凡纳滨对虾血蓝蛋白酶解多肽的凝集与抑菌活性
2017-09-12李长平钟名其陈洁辉章跃陵
李长平 黄 河 王 帆 钟名其 陈洁辉 章跃陵
(汕头大学理学院生物学系, 广东省海洋生物技术重点实验室, 汕头 515063)
凡纳滨对虾血蓝蛋白酶解多肽的凝集与抑菌活性
李长平 黄 河 王 帆 钟名其 陈洁辉 章跃陵
(汕头大学理学院生物学系, 广东省海洋生物技术重点实验室, 汕头 515063)
以凡纳滨对虾(Litopenaeus vannamei)为研究对象, 通过分子筛层析、Tricine-SDS-PAGE、Westernblotting、凝集实验、抑菌实验和Edman N端测序等方法探索血蓝蛋白酶解多肽的凝集和抑菌活性。结果发现, 血蓝蛋白经胰蛋白酶酶解后可产生分子量约为6—70 kD的7条多肽, 该酶解混合物对副溶血弧菌(Vibrio parahaemolyticus)具有显著的凝集活性, 与未酶解的血蓝蛋白相比, 其凝集活性可提高4—16倍。在此基础之上, 进一步分离纯化该7条多肽, 发现多肽-3对副溶血弧菌表现出较强的抑菌活性, 且具有较好的浓度依赖性。在浓度为75 μg/mL时, 其抑菌率为(93.76±1.60)%, 与阴性对照组相比, 存在极显著性差异 (P<0.01)。进一步研究显示该多肽位于血蓝蛋白N端α-螺旋区域。由此推测, 凡纳滨对虾血蓝蛋白在体外经胰蛋白酶酶解后可产生具有凝集、抑菌等免疫活性的多肽, 这对研究血蓝蛋白的降解机制及其在先天免疫中的作用具有重要意义。
凡纳滨对虾; 血蓝蛋白; 胰蛋白酶; 酶解多肽; 凝集; 抑菌
血蓝蛋白是存在于节肢动物和软体动物中一种含铜呼吸蛋白, 近年来研究发现其不仅具有输氧功能, 而且还具有酚氧化酶活性[1—3]、抗病毒[4,5]、抗菌[6—9]、溶血[10,11]和抗肿瘤[12,13]等多种免疫学功能。尤其是, 随着对血蓝蛋白研究的深入, 人们发现血蓝蛋白还可产生多种功能性降解多肽。Lee等[14]发现淡水小龙虾(Pacifastacus leniusculus)被感染时, 其血淋巴中可产生1种源于血蓝蛋白C-末端的抗菌肽astacidin 1。Destoumieux-Garzon等[15]从南美白对虾(Penaeus vannamei)和南美蓝对虾(Penaeus stylirostris)的血浆中分离出PvHCt (2.7 kD, 南美白对虾), PsHCt1 (7.9 kD, 南美蓝对虾), PsHCt 2 (8.3 kD, 南美蓝对虾)等3种具有抗真菌活性的多肽,其与血蓝蛋白C-末端的相似性为95%—100%。本课题组既往研究发现[16,17]凡纳滨对虾在感染副溶血弧菌(Vibrio parahaemolyticus)后, 其血清中出现分子量分别为28.5和6.0 kD的2种血蓝蛋白降解新肽段, 可能具有抗菌活性。但迄今为止, 这些功能性降解多肽形成的分子机制尚不清楚, 还有待进一步研究。
有趣的是, 我们最近发现, 对虾血蓝蛋白功能性降解多肽的产生可能与胰蛋白酶的酶解有关[18]。因此, 进一步探索对虾血蓝蛋白胰蛋白酶酶解多肽的特征及其免疫学活性, 对揭示血蓝蛋白产生降解多肽的分子机制和寻找新的对虾疾病免疫学防治策略等具有重要意义。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
实验材料 凡纳滨对虾购买于广东省汕头市鮀浦农贸市场, 实验用副溶血弧菌为本实验室保存菌种。
实验试剂 胰蛋白酶(Trypsin)、三(羟甲基)甲基甘氨酸(Tricine)、丙烯酰胺(Acrylamide)、甲叉双丙烯酰胺(Bis-acrylamide)、三羟甲基氨基甲烷(Tris)、过硫酸铵(Ammonium persulphate)等购自广州威佳科技有限公司; 十二烷基硫酸钠(Sodi-um dodecyl sulfate)、考马斯亮蓝R-250(Coomassie brilliant blue R-250)、甘氨酸(Glycine)等试剂购自上海生物工程有限公司; 兔抗对虾血蓝蛋白多克隆抗血清为本实验室接种制备, 羊抗兔IgG-HRP购于上海碧云天生物技术有限公司; PVDF膜为MILLIPORE公司产品。
1.2 实验方法
副溶血弧菌悬液的制备 采用课题组既往报道的方法进行[19]。将副溶血弧菌接种、扩培、离心、洗涤、计数, 并稀释为3.0×107CFU/mL的菌悬液, 4℃保存备用。
对虾血清的制备 参照张泽蕙等[17]的方法进行, 用1 mL注射器直接从正常对虾心脏抽取血淋巴, 4℃冰箱过夜, 12000 r/min离心20min, 取血清,–20℃保存备用。
Sephadex G-100柱层析纯化血蓝蛋白 参照Qiu等[20]的方法纯化对虾血蓝蛋白。其大致流程如下: 选用Sephadex G-100按常规方法装柱, 加入对虾血清1.0 mL, 50 mmol/L Tris-HCl (pH 8.0)洗脱,流速1 mL/min, 自动部分收集器收集血蓝蛋白洗脱峰, Bradford法测定蛋白浓度, –20℃保存备用。
血蓝蛋白的酶解 参照Cheison等[21]的方法选用胰蛋白酶酶解血蓝蛋白。其大致流程如下: 50 mmol/L Tris-HCl (pH8.0)配制1—10 μg/mL胰蛋白酶溶液, 37℃恒温水浴锅中酶解相同体积的50 μg/mL血蓝蛋白60s, 之后即刻加入还原性上样缓冲液(0.125 mol/L Tris, pH 6.8; 0.2 mol/L DTT, 4%SDS, 20%甘油, 0.02%溴酚蓝), 放入冰盒中终止反应。
Tricine-SDS-PAGE和Western-blotting
Tricine-SDS-PAGE参照Schägger[22]的方法进行, 配制4%T, 3%C浓缩胶; 10%T, 3%C夹层胶和16.5%T, 3%C分离胶。取40 μL的50 μg/mL血蓝蛋白酶解混合物进行电泳, 电泳结束后, 进行考马斯亮蓝R-250染色或选用半干式电转仪根据凝胶面积按0.8 mA/cm2电转90min。电转后, 5%脱脂奶粉(0.02 mol/L TBS, 0.5 mol/L NaCl, pH 7.4)室温封闭1h, 兔抗血蓝蛋白多克隆抗血清(1:1000)和羊抗兔IgG-HRP (1: 1000)分别室温孵育2h和1h, TTBS充分洗涤, DAB显色拍照。
切胶回收 采用上海生物工程有限公司的PAGE胶蛋白微量回收试剂盒方法, 对血蓝蛋白酶解条带进行切胶回收。
凝集活性分析 参照课题组前期报道的方法[23], 分实验组和对照组进行。实验组用TBS-Ca2+将血蓝蛋白酶解混合液进行2倍梯度稀释, 各取 10 μL滴加在洁净的载玻片上, 并分别在其上滴加等量待测副溶血弧菌悬液, 轻轻摇动1min。置37℃ 30min,显微镜观察细菌凝集状态。以各样品发生凝集反应的最高稀释度为凝集效价, 血蓝蛋白酶解混合液浓度与凝集效价的比值为凝集比活。以不添加血蓝蛋白酶解混合液的TBS-Ca2+为阴性对照。
抑菌活性分析 参照Destoumieux-Garzón等[15]和Qiu等[24]报道的方法进行。将副溶血弧菌于37℃恒温培养至对数生长期, 0.85% 无菌生理盐水配制菌浓度为1×104CFU/mL的菌悬液。取20 μL胶回收蛋白进行2倍梯度稀释, 然后分别与等体积菌液在96孔板中混合, 置37℃摇床培养1h后添加100 μL LB培养基, 再培养24h, 采用酶标仪于600 nm处测定吸光度(OD), 并按如下公式计算抑菌率: 抑菌率=(阴性对照菌OD值–实验组OD值)/阴性对照菌OD值×100%。生理盐水为阴性对照, 每个样品3个重复。
Edman N端测序分析 采用Tricine-SDSPAGE和半干式电转技术将上述血蓝蛋白酶解多肽转移至PVDF膜, 送上海生物工程有限公司进行Edman N端测序分析。
统计分析 采用SPSS 19.0对所得数据进行分析处理, 用方差分析(ANOVA)进行统计显著性分析, 所有测定结果表示为平均数±标准差(n≥3)。
2 结果
2.1 血蓝蛋白及其酶解多肽特征分析
如图 1A所示, 分子筛层析所得血蓝蛋白SDSPAGE电泳表现为两条电泳条带, 分别为75和77 kD,且与兔抗血蓝蛋白多克隆血清反应呈显著阳性。
由图 1b可知, 血蓝蛋白经胰蛋白酶酶解后可产生分子量为6—70 kD的7条多肽(分别命名为多肽1—7)。且均与兔抗血蓝蛋白血清呈显著阳性。由此推测, 该7条酶解多肽均为血蓝蛋白酶解多肽, 可用于下一步研究。
2.2 血蓝蛋白酶解多肽凝集活性分析
选取副溶血弧菌探索血蓝蛋白酶解多肽的细菌凝集活性, 结果如表 1和图 2所示, 血蓝蛋白(50 μg/ mL)经胰蛋白酶(1、5和10 μg/mL)酶解后所得酶解多肽混合物, 可与副溶血弧菌发生明显的凝集反应,其凝集活性为0.024—0.039 μg/mL, 为未酶解血蓝蛋白的4—16倍, 其中浓度为5 μg/mL的胰蛋白酶酶解血蓝蛋白所得酶解多肽混合物的凝集活性最高。
2.3 血蓝蛋白酶解多肽抑菌活性分析
在上述基础之上, 进一步采用切胶回收纯化血蓝蛋白的7条酶解多肽进行抑菌活性分析, 如图 3所示, 在多肽浓度为75 μg/mL时, 多肽3对副溶血弧菌具有较好的抑菌活性, 其抑菌率约(93.76± 1.60)%, 与阴性对照组相比, 具有极显著性差异(P<0.01)。进一步研究发现, 随着多肽浓度的逐步降低, 其抑菌活性表现出一定的浓度依赖性。
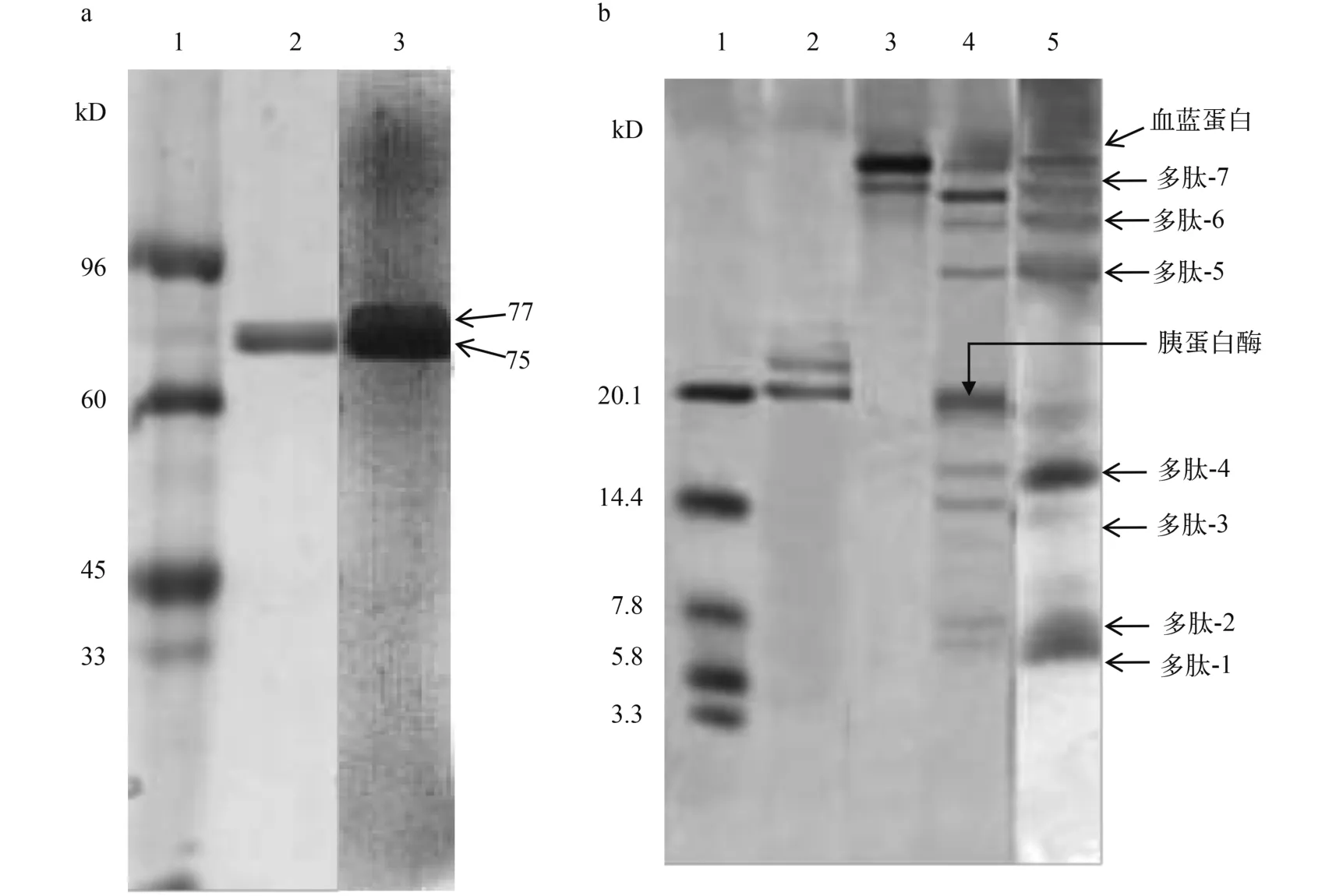
图 1 凡纳滨对虾血蓝蛋白及其胰蛋白酶酶解多肽电泳和免疫印迹分析

表 1 血蓝蛋白酶解多肽对副溶血弧菌凝集活性分析Tab. 1 Agglutinative activity of the peptides hydrolyzed from hemocyanin with trypsin against V. parahaemolyticus
选取多肽3进一步进行Edman N端测序分析,其N端10个氨基酸为DVQQXCKDVLY, 经BLAST进一步分析, 发现其位于凡纳滨对虾血蓝蛋白小亚基(序列号X82502.1)N端α-螺旋区。
3 讨论
既往研究表明, 对虾血蓝蛋白是一种具有酚氧化酶活性、抗病毒、抗菌、溶血和抗肿瘤等多种免疫学功能的蛋白, 同时其可降解产生具有免疫学功能的降解多肽[15,25], 但迄今为止, 其降解机制尚不是很清楚。可喜的是, 近年来学者们发现免疫分子衍生功能性降解多肽的形成可能与丝氨酸蛋白酶或蛋白酶复合体的降解有关, 如人潘氏细胞(Paneth cell)中defensin-5的表达与胰蛋白酶有关[26]; 亚洲蟾蜍(Bufo bufo)胃腺体细胞中的抗菌肽buforin I可能是由胃蛋白酶介导H2A (a pepsin mediated)而产生[27]。Sheshadri等[28]发现血红蛋白在天冬氨酸蛋白酶作用下可以降解产生抵抗间日疟原虫(Plasmodium vivax)的抗菌肽。尤其值得一提的是, 我们在前期研究中运用蛋白酶酶解位点预测软件Ex-PASy: PeptideCutter, http://web.expasy.org/peptide_ cutter/, 发现胰蛋白酶和胰凝乳蛋白酶等丝氨酸蛋白酶可能与血蓝蛋白降解多肽的形成有关。同时,我们还发现凡纳滨对虾在维生素C和中药的刺激下血蓝蛋白降解多肽增加的同时胰蛋白酶表达水平也明显上升[29]。这些研究结果提示, 对虾血蓝蛋白降解多肽的形成可能与胰蛋白酶的酶解作用密切相关, 故进一步对其进行研究具有重要意义。

图 2 血蓝蛋白酶解多肽对副溶血弧菌凝集活性分析(×400)

图 3 血蓝蛋白酶解多肽抑菌活性分析Fig. 3 Antibacterial activity of the peptides of hemocyanin’s hydrolyzed with trypsin**表示在P<0.01水平有显著性差异** indicates significant difference (P<0.01)
本研究采用Tricine-SDS-PAGE、Western-blot-ting等技术发现凡纳滨对虾血蓝蛋白在胰蛋白酶作用下可产生7条分子量为6—70 kD的降解多肽, 该血蓝蛋白酶解多肽不仅可以与副溶血弧菌发生明显的凝集反应, 而且与未酶解血蓝蛋白相比, 其凝集活性可提高4—16倍。在此基础之上, 进一步发现多肽3对副溶血弧菌具有明显的抑菌活性, 不过与Lee等[14]发现的淡水小龙虾1.9 kD的血蓝蛋白降解多肽的抗菌活性相比相对较弱, 可能与物种差异、多肽大小以及纯化方法等有关。尤其值得一提的是, Edma N端测序分析表明多肽3 可能源于血蓝蛋白N端的α螺旋区, 与Lee等[14]和Destoumieux-Garzon等[15]以及我们前期发现血蓝蛋白功能性降解多肽来源于血蓝蛋白C端的结果[17]存在明显的差异。由此推测, 多肽3可能是一种不同来源的新的血蓝蛋白功能性降解多肽。
综上所述, 对虾血蓝蛋白在胰蛋白酶酶解后可以产生具有细菌凝集和抑菌活性的降解多肽, 为进一步揭示血蓝蛋白的降解机制奠定了良好的基础。但其在生物内具体的降解机制以及这些降解多肽的免疫学功能等仍需进一步研究和探索。
[1]Schenk S, Schmidt J, Hoeger U, et al. Lipoprotein-induced phenoloxidase-activity in tarantula hemocyanin [J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 2015, 1854(8): 939—949
[2]Coates C J, Whally T, Wyman M, et al. A putative link between phagocytosis-induced apoptosis and hemocyanin-derived phenoloxidase activation [J]. Apoptosis, 2013, 18(11): 1319—1331
[3]Bris C L, Cudennec B, Dhulster P, et al. Melanosis in Penaeus monodon: Involvement of the Laccase-like activity of hemocyanin [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2015, 64(3): 663—670
[4]Zanjani N, Miranda-Saksena M, Valtchev P, et al. Abalone hemocyanin blocks the entry of Herpes simplex virus 1 into cells: a potential new antiviral strategy [J]. Antimicrob Agents and Chemotherapy, 2015, 60(2): 1003—1012
[5]Zanjani N T, Sairi F, Marshall G, et al. Formulation of abalone hemocyanin with high antiviral activity and stability [J]. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2014, 53(2): 77—85
[6]Zhuang J, Coates C J, Zhu H, et al. Identification of candidate antimicrobial peptides derived from abalone hemocyanin [J]. Developmental and Comparative Immunology, 2015, 49(1): 96—102
[7]Zhang Y L, Wang S Y, Xu A L, et al. Affinity proteomic approach for identification of an IgA-like protein in Litopenaeus vannamei and study on its agglutination characterization [J]. Journal of Proteome Research, 2006, 5(4): 815—821
[8]Yan F, Zhang Y L, Jiang R P, et al. Identification and agglutination properties of hemocyanin from the mud crab (Scylla serrata) [J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2011, 30(1): 354—360
[9]Wang J, Zhang F Y, Song W, et al. Characterization of hemocyanin from the mud crab Scylla paramamosain and its expression analysis in different tissues, at various stages, and under Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection [J]. Genetics and Molecular Research, 2015, 14(4): 16639—16651
[10]Zhang X Y, Lin X M, Zhang Y L, et al. Comparative analysis of hemolytic activity of hemocyanin isomers binding to diffrent bacteria in shrimp Litopenaeus vanname [J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2013, 37(6): 1079—1084 [张小瑜, 林晓敏, 章跃陵, 等. 与不同病原菌相结合的凡纳滨对虾血蓝蛋白溶血活性对比分析.水生生物学报, 2013, 37(6): 1079—1084]
[11]Yan F, Qiao J, Zhang Y L, et al. Hemolytic properties of hemocyanin from mud crab Scylla serrata [J]. Journal of Shellfish Research, 2011, 30(3): 957—962
[12]Arancibia S, Espinoza C, Salazar F, et al. A novel immunomodulatory hemocyanin from the limpet Fissurella latimarginata promotes potent anti-tumor activity in melanoma [J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(1): e87240
[13]Zheng L, Zhao X, Zhang P, et al. Hemocyanin from shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei has antiproliferative effect against HeLa cell in vitro [J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(3): e0151801
[14]Lee S Y, Lee B L, Söderhäll K. Processing of an antimicrobial peptide from hemocyanin of the freshwater crayfish Pacifastacus leniusculus [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2003, 278(10): 7927—7933
[15]Destoumieux-Garzon D, Saulnier D, Garnier J, et al. Crustacean immunity-antifungal peptides are generated from the C-terminus of shrimp hemocyanin in response to microbial challenge [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2001, 276(50): 47070—47077
[16]Zhang Y L, Ye X Q, Chen J H, et al. A novel 28.5 kDa fragment derived from shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, hemocyanin [J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2008, 15(3): 425—430 [章跃陵, 叶向群, 陈洁辉, 等. 凡纳滨对虾28.5 kD血蓝蛋白的降解新片段. 中国水产科学, 2008, 15(3): 425—430]
[17]Zhang Z H, Huang H, Wen Y, et al. A novel 6.0 kDa fragment resistant to Vibrio parahaemolyticus derived from shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, hemocyanin [J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2016, 23(1): 218—224 [张泽蕙, 黄河, 文英, 等. 与凡纳滨对虾抗副溶血弧菌有关的6.0 kD血蓝蛋白降解肽段. 中国水产科学, 2016, 23(1): 218—224]
[18]Huang H. Identification of the hemocyanin-derived fragments from shrimp Litopenaeus vennamei and investigation of their antibacterial activities and related-degradation enzymes [D]. Thesis for Master of Science. Department of Biology, Shantou University, Guangdong. 2013 [黄河. 凡纳滨对虾血蓝蛋白抗菌降解片段的鉴定、抑菌活性的分析及其相关降解酶的探索. 硕士学位论文,汕头大学生物系, 广东. 2013]
[19]Cao J S, Tang J R, Zhang Y L, et al. Identification of interaction target of human erythrocyte recognized by Litopenaeus vannamei Hemocyanin [J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2012, 19(2): 211—216 [曹劲松,汤俊荣, 章跃陵, 等. 凡纳滨对虾血蓝蛋白与人红细胞的作用靶位. 中国水产科学, 2012, 19(2): 211—216]
[20]Qiu F, He T Z, Zhang Y Q. The isolation and the characterization of two polysaccharides from the branch bark of mulberry (Morus alba, L.) [J]. Archives of Pharmacal Research, 2016, 39(7): 887—896
[21]Cheison S C, Brand J, Leeb E, et al. Analysis of the effect of temperature changes combined with different alkaline pH on the β-lactoglobulin trypsin hydrolysis pattern using MALDI-TOF-MS/MS [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2011, 59(5): 1572—1581
[22]Schägger H. Tricine-SDS-PAGE [J]. Nature Protocols, 2006, 1(1): 16—22
[23]Zhang Y L, Lin B K, Chen J, et al. Bacterial agglutinative activity of hemocyanin in shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei [J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2006, 13(6): 1006—1011 [章跃陵, 林柏坤, 陈俊, 等. 凡纳滨对虾血蓝蛋白的细菌凝集活性. 中国水产科学, 2006, 13(6): 1006—1011]
[24]Qiu C, Sun J, Liu M, et al. Molecular cloning of hemocyanin cDNA from Fenneropenaeus chinensis and antimicrobial analysis of two C-terminal fragments [J]. Marine Biotechnology, 2014, 16(1): 46—53
[25]Coates C J, Nairn J. Diverse immune functions of hemocyanins [J]. Developmental and Comparative Immunology, 2014, 45(1): 43—55
[26]Ghosh D, Porter E, Shen B, et al. Paneth cell trypsin is the processing enzyme for human defensin-5 [J]. Natural Immunology, 2002, 2(6): 589—590
[27]Kim H S, Yoon H, Minn I, et al. Pepsin-mediated processing of the cytoplasmic histone H2A to strong antimicrobial peptide Buforin I [J]. Journal of Immunology, 2000, 165(6): 3268—3274
[28]Sheshadri P, Abraham J. Antimicrobial properties of hemoglobin [J]. Immunopharmacol and Immunotoxicol, 2012, 34(6): 896—900
[29]Qiao J, Du Z H, Zhang Y L, et al. Proteomic identification of the related immune-enhancing proteins in shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei stimulatedwith vitamin C and Chinese herbs [J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2011, 31(6): 736—745
[30]Wen Y. Investigation of the functional degraded fragments from hemocyanin in shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei upon Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection [D]. Thesis for Master of Science. Department of Biology, Shantou University, Guangdong. 2015 [文英. 与对虾抵抗副溶血弧菌有关的血蓝蛋白功能性降解肽段的研究. 硕士学位论文, 汕头大学生物系, 广东. 2015]
AGGLUTINATIVE AND ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF THE PEPTIDES HYDROLYZED FROM LITOPENAEUS VANNAMEI HEMOCYANIN WITH TRYPSIN
LI Chang-Ping, HUANG He, WANG Fan, ZHONG Ming-Qi, CHEN Jie-Hui and ZHANG Yue-Ling
(Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Marine Biotechnology, Department of Biology, Shantou University, Shantou 515063, China)
Previous studies have demonstrated antibacterial and antifungal activities of hemolymph-derived hemocyanin upon pathogen infection with unknown mechanisms. To investigate how peptides derive from hemocyanin, multiple methods including size-exclusion chromatography, Tricine-SDS-PAGE, immunoblotting, bacterial agglutinative and antibacterial assays were applied. The results showed that shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei hemocyanin could produce seven peptides via trypsin digestion, ranging from 6 to 70 kD, which could be identified by rabbit anti-shrimp hemocyanin antibody specifically. These peptides aggregated with Vibrio parahaemolyticus in vitro, whose agglutinative activity was 4—16 folds higher than that of full length hemocyanin. The peptide 3 possessed obvious antibacterial activities against V. parahaemolyticus with a antibacterial rate (93.76±1.60)% at the concentration of 75 μg/mL, which was significantly higher than that of the control group (P<0.01). In addition, N-terminal Edman Sequencing analysis showed that the peptide 3 was located in the α-helix region of N-terminus of shrimp L. vannamei hemocyanin small subunit. These discoveries will help to understand how the hemocyanin derived peptides are formed and to establish effective strategies for shrimp disease control.
Litopenaeus vannamei; Hemocyanin; Trypsin; Hydrolyzed peptides; Agglutinative; Antimicrobial
S945.4
A
1000-3207(2017)05-1042-06
10.7541/2017.130
2016-07-20;
2016-11-10
国家自然科学基金(31372558); 广东省自然科学基金(S2013010015190); 广东省高等学校重大科研项目培育计划类项目(2014GKXM043)资助 [Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31372558); Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (S2013010015190); National Key Growth Project of Guangdong Province College (2014GKXM043)]
李长平(1991—), 男, 河北承德人; 硕士研究生; 主要从事水产动物免疫生物学研究。E-mail: 14cpli@stu.edu.cn
章跃陵(1971—), 教授, 博士生导师; E-mail: zhangyl@stu.edu.cn
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
水生生物学报的其它文章
- 剩余污泥资源化利用新工艺研究进展
- 草鱼野生与选育群体线粒体DNA控制区D-loop遗传变异分析
- 在患CyHV-2病的异育银鲫肠道黏膜中胆固醇、胆汁酸代谢通路基因的差异表达
- 黄颡鱼20β-羟基类固醇脱氢酶Ⅰ和Ⅱ基因特征分析和表达模式研究
- 池蝶蚌β-连环蛋白基因cDNA的克隆及表达特征分析
- MOLECULAR CLONING, CHARACTERIZATION, AND EXPRESSION ANALYSIS OF TWO ISOFORMS OF ANTI-LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE FACTOR FROM THE ORIENTAL RIVER PRAWN, MACROBRACHIUM NIPPONENSE
