不同他汀药物短期、大剂量应用对行冠状动脉介入治疗患者肾功能的保护作用
2017-11-16娄明宫海滨刘奕王璐璐曹秋玫
娄明+宫海滨+刘奕+王璐璐++曹秋玫
[摘要] 目的 探讨不同的他汀药物短期、大剂量应用对行冠脉介入治療的患者术后肾功能的影响及其可能的机制。 方法 选择2015年3月~2016年3月在徐州市中心医院心内科行冠脉介入治疗的患者180例,按随机数字表法将其随机分为瑞舒伐他汀组、阿托伐他汀组和对照组,每组各60例。术前3 d至术后3 d,瑞舒伐他汀组给予瑞舒伐他汀20 mg/d治疗,阿托伐他汀组给予阿托伐他汀80 mg/d治疗,对照组不给予任何他汀药物治疗。三组患者术前、术后48~72 h采血测定血肌酐和超敏C反应蛋白水平,比较三组对比剂肾病的发生率、术前及术后超敏C反应蛋白水平。 结果 瑞舒伐他汀组和阿托伐他汀组对比剂肾病发病率明显低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),瑞舒伐他汀组与阿托伐他汀组比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。瑞舒伐他汀组和阿托伐他汀组术后超敏C反应蛋白升高程度均低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),但瑞舒伐他汀组和阿托伐他汀组比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。 结论 瑞舒伐他汀和阿托伐他汀短期、大剂量应用可以降低对比剂肾病的发病率,并且可以降低术后超敏C反应蛋白的升高。
[关键词] 经皮冠状动脉介入治疗;他汀;对比剂肾病;血肌酐;超敏C反应蛋白
[中图分类号] R692 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-7210(2017)10(b)-0057-04
Protective effect of short-term and high dose of different statins for the renal function of patients underwent percutaneous coronary intervention
LOU Ming1 GONG Haibin2 LIU Yi1 WANG Lulu1 CAO Qiumei1
1.Department of Cardiology, Xuzhou Central Hospital, Jiangsu Province, Xuzhou 221009, China; 2.Xuzhou Institue of Cardiovascular Disease, Jiangsu Province, Xuzhou 221009, China
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the effect of short-term and high dose of different statins on the renal function of patients underwent percutaneous coronary intervention and its possible mechanism. Methods One hundred and eighty patients underwent percutaneous coronary intervention in Department of Cardiology, Xuzhou Central Hospital from March 2015 to March 2016 were selected, and they were randomly divided into Rosuvastatin group, Atorvastatin group, and control group according to the random number table, with 60 cases in each group. From 3 d before operation to 3 d after operation, Rosuvastatin group was treated with 20 mg/d, Atorvastatin group was treated with Atorvastatin 80 mg/d, the control group was not given any statins. Before operation and 48-72 h after operation, the blood of three groups was draw to detect the levels of serum creatinine and hypersensitive C-reactive protein. The incidence of contrast-induced nephropathy and the levels of hypersensitive C-reactive protein among the three groups were compared. Results The incidence of contrast-induced nephropathy in Rosuvastatin group and Atorvastatin group was lower than that of control group, there were statistically significant differences (P < 0.05), while there was no statistically significant difference between Rosuvastatin group and Atorvastatin group (P > 0.05). The increased degree of postoperative hypersensitive C-reactive protein in Rosuvastatin group and Atorvastatin group was lower than that of control group, there were statistically significant differences (P < 0.05), while there was no statistically significant difference between Rosuvastatin group and Atorvastatin group (P > 0.05). Conclusion Short-term and high dose of Rosuvastatin and Atorvastatin can decrease the incidence of contrast-induced nephropathy and the increase of postoperative hypersensitive C-reactive protein.endprint
[Key words] Percutaneous coronary intervention; Statin; Contrast-induced nephropathy; Serum creatinine; Hypersensitive C-reactive protein
早在20世紀90年代,Nash等[1]就发现冠脉介入术后患者发生肾功能不全的概率为7.2%,对比剂引起的急性肾损害-对比剂肾病在临床越来越得到重视,Gleeson等[2]和McCullough等[3]研究发现行经皮冠状动脉介入治疗(PCI)的患者中高危人群对比剂肾病的发生率可高达40%~50%。为此,2005年欧洲泌尿生殖放射协会(European society of urogenital radiology,ESUR)建议对比剂肾病的诊断标准:与基线值相比,接触对比剂后72 h内血清肌酐相对值升高25%或绝对值升高0.5 mg/dL,并除外其他可能的原因。对比剂肾病的确切发病机制尚未完全阐明。目前的研究表明,肾髓质缺血缺氧性损伤及对比剂对肾小管上皮细胞的直接毒性作用是发生对比剂肾病的主要机制[4-6]。迄今为止,指南尚未推荐某种药物来预防对比剂肾病的发生。近年来,国内外的学者开始探索在PCI术前术后短期、大剂量应用他汀来减少对比剂肾病的发生[7-9],但是样本量都不大,而且所应用的他汀几乎都是阿托伐他汀,对于瑞舒伐他汀、辛伐他汀等不同的他汀很少有研究。本研究是单中心、前瞻性随机对照研究,探讨大剂量瑞舒伐他汀和阿托伐他汀短期治疗对对比剂肾病的预防效果,同时联合检测超敏C反应蛋白,探讨炎性反应是否参与了对比剂肾病的发病过程。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
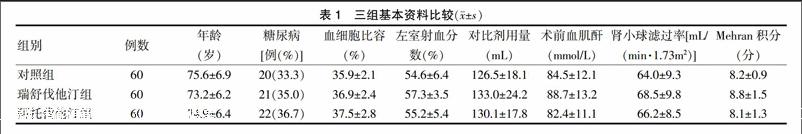
本研究入选2015年3月~2016年3月在徐州市中心医院心内科住院行PCI的患者180例。所有患者通过随机数字表法分为三组,分别为对照组、瑞舒伐他汀组和阿托伐他汀组,每组60例。纳入标准:自愿参与研究并签署书面知情同意书;年龄满18岁;Mehran积分≥6分;入选前至少14 d内未服用他汀类药物。排除标准:已知存在任何研究药物过敏反应史;怀孕或哺乳期女性;心源性休克;造影前7 d内动脉或静脉内注射其他含碘对比剂;造影前7 d内应用肾毒性药物;感染性发热,严重肝病;已经参与了另一项临床试验。使用对比剂为非离子型等渗对比剂碘克沙醇320 mgⅠ/mL。本研究方案已通过医院伦理委员会批准。三组患者术前基本资料经统计学分析,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),具有可比性。见表1。
1.2 方法
术前3 d至术后3 d,对照组不给予任何他汀药物治疗,瑞舒伐他汀组给予瑞舒伐他汀20 mg/d治疗,阿托伐他汀组给予阿托伐他汀80 mg/d治疗,术后第4天根据病情需要选择是否继续他汀治疗。三组患者入院后常规测定基线血肌酐和超敏C反应蛋白,术后48~72 h再次采血测定,若发现血肌酐相对值升高25%或绝对值升高0.5 mg/dL,则诊断为对比剂肾病,血肌酐标本采用日立7600全自动生化仪检测,超敏C反应蛋白标本采用深圳新产业MAGLUMI 2000检测仪,使用化学发光法。三组患者在术前6 h至术后6 h以1 mL/(kg·h)的速度给予生理盐水维持静滴,对于重症心衰患者采用半量水化方案。
1.3 统计学方法
采用SPSS 23.0统计软件包进行统计学分析。计量资料采用均数±标准差(x±s)表示,组内比较采用t检验,多组计量资料比较采用方差分析,计数资料以百分比(%)表示,采用χ2检验。以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 三组对比剂肾病发病率比较
瑞舒伐他汀组和阿托伐他汀组的对比剂肾病发病率(5.0%、6.7%)均低于对照组(11.7%),差异均有统计学意义(P = 0.011、0.038),瑞舒伐他汀组与阿托伐他汀组比较,差异无统计学意义(P = 0.554)。
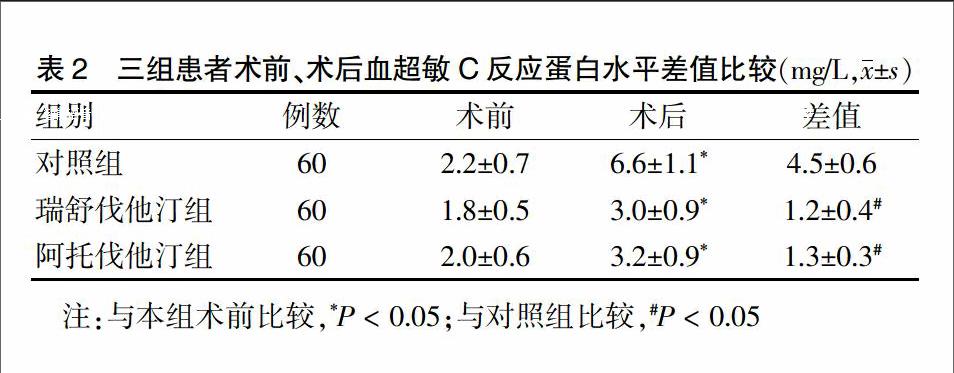
2.2 三组术前、术后血超敏C反应蛋白水平差值比较
三组术后血超敏C反应蛋白水平均较术前明显升高,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。瑞舒伐他汀组和阿托伐他汀组患者术前与术后血超敏C反应蛋白水平差值与对照组差异均有统计学意义(P = 0.005、0.010),瑞舒伐他汀组与和阿托伐他汀组比较差异无统计学意义(P = 0.125)。见表2。
3 讨论
对比剂肾病发病机制复杂,目前确切的机制尚未完全阐明。目前的研究倾向于对比剂对肾小管上皮细胞产生的直接毒性效应及影响血管活性物质导致肾血流动力学改变引起的肾髓质缺血性损伤是对比剂肾病发生的主要机制[10-13]。他汀类药物作为羟甲基戊二酰辅酶A(HMG-COA)还原酶选择性抑制剂,可降低血胆固醇水平,众多临床研究发现,他汀类药物对肾脏有保护作用,可降低对比剂肾病的发生率,可能与以下机制有关:①他汀类药物抗氧化应激。他汀类药物通过抑制Rac1介导的NADPH氧化酶活性和下调血管紧张素AT1受体的表达,从而降低血管紧张素Ⅱ诱导的超氧自由基水平。②他汀类药物可改善肾脏血流动力学。他汀类药物通过下调血管紧张素受体和减少内皮素的合成[14],增加一氧化氮的合成和生物利用度[15],从而减少肾脏血流灌注不足和局部缺血,以保护肾脏损害的发生。③他汀类药物抑制炎性反应。他汀能更进一步显著减少超敏C反应蛋白,从而通过抑制超敏C反应蛋白介导的趋化因子的分泌、细胞黏附分子(P-选择素、细胞间黏附分子-1)的上调和趋化作用而发挥抗感染作用,从而改善内皮功能,减少对比剂肾病的发生[16]。国内有学者对210例接受冠脉造影检查或介入治疗的不稳定心绞痛患者的随机化临床研究显示,围术期服用阿托伐他汀40 mg/d可明显抑制血清肌酐(Scr)峰值和△Scr的增加(P < 0.05),其对比剂肾病发生率较单纯水化患者显著降低(5.71%比14.29%,P < 0.05)[17]。有研究比较246例行冠状动脉介入诊断与治疗的患者,术前3 d服用阿托伐他汀40 mg/d,术后尿α1微球蛋白(α1-MG)及尿肌酐水平明显低于单纯水化组(P < 0.05),对比剂肾病的发生率也显著降低(0.81%比8.13%,P < 0.05)[18]。本研究中也发现他汀组均较对照组对比剂肾病发病率低,且有统计学差异(P < 0.05),但是两组他汀患者对比剂肾病发病率相比无统计学差异(P > 0.05),并没有显示出他汀的异质性。endprint
C反應蛋白是五聚体蛋白家族成员之一,是天然免疫系统的重要成分。而采用超敏感方法检测到的<10 mg/L的C反应蛋白被称为超敏C反应蛋白。近年来研究发现,超敏C反应蛋白在机体防御反应、心血管疾病、自身免疫病等疾病中扮演着极其重要的角色。超敏C反应蛋白是区分低水平炎症状态的灵敏指标,其主要作用是调理感染,激活补体,参与细胞凋亡。国内汪斌等[19]研究表明,冠脉介入诊治中患者超敏C反应蛋白的升高与对比剂肾病的发生有显著相关性;苏津自等[20]研究显示,术前超敏C反应蛋白水平升高是对比剂肾病的独立危险因素。本研究中,三组患者术后超敏C反应蛋白水平均较术前升高(P < 0.05),说明对比剂引起了患者体内炎性反应水平的升高。其中瑞舒伐他汀组和阿托伐他汀组患者术后超敏C反应蛋白升高程度均较对照组低,且有统计学差异(P < 0.05),说明他汀具有抗炎、改善肾功能的作用[21-23]。本研究发现,两组他汀患者之间术后超敏C反应蛋白升高程度相比无统计学差异(P > 0.05),从抑制炎性反应的机制来看,两种他汀并没有显示出异质性,与既往研究结论一致[24-25]。
本研究是单中心前瞻性随机对照研究,样本数量较小,没有做到双盲,故存在一定的局限性。本研究结果显示,接受PCI的患者术前短期、大剂量应用他汀类药物可减少术后对比剂肾病的发生,同时减轻体内的炎性反应。未来临床研究中需要更大样本量、多中心、随机对照、双盲的临床试验来进一步验证他汀类药物对肾功能的保护作用。
[参考文献]
[1] Nash K,Hafeez A,Hou S. Hospital-acquired renal insuf?鄄ficiency [J]. Am J Kidney Dis,2002,39(5):930-936.
[2] Gleeson TG,Bulugahapitiya S. Contrast-induced nephro?鄄pathy:Review [J]. AJR,2004,183:1673-1689.
[3] McCullough PA,Choi JP,Feghali GA. Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury [J]. J Am Coll Cardiol,2016,68(13):1465-1473.
[4] Heinrich MC,Kuhlmann MK,Grgic A,et al. Cytotoxic effects of ionic high-osmolar,nonionic monomeric,and nonionic iso-osmolar dimeric iodinated contrast media on renal tubular cells in vitro [J]. Radiology,2005,235(3):843-849.
[5] Ozkok S,Ozkok A.Contrast-induced acute kidney injury:A review of practical points [J]. World J Nephrol,2017,6(3):86-99.
[6] Fahling M,Seeliger E,Patzak A,et al. Understanding and preventing contrast-induced acute kidney injury [J]. Nat Rev Nephrol,2017,13(3):169-180.
[7] Patti G,Ricottini E,Nusca A,et al. Short-term,high-dose Atorvastatin pretreatment to prevent contrast-induced nephropathy in patients with acute coronary syndromes undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention(from the ARMYDA-CIN atorvastatin for reduction of myocardial damage during angioplasty--contrast-induced nephro?鄄pathy trial)[J]. Am J Cardiol,2011,108(1):1-7.
[8] Su X,Xie X,Liu L,et al. Comparative Effectiveness of 12 Treatment Strategies for Preventing Contrast-Induced AcuteKidney Injury:A Systematic Review and Bayesian Network Meta-analysis [J]. Am J Kidney Dis,2017,69(1):69-77.
[9] Syed MH,Khandelwal PN,Thawani VR,et al. Efficacy of Atorvastatin in Prevention of Contrast-induced Nephro?鄄pathy in High-risk Patients Undergoing Angiography:A Double-blind Randomized Controlled Trial [J]. J Phar?鄄macol Pharmacother,2017,8(2):50-53.
[10] Ilan Goldenberg,Shlomi Matetzky. Nephropathy induced by contrast media:pathogenesis,risk factors and preventive strategies [J]. Can Med Assoc,2005,172(11):1461.endprint
[11] Tumlin J,Stacul F,Adam A,et al. Pathophysiology of contrast induced nephropathy [J]. Am J Cardio,2006,98(6A):14.
[12] Hogstrom B,Ikei N. Physicochemical properties of radio?鄄graphic contrast media,potential nephrotoxicity and proph?鄄ylaxis [J]. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol,2015,42(12):1251-1257.
[13] Wichmann JL,Katzberg RW,Litwin SE,et al. Contrast-Induced Nephropathy [J]. Circulation,2015,132(20):1931-1936.
[14] Ichiki T,Takeda K,Tokunou T,et al. Downregulation of angiotensin 11 type 1 receptor by hydrophobic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors in vascular smooth muscle cells [J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol,2001,21(3):1896-1901.
[15] Sabbatini M,Pisani A,Uccello F,et al. Atorvastatin im?鄄proves the course of ischemic acute renal failure in aging rats [J]. J Am Soc Nephrol,2004,15(4):901-909.
[16] Xinwei J,Xianghua F,Jing Z,et al. Comparison of use?鄄fulness of simvastatin 20 mg versus 80 mg in preventing contrast-induced nephropathy in patients with acute coronary syndrome undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention [J]. Am J Cardiol,2009,104(16):519-524.
[17] 邵磊,董靜,海冰峰,等.阿托伐他汀预防对比剂肾损害的随机化临床研究[J].医药论坛杂志,2011,32(5):95.
[18] 张东亚,朱静,陈建昌,等.阿托伐他汀对造影剂肾病的预防作用[J].苏州大学学报,2011,31(2):290.
[19] 汪斌,刘志忠,张丰富,等.冠状动脉介入诊治中高敏C反应蛋白与造影剂肾病的相关性分析[J].中国医药,2007, 2(8):457-459.
[20] 苏津自,薛艳,蔡文钦,等.高敏C反应蛋白水平与阿托伐他汀对急性冠状动脉综合征患者对比剂所致肾功能损害影响的关系[J].中华心血管病杂志,2011,39(9):807-811.
[21] Dasari TW,Cohen DJ,Kleiman NS,et al. Statin therapy in patients with chronic kidney disease undergoing percu?鄄taneous coronary intervention(from the Evaluation of Drug Eluting Stents and Ischemic Events Registry)[J]. Am J Cardiol,2014,113(4):621-625.
[22] Leoncini M,Toso A,Maioli M,et al. Early high-dose rosuvastatin for contrast-induced nephropathy prevention in acute coronary syndrome:Results from the PRATO-ACS Study(Protective Effect of Rosuvastatin and Antiplatelet Therapy On contrast-induced acute kidney injury and myocardial damage in patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome)[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol,2014,63(1):71-79.
[23] Kaneko H,Yajima J,Oikawa Y,et al. Effects of statin treatment in patients with coronary artery disease and chronic kidney disease [J]. Heart Vessels,2014,29(1):21-28.
[24] Patti G,Leoncini M,Toso A,et al. Impact of high-dose statin pre-treatment and contrast-induced acute kidney injury on follow-up events in patients with acute coronary syndrome undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention [J]. Int J Cardiol,2014,174(2):440-441.
[25] Cheungpasitporn W,Thongprayoon C,Kittanamongkolchai W,et al. Periprocedural effects of statins on the incidence of contrast-induced acute kidney injury:a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Ren Fail,2015,37(4):664-671.
(收稿日期:2017-06-11 本文编辑:张瑜杰)endprint
