基于Hilbert-Huang变换的混流泵流动诱导振动试验
2018-02-28季磊磊施卫东杨勇飞平元峰张文全
李 伟,季磊磊,施卫东,杨勇飞,平元峰,张文全
基于Hilbert-Huang变换的混流泵流动诱导振动试验
李 伟,季磊磊,施卫东,杨勇飞,平元峰,张文全
(江苏大学国家水泵及系统工程研究中心,镇江 212013)
混流泵水力诱导的机组振动是混流泵运行失稳的重要因素之一,为了研究混流泵水力激振诱导的机组振动情况,基于本特利408数据采集系统,测量获得了空载和负载工况下混流泵泵体和泵体基座不同位置处的振动信号,通过希尔伯特-黄变换对原始振动信号进行经验筛分分解,获得了不同模函数分量的频谱分布。研究结果表明,相比空载运行,混流泵负载工况运行时水力诱导的机组振动明显加剧,但在不同方向上,水力激振引起的振动各不相同。方向上2个工况下的振动频谱分布基本相似,而在方向、方向和混流泵底座上,负载工况下波形的频带分布变窄,能量分布较为集中,且方向的原始振幅要明显大于方向,约为方向原始振幅的2倍。混流泵负载工况运行时,低频振动占据主要振动能量分布,使得不同模函数分量的主频向低频方向移动,水力诱导混流泵机组的振动以中低频振动为主。该研究可为有效降低或防止混流泵水力诱导的机组振动恶化提供参考。
泵;振动;信号分析;混流泵;空载;希尔伯特-黄变换
0 引 言
混流泵广泛应用于农业排灌、城市供排水、矿山、大型水利工程等领域。在混流泵机组的运行过程中,总是存在着不同程度的振动,一方面是由于轴向平衡共振、转子不平衡、安装原因导致的机械振动,另一方面很多已经确定的振动问题都与流动的大尺度振荡有关。当这些振动超过一定限度时,就会对设备造成不同程度的危害,不仅降低水泵效率,而且缩短了机组零部件的使用寿命,严重时甚至导致机组被迫停机[1-5]。
随着水力机械单机容量和尺寸的增加,人们对流动诱导机组振动的研究越来越重视,许多文献探讨了非定常流动诱导的水力机械系统稳定性问题[6-9]。在水轮机领域,张松松[10]研究了不同工况下额定功率为500 kW的小型混流式水轮发电机组的振动问题,研究发现在负荷变动的过程中,发电机内部磁拉力不平衡,机组的轴线不直和对中不良,以及导叶开度变化造成的水力不平衡是导致轴心轨迹出现大范围偏移的主要原因。Shi等[11]采用数值模拟的方法研究了非定常流动下导叶式水轮机内部的压力脉动特性,发现涡室内压力脉动的时域特性呈明显的周期性变化;压力脉动的主频集中在低频区域,并且是叶片通过频率的2倍。孟龙等[12]发现机组同时存在转子质量不平衡问题及间隙过大问题,根据轴心轨迹特性逐步调整上导及水导间隙。
然而,混流泵作为水力机械的一种,由于水力不稳定诱导机组振动的研究文献较少,大部分学者仅单纯的关注了泵内非定常流场结构或仅单一的研究了泵不稳定运行时的振动特征[13-15]。施卫东等[16]研究了高比转速混流泵不同工况下的叶轮进出口等位置的压力脉动时域和频域特性,研究结果表明混流泵最大压力脉动发生在叶轮进口前,泵运行偏离最优工况越远,叶轮进口处压力系数幅值越大。刘建瑞等[17]研究发现在相同流量下,径向间隙越小,监测点频域振幅越大。李伟等[18]发现流量工况的改变影响了转子系统的不平衡量和不对中程度,并且随着远离设计流量点,不平衡量引起的轴系工频振动和不对中引起的水平方向振动不断加剧。Wang等[19]研究发现,随着流量的增大,压力脉动的峰值逐渐减小,不同监测点处压力脉动的主频为叶片通过频率和其倍频,而不同监测点处的振动频率为轴频和其倍频。
在振动信号的处理方面,希尔伯特-黄变换(Hilbert-Huang transform,HHT)是在傅立叶变换、小波变换等方法的基础上构建的一种信号时频分析理论,它引入了固有模态和经验筛分(empirical mode decomposition,EMD)概念,能够将振动信号分解为有限的具有实际物理意义的本征模函数,并对每个本征模函数进行Hilbert变换,得到每个本征模函数的瞬时频谱,常用来对机械故障进行诊断[20-22]。本文以导叶式混流泵为研究对像,在前期研究其内部流动和轴系振动的基础上[23-24],基于本特利408数据采集系统和希尔伯特-黄变换,对比分析了混流泵空载和负载运行时的振动特性,探索混流泵水力非定常特性诱导的机组振动,为降低或防止混流泵运行中的机组振动恶化提供参考。
1 试验对象及试验装置
1.1 试验对象
本文研究的导叶式混流泵模型的参数如下:流量opt=380 m3/h,扬程=6m,转速=1 450 r/min,比转速s=480。叶片数=4,导叶叶片数d=7。叶轮进口直径in=92 mm,出口直径out=121 mm试验用混流泵模型泵如图1所示。

图1 混流泵模型
1.2 泵外特性试验装置
试验测量在江苏大学国家水泵及系统工程技术研究中心的250 mm不锈钢轴(混)流泵闭式试验台上进行,该试验台专门用于混流泵、轴流泵模型泵段及模型装置试验,试验装置系统如图2所示。
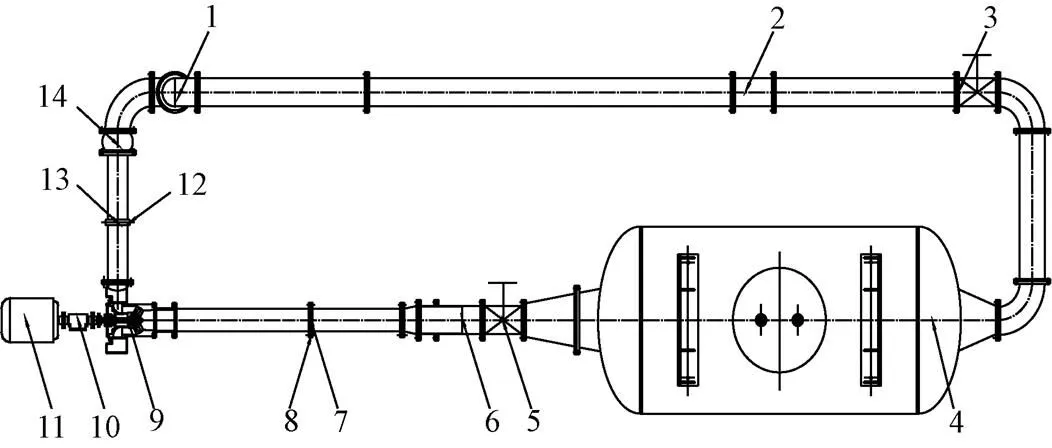
1.增压泵 2.涡轮流量计 3.出口闸阀 4.水箱 5.进口闸阀 6.伸缩管 7.排气孔 8.进口测压段 9.试验泵段 10.扭矩仪 11.电机 12.排气孔 13.出口测压段 14.橡胶软接头
在试验泵段进、出口位置各安置一个麦克公司生产压力变送器以便进行扬程的测量,压力变送器为WT-1151型电容式压力变送器;进口测量用压力变送器测量范围为±100 kPa,精度为0.2;出口测量用压力变送器测量范围为0~600 kPa,精度为0.2。流量测量采用上海自仪九生产的公称压力为1.6 MPa,精度为0.5的LWGY-250型涡轮流量计。采用上海良标智能终端股份有限公司生产的精度为0.2级的ZJ型转矩转速测量仪测量模型泵的轴转速、转矩和轴功率,转矩转速测量仪测量误差为±0.2%。测试系统达到1级精度要求。
2 振动数据采集系统与信号分析方法
2.1 振动数据采集系统
按照试验要求搭建好实验台并连接好数据采集和检测系统。将本特利加速度传感器接入本特利408数据采集系统。试验采用本特利公司生产的200350加速度传感器进行振动信号的采集,该传感器灵敏度系数为100,频率范围0.5~10 kHz,传感器头部有电磁铁,使用时直接将传感器贴于待测位置即可。为了获得混流泵泵体在不同方向上的振动特性,在泵体环形涡室的对称中心处、靠近转轴处和泵体基座上设置了传感器进行监测,传感器的现场布置如图3所示。传感器输出的信号由本特利408数据采集系统进行采集和后处理,该系统由408动态信号处理仪器(DSPi)以及ADRE Sxp软件构成。其中,ADRE Sxp软件可进行各种信号的幅值分析、频谱分析、变化趋势分析等,还可通过自选择滤波绘制伯德图和频谱图以及轴心轨迹等各种试验结果分析曲线。

1.模型泵 2.电机 3. Y方向振动传感器(CH2) 4.底座上振动传感器(CH4) 5. X方向振动传感器(CH1) 6. Z方向振动传感器(CH3) 7.本特利408数据采集系统 8.压力变送器
首先,进行额定负载工况下的试验。在试验开始阶段,将出口阀门全开,先启动泵类产品测试系统并调试好软件,开始记录数据,再启动电机,调节出口阀门,使流量计读数达到设计工况点并且稳定在380 m3/h,转速稳定在1 450 r/min时,分别获取能量性能参数,随后启动并触发本特利408数据采集系统,开始记录泵体的振动信号。关闭电源停机,待管路内流体重新稳定,重新将出口阀门全开,进行上述3次重复性试验,并记录试验数据。在相同运行条件下进行空载试验,关闭混流泵上下游管道阀门,并将泵体内的水排尽,振动信号采集方法与负载试验时相同。
2.2 振动信号的分解和变换
HHT变换是基于信号局部特征,自适应地筛选出模函数分量,克服了小波变换中选择小波基的困难[25]。同时,它可以在时间和频率同时达到很高的精度,克服了传统的傅里叶变换只能得到信号某一段时间内频率的均值,无法准确描述频率-时间变化的缺陷。HHT变换通过生成复解析信号,得到复平面上具有明确解析意义的瞬时频率[26-28]。故本文采用Hilbert-Huang变换对获得的振动信号进行处理。
EMD是用波动上、下包络平均值确定“瞬时平衡位置”的方法,分解过程相当于对原始信号进行分频滤波,最终得到不同频段的特征信号。对于任意时间序列()经过EMD分解,可以得到一系列模函数分量,其表达式如式(1)所示。
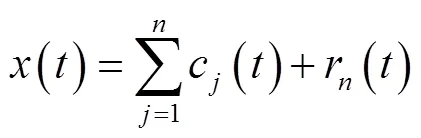
式中本征模式函数1()、2()、···、c()分别表示原始信号中所有频率下由高频到低频的信号成分;余量r()表示信号的趋势项或漂移。
在任意的某一时间序列()时,Hilbert-Huang变换()可表示为

构造解析函数

式中()和()分别称为信号()的瞬时振幅和瞬时相位。其中
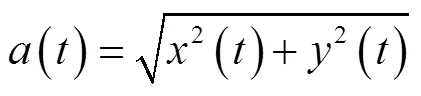
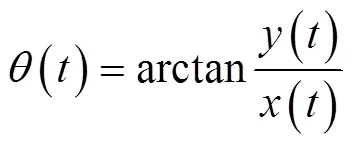
由瞬时相位可得信号的瞬时频率()
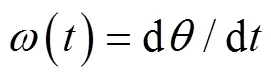
在进行Hilbert-Huang变换之后,各模函数分量可以转化为信号对应的以时间为变量的瞬时振幅和瞬时频率。由于Hilbert-Huang变换对局部特性的要求较高,所以应去除所分析信号在频域中的虚假成分。以时间和频率为自变量,振幅为因变量,就能得到Hilbert-Huang幅值谱(,),即

式中表示取实部;a(),ω()是以时间为变量函数,可以构成时间、频率、幅值的三维时频谱图。
3 试验结果与分析
3.1 能量性能试验结果
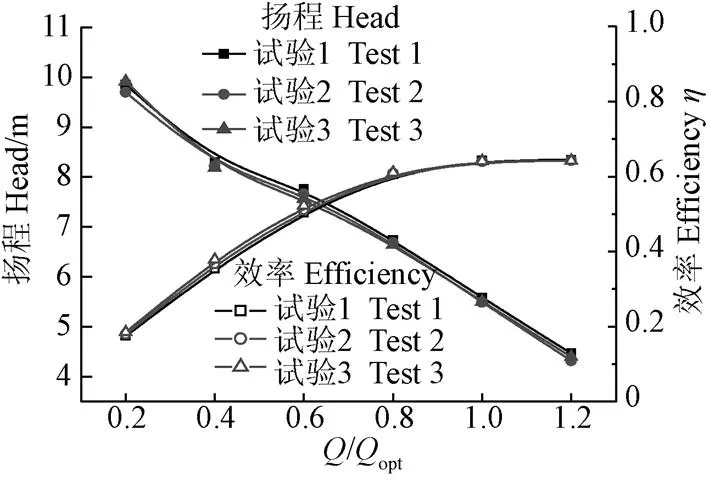
获得混流泵模型3组试验外特性数据,如图4所示。通过试验结果可知,所进行的3次试验所得的扬程和效率曲线基本一致,扬程的最大误差在3%以内而效率误差在2%以内,证明了本次试验可重复性好,试验所得结果可靠性高。
3.2 机组振动信号的EMD分解
测试得到了混流泵在设计流量工况和空载运行下泵体的(CH1)、(CH2)、(CH3)3个方向上的振动信号以及泵体底座上的振动信号(CH4),通过对4个加速度传感器所得信号进行希尔伯特-黄变换,得到了不同传感器所对应的EMD分解图(未全部标出),如图5所示。
注:Q为试验流量工况,m3·h-1;Qopt为设计流量工况,m3·h-1。
由图5可知,从原始信号可以看出,在负载工况下,各个传感器所采集的信号的幅值均有所增加,尤其是泵体上方向、方向和底座上的振动明显增大,而在方向上,振动增加不明显,从2个流量工况下方向传感器对应的EMD分解图可以看出,和空载运行时相似,混流泵在设计流量工况下运行时,方向上各个模函数分量的曲线较为相似,说明混流泵在运行时,水力激振对方向上的振动影响较小,这和混流泵的安装形式和出口方向有关。从2个流量工况下方向和方向传感器对应的原始振动信号和其EMD分解图可以看出,混流泵在空载运行时,其泵体在2个方向上的振动幅值较小,而当混流泵运行在负载工况时,2个方向上的振幅均明显增大,呈条带状分布,并且方向的原始振幅要明显大于方向,约为方向原始振幅的2倍。同时,方向EMD分解图上对应的各模函数分量和剩余项的振幅也均要大于相应的方向上的各分量幅值。
在泵体底座上,虽然传感器所测方向和方向相同,但其原始振动的幅值却略小于方向的振幅,这是由于泵体底座和试验台的接触面积较大,泵体上振动传递到底座上有所减弱,因而振幅相对较小。由于在负载工况下方向上的振幅明显增大,因此,对比方向上空载工况和负载工况下的各模函数分量和剩余项的振幅可知,随时间的变化,负载工况下各模函数分量的振幅在一段时间内存在周期性,各个波峰值和波谷值出现的频次较高且相邻波峰值和波谷值的差值相差不大,而空载工况下各模函数分量的振幅在不同时间段内会出现极值,并且波峰值和波谷值相差较大。因此,在负载工况下,混流泵泵体的整体振动幅值明显增加,而在空载运行下,虽然整泵的振幅较小,但会出现振动极值。综上所述,混流泵在负载运行时,其水力诱导的机组振动明显加剧,EMD分解图上各模函数分量上和剩余项的振幅也明显增加,但在不同方向上,水力激振引起的振动幅值各不相同。

图5 振动信号EMD分解图
3.3 设计工况和空载工况下频谱分析
获得了不同模函数分量的频谱分布(未全部标出),如图6所示。混流泵空载和额定工况载荷下振动原始信号频谱较为复杂,除主频信号及前几阶分频信号外,其余信号大多被宽频信号所覆盖,难以看出其频谱信号特征。经EMD分解后,各阶模函数的频谱分布由模函数1到残余项11,主频呈逐渐降低趋势。结合图5可知EMD成功的将振动信号按频率高低按降序分解出来,其中残余项11与模函数11频率分布主要集中于零附近,其所对应模函数信号周期性也不明显,可判定此两项为分解中产生的虚假分量[29],对于混流泵振动信号分析不具有参考意义。模函数9附近模量的频谱主要成分为轴频(24.16 Hz)以下的低频信号,这部分信号主要对应于叶轮与导叶内部液体回流以及漩涡结构等低频流动现象。模函数5~模函数7模量的频谱能量较高且分布较为集中,对应信号主要来源于转子的转动以及叶轮与导叶叶片之间的动静干涉。模函数1~模函数3模量的频谱主要反应机械的高频信号,根据文献[30]中结论,这部分信号对机组的不稳定以及故障较为敏感。
混流泵在空载时,在不同位置处的频谱分布基本相似,原始信号频谱分布的幅值约为0。而混流泵在负载工况时,各个传感器的频谱分布各不相同。在方向上,2个工况下混流泵的振动频谱分布基本相似,不同模函数分量的频谱分布也基本一致,说明水力激振对方向上的振动影响较小。相比混流泵空载时的频谱分布,在负载工况下,方向上原始信号对应的频谱幅值波动较大,频谱分布较为杂乱,分频成分较多,随着模函数分量的增大,各分量下波形的主频从高频向低频移动。同时,对比2个工况相对应的模函数分量可知,在不同模函数分量下,负载工况波形的频域分布范围略有缩减。对比方向上空载工况和负载工况下的各模函数分量和剩余项的频谱分布可知,在模函数1~模函数3分量下,各个模函数分量的振动频谱出现明显区别,在空载工况下,3个分量下的振动幅值在600 Hz附近有最高值,而在负载工况下,这3个模函数分量下的振动极值从900向300 Hz方向偏移,在其他模函数分量下,振动频谱的极值均出现在200 Hz内,说明混流泵在负载工况下,水力诱导振动以中、低频振动为主。在方向上的振动频谱分布和方向趋势类似,均是随着模函数分量的增大,频域波形的主频从高频向低频移动。同时,相比空载工况,在相同分量下,波形的频带分布变窄,能量分布较为集中,说明水力诱导的机组振动加剧了泵体的振动,并且水力振动使得振动主频向低频移动,这是水力诱导泵体振动最直观的体现。在原始振动波形的频谱分布中,在200~600 Hz内振动频谱的幅值较高,说明该频段内,振动的能量分布较多,水力诱导泵体振动较强。在泵体底座上,从原始信号的频谱分布可以看出,在0~400 Hz内,负载工况下原始波形频谱分布的幅值较高,约为其他频率下幅值的2倍,说明水力因素导致的混流泵底座的振动基本是低频振动。综上所述,混流泵在负载运行时,水力诱导振动对泵体的影响较为明显,低频振动占据主要振动能量分布,使得不同模函数分量的主频向低频方向移动,水力诱导混流泵机组的振动以中、低频振动为主。
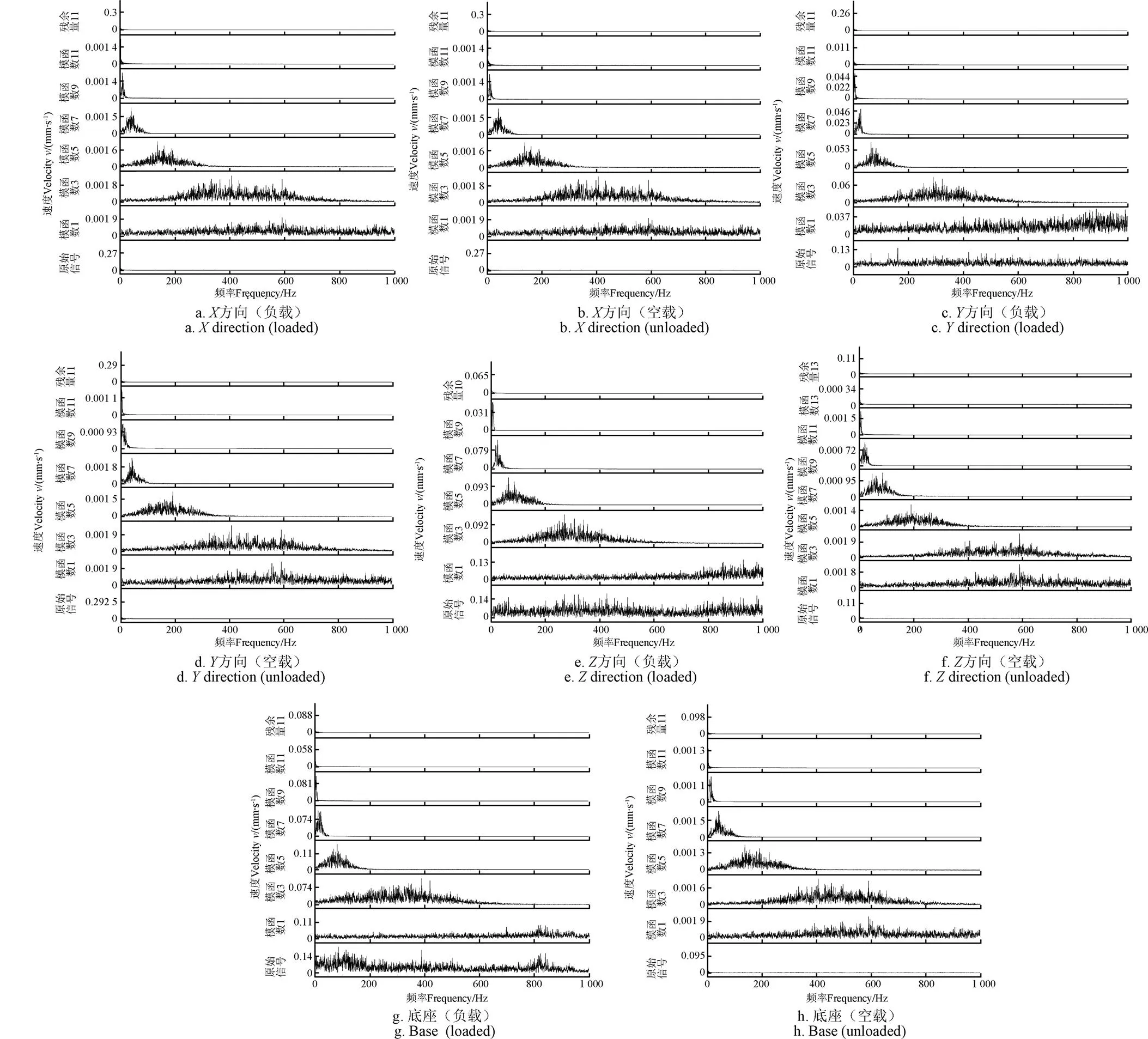
图6 不同模函数分量的频谱分布
4 结 论
1)通过对原始振动信号进行希尔伯特-黄变换可知,混流泵在负载运行时,水力诱导的机组振动明显加剧,但在不同方向上,水力激振引起的振动各不相同,方向、方向和底座上的振动明显增大,而在方向上,振动增加不明显。
2)混流泵空载运行时,在不同位置处的频谱分布基本相似,原始信号频谱分布的幅值约为0。而在负载工况运行时,方向上2个工况下的振动频谱分布基本相似,在方向、方向和混流泵底座上,波形的频带分布变窄,能量分布较为集中,水力诱导的机组振动加剧了泵体的振动。
3)混流泵在负载运行时,低频振动占据主要振动能量分布,使得不同模函数分量的主频向低频方向移动。水力诱导混流泵机组的振动以中低频振动为主。因此,减弱混流泵负载运行时的中低频振动是提高混流泵运行稳定性的关键。
[1] 吕海平. 卧式离心泵受力与轴的振动对泵体破坏分析[J]. 才智,2012,2012(17):49-50.
Lü Haiping. Failure analysis of horizontal centrifugal pump force and shaft vibration on pump body[J].Intelligence, 2012, 2012(17): 49-50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] Christopher S, Kumaraswamy S. Study of noise and vibration signal for a radial flow pump during performance test[J]. Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Power-Contemporary Research, 2017,12: 853-861.
[3] Li W, Shi W, Xu Y, et al. Effects of guide vane thickness on pressure pulsation of mixed-flow pump in pumped-storage power station[J]. Journal of Vibroengineering, 2013, 15(3): 1177-1185.
[4] 李伟, 季磊磊, 施卫东,等.不同流量工况下混流泵压力脉动试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2016, 47(12):70-76.
Li Wei, Ji Leilei, Shi Weidong, et al. Experiment on pressure fluctuation in mixed-flow pump under different flow rate conditions[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(12): 70-76. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] Li W, Ji L, Shi W, et al. Vibration characteristics of the impeller at multi-conditions in mixed-flow pump under the action of fluid-structure interaction[J]. Journal of Vibroengineering, 2016, 18(5): 3213-3224 .
[6] 潘罗平,高明. 水轮机水力稳定性的分析[J]. 长春工程学院学报:自然科学版,2002,3(4):41-43.
Pan Luoping, Gao Ming. Analysis of hydraulic stability of hydraulic turbine[J]. Journal of Changchun Institute of Technology: Natural Science Edition, 2002, 3(4): 41-43. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 陶星明,刘光宁. 高比速混流式水轮机的水力稳定性问题[J]. 大电机技术,2003(4):46-48.
Tao Xingming, Liu Guangning. Hydraulic stability problem of high specific speed mixed flow turbine[J]. Large motor technology, 2003(4): 46-48. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 刘丽娜,潘伟峰,麻志成. 混流式水轮机低负荷运行水力稳定性的研究[J]. 水电自动化与大坝监测,2015(2):20-23. Liu Lina, Pan Weifeng, Ma Zhicheng. Study on hydraulic stability of mixed flow turbine at low load[J]. Hydropower Automation and Dam Monitoring, 2015(2): 20-23. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 成立,吴璐璐,刘超. 大型轴流泵水力不稳定区研究[J]. 灌溉排水学报,2010,29(2):102-104.
Cheng Li, Wu Lulu, Liu Chao. Study on hydraulic instability zone of large axial flow pump[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2010, 29(2): 102-104. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 张松松. 小型混流式水轮发电机组振动试验与分析[D]. 邯郸:河北工程大学,2014.
Zhong Songsong. Vibration Test and Analysis of Small Mixed Flow Turbine[D]. Handan:Hebei University of Engineering, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] Shi F X, Yang J H, Wang X H. Analysis on characteristic of pressure fluctuation in hydraulic turbine with guide vane[J]. International Journal of Fluid Machinery and Systems, 2016, 9(3): 237-244.
[12] 孟龙,刘孟,支发林,等. 机械不平衡及轴瓦间隙对水轮机运行稳定性的影响分析[J]. 机械工程学报,2016,52(3):49-55.
Meng Long, Liu Meng, Zhi Faling, et al. Analysis of the effect of mechanical imbalances and bush clearance on the stability of hydraulic turbines[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2016, 52(3): 49-55. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 李伟,季磊磊,施卫东,等. 混流泵非均匀轮缘间隙流场数值计算[J]. 农业机械学报,2016,47(10):66-72.
Li Wei, Ji Leilei, Shi Weidong, et al. Numerical calculation of the flow field in the nonuniform rim clearance of mixed flow pump[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery 2016, 47(10): 66-72. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 李伟. 导叶式混流泵多工况内部流场的PIV测量[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(24):82-88.
Li Wei. PIV measurement of the internal flow field in multiple conditions of guide vane mixed flow pump[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(24): 82-88. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 季磊磊,李伟,施卫东,等. 导叶式混流泵内部非定常流动特性数值模拟[J]. 农业机械学报,2016,47(增刊1):155-162,188.
Ji Leilei, Li Wei, Shi Weidong, et al. Numerical simulation of unsteady flow in guide vane mixed flow pump[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016,47(Supp.1):155-162,188. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 施卫东,邹萍萍,张德胜,等. 高比转速斜流泵内部非定常压力脉动特性[J]. 农业工程学报,2011,27(4):147-152. Shi Weidong, Zou Pingping, Zhang Deisheng, et al. Unsteady pressure pulsation characteristics in high specific speed slanted flow pump[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2011, 27(4): 147-152. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 刘建瑞,郑俊峰,付登鹏,等. 混流泵径向间隙对内部非定常流场影响的分析[J]. 流体机械,2014(3):19-23.
Liu Jianrui, Zhen Junfemg, Fu Dengpeng, et al. Analysis of the influence of radial clearance on unsteady flow field in mixed flow pump[J]. Fluid machinery, 2014(3): 19-23. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 李伟,季磊磊,施卫东,等. 变流量工况对混流泵转子轴心轨迹的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(4):91-97.
Li Wei, Ji Leilei, Shi Weidong, et al. Effects of variable flow conditions on rotor axis orbit of mixed flow pump[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(4): 91-97. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] Wang K, Liu H, Zhou X, et al. Experimental research on pressure fluctuation and vibration in a mixed flow pump[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2016, 30(1): 179-184.
[20] 薛延刚,罗兴錡,王瀚,等. 基于改进HHT方法提取水轮机动态特征信息研究[J]. 水力发电学报,2011,30(4):214-221.
Xue Yangang, Luo Xingqi, Wang Han, et al. Study on dynamic feature extraction of hydraulic turbine based on improved HHT method[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Power Generation, 2011, 30(4): 214-221. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 梁兴,刘梅清,刘志勇,等. 立式混流泵异常振动测试分析[J]. 排灌机械工程学报,2013,31(5):373-378.
Liao Xing, Liu Meiqing, Liu Zhiyong, et al. Test and analysis of abnormal vibration of vertical mixed flow pump[J]. Drainage and Irrigation Machinery Engineering, 2013, 31(5): 373-378. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 杨国安,王泽栋. 基于改进希尔伯特-黄的泵阀故障诊断新方法[J]. 北京化工大学学报:自然科学版,2008,35(4):81-85.
Yang Guoan, Wang Zeidong. A new method for fault diagnosis of pump valve based on improved Hilbert-Huang[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Chemical Technology: Natural Science Edition, 2008, 35(4): 81-85. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] Li W, Zhou L, Shi W, et al. PIV experiment of the unsteady flow field in mixed-flow pump under part loading condition[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2017, 83(2017): 191-199.
[24] 李伟,季磊磊,施卫东,等. 混流泵起动过程转子轴心轨迹的试验研究[J]. 机械工程学报,2016, 52(22):168-177.
Li Wei, Ji Leilei, Shi Weidong, et al. Experimental study on the rotor axis orbit in the starting process of mixed flow pump[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2016, 52(22): 168-177. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] Zhu K P,Wong Y S,Hong G S. Wavelet analysis of sensor signals for tool condition monitoring: A review and some new results[J]. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, 2009, 49(2009): 537-553.
[26] Zhang Y, Tang B, Xiao X. Time-frequency interpretation of multi-frequency signal from rotating machinery using an improved Hilbert–Huang transform[J]. Measurement, 2016, 82(2016): 221-239.
[27] Interpretation of mechanical signals using an improved Hilbert–Huang transform[J]. Mechanical Systems & Signal Processing, 2008, 22(5): 1061-1071.
[28] Babu T R, Srikanth S, Sekhar A S. Hilbert–Huang transform for detection and monitoring of crack in a transient rotor[J]. Mechanical Systems & Signal Processing, 2008, 22(4): 905-914.
[29] 刘美汝. 基于HHT的主泵飞轮振动监测系统研究[D]. 哈尔滨:哈尔滨工程大学,2015.
Liu Meiru. Research on the Vibration Monitoring System of the Main Pump Flywheel based on HHT[D]. Harbin:Harbin Engineering University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 王若. 火箭发动机涡轮泵实时故障检测方法研究[D]. 成都:电子科技大学,2013.
Wang Ruo. Research on Real Time Fault Detection Method for Turbopump of Rocket Engine[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronics Technology, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Experiment of flow induced vibration of mixed-flow pump based on Hilbert-Huang transform
Li Wei, Ji Leilei, Shi Weidong, Yang Yongfei, Ping Yuanfeng, Zhang Wenquan
(,,212013,)
The vibration induced by flow is one of the important factors to the instability of the mixed-flow pump. With the increase of the capacity and the size of mixed-flow pumps, the vibration of the hydraulic components attracts more attention from researchers and engineers. In order to study the vibration of mixed-flow pump induced by hydrodynamic force, based on the Bentley 408 data acquisition system, vibration signals in 3 directions (,and) on the base under unloaded and designed flow conditions of the mixed-flow pump are tested and then analyzed using Hilbert-Huang transform (HHT). The original vibration signal is decomposed by EMD (empirical mode decomposition) using the Hilbert-Huang transform, and the spectral distribution of the different mode function components is obtained. The decomposed signal contains intrinsic modulus with 11 different orders and one residual. The acquired intrinsic modulus represents vibration signal with different frequencies, except the Intrinsic mode function 11 and the residual, which show no periodic characteristics. The results show that the vibration under loaded condition is significantly increased compared with the unloaded operating condition, but the vibrations caused by the hydraulic excitation differ in different directions. When the mixed-flow pump is working under designed operating condition, the low frequency vibration occupies the main vibration energy distribution, making the main mode of the different mode function components move to the low frequency direction, and the hydraulic induced vibration is dominated by the middle and low frequency vibration. In thedirection, the vibration spectrum distribution is similar in the 2 cases, while in theanddirection and on the base of mixed-flow pump the frequency distribution of the waveform is narrowed and the energy distribution is concentrated under loaded condition. Under both loaded and unloaded conditions, the main frequency of the spectrum moves toward the low frequency region with the increase of the modulus order. The difference of the frequency spectrum under loaded and unloaded conditions is more obvious for the intrinsic modulus with lower order, namely Intrinsic mode function 1-3. Under unloaded condition, frequency spectrum of the Intrinsic mode function 1-3 reaches the highest value near 600 Hz; while under loaded operating condition, the position for the peak values moves from 900 to 300 Hz for the spectrum of the intrinsic modulus of the first 3 orders. For the other intrinsic moduli, the peak of the frequency spectrum is distributed below 200 Hz, which indicates that the vibration induced by flow is mainly composed of low and middle frequency vibrations. Compared with the frequency spectrum of vibration signal under unloaded condition, the distribution of vibration spectrum under loaded operating condition is narrower, and the power distribution of the vibration is more concentrated, indicating that the vibration induced by flow increases the vibration of the pump and the hydraulic vibration makes the main frequency of the pump vibration move toward the low frequency region in the frequency spectrum. In the original spectrum under loaded operating condition, the amplitude of the vibration spectrum is higher in the region of 200-600 Hz, which indicates that the vibration power is high in this frequency section, and the vibration caused by hydraulic force is greater there. According to the original vibration signal on the base of the pump, it was found that in the frequency region from 0 to 400 Hz, the amplitude of the vibration spectrum under loaded operating condition is 2 times higher than that of other frequencies, which indicates that low frequency vibration occupies the vibration on the base of the mixed-flow pump. The research results have important engineering application value and theoretical guidance for effectively reducing or preventing the vibration of mixed-flow pumps.
pumps; vibrations; signal analysis; mixed-flow pump; unloaded condition; Hilbert-Huang transform
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.02.007
TH313
A
1002-6819(2018)-02-0047-08
2017-07-02
2017-12-08
国家自然科学基金项目(51679111、51579118);江苏省自然科学基金项目(BK20161472);江苏高校优势学科建设工程资助项目(PAPD)
李 伟,博士,研究员,博士生导师,主要研究方向为流体机械(泵)的优化设计、流场计算和动力学特性研究。Email:lwjiangda@ujs.edu.cn
李 伟,季磊磊,施卫东,杨勇飞,平元峰,张文全. 基于Hilbert-Huang变换的混流泵流动诱导振动试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(2):47-54. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.02.007 http://www.tcsae.org
Li Wei, Ji Leilei, Shi Weidong, Yang Yongfei, Ping Yuanfeng, Zhang Wenquan. Experiment of flow induced vibration of mixed-flow pump based on Hilbert-Huang transform[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(2): 47-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.02.007 http://www.tcsae.org
