富勒醇的生物医学应用*
2016-12-22李红亮杨胜韬
李红亮,杨胜韬
(西南民族大学化学与环境保护工程学院,四川 成都 610041)
富勒醇的生物医学应用*
李红亮,杨胜韬
(西南民族大学化学与环境保护工程学院,四川 成都 610041)
富勒烯(C60)作为最具代表性的碳纳米材料之一,由于其独特的结构和物理化学性质,在许多领域有着极为广阔的应用前景,如电子、生物、医学、材料及催化等。富勒醇是通过化学方法在富勒烯的碳笼上引入羟基而得到的功能化衍生物。由于容易合成,结构简单,生物相容性好,受到了研究者的广泛关注和研究。本文在总结国内外相关研究基础上,系统阐述了富勒醇的生物医学应用研究情况。
富勒醇;生物医学;生物安全性
富勒烯C60是由 sp2碳原子组成的球形笼状分子,难溶于水[1],限制了其生物医学应用。获得水溶性富勒烯衍生物最普遍的方法是羟基化反应[2],富勒醇不仅结构简单,容易合成,生物相容性和水溶性也很好。当羟基数目达到20个左右时,富勒醇具有良好的水溶性[3]。人们在生物医学领域中对富勒醇的研究十分广泛。富勒醇具有电子亲和力,表现出很强的抗氧化能力,可减少体内自由基[4-5]。富勒醇也可作为纳米药物运载体[6],在药物开发领域有举足轻重的地位。
人们也注意到纳米粒子将进入土壤、水和空气,并通过各种途径进入动植物和人体内[7]。近来的研究表明富勒稀衍生物可能存在潜在的毒性[8-9]。高浓度的富勒醇会诱导细胞调亡[10]。研究发现,当富勒醇的剂量为100 mg/mL时,会引起细胞死亡,其机制是导致细胞中蛋白质泛素化降解[11]。因此在富勒醇生物医药应用过程中需要关注其副作用。
本文综述了富勒醇在生物医学领域中的应用,探讨富勒醇的应用前景和影响因素,并对未来的研究进行展望。
1 抗氧化和神经保护作用
生理过程离不开活性氧,但是当活性氧水平过高又会产生损伤性作用[12]。许多神经性疾病如帕金森综合症、阿尔茨海默病和肌萎缩性侧索硬化症,是由活性氧自由基过多引发的。机体衰老也与此密切相关[13-14]。富勒烯的表面上有大量C=C共价双键,容易与游离的自由基反应,被称为是吸收游离自由基的海绵[15]。在富勒烯表面引入了供电子基团羟基的富勒醇,降低了C60电负性、保留了C60自由基加成反应的活性,因而降低了生物毒性。
富勒醇几乎能够清除所有的活性氧(ROS)以及活性氮(RNS)[16-17]。富勒醇抵御由 H2O2引起的氧化应激[13, 18]、保护超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、谷胱甘肽(GSH)的氧化和减少肝脂质过氧化作用,抑制电离辐射引起的细胞凋亡[2, 19-20]。在狗小肠移植过程中,富勒醇可以减少氧化应激[21-22]。Injac等[23]证实富勒醇前处理可以消除抗癌药物─阿霉素(DOX)引起的有害影响,保护心脏。Dugan等[9]通过电子自旋光谱证明,C60(OH)12具有良好的抗氧化性能,减少由氧化应激引起的神经元细胞死亡,从而保护神经。
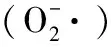
此外,富勒醇可以用作神经保护剂,原理是阻断谷氨酸受体,降低细胞间的钙离子浓度。通过实验研究发现,在中性培养液中,50 μM C60(OH)x能降低由谷氨酸引起的神经毒性的80%,且C60(OH)x抑制谷氨酸受体具有浓度依赖性[27]。
2 肿瘤治疗
富勒醇可以用于肿瘤治疗,因为富勒醇能“监禁”肿瘤细胞,抑制肿瘤生长和转移,并且没有体内毒副作用,不诱发肿瘤的抗药性。Zhu等[28]研究了C60(OH)x对肿瘤生长的抑制作用。注射C60(OH)x的时间越早、剂量越大,肿瘤抑制率越高。C60(OH)x抑制肿瘤生长的机理是激活胞内酸性磷酸酶和精氨酸酶,增强巨噬细胞的吞噬作用,从而增强小鼠的先天免疫力。陈滇宝等[29]证实,富勒醇可用于光动力杀伤和诱导癌细胞凋亡,抑制人宫颈癌细胞株 Hela以及人喉癌细胞株Hep-2的生长。
金属富勒醇[Gd@C82(OH)22]n是富勒烯的另一种衍生物,具有更强的抗肿瘤效应,可刺激免疫细胞成熟。Yin 等[5]研究表明,腹腔注射[Gd@C82(OH)22]n纳米颗粒降低了代谢相关酶的活性,作为良好的自由基清除剂,抑制肿瘤生长。Meng等[30]以MCF-7、ECV304 为模型测定[Gd@C82(OH)22]n对肿瘤细胞生长抑制,证实[Gd@C82(OH)22]n对肿瘤细胞有很强的杀伤作用。另外,梁兴杰等[31]在动物水平证实,[Gd@C82(OH)22]n促进抗性细胞的内吞作用,增加肿瘤细胞对顺铂的摄入量,进而阻断DNA 遗传物质的复制,抑制耐药肿瘤细胞的繁殖[32-33]。肿瘤细胞会释放基质金属蛋白酶(MMP)降解到细胞外基质(ECM),进而渗透到血管攻击正常的细胞,最终导致癌细胞转移。Zhao等[34]发现 Gd@C82(OH)22能够抑制 MMP。MMP会形成一个纤维笼将肿瘤细胞限定到自己的 ECM,以达到减少 MMP 的表达,从而抑制肿瘤细胞的转移[35]。Zhou等[36]使用分子动力学模拟研究表明,Gd@C82(OH)22能够与这两个结构域作用。
3 药物载体
富勒醇用于载药是另一个研究热点。富勒醇表面连接着极性基团羟基,这使它能够用作“锚”被红血球细胞骨架蛋白吸收,从而延长药物的停留时间[37]。Chaudhuri等[6]报道,富勒醇与DOX通过氨基甲酸酯实现共轭连接,可超高负载DOX。与肿瘤裂解物一起培养时会将 DOX 释放出来,进而杀死癌细胞。体内实验表明游离的 DOX与富勒醇-DOX 复合物具有相似的抗肿瘤活性,但负载后副作用消除。此外,富勒醇不仅可以输送亲水性的药物,还可以输送疏水性的药物,比如微溶于水的顺铂。
李宇国等[38]运用放射性核素67Ga 标记富勒烯衍生物C60(OH)x,定量测定富勒醇在小鼠体内的分布与转运。富勒醇在小鼠体内转运容易,主要分布在骨髓、骨、肝脏和脾中,但血脑屏障难以穿越,有望用于恶性淋巴肿瘤导向治疗的药物载体。Bhattacharya等[39]将聚酰胺-胺型树枝状大分子(PAMAM)通过伯胺与富勒醇结合,形成自组装树状分子。其中,氢键、静电作用和离子键等均是复合物形成的驱动力。这种树状分子的特殊结构使其可以用作新型药物载体。
4 基因探针
Pinteala等[40]在生理学pH条件下制备了 C60(OH)24与ds DNA 的络合物,测定其在水相中的荧光性质。在DNA浓度维持不变的条件下,在富勒醇浓度为1.6×10-5~4.4×10-5mol/L时,C60(OH)24-DNA 复合物的荧光强度与浓度呈线形关系。DNA浓度低至纳摩尔级别,富勒醇的荧光强度也会数倍增长,可用于DNA探测。
5 防辐射
电离辐射有“直接作用”和“间接作用”两种,由于机体内含有大量的水份,间接作用在辐射损伤中占主要地位。“间接作用”是电离辐射作用于机体内的水或生物分子,引起水或生物分子的活化和自由基形成,这些活化的分子和自由基作用于另一生物分子,造成该生物分子的损伤[41]。富勒醇能够清除活性氧自由基,而电离辐射作用于生物体内产生超氧阴离子自由基,从而富勒醇对辐射造成的氧化损伤有防护作用。李宇国等[42]报道在紫外照射下,富勒醇吸收紫外照射产生的自由基使细胞膜不被紫外照射产生损伤,使得富勒醇对细胞具有保护作用。蔡小青等[43]报道了富勒醇不仅对辐射具有防护作用,并对辐射损伤的机体具有恢复治疗作用。可能的机制是通过直接吸收照射后产生的大量活性氧自由基,还可能通过提高体内的抗氧化酶活性,增强细胞免疫功能,促进造血和免疫细胞的增殖和生长,从而提高细胞对辐射的抵抗,使辐射损伤组织得到恢复。
6 MRI造影剂
在临床诊断中,核磁共振成像(MRI)技术是重要的疾病诊断方法,通过检测人体暴露于横向磁场时水分子内质子的弛豫时间,增强剂延长弛豫时间从而缩短扫描时间并获得更清晰的图像。临床用MRI 造影剂主要是以高顺磁性金属为形成体的螯合物,其中Gd-DTPA配合物最为常用。然而,螯合导致金属弛豫能力下降,造影剂的组织特异性不强,有释放有毒Gd原子的风险,容易造成机体损伤。Mikawa等[44]报道了Gd@C82的水溶性多羟基衍生物Gd@C82(OH)n的弛豫效应,其磁共振弛豫效率是目前商用造影剂Gd-DTPA的20多倍,很低剂量即可产生高清晰图像。Gd@C82(OH)x的球形结构能包裹Gd原子,防止Gd与细胞接触,同时在复杂的生化环境中不会分解释放Gd离子。卢兴等[45]发现[Gd@C82(OH)22]n的弛豫能力明显高于Gd@C82(OH)6(NHCH2CH2SO3H)8。作为一种新型的核磁成像造影剂,金属富勒醇有望在医学诊断中发挥重要作用。
7 展 望
富勒醇在药物/基因载体、生物成像、肿瘤治疗、抗病毒/抗菌以及生物传感等生物医学领域具有潜在的应用,应进一步深入系统研究。在关注其正面应用的同时,应该加强其生物安全性问题方面研究。如何使富勒烯及其衍生物在复杂的生物体内发挥其有利的作用是亟待深入研究的问题。
[1] Semenov K N, Charykov N A, Keskinov V A, et al. Solubility of light fullerenes in organic solvents[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2009, 55(1): 13-36.
[2] Grebowski J, Kazmierska P, Krokosz A. Fullerenols as a new therapeutic approach in nanomedicine[J]. Biomed research international, 2013, 2013(6):751913-751913.
[3] Bezmel’nitsyn VN, Eletskii AV, Okun’MV. Fullerenes in solutions[J]. Physics-Uspekhi, 1998, 41(11): 1091-1114.
[4] Semenov K N, Charykov N A, Postnov V N, et al. Fullerenols: Physicochemical properties and applications[J]. Progress in Solid State Chemistry, 2016, 44(2): 59-74.
[5] Yin JJ, Lao F, Meng J, et al. Inhibition of tumor growth by endohedralmetallofullerenol nanoparticles optimized as reactive oxygen species scavenger[J]. Molecular Pharmacology, 2008, 74(4): 1132-1140.[6] Mielke C, Maass K, Tümmler M, et al. Anatomy of highly expressing chromosomal sites targeted by retroviral vectors[J]. Biochemistry, 1996, 35(7): 2239-2252.
[7] Dreher K L. Health and environmental impact of nanotechnology: toxicological assessment of manufactured nanoparticles[J]. Toxicological Sciences, 2004, 77(1): 3-5.
[8] Wang J, Wages M, Yu S, et al. Bioaccumulation of fullerene (C60) and corresponding catalase elevation in Lumbriculusvariegatus[J]. Environmental toxicology and chemistry, 2014, 33(5): 1135-1141.
[9] Dugan LL, Gabrielsen JK, Shan PY, et al. Buckminsterfullerenol free radical scavengers reduce excitotoxic and apoptotic death of cultured cortical neurons[J]. Neurobiology of disease, 1996, 3(2): 129-135.
[10]Isakovic A, Markovic Z, Todorovic-Markovic B, et al. Distinct cytotoxic mechanisms of pristine versus hydroxylated fullerene[J]. Toxicological Sciences, 2006, 91(1): 173-183.
[11]Yamawaki H, Iwai N. Cytotoxicity of water-soluble fullerene in vascular endothelial cells[J]. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology, 2006, 290(6): C1495-C1502.
[12]Sayes CM, Gobin AM, Ausman KD, et al. Nano-C60cytotoxicity is due to lipid peroxidation[J]. Biomaterials, 2005, 26(36): 7587-7595.[13]Xiao L, Aoshima H, Saitoh Y, et al. Highly hydroxylated fullerene localizes at the cytoskeleton and inhibits oxidative stress in adipocytes and a subcutaneous adipose-tissue equivalent[J]. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 2011, 51(7): 1376-1389.
[14]Yang X, Jin L, Yao L, et al. Antioxidativenanofullerol prevents intervertebral disk degeneration[J]. International journal of nanomedicine, 2014, 9: 2419.
[15]Xiao L, Takada H, huiGan X, et al. The water-soluble fullerene derivative ‘Radical Sponge®’exertscytoprotective action against UVA irradiation but not visible-light-catalyzed cytotoxicity in human skin keratinocytes[J]. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters, 2006, 16(6): 1590-1595.
[16]Yin JJ, Lao F, Fu PP, et al. The scavenging of reactive oxygen species and the potential for cell protection by functionalized fullerene materials[J]. Biomaterials, 2009, 30(4): 611-621.
[17]Mirkov SM, Djordjevic AN, Andric NL, et al. Nitric oxide-scavenging activity of polyhydroxylatedfullerenol, C60(OH)24[J]. Nitric Oxide, 2004, 11(2): 201-207.
[18]Lao F, Li W, Han D, et al. Fullerene derivatives protect endothelial cells against NO-induced damage[J]. Nanotechnology, 2009, 20(22): 225103.
[19]TSAI MC, Chen YH, Chiang LY. Polyhydroxylated C60, Fullerenol, a Novel Free-radical Trapper, Prevented Hydrogen Peroxideand CumeneHydroperoxide-elicited Changes in Rat Hippocampus In-vitro[J]. Journal of pharmacy and pharmacology, 1997, 49(4): 438-445.[20]Djordjevic A, Srdjenovic B, Seke M, et al. Review of synthesis and antioxidant potential of fullerenolnanoparticles[J]. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2015, 16(1): 280.
[21]XuJY, Su YY, Cheng JS, et al. Protective effects of fullerenol on carbon tetrachloride-induced acute hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in rats[J]. Carbon, 2010, 48(5): 1388-1396.
[22]Lai YL, Chiang LY. Water-soluble fullerene derivatives attenuate exsanguination-induced bronchoconstriction of guinea-pigs[J]. Journal of autonomic pharmacology, 1997, 17(4): 229-235.
[23]Injac R, Perse M, Cerne M, et al. Protective effects of fullerenol C60(OH)24against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and hepatotoxicity in rats with colorectal cancer[J]. Biomaterials, 2009, 30(6): 1184-1196.[24]Chiang LY, Lu FJ, Lin JT. Free radical scavenging activity of water-soluble fullerenols[J]. Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical Communications, 1995 (12): 1283-1284.
[25]祝严师, 孙大勇. 富勒醇清除 OH 自由基的ESR研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 1996, 17(7): 1127-1129.
[26]Chueh SC, Lai MK, Chen SC, et al. Fullerenols in canine renal preservation-A preliminary report[A].Transplantation proceedings[C]. Elsevier, 1997, 29(1): 1313-1315.
[27]Jin H, Chen WQ, Tang XW, et al. Polyhydroxylated C60, fullerenols, as glutamate receptor antagonists and neuroprotective agents[J]. Journal of neuroscience research, 2000, 62(4): 600-607.
[28]Zhu J, Ji Z, Wang J, et al. Tumor-Inhibitory Effect and Immunomodulatory Activity of FullerolC60(OH)x[J]. Small, 2008, 4(8): 1168-1175.
[29]陈滇宝,陈红蕾,刘青.一种制备富勒醇的新方法[P]. 2003.
[30]Meng J, Xing J, Wang Y, et al. Epigenetic modulation of human breast cancer by metallofullerenol nanoparticles: in vivo treatment and in vitro analysis[J]. Nanoscale, 2011, 3(11): 4713-4719.
[31]Liang XJ, Meng H, Wang Y, et al. Metallofullerene nanoparticles circumvent tumor resistance to cisplatin by reactivating endocytosis[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2010, 107(16): 7449-7454.
[32]Wang J, Chen C, Li B, et al. Antioxidative function and biodistribution of [Gd@C82(OH)22]nnanoparticles in tumor-bearing mice[J]. Biochemical pharmacology, 2006, 71(6): 872-881.
[33]Meng J, Liang X, Chen X, et al. Biological characterizations of [Gd@C82(OH)22]n nanoparticles as fullerene derivatives for cancer therapy[J]. Integrative Biology, 2013, 5(1): 43-47.
[34]Meng H, Xing G, Sun B, et al. Potent angiogenesis inhibition by the particulate form of fullerene derivatives[J]. Acs Nano, 2010, 4(5): 2773-2783.
[35]Meng H, Xing G, Blanco E, et al. Gadolinium metallofullerenol nanoparticles inhibit cancer metastasis through matrix metalloproteinase inhibition: imprisoning instead of poisoning cancer cells[J]. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine, 2012, 8(2): 136-146.
[36]Kang S, Huynh T, Zhou R. Metallofullerenol Gd@C82(OH)22distracts the proline-rich-motif from putative binding on the SH3 domain[J]. Nanoscale, 2013, 5(7): 2703-2712.
[37]Grebowski J, Krokosz A, Puchala M. Fullerenol C60(OH)36could associate to band 3 protein of human erythrocyte membranes[J]. Biochimicaet Biophysica Acta(BBA)-Biomembranes, 2013, 1828(9): 2007-2014.
[38]李宇国,黄旋,张晓东,等. Ga标记C60衍生物 C60(OH)x的生物分布研究[J].核技术,2003, 26(5): 393-396.
[39]Bhattacharya P, Kim SH, Chen P, et al. Dendrimer-fullerenol soft-condensed nanoassembly[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012, 116(29): 15775-15781.
[40]Pinteala M. Binding fullerenol C60(OH)24to dsDNA[J]. International journal of nanomedicine, 2009, 4: 193-199.
[41]夏寿萱.放射生物学[M].北京:军事医学科学出版社,1998: 245-248.[42]李宇国,倪瑾,韩玲,等.紫外光照射下富勒醇对细胞的防护作用[J].辐射研究与辐射工艺学报, 2004, 22(6): 356-360.
[43]蔡小青,李宇国,吴胜伟,等.富勒醇对60Co γ射线致小鼠损伤的防护作用[J].中华放射医学与防护杂志, 2004, 24(6): 520-522.
[44]Mikawa M, Kato H, Okumura M, et al. Paramagnetic water-soluble metallofullerenes having the highest relaxivity for MRI contrast agents[J]. Bioconjugate chemistry, 2001, 12(4): 510-514.
[45]卢兴,徐建勋,施祖进,等.新型核磁成像对比剂——两种 Gd@C82水溶性衍生物的弛豫性能研究[J].高等学校化学学报,2004, 25(4): 697-700.
Biomedical Applications of Fullerenols*
LIHong-liang,YANGSheng-tao
(College of Chemistry and Environment Protection Engineering, Southwest University for Nationalities,Sichuan Chengdu 610041, China)
Fullerene(C60) is one of the most representative nanomaterials. Due to their excellent structure and physiochemical properties, it has a wide range of potential applications in biomedical, material science, catalysis and many other fields. Fullerenol is the derivative of fullerene after hydroxylation. Because of the easy synthesis, simple structure, good biocompatibility, fullerenol has been received extensive attention and research. Herein, bysummarizing relevant researches, the biomedical applications of fullerenol were reviewed systematically.
fullerenol; biomedicine; biosafety
西南民族大学中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金项目国家重大项目孵化项目(No:2016NZDFH01)。
李红亮(1990-),男,本科生,研究方向为纳米材料的生物安全效应。
杨胜韬(1985-),男,副教授,从事纳米材料的环境生物效应研究。
X131
A
1001-9677(2016)023-0021-03
