白藜芦醇对肠缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用
2017-09-27荣愈平刘胜武赵端仪
魏 莱,荣愈平,刘胜武,赵端仪
白藜芦醇对肠缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用
魏 莱1,2,荣愈平3,刘胜武1,赵端仪2
目的探讨白藜芦醇(Resveratrol,RSV)对肠缺血再灌注损伤的作用及分子机制。方法30只SD大鼠随机分成假手术组(Sham组)、肠缺血再灌注损伤组(IRI组)和白藜芦醇预处理组(RSV组)。检测各组沉默信息调节因子1(SIRT1)、乙酰化p53(Acetylp53)、p53、bax、bcl-2、凋亡诱导因子(AIF)和TUNEL,观察肠组织病理形态。结果与Sham组相比,IRI组肠组织病理形态改变以及Acetylp53、bax、细胞浆AIF、TUNEL表达明显增加,而SIRT1和bcl-2表达明显降低。与IRI组相比,RSV组肠组织病理形态改变及Acetylp53、bax、细胞浆AIF、TUNEL表达明显减少,而SIRT1和bcl-2表达明显增加。此外,三组之间p53表达差异无统计学意义。结论RSV可通过抗凋亡减轻肠缺血再灌注损伤,其作用机制与SIRT1/p53信号通路相关。
白藜芦醇;肠缺血再灌注损伤;SIRT1/p53
0 引言
肠缺血再灌注损伤(Intestinal ischemia reperfusion injury)是指肠道血供中断或减少,重新恢复肠道血供导致肠道损伤进一步加重的临床危相,其发病机制复杂,目前尚未完全阐明,既往研究提示,凋亡与肠缺血再灌注损伤密切相关[1-4]。白藜芦醇(Resveratrol,RSV)是一种来源于多种植物的类黄酮化合物[5-7]。既往研究发现,其可通过凋亡减轻脑和肝脏缺血再灌注损伤[8-9]。因此,本实验拟探讨RSV对肠缺血再灌注损伤的作用及其分子机制。
1 材料和方法
1.1 材料 白藜芦醇(Sigma,USA)经HPLC鉴定纯度超过99%,水合氯醛(武汉谷歌),SIRT1(CST,USA),AIF(CST,USA),Acetylp53(CST,USA),p53(CST,USA),bax(CST,USA),bcl-2(CST,USA),TUNEL(CST,USA),β-actin(Abgent,USA)。HE试剂由湖北省人民医院病理实验室配制。显微镜(Olympus BX51)及成像系统(HITMAS-30)均由湖北省人民医院病理实验室提供。胞浆和线粒体试剂提取盒(碧云天,武汉)。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 分组及建模 雄性SD大鼠30只,体重(220±20)g,合格证号:SCXK(京)2012-2017,由武汉大学实验动物中心提供。放置在SPF动物饲养室内喂养。适应性喂养1周后,状态良好,按体重随机分为假手术组(Sham组)、肠缺血再灌注损伤组(IRI组)和白藜芦醇预处理组(RSV组),每组10只。RSV组术前1 h给予RSV腹腔注射(20 mg/kg),剂量参考文献[10]。Sham组和IRI组则给予等量生理盐水腹腔注射,IRI组和RSV组行小肠缺血再灌注损伤手术。具体手术方式如下:大鼠在腹腔注射10%水合氯醛(4 mL/kg)麻醉状态下,行腹部正中切口,钝性分离肠系膜上动脉根部(SMA),用微血管夹夹闭SMA根部,完全阻断血流45 min后松开血管夹,恢复肠道血流形成再灌注。缝合腹部,再灌注4 h后处死大鼠,收集标本。Sham组操作同上,但开腹后不夹闭肠系膜上动脉。
1.2.2 肠道组织学检查 小肠组织切片经10%中性甲醛固定、石蜡包埋,HE染色之后,在光镜下观察小肠组织病理学变化。小肠损伤程度参考文献[11]报道的积分法评估。0分为正常绒毛和腺体;1分为部分绒毛顶部上皮轻度受损;2分为上皮下腺体轻度受损;3分为上皮下间隙扩大,毛细血管充血;4分为上皮与固有层中度分离,腺体受损;5分为部分绒毛顶部脱落;6分为绒毛脱落明显,毛细血管扩张;7分为固有层绒毛脱落,腺体受损明显;8分为固有层开始消化分解;9分为出血、溃疡。
1.2.3 TUNEL法检测大鼠肠道细胞凋亡 按照试剂盒说明书检测肠道TUNEL表达,显微镜下观察。
1.2.4 Western blot检测 取肠道组织,按照每50 mg组织中加入1 mL RIPA裂解液(以1∶50加入50×cocktail),冰上匀浆,裂解30 min后,4 ℃ 12 000 r/min离心30 min后取上清,BCA法测定蛋白浓度,检测AIF、p53、Acetylp53、SIRT1、bax和bcl-2蛋白表达水平,具体方法参考文献[11-12]。

2 结果
2.1 RSV对肠缺血再灌注损伤导致的病理改变的影响 与Sham组相比,IRI组小肠腺体受损,毛细血管充血、水肿及绒毛脱落、糜烂、炎性细胞浸润明显增加(P<0.05),其损伤评分为(5.5±1)分,而Sham组损伤评分为(0.5±0.2)分。与IRI组相比,RSV组小肠腺体受损及毛细血管充血、水肿及绒毛脱落、糜烂、炎性细胞浸润明显减少(P<0.05),其损伤评分为(1.5±0.5)分。提示RSV预处理可减轻肠缺血再灌注损伤诱导的肠道病理改变。见图1。
2.2 RSV对各组大鼠TNUEL表达的影响 与Sham组相比,IRI组TUNEL表达明显增高(P<0.05);与IRI组相比,RSV组TUNEL表达明显降低(P<0.05)。见图2。

图1 HE检测RSV对肠组织病理改变的影响(×100)
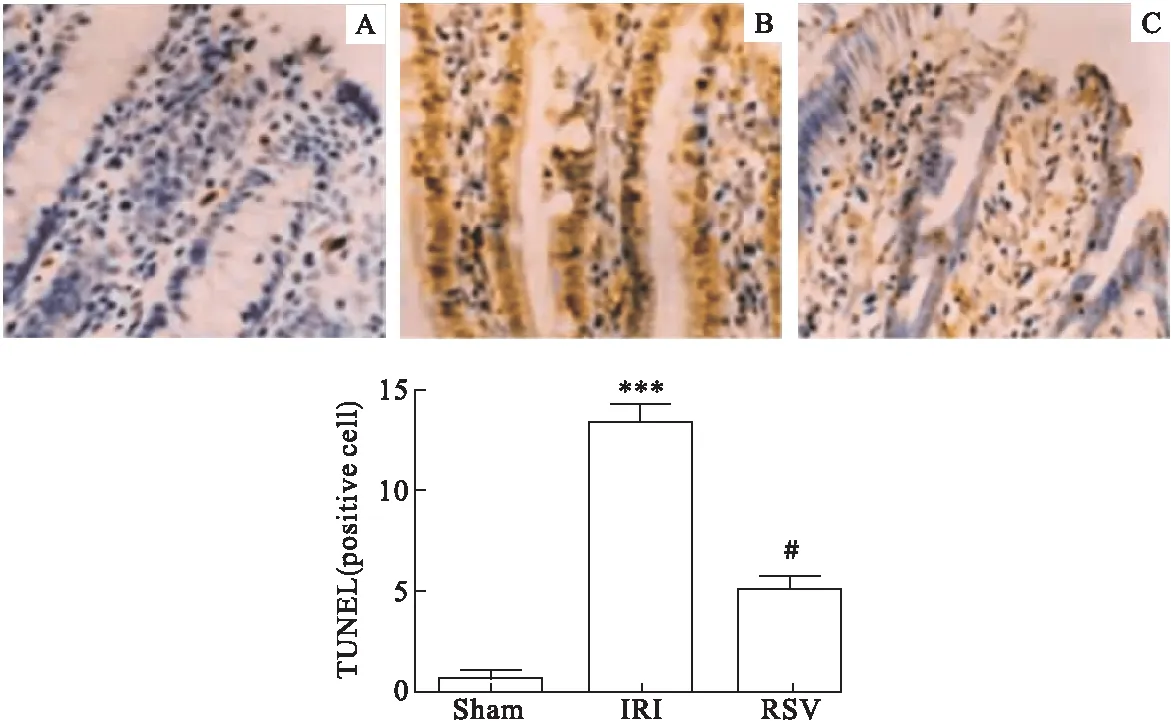
图2 免疫组化检测RSV对肠细胞凋亡的影响(×100)
2.3 RSV对肠组织凋亡相关蛋白的影响 与Sham组相比,IRI组促凋亡蛋白bax表达明显增加(P<0.05),而抗凋亡蛋白bcl-2表达明显减少(P<0.05)。与IRI组相比,RSV组促凋亡蛋白bax表达明显减少(P<0.05),而抗凋亡蛋白bcl-2表达明显增加(P<0.05)。见图3。
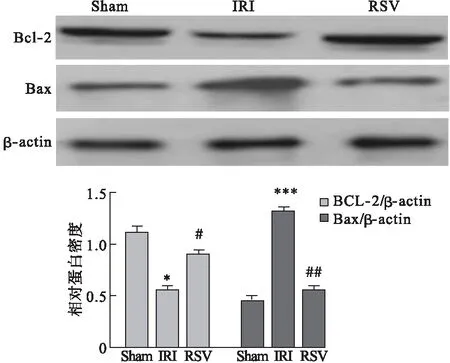
图3 Western blot检测RSV对bax和bcl-2蛋白表达影响
注:与Sham组比较,*P<0.05,***P<0.001;与IRI组比较, #P<0.05,##P<0.01
2.4 RSV对SIRT1表达的影响 Western blot结果显示,与Sham组相比,IRI组SIRT1蛋白表达明显降低(P<0.05),而RSV组SIRT1蛋白表达明显增加(P<0.05)。见图4。
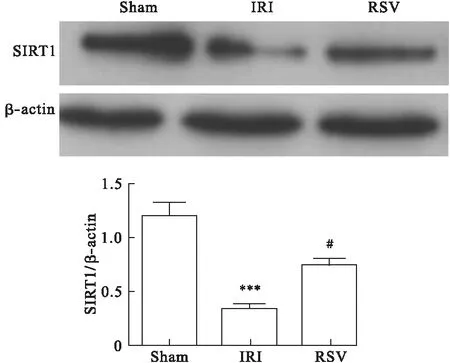
图4 Western blot检测RSV对SIRT1蛋白表达的影响
2.5 RSV对p53信号蛋白的影响 Western blot结果显示,与Sham组相比,IRI组Acetylp53蛋白表达明显增加(P<0.05),而RSV组Acetylp53蛋白表达明显减少(P<0.05),三组之间p53蛋白表达差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见图5。
2.6 RSV对细胞浆和线粒体AIF表达的影响 与Sham组相比,IRI组细胞浆AIF表达明显增高(P<0.05),而线粒体AIF表达明显减少(P<0.05);与IRI组相比,RSV组细胞浆AIF表达明显降低(P<0.05),而线粒体AIF表达明显增加(P<0.05)。见图6。
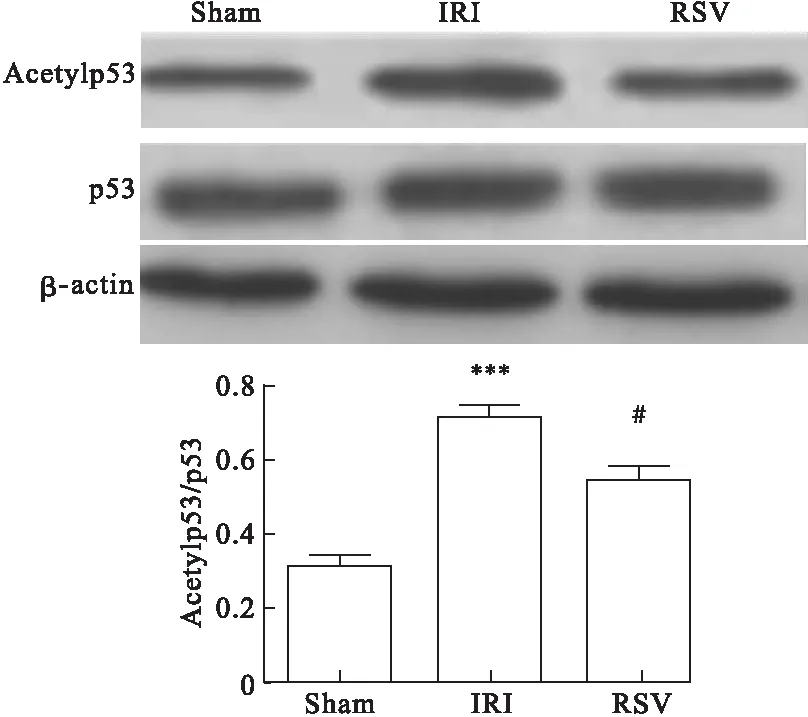
图5 Western blot检测RSV对Acetylp53和p53蛋白表达的影响

图6 Western blot检测RSV线粒体和细胞浆AIF蛋白表达的影响
3 讨论
缺血再灌注损伤是休克、创伤及移植等疾病共同存在的病理生理过程,可诱发许多严重并发症。小肠是机体对缺血再灌注损伤最敏感的器官之一[1-3]。在肠系膜血管缺血性疾病,如小肠移植、肠绞窄、肠梗阻等情况下,均会导致不同程度的小肠缺血性损伤,在肠组织恢复供血时,再灌注会进一步加重小肠的损伤[1,4]。既往许多研究证实,小肠是机体最大的细菌和内毒素库,肠缺血再灌注损伤会加重消化道损伤,降低小肠的生理屏障功能,导致肠内细菌和内毒素移位,诱导肠道网状内皮系统广泛激活,导致大量炎症因子释放入血,诱发毒血症、全身炎症反应综合征,乃至多器官功能不全综合征的发生[1-4]。随着研究的深入,多项研究结果显示,凋亡在肠缺血再灌注损伤中发挥重要作用[1-4]。因此,抑制凋亡是减轻肠缺血再灌注损伤的有效途径。RSV是SIRT1激动剂,既往研究提示,其可通过凋亡减轻肝脏、脑等器官缺血再灌注损伤[8-9]。本研究结果提示,RSV预处理可明显降低肠道病理改变和凋亡细胞标志物TUNEL表达。提示RSV可通过抗凋亡作用减轻肠缺血再灌注损伤。
SIRT1是一种去乙酰化修饰酶,可调节多种信号蛋白酶的活性,如p65、p53等[13-14]。既往研究显示,激活SIRT1可通过抗凋亡减轻心脏缺血再灌注损伤[15],其作用机制为促进p53去乙酰化修饰,减少线粒体膜电位和膜通透性改变,抑制AIF等从线粒体释放,减少促凋亡蛋白bax表达,增加抗凋亡蛋白bcl-2表达,进而减少TUNEL表达[16-19]。本研究结果表明,RSV在肠缺血再灌注损伤时,可增加SIRT1、bcl-2和线粒体AIF表达,减少p53乙酰化修饰、bax和胞浆AIF表达。
综上所述,RSV通过抗凋亡信号通路减轻肠缺血再灌注损伤,其作用机制与SIRT1/p53信号通路相关。
[1] Gonzalez LM,Moeser AJ,Blikslager AT.Animal models of ischemia-reperfusion-induced intestinal injury:progress and promise for translational research[J].Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol,2015,308(2):G63-G75.
[2] Lenaerts K,Ceulemans LJ,Hundscheid IH,et al.New insights in intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury:implications for intestinal transplantation[J].Curr Opin Organ Transplant,2013,18(3):298-303.
[3] Dalal A.Intestinal transplantation:the anesthesia perspective[J].Transplant Rev (Orlando),2016,30(2):100-108.
[4] Slone EA,Fleming SD.Membrane lipid interactions in intestinal ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury[J].Clin Immunol,2014,153(1):228-240.
[5] Huang Z,Huang Q,Ji L,et al.Epigenetic regulation of active Chinese herbal components for cancer prevention and treatment:a follow-up review[J].Pharmacol Res,2016,114:1-12.
[6] Diaz M,Degens H,Vanhees L,et al.The effects of resveratrol on aging vessels[J].Exp Gerontol,2016,85:41-47.
[8] Abdel-Aleem GA,Khaleel EF,Mostafa DG,et al.Neuroprotective effect of resveratrol against brain ischemia reperfusion injury in rats entails reduction of DJ-1 protein expression and activation of PI3K/Akt/GSK3b survival pathway[J].Arch Physiol Biochem,2016,122(4):200-213.
[9] Shimizu K,Miyagi S,Miyazawa K,et al.Resveratrol prevents warm ischemia-reperfusion injury in liver grafts from non-heart-beating donor rats[J].Transplant Proc,2016,48(4):1221-1215.
[10]Ji YY,Wang ZD,Wang SF,et al.Ischemic preconditioning ameliorates intestinal injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion in rats[J].World J Gastroenterol,2015,21(26):8081-8088.
[11]Kalimeris K,Briassoulis P,Ntzouvani A,et al.N-acetylcysteine ameliorates liver injury in a rat model of intestinal ischemia reperfusion[J].J Surg Res,2016,206(2):263-272.
[12]Zu G,Guo J,Che N,et al.Protective effects of ginsenoside Rg1 on intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis via activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway[J].Sci Rep,2016,6:38480.
[13]Hattori Y,Ihara M.SIRT1[J].Nihon Rinsho,2016,74(4):589-594.
[14]Subramaniyan B,Jagadeesan K,Ramakrishnan S,et al.Targeting the interaction of Aurora kinases and SIRT1 mediated by Wnt signaling pathway in colorectal cancer:a critical review[J].Biomed Pharmacother,2016,82:413-424.
[15]Feng J,Yang Y,Zhou Y,et al.Bakuchiol attenuates myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury by maintaining mitochondrial function:the role of silent information regulator 1[J].Apoptosis,2016,21(5):532-545.
[16]Kai-lan W,Si Z.Pretreatment with erythropoietin attenuates intestinal ischemia reperfusion injury by further promoting PI3K/Akt signaling activation[J].Transplant Proc,2015,47(6):1639-1645.
[17]Sin TK,Yu AP,Yung BY,et al.Modulating effect of SIRT1 activation induced by resveratrol on foxo1-associated apoptotic signalling in senescent heart[J].J Physiol,2014,592(12):2535-2548.
[18]Yamamoto T,Tamaki K,Shirakawa K,et al.Cardiac sirt1 mediates the cardioprotective effect of caloric restriction by suppressing local complement system activation after ischemia-reperfusion[J].Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol,2016,310(8):H1003-H1014.
[19]Nadtochiy SM,Urciuoli W,Zhang J,et al.Metabolomic profiling of the heart during acute ischemic preconditioning reveals a role for SIRT1 in rapid cardioprotective metabolic adaptation[J].J Mol Cell Cardiol,2015,88:64-72.
ProtectiveeffectofRSVonintestineischemiareperfusioninjury
WEI Lai1,2,RONG Yu-ping3,LIU Sheng-wu1,ZHAO Duan-yi2
(1.Wuhan University School of Basic Medical Sciences,Wuhan 430071,China;2.Sixth Surgery Department, Armed Police Corps Hospital of Hubei Province, Wuhan 430061,China;3.Hubei General Hospital,Wuhan 430060, China)
ObjectiveTo explore the effect and molecular mechanism of resveratrol (RSV) on intestine ischemia reperfusion injury in rats.MethodsThirty SD rats were randomly divided into Sham group,intestinal ischemia reperfusion injury group (IRI group) and RSV group.The expression level of SIRT1,Acetylp53,p53,bax,bcl-2,TUNEL and the pathological morphology of intestinal tissue were examined.ResultsCompared with Sham group,the pathological change of intestinal and the expression of Acetylp53,bax,cytoplasm of AIF and TUNEL in IRI group were significantly increased with the decrease of expression of bcl-2 and SIRT1.Compared with IRI group,the pathological change of intestinal and the expression of Acetylp53,bax,cytoplasm of AIF and TUNEL in RSV group were significantly decreased with the increase of expression of SIRT1 and bcl-2.There was no significant difference in the expression of p53 among the three groups.ConclusionRSV can alleviate intestine ischemia reperfusion injury by anti-apoptosis,the mechanism of which is associated with SIRT/p53 signal pathway.
RSV;Intestine ischemia reperfusion injury;SIRT1/p53
2016-11-28
1.武汉大学基础医学院,武汉 430071;2.武警湖北省总队医院六外科,武汉 430061;3.湖北省人民医院,武汉 430060
10.14053/j.cnki.ppcr.201709004
