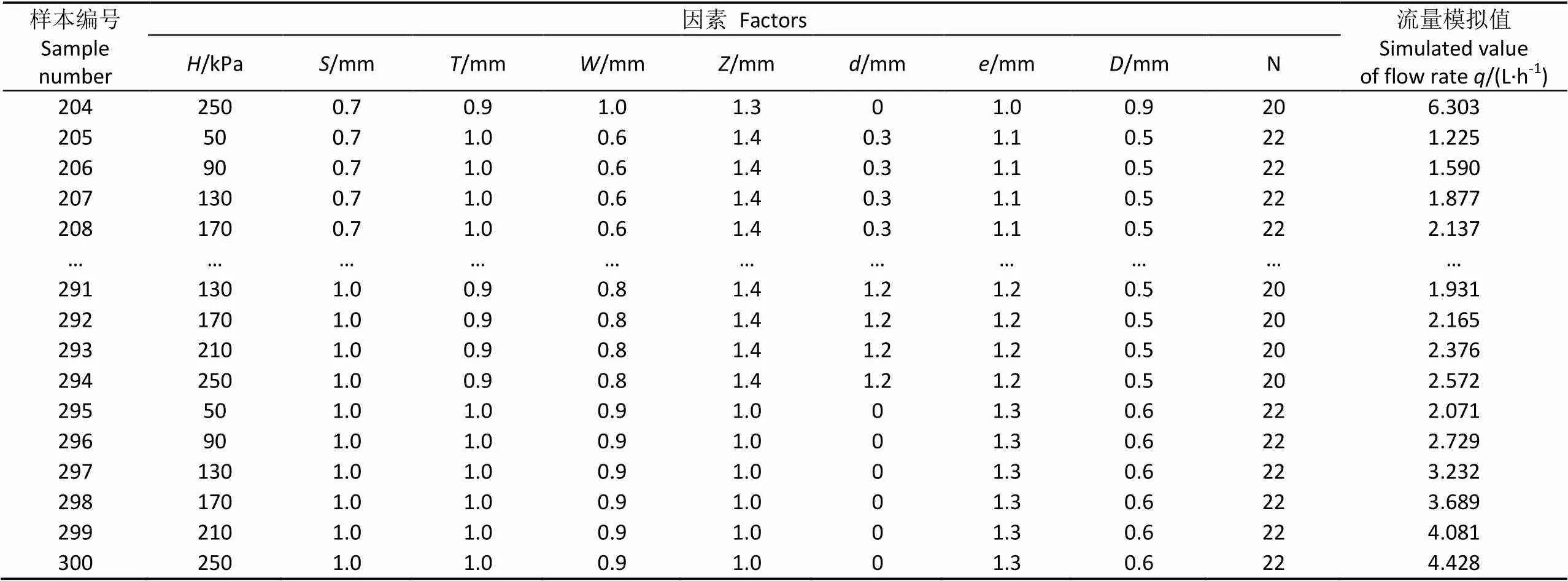
续表
注:表示灌水器的工作压力,kPa,下同。
Note:is working pressure of emitter, kPa, same as below.
4.2 SVM检测样本流量预测结果与分析
在约束条件范围内采用遗传算法工具箱计算得到当为100、为20时,灌水器检测样本的SVM流量预测值与模拟值的相对误差最小,为1.91%,检测样本集中的30组灌水器样本(样本编号为301~330)的流量预测结果如表4所示。

表4 检测样本结果
表4分别采用回归拟合方法和SVM方法预测灌水器流量,对2种预测流量方法进行误差对比,其结果如图3所示。回归拟合得到的流量预测值与模拟值的相对误差为0.15%~26.69%,平均相对误差为6.45%,决定系数为0.93,其中检测样本307的相对误差最大,为26.69%,很大程度偏离了灌水器的真实流量值;而采用SVM计算得到的流量预测值与模拟值的相对误差为0.09%~6.43%,平均相对误差为1.91%,决定系数为0.98,预测值与模拟值的相关性好,完全满足对灌水器流量预测的需求,从而说明本文提出的采用SVM预测灌水器流量方法的优越性。
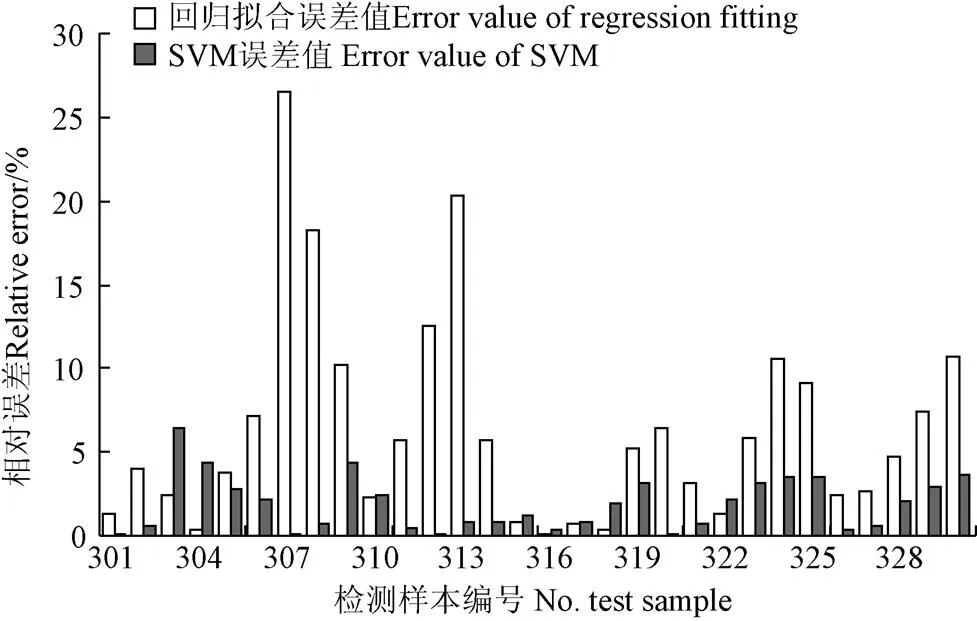
图3 预测流量的相对误差
4.3 预测模型试验验证
为进一步验证SVM预测流量方法的可靠性,选取5组灌水器流道几何参数组合作为试验验证方案,对比流量试验值与回归拟合方法和SVM预测方法计算的流量预测值的误差,验证方案参数取值及计算结果如表5所示,试验采用EM-G32S-X32型高精密雕刻机同比例加工灌水器样机,并参照GB/T17187-2009《农业灌溉设备-滴头和滴灌管-技术规范和试验方法》的技术要求搭建试验平台,对灌水器样机进行流量测试,每组灌水器样机分别安装5个,并在工作压力为50~250 kPa范围内同时进行流量测试,每组测试时间均为5 min,测试3次,取3次流量测试的平均值作为灌水器流量的试验值。
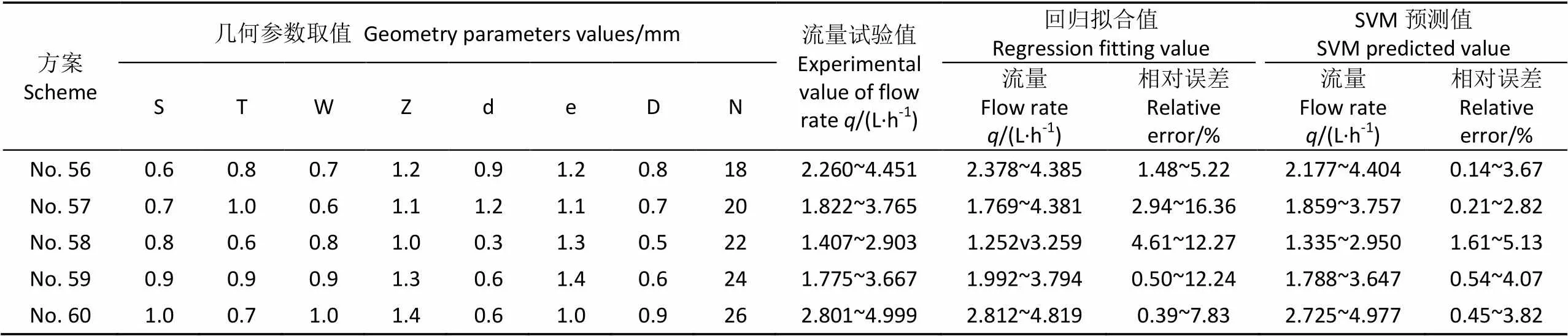
表5 试验验证方案及结果
表5中每组灌水器的验证方案均测试6个工作压力的流量,即共有30组试验验证样本(样本编号为331~360),试验验证样本的相对误差如图4所示。误差计算结果表明回归拟合得到的流量预测值与试验值的相对误差为0.39%~16.36%,平均相对误差为5.52%,与流量试验值的误差较大;而采用SVM计算得到的流量预测值与试验值的相对误差为0.14%~5.13%,平均相对误差为2.25%,在误差范围之内,决定系数为0.98,表明建立预测流量的SVM响应面可以准确地反映灌水器进口工作压力、流道几何参数与流量的关系,并通过SVM模型的建立可直接对灌水器的流量和水力性能进行预测和评估,一定程度上缩短灌水器试验周期,提高灌水器研发效率。
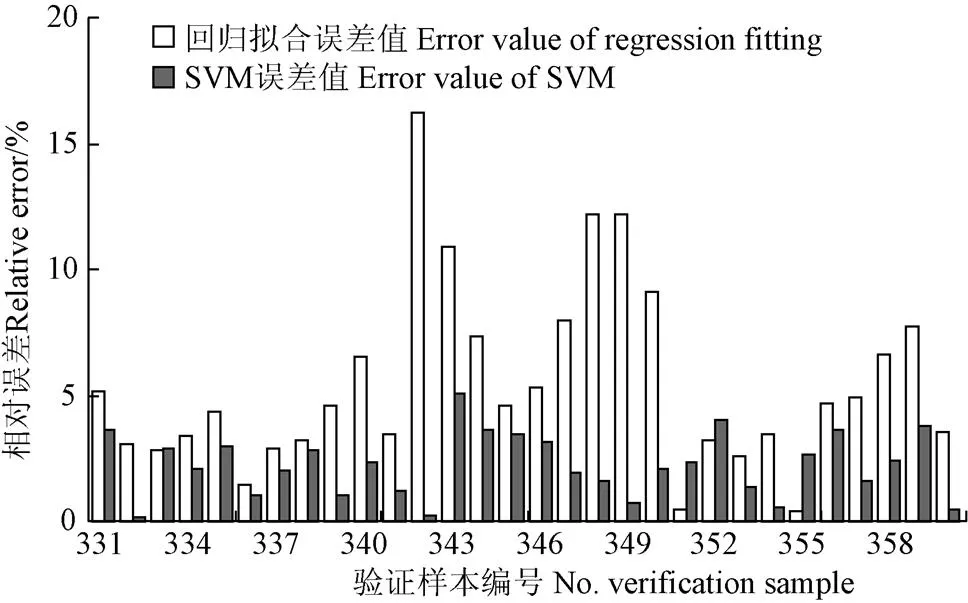
图4 试验验证样本的相对误差
5 结论与讨论
1)本文基于SVM预测方法建立灌水器流量预测响应面,并对SVM中的惩罚参数和不敏感损失参数进行优化,其中最优值为100、为20时,SVM预测流量的平均相对误差最小,为1.91%,满足灌水器流量预测的精度需求。
2)对比回归拟合方法和SVM方法的预测流量精度,前者预测流量的平均相对误差为6.45%,后者平均相对误差为1.91%,精度更高,说明采用SVM预测流量的优越性。
3)灌水器流量试验验证得到SVM的流量预测值与试验值的平均相对误差为2.25%,在误差范围内,证明建立预测灌水器流量的SVM响应面的可靠性。
文中主要从直接预测灌水器流量的角度提出了SVM响应面方法,初步得到SVM预测流量的平均相对误差为1.91%,在预测精度方面有一定的增强,并可降低灌水器的研发成本,提高研发效率,有深入研究的必要。但由于灌水器的研究最终是要对流道结构进行优化,设计性能最优的灌水器,因此,后期应更多的从灌水器性能角度出发,将SVM流量预测方法与流道结构优化算法相结合,实现SVM预测流量和性能到结构优化算法的数据传输与循环,直接预测和设计灌水器流道最优几何参数,弥补现有灌水器研发过程中的不足,有助于实现灌水器研发的模块化、数字化以及精确化,提高灌水器研发效率和农业工程使用价值。
[1] 苑伟静,魏正英,楚华丽,等. 分流式灌水器结构优化设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(17):117-124.
Yuan Weijing, Wei Zhengying, Chu Huali, et al. Optimal design and experiment for divided-flow emitter in drip irrigation[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(17): 117-124. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 刘洁,魏青松,史玉升,等. 滴灌灌水器复杂流道局部阻力特征的试验研究[J]. 中国农村水利水电,2011(6):55-60.
Liu Jie, Wei Qingsong, Shi Yusheng, et al. Experimental research on local resistance characteristics of drip irrigation emitters with complex flow channel[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2011(6): 55-60. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] Patil S S, Nimbalkar P T, Joshi A. Hydraulic study, design & analysis of different geometries of drip irrigation emitter labyrinth[J]. International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Technology, 2013, 2(5): 455-462.
[4] De Jesus Souza W, Sinobas L R, Sánchez R, et al. Prototype emitter for use in subsurface drip irrigation: Manufacturing, hydraulic evaluation and experimental analyses[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2014, 128: 41-51.
[5] 仵峰,董晓爽,吴玉博,等. 渐缩-突扩流道水力特性研究[J]. 华北水利水电大学学报:自然科学版,2017,38(2):61-67.
Wu Feng, Dong Xiaoshuang, Wu Yubo, et al. Hydraulic properties of the flow in a gradual shrinking and sudden enlarging channel[J]. Journal of North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power: Natural Science Edition, 2017, 38(2): 61-67. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] GB/T 50485-2009,微灌工程技术规范[S].
[7] Tayel M, Lightfoot D, Mansour H. Effects of drip irrigation circuit design and lateral line lengths: I-on pressure and friction loss[J]. Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 3(3): 392-399.
[8] Zhang Lin, Merkley G P. Relationships between common irrigation application uniformity indicators[J]. Irrigation Science, 2012, 30(2): 83-88.
[9] 张林,吴普特,朱德兰,等. 基于制造偏差的滴灌系统综合流量偏差率[J]. 农业机械学报,2013,44(12):135-139.
Zhang Lin, Wu Pute, Zhu Delan, et al. Integrated flow deviation rate of drip irrigation system based on manufacturing variation[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2013, 44(12): 135-139. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 魏正英,苑伟静,周兴,等. 我国压力补偿灌水器的研究进展[J]. 农业机械学报,2014,45(1):94-101.
Wei Zhengying, Yuan Weijing, Zhou Xing, et al. Research progress of pressure compensating emitters in micro-irrigation systems in china[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2014, 45(1): 94-101. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] Madramootoo C A, Morrison J. Advances and challenges with micro-irrigation[J]. Irrigation and Drainage, 2013, 62(3): 255-261.
[12] Gilaad Y, Krystal L, Zanker K.Hydraulic and mechanical properties of drippers[C]//Proceedings of the 2nd International Drip Irrigation Congress. Riverside, USA: University of California, 1974.
[13] 喻黎明. 结构参数对梯形流道水力性能及抗堵塞性能的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报:自然科学版,2011,39(8):197-202.
Yu Liming. Influence of the structural parameters of trapezoidal-channel emitters on hydraulic and anti-clogging performance[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University: Natural Science Edition, 2011, 39(8): 197-202. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 杜少卿,曾文杰,施泽,等. 工作压力对滴灌管迷宫流道灌水器水力性能的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2011,27(增刊2):55-60.
Du Shaoqing, Zeng Wenjie, Shi Ze, et al. Effects of working pressure on hydraulic performances of labyrinth path emitters[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2011, 27(Supp.2): 55-60. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 郭霖,白丹,王新端,等.双向对冲流滴灌灌水器水力性能与消能效果[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(17):77-82.
Guo Lin, Bai Dan, Wang Xinduan, et al. Hydraulic performance and energy dissipation effect of two-ways mixed flow emitter in drip irrigation[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(17): 77-82. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 郭霖,白丹,王新端,等. 双向对冲流灌水器水力性能和消能机理模拟与验证[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(14):100-107.
Guo Lin, Bai Dan, Wang Xinduan, et al. Numerical simulation and verification of hydraulic performance and energy dissipation mechanism of two-ways mixed flow emitter[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(14): 100-107. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 范永申,仵峰,宰松梅,等. 新型微压滴灌灌水器水力性能试验研究[J]. 灌溉排水学报,2006,25(5):39-41.
Fan Yongshen, Wu Feng, Zai Songmei, et al. Experimental study on hydraulic property of emitters with tiny water pressure[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2006, 25(5): 39-41. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 蔡耀辉,吴普特,张林,等. 设计流量和土壤质地对微孔陶瓷灌水器入渗特性的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(7):100-106.
Cai Yaohui, Wu Pute, Zhang Lin, et al. Effects of designed flow rate and soil texture on infiltration characteristics of porous ceramic irrigation emitters[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(7): 100-106. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 黎安,刘洁,魏青松,等. 滴灌灌水器多类型流道的微压水力性能研究[J]. 中国农村水利水电,2012(2):4-7.
Li An, Liu Jie, Wei Qingsong, et al. The hydraulic properties of multiple flow channels of drip emitters under micro-pressure[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2012(2): 4-7. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
[20] Hezarjaribi A, Dehghani A A, Helghi M M, et al. Hydraulic performances of various trickle irrigation emitters[J]. Journal of Agronomy, 2008, 7(3): 265-271.
[21] 李治勤,马静. 迷宫灌水器水流流态试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(1):82-86.
Li Zhiqin, Ma Jing. Experiment on flow pattern in labyrinth emitter[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(1): 82-86. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 田济扬,白丹,任长江,等. 滴灌双向流流道灌水器水力特性分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(20):89-94.
Tian Jiyang, Bai Dan, Ren Changjiang, et al. Analysis on hydraulic performance of bidirectional flow channel of drip irrigation emitter[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(20): 89-94. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 李向明,杨建国. 微孔陶瓷灌水器流量影响因素研究[J]. 农业机械学报,2016,47(4):73-78.
Li Xiangming, Yang Jianguo. Factors influencing flow rate of microporous ceramic irrigation emitters[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(4): 73-78. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 刘春景,唐敦兵,郑加强,等. 滴灌梯形迷宫滴头流道水力性能的响应曲面法优化[J]. 农业工程学报,2011,27(2):46-51.
Liu Chunjing, Tang Dunbing, Zheng Jiaqiang, et al. Optimization of hydraulic performance for drip irrigation trapezoidal labyrinth channel of emitter using response surface methodology[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2011, 27(2): 46-51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 刘春景,唐敦兵,何华,等. 滴灌三角形迷宫滴头水力性能稳健性分析[J]. 农业机械学报,2013,44(1):67-72.
Liu Chunjing, Tang Dunbing, He Hua, et al. Hydraulic performance robustness analysis for drip irrigation triangle labyrinth channel of emitter[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2013, 44(1): 67-72. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] Li Guangyong, Wang Jiandong, Alam M, et al. Influence of geometrical parameters of labyrinth flow path of drip emitters on hydraulic and anti-clogging performance[J]. Transactions of the ASABE, 2006, 49(3): 637-643.
[27] Li Yunkai, Yang Peiling, Xu Tingwu, et al. Hydraulic property and flow characteristics of three labyrinth flow paths of drip irrigation emitters under micro-pressure[J]. Transactions of the ASABE, 2009, 52(4): 1129-1138.
[28] Celik H K, Karayel D, Caglayan N, et al. Rapid prototyping and flow simulation applications in design of agricultural irrigation equipment: Case study for a sample in-line drip emitter[J]. Virtual and Physical Prototyping, 2011, 6(1): 47-56.
[29] Vekariya P B, Subbaiah R, Mashru H H. Hydraulics of microtube emitters: A dimensional analysis approach[J]. Irrigation Science, 2011, 29(4): 341-350.
[30] Demir V, Yurdem H, Degirmencioglu A. Development of prediction models for friction losses in drip irrigation laterals equipped with integrated in-line and on-line emitters using dimensional analysis[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2007, 96(4): 617-631.
[31] 刘春景,郑加强,周宏平,等. 滴灌滴头水力性能预测模型[J]. 水利学报,2010,41(11):1353-1359.
Liu Chunjing, Zheng Jiaqiang, Zhou Hongping, et al. Prediction model for hydraulic performance of trickle irrigation emitters[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2010, 41(11): 1353-1359. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 王建国,张文兴. 支持向量机建模及其智能优化[M]. 北京:清华大学出版社,2015.
[33] Vapnik V N. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory[M]. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1999.
[34] Deo R C, Kisi O, Singh V P. Drought forecasting in eastern Australia using multivariate adaptive regression spline, least square support vector machine and M5Tree model[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2017, 184: 149-175.
[35] 杨绍锷,黄元仿. 基于支持向量机的土壤水力学参数预测[J]. 农业工程学报,2007,23(7):42-47.
Yang Shao’e, Huang Yuanfang. Prediction of soil hydraulic characteristic parameters based on support vector machine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2007, 23(7): 42-47. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[36] 张强,黄生志,陈晓宏. 基于支持向量机的土壤湿度模拟及预测研究[J]. 土壤学报,2013,50(1):59-67.
Zhang Qiang, Huang Shengzhi, Chen Xiaohong. Simulation and prediction of soil moisture based on support vector machine technique[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2013, 50(1): 59-67. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[37] 雷国庆,樊贵盛. 基于支持向量机的土壤水分入渗参数预测研究[J]. 节水灌溉,2015(12):28-30.
Lei Guoqing, Fan Guisheng. Research on soil infiltration parameters prediction based on support vector machine[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2015(12): 28-30. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[38] Guo Lin, Bai Dan, Zhou Wen, et al. Evaluation of numerical simulation accuracy for two-ways mixed flow drip irrigation emitter based on CFD[J]. International Journal of Heat and Technology, 2017, 35(2): 384-392.
[39] Anguita D, Ridella S, Rivieccio F, et al. Hyperparameter design criteria for support vector classifiers[J]. Neurocomputing, 2003, 55(1): 109-134.
[40] Tharwat A, Hassanien A E, Elnaghi B E. A ba-based algorithm for parameter optimization of support vector machine[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2017, 93: 13-22.
Establishment and validation of flow rate prediction model for drip irrigation emitter based on support vector machine
Guo Lin1, Bai Dan1※, Wang Xinduan1, Wang Cheng1, Zhou Wen2, Cheng Peng2
(1.,,71004,; 2.,,450011,)
To carry out the prediction and calculation of the flow rate for further study the hydraulic performance and the structure optimization of the flow channel in drip irrigation emitter is of great significance. In order to predict and calculate the flow rate of the emitter accurately, in this study, the prediction and calculation method of Support Vector Machine (SVM) with strong generalization ability was introduced, and the flow rate prediction model of the SVM was built. We chose six working pressures and eight geometric parameters of the flow channel as factors, and arranged 300 sets of emitter schemes as training sample of SVM according to the orthogonal experimental design method, and 30 sets of schemes as test sample. Based on these, the prediction model sample set of flow rate of SVM was established. The flow rate of the emitter was simulated by the SST k-ω model with high precision in the sample set, and compared with the predicted value of flow rate of the SVM. The pressure and geometric parameter of the emitter was taken as the input item, and the flow rate was taken as the output item of SVM. The prediction and simulation of the flow rate were carried out in State Key Laboratory Base of Eco-hydraulic Engineering in Arid Area, Xi’an University of Technology. In order to eliminate the impact of each factor on the predicted results, the input and output item in the emitter sample were normalized before predicting flow rate. At the same time, the Genetic Algorithm was used to optimize the C and δ parameter in the Radial Basis Function (RBF) kernel of the SVM, and then the minimum error between the predicted value and simulated value of flow rate was obtained. The results showed that the relative error between the predicted value of flow rate using SVM and the simulated value was from 0.09% to 6.43%, the average relative error was 1.91%, and the determination coefficient was 0.98 when the optimal values of SVM parameterandwere 100 and 20, respectively. The predicted value of flow rate of SVM had a good correlation with the simulated value, which satisfied the predicted demand for the flow rate of the emitter. However, when the regression fitting method was adopted and calculated, the relative error between the predicted value and the simulated value was from 0.15% to 26.69%, the average relative error was 6.45%, and the determination coefficient was 0.93, which indicated excellent superiority based on SVM. To further verify the reliability of SVM, the five experimental verification schemes were chosen, and manufactured by using high-precision engraving technology. The flow rate value of experimental verification sample was tested under different pressure range, and was compared with the predicted value of flow rate. The relative error between the predicted value of flow rate using SVM and the experimental value was from 0.14% to 5.13%, and the average relative error was 2.25%, which were within the error range, verifying the accuracy and reliability of predicting flow rate using SVM. The establishment of the flow rate prediction response surface based on SVM can effectively improve the development efficiency of the emitter, and provide the evidence and guidance for the hydraulic performance evaluation, the flow channel structure design and optimization.
flow rate; numerical analysis; models; drip irrigation emitter; working pressure; geometric parameter; support vector machine; optimization
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.02.010
S275.6
A
1002-6819(2018)-02-0074-09
2017-10-17
2017-12-20
国家自然科学基金资助项目(51279156、41571222);高等学校博士学科点专项科研基金联合资助课题(20116118110010)
郭 霖,博士生,主要从事节水灌溉技术研究。Email:guolinedu@126.com
白 丹,教授,博士生导师,主要从事节水灌溉理论与技术研究。Email:baidan@xaut.edu.cn
郭 霖,白 丹,王新端,王 程,周 文,程 鹏. 基于支持向量机的滴灌灌水器流量预测模型建立与验证[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(2):74-82. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.02.010 http://www.tcsae.org
Guo Lin, Bai Dan, Wang Xinduan, Wang Cheng, Zhou Wen, Cheng Peng. Establishment and validation of flow rate prediction model for drip irrigation emitter based on support vector machine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(2): 74-82. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.02.010 http://www.tcsae.org
