香芹酚诱导非小细胞肺癌1299细胞凋亡的实验研究
2017-01-09罗磊王永坤李世康
罗磊,王永坤,李世康
香芹酚诱导非小细胞肺癌1299细胞凋亡的实验研究
罗磊,王永坤,李世康△
目的 探讨香芹酚(CV)对人非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)NCI-H1299细胞的增殖、凋亡及侵袭的作用及可能机制。方法以不同浓度的CV(20、40、60、80 μmol/L)处理NCI-H1299细胞,以未经CV处理的细胞为对照组。采用四甲基偶氮唑蓝(MTT)比色法检测细胞存活率;流式细胞术检测各组细胞凋亡率;Transwell法检测40 μmol/L CV处理组和对照组细胞侵袭能力;实时荧光定量PCR及Western blot检测40 μmol/L CV处理组和对照组的半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶(caspase)-9、基质金属蛋白酶(MMP)-9、TIMP-1的mRNA及蛋白水平的表达变化。结果与对照组比较,CV各处理组NCI-H1299细胞存活率均明显降低,而凋亡率增加(P<0.05),但抑制效应均不呈浓度依赖性(P>0.05)。CV处理组侵袭细胞数(40.67±3.63)个明显低于对照组(76.00±5.78)个(P<0.01)。CV处理组较对照组caspase-9、TIMP-1的mRNA和蛋白表达水平均增高,MMP-9的mRNA和蛋白表达水平均降低(P<0.01)。结论CV可诱导人NSCLC NCI-H1299细胞凋亡,抑制其侵袭,作用机制可能与caspase-9的活性增加及MMP-9的下调有关。
非小细胞肺癌;细胞凋亡;肿瘤侵润;半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶9;基质金属蛋白酶9;金属蛋白酶类组织抑制剂;香芹酚;人非小细胞肺癌NCI-H1299细胞
研究显示,在全世界癌症中,肺癌发病率和死亡率均较高,每年可造成约150万人死亡[1-2]。肺癌分为非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)和小细胞肺癌(SCLC),其中NSCLC占所有肺癌的85%,而约75%的NSCLC患者在发现时已处于中晚期[3]。研究显示,NSCLC的5年生存率仅为15%[4]。因此,探索肺癌发生、恶化的机制,寻找有效的诊断和治疗靶标非常重要。香芹酚(Carvacrol,CV)为一种单帖酚,化学结构为5-异丙基-2-甲基苯酚,是百里香油、香薷精油的主要成分,作为安全的添加剂广泛用于食品及日用品的生产过程中[5-7]。既往研究表明,CV具有抗炎[8]、抗氧化应激[9]及抗肿瘤[10]等多种生物学活性。近年研究发现,CV对多种肿瘤细胞均具有抑制增殖和诱导凋亡作用,如肝癌HepG2[11]、转移性乳腺癌MDAMB231[10]等。目前,有关CV抗肺癌的作用及机制研究少见。因此,本研究将CV作用于NSCLCNCIH1299细胞,选择半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶-9(caspase-9)、基质金属蛋白酶-9(MMP-9)及其抑制剂(TIMP-1)为作用靶点,观察CV对肿瘤细胞凋亡和侵袭作用的影响,并初步探讨相关机制,以期为NSCLC的精准治疗提供参考。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料人NSCLCNCI-H1299细胞(中科院上海细胞生物学研究所细胞库);RPMI1640培养基及胎牛血清(美国Gibco公司);细胞裂解液和BCA蛋白含量测定试剂、Western blot检测试剂盒(江苏碧云天公司);PVDF膜(Millipore公司);caspase-9、MMP-9、TIMP-1抗体及GAPDH IgG抗体(武汉博士德);四甲基偶氮唑盐(MTT)、二甲亚砜(DMSO)、CV(美国SIGMA公司);凋亡检测试剂盒AnnexinV-FITC/PI KIT、Matrigel基质胶、流式细胞仪(美国BD公司);Transwell板(美国Corning公司);逆转录试剂盒(日本TaKaRa公司);TRIzol(美国Invitrogen公司)。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 NCI-H1299细胞培养在含10%胎牛血清、链霉素100 mg/L和青霉素100 U/mL的RPMI 1640培养基中,置于37℃、5%CO2、95%饱和湿度的培养箱中培养,2.0%胰蛋白酶进行消化传代,取对数生长期细胞用于后续实验。
1.2.2 MTT法检测细胞存活率取对数生长期细胞消化、计数,以5×104/mL接种于96孔培养板(每孔100 μL),待细胞生长至90%融合后,加入0(对照组)、20、40、60、80 μmol/L浓度的CV处理48 h,其中,对照组细胞存活率设置为100%,加入MTT。各组分别于24和48 h在570 nm波长处测定吸光度(A)值,给药组细胞存活率=给药组A/对照组A× 100%,对照组细胞存活率=(24或48 h)对照组A/0 h对照组A×100%,实验重复5次。
1.2.3 流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡率取对数生长期NCIH1299细胞,每孔以5×104/mL接种于6孔板中,每孔2 mL,分组同1.2.2,处理24 h后收集各组细胞,与AnnexinV-FITC结合,加入碘化丙啶染色液,轻轻混匀后避光冰浴孵育,流式细胞仪检测,实验重复5次。
1.2.4 Transwell检测细胞侵袭能力Matrigel基质胶包被Transwell上室内膜。调整NCI-H1299细胞密度,按5×103/mL的密度接种上室,根据1.2.2的结果加入终浓度为40 μmol/L的CV进行处理(CV处理组);下室为含有10%胎牛血清的RPMI1640培养液,置于细胞培养箱中培养。以未加入CV处理的细胞为对照组,各组于48 h后取出上室,PBS淋洗,4%甲醛固定15 min,晾干后结晶紫染液染色5 min,倒置显微镜下(×100)计数移至微孔膜下层的细胞。每个样本计数10个视野。实验重复3次。
1.2.5 实时荧光定量PCR检测caspase-9、MMP-9、TIMP-1 mRNA的表达分组同1.2.4。按TRIzol试剂盒说明书提取细胞总RNA,电泳鉴定并定量后,依据TaKarRa公司逆转录说明书将提取的RNA逆转录成cDNA,实时荧光定量PCR反应:SYBR反应体系共25 μL。目的基因和内参基因引物序列设计由上海吉凯生物工程有限公司完成,见表1。扩增条件:95℃2 min;95℃10 s,60℃30 s,30个循环。熔解条件:95℃2 min,95℃15 s,60℃1 min,95℃15 s。以2-ΔΔCt计算目的基因mRNA的相对表达量,每组重复3次取平均值。

Tab.1 Primer sequence of quantitative real time-PCR表1 实时荧光定量PCR引物序列
1.2.6 Western blot检测caspase-9、MMP-9、TIMP-1蛋白的表达分组同1.2.4。取2组细胞各加入RIPA裂解液提取总蛋白,BCA法进行蛋白定量。取各组总蛋白40 μg进行电泳,转膜,封闭,一抗4℃孵育过夜。加入1∶5 000倍稀释二抗,37℃孵育,ECL法进行底物发光,曝光成像后分析。图片结果用图像分析软件AlphaimagerTM 2200进行分析,以目的条带灰度值/内参条带灰度值反映相对蛋白表达量,以上步骤重复3次。
1.3 统计学方法采用SPSS 13.0统计软件作统计分析。符合正态分布的计量资料以表示,多组间均数比较用单因素方差分析,组间多重比较用LSD-t法;2组间比较采用t检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 CV对NCI-H1299细胞存活率的影响与对照组比较,CV各处理组NCI-H1299细胞存活率均明显降低(P<0.05),但处理组间细胞存活率差异均无统计学意义,抑制效应不呈浓度依赖性(P>0.05),见表2。
2.2 CV对NCI-H1299细胞凋亡的影响对照组和20、40、60、80 μmol/L组处理24 h后的细胞凋亡率分别为(0.12±0.02)%、(94.12±2.79)%、(95.27± 2.34)%、(93.93±4.57)%、(96.12±2.79)%,各处理组均高于对照组(F=13.726,P<0.05),但处理组间细胞凋亡率差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05),见图1。
2.3 CV对NCI-H1299细胞侵袭能力的影响CV处理组侵袭细胞数(40.67±3.63)个,明显低于对照组(76.00±5.78)个(t=43.296,n=3,P<0.01),见图2。
2.4 各组caspase-9、MMP-9、TIMP-1 mRNA和蛋白表达情况比较CV处理组较对照组caspase-9、TIMP-1的mRNA和蛋白表达水平均增高,MMP-9的mRNA和蛋白表达水平均降低(P<0.01),见表3、图3。
Tab.2 The proliferation of NCI-H1299 cells treated with different concentrations and different time points of carvacrol表2 CV对NCI-H1299细胞存活率的影响(n=5,%,)
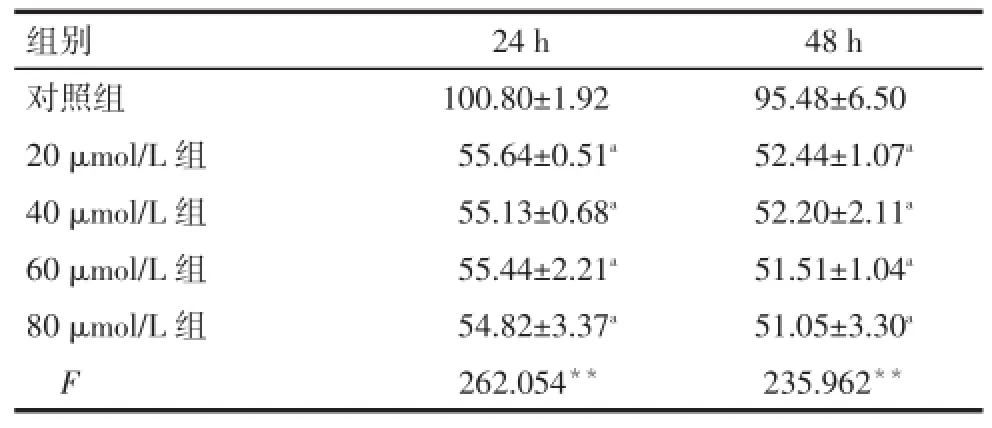
Tab.2 The proliferation of NCI-H1299 cells treated with different concentrations and different time points of carvacrol表2 CV对NCI-H1299细胞存活率的影响(n=5,%,)
**P<0.01;a与对照组比较,P<0.05
组别对照组20 μmol/L组40 μmol/L组60 μmol/L组80 μmol/L组F 24 h 100.80±1.92 55.64±0.51a55.13±0.68a55.44±2.21a54.82±3.37a262.054**48 h 95.48±6.50 52.44±1.07a52.20±2.11a51.51±1.04a51.05±3.30a235.962**
Tab.3 The mRNA and protein expressions of caspase-9, MMP-9 and TIMP-1 in control group and carvacrol treatment group表3 对照组和CV处理组caspase-9、MMP-9、TIMP-1 mRNA和蛋白表达情况(n=3,)
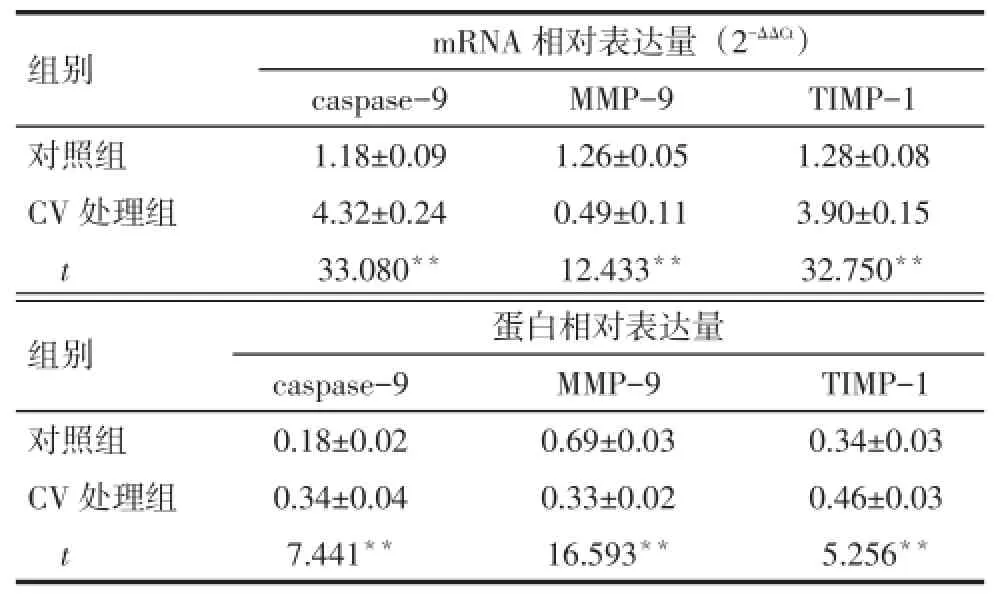
Tab.3 The mRNA and protein expressions of caspase-9, MMP-9 and TIMP-1 in control group and carvacrol treatment group表3 对照组和CV处理组caspase-9、MMP-9、TIMP-1 mRNA和蛋白表达情况(n=3,)
**P<0.01
组别对照组CV处理组t mRNA相对表达量(2-ΔΔCt)caspase-9 1.18±0.09 4.32±0.24 33.080**MMP-9 1.26±0.05 0.49±0.11 12.433**TIMP-1 1.28±0.08 3.90±0.15 32.750**组别对照组CV处理组t caspase-9 0.18±0.02 0.34±0.04 7.441**蛋白相对表达量MMP-9 0.69±0.03 0.33±0.02 16.593**TIMP-1 0.34±0.03 0.46±0.03 5.256**

Fig.1 The apoptosis of NCI-H1299 cells treated with different concentrations of carvacrol图1 不同浓度CV对NCI-H1299细胞凋亡的影响
3 讨论
研究显示,CV具有广泛的抗肿瘤活性,抗肿瘤机制主要集中在丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogenactivated protein kinase,MAPK)通路[10-11],MAPK参与MMPs家族及caspase家族的表达调节[12-13]。
肺癌是最常见的恶性肿瘤之一,通常情况下其发生发展与癌细胞增殖、凋亡、侵袭密切相关。癌细胞凋亡作为一种主动性的程序性死亡,在肺癌治疗中发挥重要作用[14];这一过程包括凋亡相关蛋白表达失衡(如Bax、Bcl-2)、激活启始caspase酶及效应caspase酶、特异性结合细胞色素C等一系列生化级联反应[15]。caspase家族参与调控细胞内的一系列凋亡级联反应,可通过激活caspase-9、阻滞细胞周期从而发挥抗肿瘤作用[16-17]。caspase-9是主要的凋亡启动分子,是线粒体凋亡及死亡途径的关键蛋白酶[18]。在接受外界凋亡信号后,caspase-9可被细胞色素C激活,继而阻碍DNA修复、降解细胞外基质及骨架等,最终导致细胞凋亡[19]。有研究认为,以caspase-9为靶点,可以干预肿瘤进程,这可作为肺癌治疗的策略之一[20]。
肺癌细胞侵润转移为一个多步骤的生物学过程,其中肺癌细胞外基质和基底膜的降解是肿瘤转移的重要环节。MMPs能有效降解肺癌细胞的细胞外基质[21-22];其中MMP-9在肺癌细胞侵袭转移过程中起着重要作用[23]。

Fig.2 The invasion ability of NCI-H1299 cells inhibited by carvacrol(crystal violet staining,×100)图2 CV对NCI-H1299细胞侵袭能力的影响(结晶紫染色,×100)
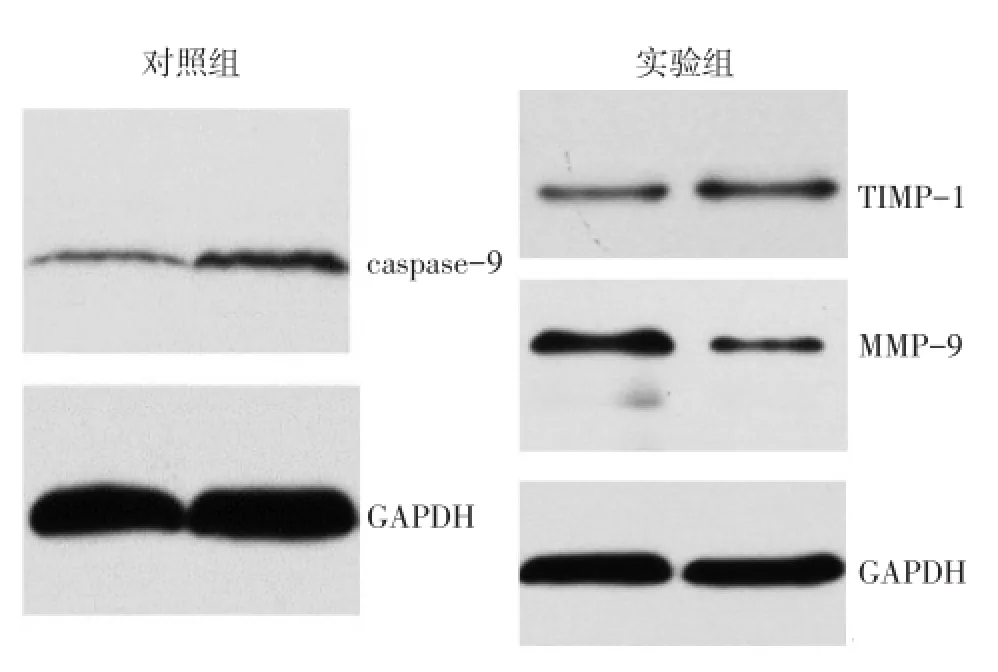
Fig.3 Comparison of protein expressions of caspase-9,MMP-9 and TIMP-1 between control and carvacrol treatment grounds图3 对照组和CV处理组caspase-9、MMP-9、TIMP-1蛋白表达情况
本研究结果显示,NCI-H1299细胞经CV处理后,与对照组比较,CV各处理组NCI-H1299细胞存活率均明显降低,凋亡率增加,表明NCI-H1299细胞增殖活性受到抑制,细胞凋亡显著增加,但不呈浓度-效应依赖关系;而CV处理组侵袭细胞数明显低于对照组,提示CV在抑制NCI-H1299细胞侵袭转移的过程中也发挥作用。另外,本研究显示,CV处理组较对照组caspase-9和TIMP-1的mRNA和蛋白表达水平均增高,而MMP-9的mRNA和蛋白表达水平均降低,其中,caspase-9的mRNA和蛋白表达水平增高表明作用机制可能涉及caspase-9激活,进而引起凋亡级联反应,从而发挥了抗肿瘤作用的过程;MMP-9表达受到抑制而TIMP-1表达升高,提示MMP-9可能参与抑制NCI-H1299细胞的侵袭活性,而上述作用是否具有浓度依赖性抑或是否与激活时间有关等尚不明确,并且这一过程是否涉及其他信号转导通路亦有待于后续实验的验证。
综上所述,CV能诱导NCI-H1299细胞凋亡并抑制癌细胞侵袭,可能机制是通过增加caspase-9的活性和抑制MMP-9的表达来完成,因此,CV有可能成为临床治疗NSCLC的潜在有效药物。
[1]Siegel R,Naishadham D,Jemal A.Cancer statistics,2013[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2013,63(1):11-30.doi:10.3322/caac.21166.
[2]Kim AW,Faber LP,Warren WH,et al.Bilobectomy for non-small cell lung cancer:a search for clinical factors that may affect perioperativemorbidityandlong-termsurvival[J].Thorac Cardiovasc Surg,2010,139:606-611.doi:10.1016/j.jtcvs.2009. 05.044.
[3]Reck M,Heigener DF,Mok T,et al.Management of non-small-cell lung cancer:recent developments[J].Lancet,2013,382(9893):709-719.doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(13):61502-0.
[4]Ding L,Getz G,Wheeler DA,et al.Somatic mutations affect key pathways in lung adenocarcinoma[J].Nature,2008,455(7216):1069-1075.doi:10.1038/nature07423.
[5]De L Guimarães LG,da Silva ML,Reis PC,et al.General Characteristics,PhytochemistryandPharmacognosyof Lippiasidoides[J].Nat Prod Commun,2015,10(11):1861-1867.
[6]Friedman M.Chemistry and multibeneficial bioactivities of carvacrol(4-isopropyl-2-methylphenol),a component of essential oils produced by aromatic plants and spices[J].J Agric Food Chem,2014,62(31):7652-7670.doi:10.1021/jf5023862.
[7]Hassanien MF,Assiri AM,Alzohairy AM,et al.Health-promoting value and food applications of black cumin essential oil:an overview[J].J Food Sci Technol,2015,52(10):6136-6142.doi:10.1007/ s13197-015-1785-4.
[8]Botelho MA,Nogueira NA,Bastos GM,et al.Antimicrobial activity of the essential oil from Lippiasidoides,carvacrol and thymolagainst oral pathogens[J].Braz J Med Biol Res,2007,40(3):349-356.
[9]Kianmehr M,Rezaei A,Boskabady MH.Effect of carvacrol on various cytokines genes expression in splenocytes of asthmatic mice[J].Iran J Basic Med Sci,2016,19(4):402-410.
[10]Arunasree KM.Anti-proliferative effects of carvacrol on a human metastaticbreastcancercellline,MDA-MB231[J]. Phytomedicine,2010,17(8):581-588.doi:10.1016/j. phymed.2009.12.008.
[11]Yin QH,Yan FX,Zu XY,et al.Anti-proliferative and proapoptotic effect of carvacrol on human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HepG-2[J].Cytotechnology,2012,64(1):43-51.doi: 10.1007/s10616-011-9389-y.
[12]Su Y,Wan D,Song W.Dryofragin inhibits the migration and invasion of human osteosarcoma U2OS cells by suppressing MMP-2/9 and elevating TIMP-1/2 through PI3K/AKT and p38 MAPK signaling pathways[J].Anticancer Drugs,2016,27(7):660-668. doi:10.1097/CAD.0000000000000381.
[13]Zhang M,Wang X,Bai B,et al.Oxymatrine protects against sepsisinduced myocardial injury via inhibition of the TNF-α/p38-MAPK/ caspase-3 signaling pathway[J].Mol Med Rep,2016,14(1):551-559.doi:10.3892/mmr.2016.5250.
[14]Wu SH,Bau DT,Hsiao YT,et al.Bufalin induces apoptosis in vitro and has Antitumor activity against human lung cancer xenografts in vivo[J].Environ Toxicol,2016,Jul 22.doi:10.1002/tox.22325.[Epub ahead of print].
[15]Hu Y,Benedict MA,Ding L,et al.Role of cytochromec and dATP/ ATP hydrolysis in Apaf-1-mediated caspase-9 activation and apoptosis[J].EMBO J,1999,18(13):3586-3595.
[16]Lin L,Baehrecke EH.Autophagy,cell death,and cancer[J].Mol Cell Oncol,2015,2(3):e985913.doi:10.4161/23723556.2014. 985913.
[17]Tewary P,Gunatilaka AA,Sayers TJ.Using natural products to promote caspase-8-dependent cancer cell death[J].Cancer Immunol Immunother,2016 Jun 10.[Epub ahead of print].
[18]Marek Ł.The role of the apoptosome in the activation of procaspase-9[J].PostepyHig Med Dosw,2013,67:54-64.
[19]Lai GH,Zhang Z,Sirica AE.Celecoxib acts in a cyclooxygenase-2-independent manner and in synergy with emodin to suppress rat cholangiocarcinoma growth in vitro through a mechanism involving enhanced Akt inactivation and increased activation of caspases-9 and-3[J].Mol Cancer Ther,2003,2(3):265-271.
[20]Shultz JC,Chalfant CE.Caspase 9b:a new target for therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer[J].Expert Rev Anticancer Ther,2011,11(4):499-502.doi:10.1586/era.11.23.
[21]Wang G,Tian W,Liu Y,et al.Visfatin Triggers the Cell Motility of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer via Up-Regulation of Matrix Metalloproteinases[J].Basic ClinPharmacolToxicol,2016 May 25. doi:10.1111/bcpt.12623.[Epub ahead of print].
[22]FinkK,BoratyńskiJ.Theroleofmetalloproteinasesin modification of extracellular matrix in invasive tumor growth,metastasis and angiogenesis[J].PostepyHig Med Dosw(Online),2012,66:609-628.
[23]Pietruszewska W,Bojanowska-Poźniak K,Kobos J.Matrix metalloproteinases MMP1,MMP2,MMP9 and their tissue inhibitors TIMP1,TIMP2,TIMP3inheadandneckcancer:an immunohistochemical study[J].Otolaryngol Pol,2016,70(3):32-43.doi:10.5604/00306657.1202546.
(2016-06-28收稿 2016-09-12修回)
(本文编辑 陆荣展)
Study on the carvacrol induced apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer cell line H1299
LUO Lei,WANG Yongkun,LI Shikang△
Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Diseases,the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021,China
△
ObjectiveTo study whether carvacrol can cause apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer(NSCLC)cell line NCI-H1299,and explore its possible molecular mechanism.MethodsNCI-H1299 cells were treated with different concentrations of carvacrol(20,40,60 and 80 μmol/L)for 24 or 48 h.The viability of cells was evaluated by MTT assay, apoptosis was analyzed by flow cytometry(FCM)and the effect of carvacrol on metastasis of NCI-H1299 was analyzed by Transwell assay.The expression level of caspase-9,MMP-9 and TIMP-1 were detected by quantitative realtime-PCR and Western blot assay.ResultsAfter treatment with carvacrol,the viability of NCI-H1299 cells was suppressed dramatically (P<0.05),without dose-dependent manner(P>0.05).After being incubated with carvacrol for 24 h,FCM analysis indicated that carvacrol effectively induced apoptosis in NCI-H1299 cells(P<0.05),without dose-dependent manner(P>0.05).The ability of invasion was decreased(40.67±3.63 vs.76.00±5.78).Carvacrol inhibited the protein and mRNA expression levels of caspase-9,but increased the expression of MMP-9 and TIMP-1(P<0.05).ConclusionCarvacrol can induce apoptosis of NCI-H1299 cells and inhibit their invasion,which may be associated with up-regulation of caspase-9 expression and down-regulation of MMP-9 expression.
carcinoma,non-small-cell lung;apoptosis;neoplasm invasiveness;caspase 9;matrix metalloproteinases 9; tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases;Carvacrol;human non-small cell lung cancer NCI-H1299 cells
R285.5,R734.2
A
10.11958/20160597
广西医科大学第一附属医院心胸外科(邮编530021)
罗磊(1983),男,主治医师,硕士在读,主要从事肺癌研究
△通讯作者E-mail:shikangli@hotmail.com
