Rad51C在DNA损伤修复中的研究进展*
2016-11-14丁新敏陈秀丽综述王平审校
丁新敏陈秀丽综述 王平审校
·综述·
Rad51C在DNA损伤修复中的研究进展*
丁新敏①陈秀丽②综述 王平②审校
细胞毒性物质及电离辐射等易致细胞DNA损伤,真核生物中DNA双链断裂(double strand breaks,DSBs)修复的主要通路是同源重组(homologous recombination,HR)。Rad51C蛋白作为HR通路的关键因子,其表达异常可致DNA损伤修复的失调,引起基因组的不稳定,最终导致肿瘤的发生发展。近年来随着对Rad51C基因的研究,发现Rad51C可能会成为恶性肿瘤治疗的潜在靶点。本文就Rad51C在DNA损伤修复及放疗中作用的研究进展进行综述。
肿瘤 基因 DNA损伤 重组/同源重组 Rad51C
DNA双链断裂(double strand breaks,DSBs)是DNA损伤的主要形式,主要包括同源重组修复(homologous recombination,HR)和非同源末端链接(nonhomologous end joining,NHEJ)两种修复方式,两者可相互协调共同完成DSBs修复[1]。真核生物中DSBs修复的主要通路是HR,参与HR途径的主要分子有MER11-Rad51-NSB1复合物、Rad51蛋白和Rad51蛋白类似体[2]。Rad51蛋白是HR的核心蛋白之一,除直接参与前两种复合物外,还在Rad51蛋白类似体中发挥重要作用,包括XRCC3-Rad51C异二聚复合蛋白体(CX3)和Rad51B-Rad51C-Rad51D-XRCC2异四聚复合蛋白体(BCDX2)[3],这两种复合物成员在HR的早期和晚期反应中起着关键作用并参与HR修复通路的整个进程[4]。近年研究发现,Rad51C蛋白表达异常与多种恶性肿瘤的发生、发展相关[5-9]。本文就Rad51C蛋白在DNA损伤修复中的作用,并进一步阐述Rad51C与肿瘤发生发展、放疗抵抗等的关系并介绍其临床应用潜力。
1 Rad51家族与Rad51C
Rad51定位于15号染色体q15.1,含339个氨基酸,包括XRCC2(BCDX2)、XRCC3(CX3)、Rad51B、Rad51C及Rad51D共5种同系物。Rad51同系物间可结合成Rad51B/Rad51C/Rad51D/XRCC2和Rad51C/ XRCC3等聚合物[3]。Rad51C为Rad51家族的旁系同源基因,位于染色体17q23,含376个氨基酸,在人类的睾丸、心肌、脾脏及前列腺等正常组织处表达,与Rad51家族其他成员相同氨基酸比例占到10%~26%[10]。在DNA损伤修复过程中,Rad51C可促进Rad51蛋白聚集,但Rad51C是直接与Rad51作用还是与其他蛋白协同,发挥间接作用,目前仍尚不明确。已有研究证实Rad51B与Rad51C复合物也可促进Rad51蛋白参与DNA链的交换[11],另有研究发现Rad51C/XRCC3复合物可参与DNA交叉链的切割反应[12],也有研究检测到Rad51与Rad51C之间存在着直接的相互作用[13],因此Rad51C与Rad51在HR修复过程中均起到重要作用。
2 Rad51C与DNA损伤修复
DNA损伤修复是肿瘤学的研究热点,已有研究显示放化疗诱导肿瘤细胞死亡的主要机制是DNA DSB,而DSB的修复方式主要有两种,HR和NHE)。HR可修复由DNA损伤剂诱导或在DNA复制过程中出现的双链断裂DNA,是维持基因组稳定性及产生遗传多样性的一个重要的进化性保守机制。双链断裂(DSBs)修复离不开HR机制,而HR相关基因的表达上调可能会增加基因组的不稳定性及基因的自发性重组,促进肿瘤的发生[14-15]。Rad51C作为Rad51旁系同源基因中的一种,在DNA损伤修复过程中发挥的作用与Rad51同等重要;Rad51C的表达下降可影响DNA双链损伤后Rad51焦点的形成,进而抑制DNA损伤修复[13]。此外,有研究报道Rad51C可识别并检测DNA损伤信号进而将信号传递至下游通路,Rad51C在DNA损伤包括DSBs等修复过程中的具体作用途径如下图1[4]。
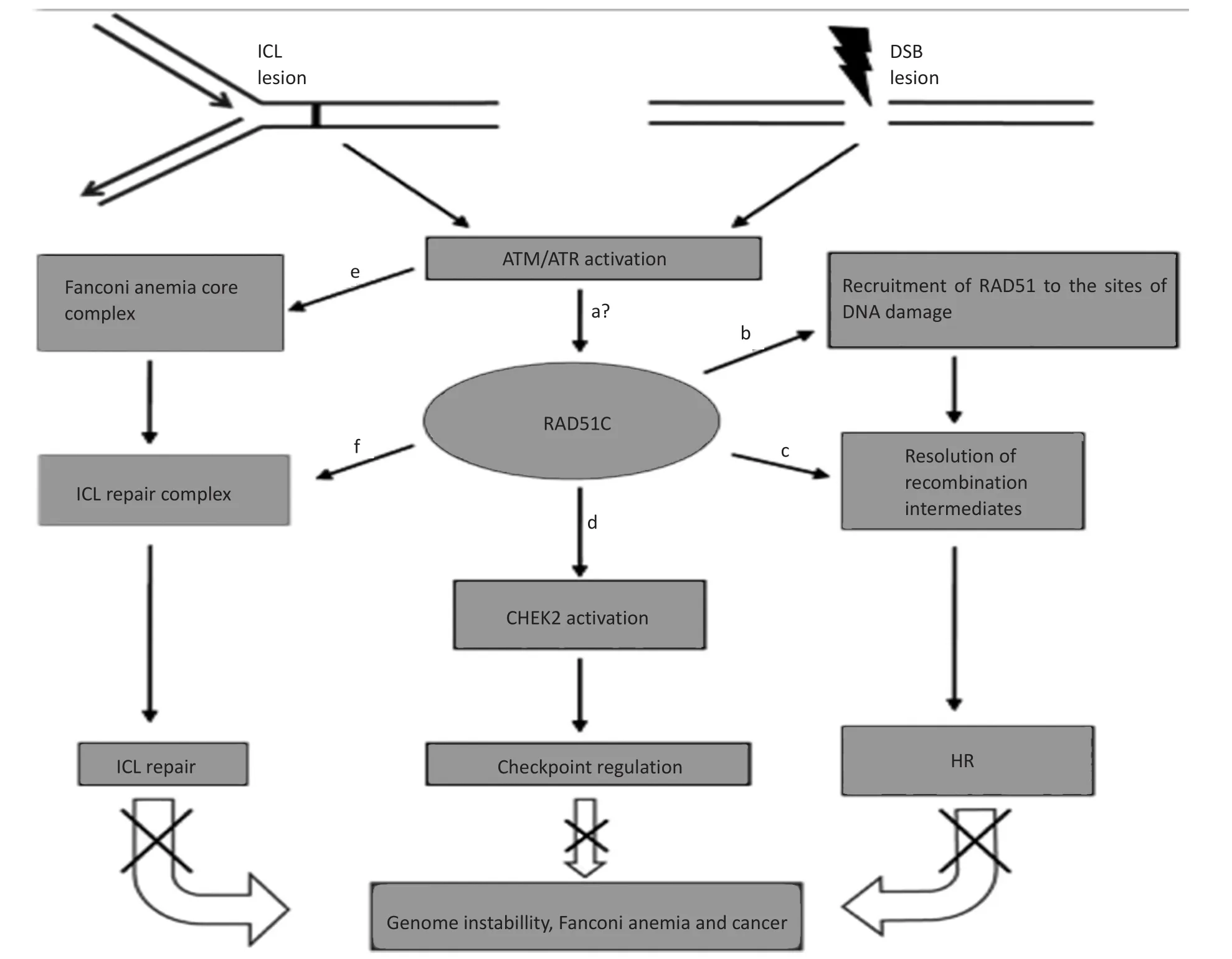
图1 Rad51C基因在DNA损伤修复中的作用途径Figure 1Role of Rad51C gene in DNA damage repair pathways
参与HR修复途径的相关因子主要包括MRN同源重组修复复合物(MRE11-RAD50-NBS1复合体)、Rad51、Rad51同系物Rad52、Rad54及Rad51B、C、D等[2,16]。HR修复DNA损伤[7]可分为联会前期、联会期及联会后期3个阶段[18-20],当DSBs时,首先是Rad52蛋白与断端结合,后促使Rad51聚集,形成Rad51-DNA单链复合物,Rad54再特异性结合到Rad51蛋白上,这就保证了HR活动启动[21]。
Badie等[22]研究发现,HR反应的早期,Rad51C在ATM、NBS1及RPA共同作用下,在DNA损伤发生的即刻便聚集到了损伤处,与XRCC3共同作用磷酸化激活CHK2蛋白,启动细胞周期检测[23]。Rad51C也可作用于G1期CHK2的激活,并在HR的后期继续作用[4],Rad51C在Holiday交叉(holiday junction,HJ)过程中发挥作用,并保证了HR的完成[12]。Kuznetsov等[24]进一步证实了Rad51C基因表达减少能明显抑制HJ的迁移及拆分。此外,Rad51C也可通过DNA链间交联(interatrand crosslinks,ICL)修复而募集HR相关修复因子而启动HR过程,且参与了范科尼贫血(Fanconi anemia,FA)的发生[4]。
3 Rad51C与肿瘤
HR相关基因突变可造成基因组或染色体的不稳定性,增加肿瘤的发病风险[25-26],HR修复相关因子BRCA1、BRCA2与乳腺癌、卵巢癌的发病相关[27],Rad51与乳腺癌的发病相关[28],Rad52突变后的蛋白高表达与多种恶性肿瘤发病相关[29]。Meindl等[30]研究提示Rad51C基因存在14个突变位点,其中G125V和L138F突变点可引起HR功能的缺陷,而D159N、G264S、R366Q等突变点可减弱Rad51C蛋白的活性,研究发现Rad51C高表达与头颈恶性肿瘤及结直肠癌存在相关性[7,9],但Min等[31]发现胃癌肿瘤组织中Rad51C的表达却显著低于癌旁组织。因此,Rad51C作为HR通路的关键蛋白之一,在肿瘤发生中的作用,仍尚不明确,深入研究Rad51C与肿瘤发生的相关分子机制有助于研究肿瘤对放、化疗的抗拒和新治疗靶点的开发。
4 Rad51C与放疗
DNA是射线照射的主要靶点,射线照射导致细胞DSB,进而发生致死性细胞损伤[32]。HR主要作用就是参与DSBs修复,但在肿瘤细胞中,HR通路的诸多基因可通过多种机制发生突变,导致激活或失活,进而使HR通路在肿瘤中的作用更加复杂化[33]。在对RAD51C的突变研究中发现[34],中国仓鼠突变细胞CL-V4B存在RAD51C缺陷,有132个bp出现缺失,导致产生可变剪接转录物与缺乏外显子5的CL-V4B,具有此种剪接体的突变细胞对DNA交联剂如丝裂霉素C(MMC)、顺铂、烷化剂甲基甲磺酸酯和拓扑异构酶I抑制剂campthotecin等均具有高敏性,并表现出DNA损伤后Rad51克隆形成能力受损。RAD51C缺陷还导致MMC诱导染色体畸变的自发性增加以及姐妹染色单体交换减少,但中心体的形成并没有受到影响,是否在射线照射中也存在类似现象,仍需要进一步研究。
另有研究显示RAD51C的功能在Rad51蛋白旁系中的独特性[35]。与RAD51C-/-的鸡DT40细胞相比,CL-V4B仓鼠细胞对交联剂更敏感。相较于鸡的Rad51旁系敲除细胞、XRCC2-和XRCC3缺陷的啮齿动物细胞,CL-V4B仓鼠细胞对X射线照射更加敏感,约增加了2倍[35-36],这显示在不同的细胞类型或不同物种之间,RAD51C依赖性的DNA修复途径可能对化疗药物及X射线诱导的DNA损伤修复起更重要的作用。通过抑制HR修复关键因子Rad51C的表达而减弱肿瘤细胞的损伤修复,有望逆转放化疗的抵抗而改善患者的整体预后。
5 小结
Rad51C是HR通路的关键蛋白之一,其过表达或突变可导致HR修复能力改变并引起基因组的不稳定性,与肿瘤的发生发展及对放化疗等治疗手段的耐受等相关。因此,检测Rad51C的突变和表达可为临床治疗策略提供依据并可评估治疗预后等,具有重要的临床应用前景。
[1]Ciccia A,Elledge SJ.The DNA damage response:making it safe to play with knives[J].Mol Cell,2010,40(2):179-204.
[2]Carvalho JF,Kanaar R.Targeting homologous recombination-mediated DNA repair in cancer[J].Expert Opin Ther Targets,2014,18(4): 427-458.
[3]Compton SA,Ozgur S,Griffith JD.Ring-shaped Rad51 paralog protein complexes bind Holliday junctions and replication forks as visualized by electron microscopy[J].J Biol Chem,2010,285(18):13349-13356.
[4]Somyajit K,Subramanya S,Nagaraju G.RAD51C:a novel cancer susceptibility gene is linked to Fanconi anemia and breast cancer[J]. Carcinogenesis,2010,31(12):2031-2038.
[5]Li J,Meeks H,Feng BJ,et al.Targeted massively parallel sequencing of a panel of putative breast cancer susceptibility genes in a large cohort of multiple-case breast and ovarian cancer families[J].J Med Genet,2016,53(1):34-42.
[6]Song H,Dicks E,Ramus SJ,et al.Contribution of Germline Mutations in the RAD51B,RAD51C,and RAD51D Genes to Ovarian Cancer in the Population[J].J Clin Oncol,2015,33(26):2901-2907.
[7]Kalvala A,Gao L,Aguila B,et al.Overexpression of Rad51C splice variants in colorectal tumors[J].Oncotarget,2015,6(11):8777-8787.
[8]Couch FJ,Hart SN,Sharma P,et al.Inherited mutations in 17 breast cancer susceptibility genes among a large triple-negative breast cancer cohort unselected for family history of breast cancer[J].JClin Oncol,2015,33(4):304-311.
[9]Gresner P,Gromadzinska J,Twardowska E,et al.Rad51C:a novel suppressor gene modulates the risk of head and neck cancer[J]. Mutat Res,2014,762,47-54.
[10]Dosanjh MK,Collins DW,Fan W,et al.Isolation and characterization of RAD51C,a new human member of the RAD51 family of related genes[J].Nucleic Acids Res,1998,26(5):1179-1184.
[11]Lio YC,Mazin AV,Kowalczykowski SC,et al.Complex formation by the human Rad51B and Rad51C DNA repair proteins and their activities in vitro[J].J Biol Chem,2003,278(4):2469-2478.
[12]Liu Y,Masson JY,Shah R,et al.RAD51C is required for Holliday junction processing in mammalian cells[J].Science,2004,303(5655): 243-246.
[13]Rodrigue A,Lafrance M,Gauthier MC,et al.Interplay between human DNA repair proteins at a unique double-strand break in vivo[J].EMBO J,2006,25(1):2222-2231.
[14]Dion V,Gasser SM.Chromatin movement in the maintenance of genome stability[J].Cell,2013,152(6):1355-1364.
[15]Helleday T.Homologous recombination in cancer development,treatment and development of drug resistance[J].Carcinogenesis,2010,31(6):955-960.
[16]Fiume L.Comment on:targeting homologous recombination-mediated DNA repair in cancer[J].Expert Opin Ther Targets,2014,18(7): 833.
[17]Renkawitz J,Lademann CA,Jentsch S.Mechanisms and principles of homology search during recombination[J].Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,2014,15(6):369-383.
[18]Cerbinskaite A,Mukhopadhyay A,Plummer ER,et al.Defective homologous recombination in human cancers[J].Cancer Treat Rev,2012,38(2):89-100.
[19]Hunt CR,Ramnarain D,Horikoshi N,et al.Histone modifications and DNA double-strand break repair after exposure to ionizing radiations[J].Radiat Res,2013,179(4):383-392.
[20]Makharashvili N,Tubbs AT,Yang SH,et al.Catalytic and noncatalytic roles of the CtIP endonuclease in double-strand break end resection[J].Mol Cell,2014,54(6):1022-1033.
[21]Sugiyama T,Kowalczykowski SC.Rad52 protein associates with replication protein A(RPA)-single-stranded DNA to accelerate Rad51-mediated displacement of RPA and presynaptic complex formation[J].J Biol Chem,2002,277(35):31663-31672.
[22]Badie S,Liao C,Thanasoula M,et al.RAD51C facilitates checkpoint signaling by promoting CHK2 phosphorylation[J].J Cell Biol,2009,185(4):587-600.
[23]Somyajit K,Basavaraju S,Scully R,et al.ATM-and ATR-mediated phosphorylation of XRCC3 regulates DNA double-strand break-induced checkpoint activation and repair[J].Mol Cell Biol,2013,33(9):1830-1844.
[24]Kuznetsov S,Pellegrini M,Shuda K,et al.RAD51C deficiency in mice results in early prophase I arrest in males and sister chromatid separation at metaphase II in females[J].J Cell Biol,2007,176(5):581-592.
[25]Tariq K,Ghias K.Colorectal cancer carcinogenesis:a review of mechanisms[J].Cancer Biol Med,2016,13(1):120-135.
[26]Ceccaldi R,Liu JC,Amunugama R,et al.Homologous-recombinationdeficient tumours are dependent on Poltheta-mediated repair[J]. Nature,2015,518(7538):258-262.
[27]Narod SA,Foulkes WD.BRCA1 and BRCA2:1994 and beyond[J].Nat Rev Cancer,2004,4(9):665-676.
[28]Wang Z,Dong H,Fu Y,et al.RAD51 135G>C polymorphism contributes to breast cancer susceptibility:a meta-analysis involving 26,444 subjects[J].Breast Cancer Res Treat,2010,124(3):765-769.
[29]Lieberman R,Xiong D,James M,et al.Functional characterization of RAD52 as a lung cancer susceptibility gene in the 12p13.33 locus[J].Mol Carcinog,2016,55(5):953-963.
[30]Meindl A,Hellebrand H,Wiek C,et al.Germline mutations in breast and ovarian cancer pedigrees establish RAD51C as a human cancer susceptibility gene[J].Nat Genet,2010,42(5):410-414.
[31]Min A,Im SA,Yoon YK,et al.RAD51C-deficient cancer cells are highly sensitive to the PARP inhibitor olaparib[J].Mol Cancer Ther,2013,12(6):865-877.
[32]Qian D,Zhang B,Zeng XL,et al.Inhibition of human positive cofactor 4 radiosensitizes human esophageal squmaous cell carcinoma cells by suppressing XLF-mediated nonhomologous end joining[J]. Cell Death Dis,2014,5(10):1461.
[33]Birkelbach M,Ferraiolo N,Gheorghiu L,et al.Detection of impaired homologous recombination repair in NSCLC cells and tissues[J].J Thorac Oncol,2013,8(3):279-286.
[34]Godthelp BC,Wiegant WW,van Duijn-Goedhart A,et al.Mammalian Rad51C contributes to DNA cross-link resistance,sister chromatid cohesion and genomic stability[J].Nucleic Acids Res,2002,30(10):2172-2182.
[35]Takata M,Sasaki MS,Tachiiri S,et al.Chromosome instability and defective recombinational repair in knockout mutants of the five Rad51 paralogs[J].Mol Cell Biol,2001,21(8):2858-2866.
[36]Takata M,Sasaki MS,Sonoda E,et al.The Rad51 paralog Rad51B promotes homologous recombinational repair[J].Mol Cell Biol,2000,20(17):6476-6482.
(2016-04-29收稿)
(2016-07-27修回)
(编辑:杨红欣校对:武斌)

丁新敏专业方向为恶性肿瘤的诊断、分期及多学科综合治疗。
E-mail:15822188031@163.com
Research progress on Rad51C in DNA damage repair
Xinmin DING1,Xiuli CHEN2,Ping WANG2
Correspondence to:Ping WANG;E-mail:tjdoctorwang@163.com
1Department of Oncology,The People's Hospital of Tianjin Seaside,Tianjin 300280,China;2Department of Radiotherapy Oncology,Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital,National Clinical Research Center for Cancer,Tianjin Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Therapy,Tianjin 300060,China
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(No.81372518)
Cytotoxic substances and ionizing radiation can easily induce DNA damage,and double strand breaks(DSBs)are the main form of DNA damage.DNA damage can activate intracellular DNA damage responses and further induce related biological effects,such as DNA damage repair and cell cycle arrest.Homologous recombination(HR)is the primary DSB repair mechanism in eukaryotes. Abnormal expression of Rad51C,which is a key factor in the HR pathway,may result in DNA repair disorder,genomic instability,and eventually lead to tumor formation.In recent studies,researchers considered Rad51C as a potential target for cancer treatment.We reviewed the research progress on Rad51C in DNA damage repair and radiotherapy.
neoplasm,gene,DNA damage,recombination/homologous recombination,Rad51C
10.3969/j.issn.1000-8179.2016.18.502
①天津海滨人民医院肿瘤科(天津市300280);②天津医科大学肿瘤医院放疗科,国家肿瘤临床医学研究中心,天津市肿瘤防治重点实验室
*本文课题受国家自然科学基金(编号:81372518)资助
王平tjdoctorwang@163.com
