ApoEε4等位基因对认知正常老年人脑微观结构影响的扩散峰度成像研究
2017-04-19赵燕凌王效春郝晓勇
赵燕凌 王 军 王效春 张 辉 郝晓勇 李 丹
(1.山西医科大学医学影像学系,太原 030001;2.山西医科大学第一医院影像科,太原 030001)
·临床研究 ·
ApoEε4等位基因对认知正常老年人脑微观结构影响的扩散峰度成像研究
赵燕凌1王 军1王效春2*张 辉2郝晓勇1李 丹1
(1.山西医科大学医学影像学系,太原 030001;2.山西医科大学第一医院影像科,太原 030001)
目的 通过应用磁共振扩散峰度成像(diffusion kurtosis imaging, DKI)技术评估认知正常的老年人中携带和非携带载脂蛋白 Eε4 (apolipoprotein Eε4,ApoEε4)等位基因者脑微观结构的差异,进而探讨ApoEε4等位基因对脑微观结构的影响。方法 收集18例正常老年人口腔黏膜,检测是否携带ApoEε4基因;同时对其行常规核磁共振成像(magnetic resonance imaging,MRI)平扫及DKI扫描,分别于双侧额、顶、颞叶,后扣带回、胼胝体压部及海马测量平均峰度(mean kurtosis, MK)值及各项异性分数(fractional anisotraphy, FA)值,采用两样本t检验对携带与非携带ApoEε4基因所得的参数进行比较。结果 认知正常老年人携带ApoEε4等位基因组与非携带组比较,颞叶及海马MK值减低,且差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);海马的FA值减低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 认知正常老年人携带ApoEε4等位基因的受试者脑微观结构改变更加明显,DKI能够早期发现该等位基因对于脑微观结构改变的影响。
正常老年人;扩散峰度成像;ApoEε4等位基因
载脂蛋白 Eε4 (apolipoprotein Eε4,ApoEε4)是脂蛋白调解系统中的重要的蛋白,同时还具有维护和修复神经细胞的作用[1]。编码基因位于19号染色体上ApoE基因,由于基因具有多态性,分别为ApoEε2、ApoEε3和ApoEε4,其中与阿尔茨海默病(Alzheimer disease, AD)关系最密切是ApoEε4基因,也是目前被公认的AD的高危遗传因素[2]。AD病人中携带该等位基因的人数超过一半,同时该基因的表达会提高AD的发病风险,将使认知功能障碍的出现提前7~9年[3]。ApoEε4基因的作用机制包括β淀粉样蛋白(amyloid-β, Aβ)依赖效应,即调节Aβ的聚集、神经毒性等,以及非Aβ依赖效应的神经细胞的发育、脂类及葡萄糖代谢等[4]。有研究[5]发现,在临床症状出现前ApoEε4基因就开始改变大脑的微观结构了。
磁共振成像技术发展迅猛,从传统的形态学成像,到近年来发展的血氧浓度依赖功能磁共振成像(blood oxygen level dependent-functional magnetic resonance imaging,BOLD-fMRI)、波谱成像(magnetic resonance spectroscopy, MRS)、扩散成像等,为脑微观结构评估提供了更多的方法[6-7]。其中扩散峰度成像(diffusion kurtosis imaging,DKI)技术能真实反映脑微观结构的改变[8-9],但在ApoEε4等位基因者脑微观结构的评估方面,尚处于初始阶段10-12]。本研究通过应用DKI技术评估认知正常的老年人中携带和非携带ApoEε4等位基因者脑微观结构的差异,进而探讨ApoEε4等位基因者脑微观结构的影响。
1 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象
招募2015年1月至2016年1月18例正常认知老年人18人,其中,男性9例,女性9例,年龄50~76岁,平均年龄(67.1±4.2)岁;ApoEε4基因分析结果所有对照组成员均除外颅脑手术史、脑血管病史、脑肿瘤史、脑外伤史及精神方面等病史,认知功能正常,同时 MMSE≥28分。
1.2 磁共振成像(magnetic resonance imaging,MRI)扫描技术
使用GE Signa HDxT 3.0T MRI扫描仪,16通道头颈联合线圈。受试者仰卧,固定头部并戴耳机以减少噪音影响。先进行常规MRI平扫,包括横轴位TIWI和T2WI及低场液体衰减反转恢复(fluid attenuated inversion recovery, FLAIR)像,及矢像状位TIWI,然后行DKI扫描,选用平面回波EPI序列。
1.2.1 常规平扫
常规MRI扫描序列参数:T1WI (T1-weighted imaging)序列参数:回波时间(time of repetition, TR) 1 680 ms,重复时间(time of echo, TE) 22 ms,视野(field of view, FOV) 24.4 cm,层厚6.0 mm;T2WI (T2-weighted imaging)序列参数:TR 6 800 ms,TE 116 ms,FOV 22 cm,层厚6.0 mm;T2WI-FLAIR序列参数:TR 8 012 ms,TE 126.8 ms,FOV 24 cm,层厚6.0 mm。
1.2.2 DKI成像
选用单次激励平面回波序列 (echo planner imaging,EPI)序列进行扫描,参数为30个扩散敏感梯度场,b值分别为0、1 000、2 000 s/mm2,TR 6 506 ms,TE 115 ms,FOV 24cm,层厚6.0 mm。
1.3 DKI数据处理
将所得原始DKI数据传至工作站(GE Advantage Workstation4.4),利用Functools图像处理软件处理,得到平均峰度(mean kurtosis, MK)图、平均扩散(mean diffusivity, MD)图、各向异性分数(fractional anisotropy, FA)图。分别于双侧额、顶、颞叶、后扣带回、胼胝体压部及海马设置类圆形感兴趣区(region of interest,ROI),面积15~30 mm2,除胼胝体压部外均采用镜面对照的方式设置,同一位置行3次重复测量,最终取测量的均值。
1.4ApoEε4基因采集及单核苷酸多态性(single nucleotide polymorphism, SNP)位点检测
1.4.1ApoEε4基因采集
嘱受试者在采集样本前1 h内禁食,饮约50 mL清水清洁口腔;取口腔试子(过程中手绝不能触碰试子),用拭子在口腔内壁旋转取样,待第一根取完后,用第二根于对侧口腔内壁重复操作,以取得满意的样本为宜。
1.4.2ApoEε4基因 SNP位点检测
使用口腔试子提取试剂盒从样品中提取DNA;根据位点信息(ApoeE4的SNP号码为:rs7412和rs429358)设计合成引物,随后行聚合酶链反应(polymerase chain reaction, PCR)扩增;对扩增出的样品进行测序;使用Sequence Scanner软件对结果进行分析,最后得出结论。
1.5 统计学方法
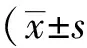
2 结果
2例携带ApoEε4基因,16例未携带ApoEε4基因,携带率为11.1%。
认知正常老年人携带ApoEε4等位基因组与非携带组比较,颞叶及海马MK值减低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05,表1);海马的FA值减低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05,表2)。
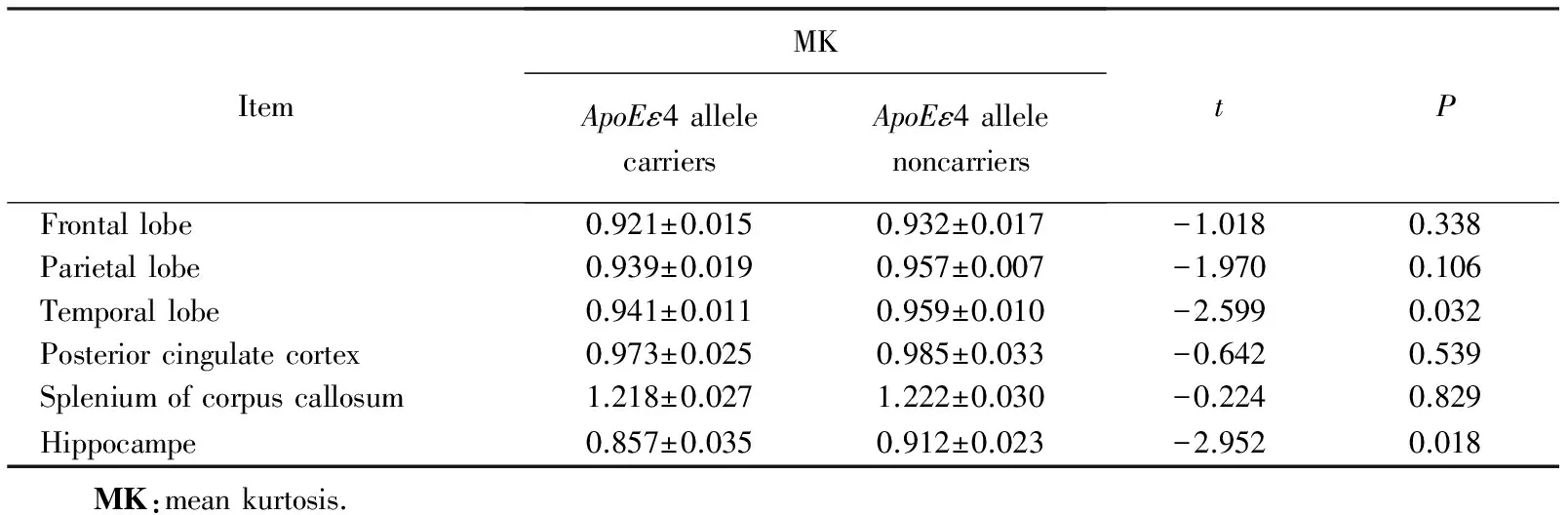
表1 携带ApoEε4等位基因组与非携带组的MK值比较
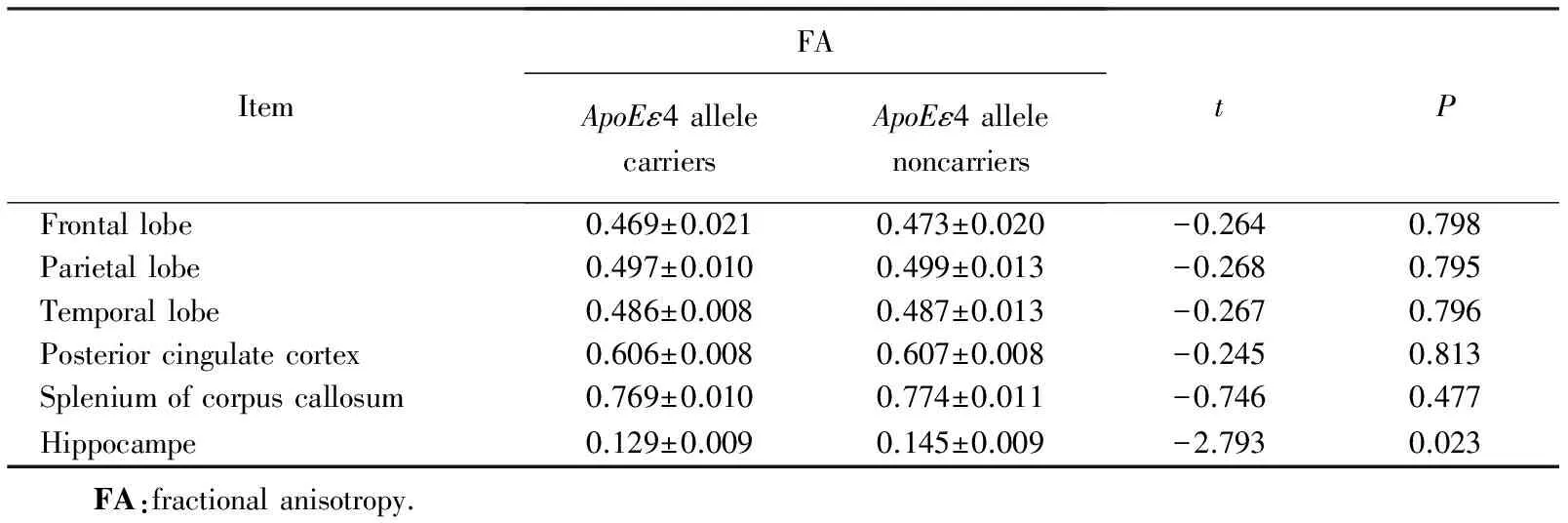
表2 携带ApoEε4等位基因组与非携带组的FA值比较
3 讨论
DKI是扩散张量成像(diffusion tensor imaging,DTI)技术上延伸出的一种新的磁共振成像技术。DTI 的原理是假设人体组织内水分子呈高斯分布,通过其弥散的各向异性程度来了解组织的微观结构。DTI 的主要参数是FA和MD, FA 是描述水分子在组织内弥散的各向异性的程度,以此来反映白质纤维的完整性,扩散的方向性越强, FA 值越大[13];而MD反映的是整体水分子的扩散,它仅表示扩散的程度,与方向无关,扩散受限越小,MD值越大。在AD病人中,由于髓鞘的脱失导致神经纤维的完整性破坏,水分子扩散的各向异性降低,FA值下降。MD 值受多方面因素的影响,由于AD会导致神经元的破坏以及丢失,使得局部水分子的扩散受限减低,MD值也相应增加。
DKI技术是对人体组织内水分子真实扩散的认识的改变发展而来的[14],在人体组织内,由于细胞膜、细胞器等复杂的细胞结构的存在,使得水分子的扩散不是呈理想的高斯分布,而是呈非高斯分布,DKI正是在此基础上发展而来的,理论上此种非高斯扩散模型对于组织微观结构的描述更加准确[15-16]。DKI在DTI技术的基础上,通过引入了MK这个无量纲参数来描述人体内水分子的非高斯扩散与理论上的高斯扩散的位移偏离度,这样就能更真实描述人体组织的微观结构; DKI还引入一个四阶修正项到DTI的二阶成像公式上,来解决多纤维交叉的问题;同时DTI对于各项同性的灰质的检测并不敏感,而DKI并不受此种限制,这就为诊断提供了更多可选择的区域[17-18]。MK作为DKI的代表参数,可以反映组织微观结构的复杂程度,即水分子扩散受限越明显,MK值越大,表明结构越复杂,反之亦然。
本研究利用DKI技术,将认知正常老年人中携带与非携带ApoEε4基因组的进行比较,发现在颞叶及海马MK值的下降差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),说明该基因在早期就已经开始影响这两个区域,使得其复杂性明显减低,这与既往应用BOLD-fMRI的研究[19]结果相一致,表明该区域对于ApoEε4基因的影响更敏感,其原因可能与AD的发病规律有关,其发病最早累及内嗅皮层、海马等,然后逐渐其他区域。而海马的FA值下降差异也有统计学意义,与Adluru等[20]应用DTI得到的结果相一致,表明ApoEε4基因对于海马区域神经纤维的完整性的破坏显著。关于海马,既往研究[21]还发现,ApoEε4基因不仅影响其微观结构,还发现早期导致海马体积的萎缩,加速病程发展。所以较DTI而言,DKI能够更敏感、更全面的检出脑组织微观结构的改变。
总之,认知正常老年人携带ApoEε4等位基因的受试者脑微观结构改变更加明显,DKI能够早期发现该等基因对于脑微观结构改变的影响,为临床早期预防认知功能下降提供更多的影像学依据。本研究样本量有限,有待在以后的进一步研究中扩大样本量,以期得到的结果减少偏移,从而指导临床实践。
[1] Dowell N G, Evans S L, Tofts P S, et al. Structural and resting-state MRI detects regional brain differences in young and mid-age healthy APOE-e4 carriers compared with non-APOE-e4 carriers[J]. NMR Biomed, 2016, 29(5):614-624.
[2] Liu C C, Kanekiyo T, Xu H, et al. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer disease:risk, mechanisms and therapy[J]. Nat Rev Neurol, 2013, 9(2): 106-118.
[3] Leoni V. The effect of apolipoprotein E (ApoE) genotype on biomarkers of amyloidogenesis, tau pathology and neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Clin Chem Lab Med, 2011, 49(3): 375-383.
[4] 秦江波, 王效春, 张辉.ApoEε4等位基因携带者脑结构与功能的影像学纵向研究进展[J]. 国际医学放射学杂志, 2012, 35(1): 17-20.
[5] Heise V, Filippini N, Trachtenberg A J, et al.Apolipoprotein E genotype, gender and age modulate connectivity of the hippocampus in healthy adults[J]. Neuroimage, 2014,98:23-30.
[6] Laakso M P, Jukarainen N M, Vepsäläinen J. Diagnosis of dementias by high-field 1H MRS of cerebrospinal fluid[J]. Neurol Neurosurg Psychatr, 2015, 86 (12):1286-1290.
[7] Demirhan A, Nir T M, Zavaliangos-Petropulu A, et al. Feature selection improves the accuracy of classifying Alzheimer disease using diffusion tensor images[J]. Proc IEEE Int Symp Biomed Imaging, 2015:126-130.
[8] Steven A J, Zhuo J, Melhem E R. Diffusion kurtosis imaging: an emerging technique for evaluating the microstructural environment of the brain [J]. Ame Roentgenol, 2014, 202(1):W26-W33.
[9] Blockx I, Verhoye M, Van Audekerke J, et al.Identification and characterization of Huntington related pathology: an in vivo DKI imaging study[J]. Neuroimage,2012, 63(2): 653-662.
[10]Bigler E D, Lowry C M, Anderson C V, et al. Dementia,quantitative neuroimaging, and apolipoprotein E genotype[J]. Am J Neuroradiol, 2000, 21(10): 1857-1868.
[11]Adluru N, Destiche D J, Lu S Y, et al. White matter microstructure in late middle-age: effects of apolipoprotein E4 and parental family history of Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Neuroimage Clin, 2014, 4: 730-742.
[12]Smith J C, Lancaster M A, Nielson K A, et al. Interactive effects of physical activity and APOE-ε4 on white matter tract diffusivity in healthy elders[J]. Neuroimage, 2016, 131: 102-112.
[13]Byrnes T J, Barrick T R, Bell B A, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging discriminates between glioblastoma and cerebral metastases in vivo [J]. NMR Biomed, 2011, 24(1): 54-60.
[14]Jensen J H, Helpen J A. MRI quantification of non-Gaussian water diffusion by kurtosis analysis[J]. NMR Biomed, 2010, 23(7): 698-710.
[15]De Santis S, Gabrielli A, Palombo M, et al. Non-Gaussian diffusion imaging: a brief practical review [J]. Magn Reson imaging, 2011, 29(10): 1410-1416.
[16]Yuan L, Sun M, Chen Y, et al. Non-Gaussian diffusion alterations on diffusion kurtosis imaging in patients with early Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2016,616:11-18.
[17]Lanzafame S, Giannelli M, Garaci F, et al. Differences in Gaussian diffusion tensor imaging and non-Gaussian diffusion kurtosis imaging model-based estimates of diffusion tensor invariants in the human brain[J].Med Phys,2016, 43(5):2464.
[18]梁里昂,李力仙,邢晓辉,等.磁共振技术在大鼠缺血性卒中的研究进展[J]. 中国脑血管病杂志, 2014 ,11(8):445-448.
[19]Wang L,Zang Y,He Y,et al. Changes in hippocampal connectivity in the early stages of Alzheimer′ s disease:evidence from resting state fMRI[J]. Neuroimage,2006,31(9):496-504.
[20]Adluru N, Destiche D J, Lu S Y, et al. White matter microstructure in late middle-age: Effects of apolipoprotein E4 and parental family history ofAlzheimer’s disease[J]. Neuroimage Clin, 2014, 4:730-742.
[21]Smith J C, Lancaster M A, Nielson K A, et al. Interactive effects of physical activity and APOE-ε4 on white matter tract diffusivity in healthy elders[J]. Neuroimage,2016,131:102-112.
编辑 慕 萌
Diffusion kurtosis imaging study: the effects ofApoEepsilon4 alleles on brain microstructure in healthy elders
Zhao Yanling1, Wang Jun1, Wang Xiaochun2*, Zhang Hui2, Hao Xiaoyong1, Li Dan1
(1.DepartmentofMedicalImaging,ShanxiMedicalUniversity,Taiyuan030001,China;2.DepartmentofRadiology,TheFirstClinicalMedicalCollege,ShanxiMedicalUniversity,Taiyuan030001,China)
Objective To compare the difference of the brain microstructure between apolipoprotein Eε4 (ApoEε4) allele carriers and noncarriers of normal elderly people with normal cognitive state and to explore the influence ofApoEε4 alleles on its brain microstructure by using diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) magnetic resonance technology. Methods TheApoEε4 alleles was detected in oral mucosa of 18 normal elders; All subjects underwent routine magnetic resonance imaging(MRI) scanning and DKI scanning. Mean kurtosis(MK) and fractional anisotraphy(FA) values were measured in bilateral frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, posterior cingulate cortex, splenium of corpus callosum and hippocampe. The two-sample t-test was used to compare the parameters between theApoEε4 allele carriers and noncarriers. Results MK value in the temporal lobe and hippocampus of theApoEε4 allele carriers was significantly lower than in that of noncarriers (P<0.05). FA value in the hippocampus of theApoEε4 allele carriers was significantly lower than in that of noncarriers (P<0.05). Conclusion Microstructural changes of the brain ofApoEε4 alleles carriers in normal elderly persons with normal cognitive state are more obvious. DKI could detect the influence ofApoEε4 allele on the microstructural changes of the brain in the eraly time.
normal elderlys; diffusion kurtosis imaging;ApoEε4 alleles
山西省科技攻关项目(20130313020-5),山西省卫生厅科技攻关计划项目(2011030)。This study was supported by Key Scientific and Technological Project of Shanxi Province(20130313020-5), Health Department of Science and Technology Research Project of Shanxi Province(2011030).
时间:2017-04-13 19∶38
http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3662.R.20170413.1938.012.html
10.3969/j.issn.1006-7795.2017.02.027]
R445.2
2016-11-21)
*Corresponding author, E-mail:2010xiaochun@163.com
