MicroRNA-30a在膀胱癌中的表达及作用
2017-09-03尤泊森马景光邢丽娜
柳 清 尤泊森 马景光 邢丽娜
MicroRNA-30a在膀胱癌中的表达及作用
柳 清 尤泊森 马景光 邢丽娜
目的 探究微小RNA(miRNA)在人膀胱癌细胞系中的表达及其对人膀胱癌细胞增殖、凋亡及迁移侵袭能力的影响。方法 应用荧光实时定量PCR(qRT-PCR)法检测膀胱癌细胞系(5637和T24)和膀胱上皮永生化细胞(SV-HUC-1)中miRNA-30a的表达水平。通过对T24细胞转染miR-30a mimic和5637细胞转染miR-30a inhibitor上调或下调miR-30a的表达,并对其分别转染NC mimic和NC inhibitor作为对照。利用流式细胞技术、MTT法和Transwell法探究miR-30a的表达对膀胱癌细胞增殖、凋亡以及侵袭能力的影响。结果 在两种膀胱癌细胞系(5637和T24)中miRNA-30a的表达显著低于正常膀胱细胞系SV-HUC-1,并且在恶性度较高的T24膀胱癌细胞中其表达水平明显低于恶性度相对较低的5637细胞系。细胞转染72 h后,miR-30a mimic组T24细胞OD值(0.83±0.09)明显低于NC mimic组(1.21±0.12)(P=0.003);miR-30a inhibitor组5637细胞OD值(1.28±0.14)高于NC inhibitor组(1.09±0.14)(P=0.019)。miR-30a mimic组T24细胞凋亡率(21.27±2.42)%明显高于NC mimic组(10.61±1.29)%;miR-30a inhibitor组5637细胞凋亡率(6.78±2.57)%明显低于NC mimic组(13.42±1.40)%,差异均具有统计学意义(P=0.0002,P=0.0014)。miR-30a mimic组穿膜细胞数(183.57±16.61)低于NC mimic组(465.80±9.20)(P<0.0001);miR-30a inhibitor组(581.25±11.02)高于NC mimic组(397.13±7.57)(P<0.0001)。结论 miR-30a表达的上调能够抑制膀胱癌细胞的增殖,促进细胞的凋亡,并降低膀胱癌细胞的迁移及侵袭的能力。膀胱癌细胞中miR-30a的低表达可能与膀胱癌的发生发展及转移有关。
膀胱癌细胞;miRNA-30a;增殖;凋亡;侵袭
膀胱尿路上皮癌为泌尿系统常见的肿瘤,仅2012年,全球就有超过四十万新发病例被确诊,约16.5万名患者死于该疾病[1]。膀胱癌(Bladder cancer,BC)病理类型可大致分为2型:非浸润型BC和浸润型BC。非肌层浸润性膀胱癌(Non-muscle invasive bladder cancer,NMIBC)约占50%~80%,可通过经尿道肿瘤切除治疗。NMIBC的患者术后易出现复发,其中约25%的患者将进展为肌层浸润性膀胱癌(Muscle invasive bladder cancer,MIBC)。进展期BC患者预后较差,治疗以联合化疗(吉西他滨和顺铂)为主,无进展生存期(Progression-free survival,PFS)较短。因此,寻找一种可靠的生物学标记物,将对膀胱癌的早期诊断,患者的预后判断,以及个体化治疗指导具有重要的意义。
MicroRNA(miRNA)是一类可在转录后调控基因表达的单链非编码RNA,约含有18~25个碱基,在肿瘤的早期诊断、预后判断、监测及治疗方面具有重要价值[2]。miRNA在多种肿瘤中异常表达并发挥抑癌或促癌基因的作用,其通过参与肿瘤细胞的增殖、侵袭、迁移以及凋亡过程,影响肿瘤的发生发展以及患者的预后[3-4]。既往研究发现miR-30a在膀胱癌组织中呈低表达[5],提示miR-30a可能作为一种抑癌基因参与了膀胱癌的发生发展。本研究检测了miR-30a在膀胱癌细胞中的表达情况及miR-30a的表达与膀胱癌细胞的增殖、凋亡及侵袭性之间的关系,明确了miR-30a对膀胱癌发生发展及转移的影响。
1 材料与方法
1.1 细胞来源
膀胱癌细胞株5637和T24以及正常膀胱上皮细胞SV-HUC-1购自ATCC。含1%链霉素-氨苄青霉素的10%胎牛血清的DMEM,在37℃,5%CO2的细胞培养箱中培养。RNA提取试剂盒购自美国Thermo公司。反转录试剂盒、实时PCR试剂盒均购自德国QIAGEN公司。
1.2 细胞转染
根据Lipofectamine 2000的使用说明,对细胞进行瞬时转染,转染后,提取细胞RNA核蛋白以便进行实时定量PCR(qRT-PCR)。
1.3 细胞分组
对T24细胞进行miR-30a mimic和NC mimic的转染,分为miR-30a mimic组(miR-30a表达上调组)和NC mimic对照组;对5637细胞行miR-30a inhibitor和NC inhibitor的转染,分为miR-30a inhibitor组(miR-30a表达下调组)和NC inhibitor对照组。
1.4 RNA提取和qRT-PCR
按照试剂使用说明,使用Trizol(Life Technologies)提取细胞的总RNA。使用小核RNA U6作为miRNA定量的内参。采用SYBR Green PCR Master Mix(Life Technologies)进行qRT-PCR,对RNA进行定量。β-actin用作mRNA定量的内参。miRNA表达水平以2-ΔΔCt表示,所用引物如下,miR-30a,F:5′-GCCTGTAAACATCCTCGACTGGAAG-3′,R:5′-GCGAGCACAGAATTAATACGAC-3′;β-actin,F:5′-AGCGAGCATCCCCCAAAGTT-3′,R:5′-GGGCACGAAGGCTCATCATT-3′。反应条件:95℃ 5 min,95℃ 5 s,60℃ 30 s,45个循环。
1.5 MTT法检测细胞增殖能力
行miR-30a mimic和inhibitor细胞转染,24 h后胰酶消化后进行细胞计数。96孔板铺板,每组设置6个复孔,细胞密度为1 500个/孔。37℃、5%CO2培养箱培养,连续检测96 h。自铺板后48 h起,向每孔加入10 μL 5 g/L的MTT,继续培养4 h后弃培养液,向每孔加入150 μL二甲基亚砜(DMSO),振荡使之充分反应,检测490 nm处吸光度值。
1.6 流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡
收集转染48 h后的T24细胞和5637细胞,4℃预冷的磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS)冲洗细胞1次,再用1×缓冲液250 μL制备单细胞悬液,调整浓度为1×106个/孔。按照Annexin V/异硫氰酸荧光素(FITC)试剂盒说明书,在5 mL流式管中加入100 μL细胞悬液、5 μL Annexin V/FITC及10 μL碘化丙锭(PI)标记,室温避光15 min,使其充分反应。流式细胞仪检测各组细胞凋亡率。
1.7 Transwell小室检测细胞侵袭能力
50 mg/L Matrigel胶以DMEM 1∶8稀释后取60 μL包被Transwell小室底部膜的上室面,使其凝结成胶。用DMEM培养液将转染后的细胞配置成5×108/L的细胞悬液。Transwell上室加入200 μL细胞,下室加入500 μL含10%FBS的培养基,每组3个复孔。37℃、5%CO2培养48 h后棉棒拭去上室底部未迁移的细胞。4%多聚甲醛固定30 min,PBS冲洗2次,HE染色30 min。200倍光镜下计算穿膜细胞数。
1.8 统计分析
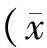
2 结果
2.1 miR-30a在不同膀胱癌细胞系中的表达
qRT-PCR分析结果显示,miR-30a在膀胱癌细胞系5637和T24中的表达分别为(0.70±0.05)、(0.44±0.07),明显低于正常膀胱移行上皮细胞系SV-HUC-1(1.02±0.02),并且在恶性度较高的T24膀胱癌细胞中其表达水平低于恶性度相对较低的5637细胞系,差异均具有统计学意义(F=216.8,P<0.001)(图1)。
2.2 miR-30a的表达对膀胱癌细胞增殖的影响
首先对miR-30a表达较低的T24细胞和miR-30a表达较高的5637细胞分别转染miR-30a mimic/NC mimic或miR-30a inhibitor/NC inhibitor,转染24 h后对miR-30a表达进行定量(图2)。使用MTT法检测miR-30a对细胞增殖的作用,72 h:miR-30a mimic组T24细胞OD值(0.83±0.09)明显低于NC mimic组(1.21±0.12),差异具有统计学意义(P=0.003);72 h:miR-30a inhibitor组5637细胞OD值(1.28±0.14)高于NC inhibitor组(1.09±0.14),差异具有统计学意义(P=0.019)。结果表明膀胱癌细胞中miR-30a的高表达能够抑制癌细胞增殖;抑制miR-30a后,可以促进细胞的增殖(图3)。
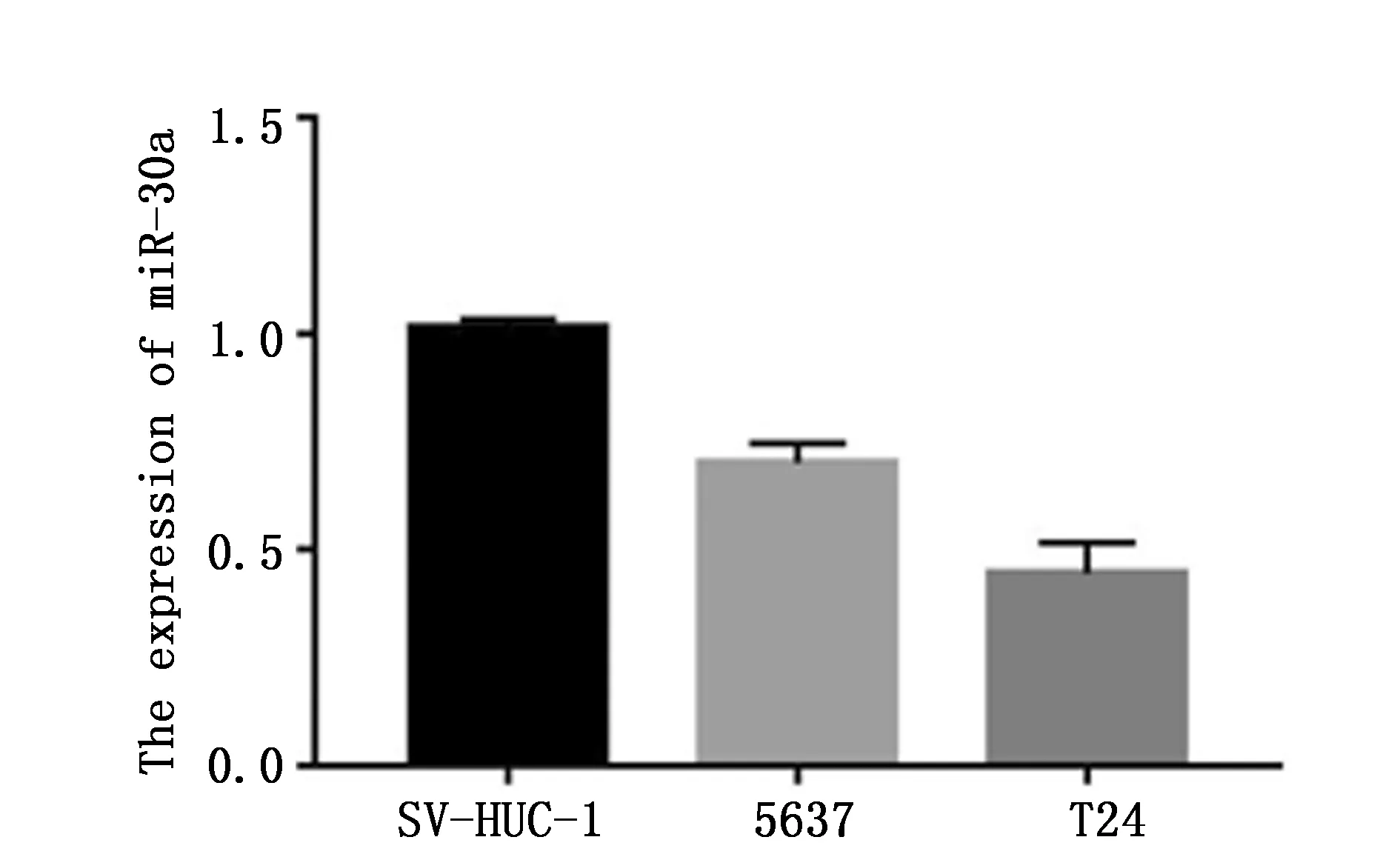
图1 人正常膀胱上皮细胞SV-HUC-1和膀胱癌细胞系T24、5637中miR-30a的相对表达Figure 1 The expression of miR-30a in human normal bladder epithelial immotalized cell and bladder cancer cell lines
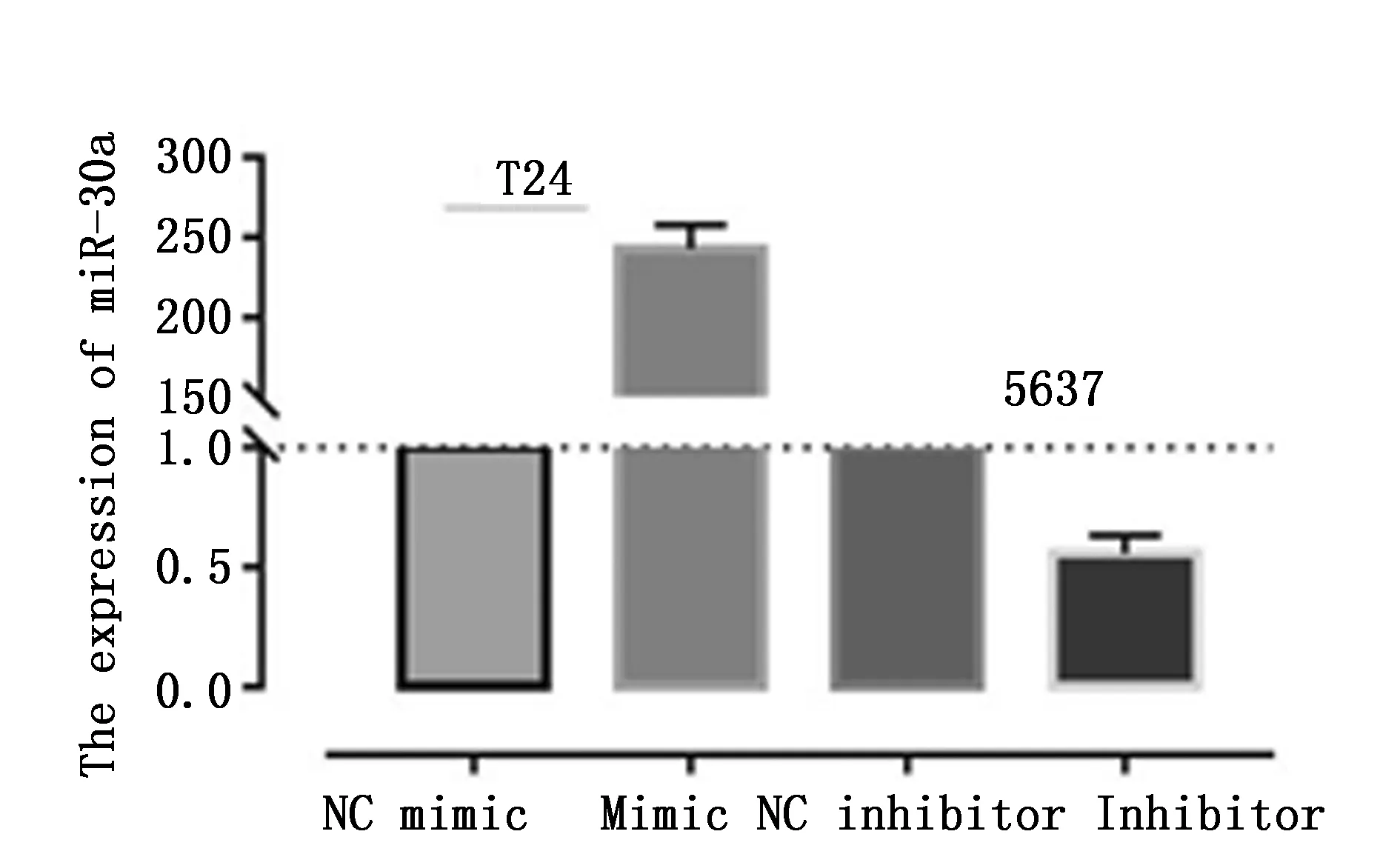
图2 细胞转染后miRNA-30a的相对表达Figure 2 The expression of miR-30a after cell transfection
2.3 miR-30a促进了膀胱癌细胞的凋亡
miR-30a mimic组T24细胞凋亡率(21.27±2.42)%明显高于NC mimic组(10.61±1.29)%(P=0.0002);miR-30a inhibitor组5637细胞凋亡率(6.78±2.57)%明显低于NC mimic组(13.42±1.40)%(P=0.0014),差异均具有统计学意义(图4)。结果显示miR-30a表达上调诱导T24细胞发生凋亡,抑制miR-30a的表达后凋亡率明显下降。
2.4 miR-30a的表达对膀胱癌细胞迁移和侵袭能力的影响
Transwell小室检测细胞迁移结果显示,miR-30a mimic组穿膜细胞数显著低于NC mimic组,分别为(183.57±16.61)个和(465.80±9.20)个(P<0.0001);miR-30a inhibitor组穿膜细胞数显著高于NC mimic组,分别为(581.25±11.02)个和(397.13±7.57)个(P<0.0001)(图5)。Transwell小室上层细胞穿透到下室的数量反应了细胞侵袭能力的强弱,提示miR-30a表达的上调能够降低膀胱癌细胞在滤膜中迁移及侵袭的能力;相反,膀胱癌细胞中miR-30a的低表达会增强其迁移及侵袭的能力。
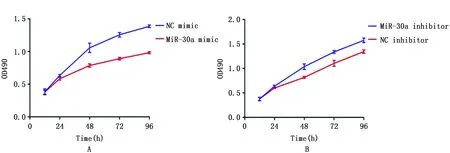
图3 MiR-30a的表达水平对细胞增殖的影响 Figure 3 The proliferative curves of miR-30a in T24 cells and 5637 cells Note:A.T24 cells;B.5637 cells.

图4 MiR-30a的表达水平对膀胱癌细胞凋亡的影响Figure 4 The apoptotic rate of miR-30a in T24 cells and 5637 cellsNote:A.T24 cells;B.5637 cells.*P<0.05,#P<0.01,vs. NC minmic.
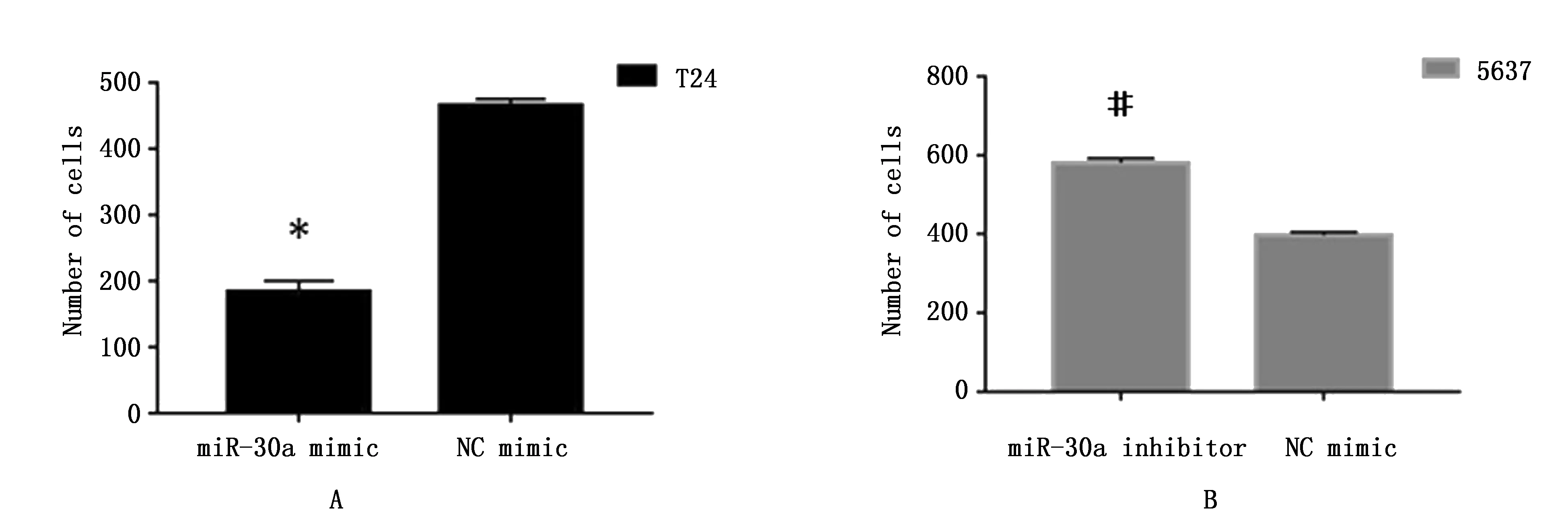
图5 miR-30a的表达对膀胱癌细胞迁移的影响Figure 5 The number of migration cell of miR-30a in T24 cells and 5637 cellsNote:A.T24 cells;B.5637 cells.* P<0.05,#P<0.01,vs. NC minmic.
3 讨论
miRNAs在恶性肿瘤中表达异常,并通过调控癌基因的表达参与恶性肿瘤的发生发展过程[6]。大量证据表明,异常表达的miRNAs能使原本受控良好的细胞内RNA网络失去调控,进而促进癌细胞的发生、发展和转移[7-8]。miRNAs的异常表达及其所调控的RNA网络的改变为我们阐述癌细胞发展和转移的机制提供了新的理论依据。现已证实表达异常的miRNAs在膀胱癌细胞的发展过程中扮演了重要的角色[7]。与膀胱癌细胞相关的miRNAs包括miR-1/133a(靶基因:TAGLIN2)、miR-23b/27b/24-1(靶基因:EGFR,MET,和FOXM1)以及miR-195/497(靶基因:BRIC5,WNT7A),通过对一些癌基因及其通路的调节起到抑制肿瘤的作用[9-12]。
既往研究表明,miR-30在肝癌、乳腺癌和肺癌等多种人类肿瘤中表达异常,其通过发挥抑癌或促癌基因的作用参与细胞的增殖、迁移和凋亡,影响恶性肿瘤的发生发展[13-16]。在结肠癌中,miR-30a靶向作用于DTL(Denticleless protein homolog)抑制结肠癌细胞的增殖[17]。在肺腺癌A549细胞系中,过表达的miR-30a能够抑制癌细胞的侵袭转移[18]。鼻咽癌细胞中高表达的miR-30a具有促进细胞侵袭转移的能力,miR-30a的表达水平在转移性鼻咽癌中明显高于早期鼻咽癌,在恶性度较高的鼻咽癌细胞系中其表达水平也显著高于恶性度低的细胞系[4]。上皮间质转化(Epithelial-mesenchymal transition,EMT)对恶性肿瘤的侵袭和迁移至关重要[19]。MicroRNA通过调控EMT相关分子通路,促进或抑制EMT这一过程,在恶性肿瘤的发生、发展、侵袭和转移中起到了重要作用[19]。在乳腺癌和非小细胞肺癌中,miR-30a靶向作用于Vimentin和Snail 3端非编码区(3′-UTR),抑制肿瘤的侵袭和转移[16,20]。
相较于正常人膀胱上皮组织,miR-30a在膀胱癌组织中呈低表达[5]。本实验中miR-30a在膀胱癌细胞系中表达下降这一结果与以往研究相吻合,在此基础上进一步发现miR-30a在恶性度较高的T24膀胱癌细胞中的表达水平明显低于恶性度相对较低的5637细胞系,提示其表达水平可能与肿瘤恶性度相关。通过上调或下调miR-30a的表达观察膀胱癌细胞增殖、凋亡及迁移侵袭的能力,证实miR-30a在膀胱癌细胞中发挥了抑癌作用。由此推测,膀胱癌组织中miR-30a的低表达可能促进了膀胱癌的发生发展的过程,其表达水平可能与肿瘤的侵袭性、预后和治疗的敏感性有关。
本研究仅在体外细胞学实验证实了miR-30a在膀胱癌中的抑癌作用,下一步我们将进一步探讨其作用途径和相关机制,以及体内动物实验的验证。未来还需要进一步研究以明确miR-30a在膀胱癌中与患者临床特征和预后的关系。miR-30a有望成为早期诊断和、预后评估和指导治疗的生物学标志物而应用于临床,此外,其靶基因及相关通路的进一步研究有助于我们寻找膀胱癌中新的治疗靶点。
1 Torre LA,Bray F,Siegel RL,et al.Global cancer statistic,2012[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2015,65(2):87-108.
3 Yoshino H,Seki N,Itesako T,et al.Aberrant expression of microRNAs in bladder cancer[J].Nat Rev Urol,2013,10(7):396-404.
4 Wang HY,Li YY,Sha F,et al.MicroRNA-30a promotes invasiveness and metastasis in vitro and in vivo through epithelial-mesenchymal transition and results in poor survival of nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients[J].Exp Biol Med,2014,239(7):891-898.
5 Ichimi T,Enokida H,Okuno Y,et al.Identification of novel microRNA targets based on microRNA signatures in bladder cancer[J].Int J Cancer,2009,125(2):345-352.
6 Farazi TA,Hoell JI,Morozov P,et al.microRNAs in human cancer[J].Adv Exp Med Biol,2011,223(2):102-115.
7 Garzon R,Marcucci G,Croce CM.Targeting microRNAs in cancer:rationale,strategies and challenges[J].Nat Rev Drug Discov,2010,9(10):775-789.
8 Arora S,Rana R,Chhabra A,et al.miRNA-transcription factor interactions:a combinatorial regulation of gene expression[J].Mol Genet Genom,2013,288(3):77-87.
9 Toshihiko I,Naohiko S,Hirofumi Y,et al.The MicroRNA expression signature of bladder cancer by deep sequencing:The functional significance of the miR-195/497Cluster[J].PLoS One,2014,9(2):e84311.
10 Yoshino H,Chiyomaru T,Enokida H,et al.The tumour-suppressive function of miR-1 and miR-133a targeting TAGLN2 in bladder cancer[J].Brit J Cancer,2011,104(5):808-818.
11 Chiyomaru T,Seki N,Inoguchi S,et al.Dual regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase genes EGFR and c-Met by the tumor-suppressive microRNA-23b/27b cluster in blad-der cancer[J].Int J Oncol,2014,46(2):487-496.
12 Inoguchi S,Seki N,Chiyomaru T,et al.Tumour suppressive microRNA 24 1 in-hibits cancer cell proliferation through targeting FOXM1 in bladder cancer[J].Febs Letters,2014,588(17):3170-3179.
13 Liu Z,Tu K,Liu Q.Effects of microRNA-30a on migration,invasion and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Febs Letters,2014,588(17):3089-3097.
14 Maria O,Tri V,Pierre-Benoit A,et al.MicroRNA miR-30 family regulates non-attachment growth of breast cancer cells[J].BMC Genomics,2013,14(1):139.
15 Li N,Kaur S,Greshock J,et al.A combined array-based comparative genomic hybridization and functional library screening approach identifies miR-30d as an on-comir in cancer[J].Cancer Res,2012,72(1):154-164.
16 Kumarswamy R,Mudduluru G,Ceppi P,et al.MicroRNA-30a inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by targeting snai1 and is downregulated in non-small cell lung cancer[J].Int J Cancer,2012,130(9):2044-2053.
17 Baraniskin A,Birkenkamp-Demtroder K,Maghnouj A,et al.Mir-30a-5p suppresses tumor growth in colon carcinoma by targeting dtl[J].Carcinogenesis,2012,33(4):732-739.
18 Yuan Y,Zheng S,Li Q,et al.Overexpression of miR-30a in lung adenocarcinoma A549 cell line inhibits migration and invasion via targeting EYA2[J].Acta Bioch Bioph Sin,2016,48(3):220-228.
19 Tang J,Li Y,Wang J,et al.Molecular mechanisms of microRNAs in regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in human cancers[J].Cancer Letters,2015,371(2):301-313.
20 Cheng CW,Wang HW,Chang CW,et al.MicroRNA-30a inhibits cell migration and invasion by downregulating vimentin expression and is a potential prognostic marker in breast cancer[J].Breast Cancer Res Treat 2012,134(3):1081-1093.
(收稿:2017-03-29)
The expression and function of microRNA-30a in bladder cancer
LIUQing,YOUBosen,MAJingguang,XINGLina
The Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University,Harbin 150086,China
Objective The aims of this study were to investigate the expression of microRNA-30a(miR-30a)in human bladder cancer cell lines and their effects on the proliferation,apoptosis and migration of human bladder cancer cells.Methods The expression levels of miR-30a in bladder cancer cell lines(5637 and T24)and bladder epithelial immortalized cells(SV-HUC-1)were detected by real-time quantitative PCR(qRT-PCR).The expression of miR-30a was up-regulated or down-regulated by T24 cells transfected with miR-30a mimic or 5637 cells transfected with miR-30a inhibitors and controls using NC mimic or NC inhibitor.The effects of miR-30a expression on the proliferation,apoptosis and invasion of bladder cancer cells were investigated by flow cytometry,MTT and Transwell assays.Results The expression level of miR-30a in two bladder cancer T24 and 5637 cell lines was significantly lower than that in normal bladder SV-HUC-1 cell line(P<0.05),and the expression level of miR-30a was lower in the high degree of malignancy in bladder cancer T24 cells than that in malignant degree of relatively low 5637 cells.After 72 h transfection,the values of optical density(OD)in the miR-30a mimic group(0.83±0.09)was significantly lower than that in NC mimic group(1.21±0.12)in T24 cells(P<0.01).The OD values of miR-30a inhibitor group(1.28±0.14)was significantly lower than that in the NC inhibitor group(1.09±0.14)in 5637 cells(P<0.01).The apoptotic rate of miR-30a mimic group in T24 cells(21.27±2.42)% was significantly higher than that in the NC mimic group(10.61±1.29)%(P<0.01).The apoptotic rate of the miR-30a inhibitor group in 5637 cells(6.78±2.57)% was significantly lower than that in the NC mimic group(13.42±1.40)%(P<0.01).The number of transmembrane cells in miR-30a mimic group in T24 cells(183.57±16.61)was significantly lower than that in NC mimic group(465.80±9.20)(P<0.01).The number of transmembrane cells in the miR-30a inhibitor group in 5637 cells(581.25±11.02)was significantly lower than that in NC mimic group(397.13±7.57)(P<0.01).Conclusion Up-regulation of miR-30a can inhibit the proliferation of bladder cancer cells,promote cell apoptosis and reduce the ability of migration and invasion in bladder cancer cells.The low expression of miR-30a in bladder cancer cells may be related to the development and metastasis in bladder cancer.
Bladder cancer cell;miRNA-30a;Proliferation;Apoptosis;Invasion
哈尔滨医科大学附属第二医院(哈尔滨 150086)
柳清,女,(1989-),硕士,住院医师,从事基因靶向治疗的研究。
邢丽娜,E-mail:xinglina@medmail.com.cn
R737.14
A
10.11904/j.issn.1002-3070.2017.04.005
