乳腺癌新辅助化疗患者病理完全缓解的影响因素及生存分析*
2016-11-14张恒伟李军涛郭旭辉吕民豪秦丽卢振铎李连方崔树德刘真真
张恒伟 李军涛 郭旭辉 吕民豪 秦丽 卢振铎 李连方 崔树德 刘真真
·临床研究与应用·
乳腺癌新辅助化疗患者病理完全缓解的影响因素及生存分析*
张恒伟 李军涛 郭旭辉 吕民豪 秦丽 卢振铎 李连方 崔树德 刘真真
目的:探讨乳腺癌新辅助化疗患者病理完全缓解的影响因素及病理完全缓解对预后的影响。方法:选择河南省肿瘤医院乳腺科2008年1月至2014年12月女性乳腺癌新辅助化疗患者267例作为研究对象,收集患者的临床和病理资料,随访患者的生存情况。结果:单因素分析显示新辅助化疗病理完全缓解患者的体质量、哺乳时间、化疗周期、肿瘤直径和未病理完全缓解患者比较,差异均具有统计学意义(P<0.05);病理完全缓解患者ER、PR、HER-2和分子分型与未病理完全缓解比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。多因素分析发现体质量和ER是乳腺癌患者新辅助化疗病理完全缓解的独立预测因素(P<0.05)。生存分析病理完全缓解患者和未病理完全缓解患者的无病生存期和总生存期比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论:乳腺癌患者体质量和ER是新辅助化疗病理完全缓解的独立预测因素,新辅助化疗病理完全缓解对患者生存无显著影响。
乳腺癌 新辅助化疗 病理完全缓解 影响因素 预后
随着乳腺癌治疗理念和技术的发展,新辅助化疗在临床中被广泛应用,使一些晚期乳腺癌患者获得手术的机会[1-2],近年来,新辅助化疗不仅用于晚期乳腺癌患者的治疗,在一些ⅡA期和ⅡB期患者中也有应用[3-4]。病理完全缓解是评价乳腺癌患者新辅助化疗预后的重要指标,有研究发现病理完全缓解可以有更长的生存获益[5],但也有研究发现新辅助化疗的病理完全缓解的生存获益和辅助化疗无差异[6]。因此探讨新辅助化疗患者病理完全缓解对预后的影响以及新辅助化疗病理完全缓解的影响因素具有重要意义。本研究对267乳腺癌新辅助化疗患者病理完全缓解的影响因素进行研究,并探讨病理完全缓解对预后的影响。
1 材料与方法
1.1临床资料
1.1.1研究对象选择河南省肿瘤医院乳腺科2008年1月至2014年12月女性乳腺癌接受新辅助化疗患者267例进行观察,所有患者均经医院理伦委员会同意,签署知情同意书,其中28例因失访、自动放弃等原因没有如期完成化疗者被剔除,对如期完成新辅助化疗的239例患者进行研究。239例患者中位年龄(56.26±12.71)岁,110例绝经,129例未绝经,15例有乳腺癌家族史,224例无乳腺癌家族史,TNM分期Ⅰ期6例、Ⅱ期163例、Ⅲ期70例,HER-2(0)-(1+)179例,HER-2(2+)-(3+)60例,ER阳性168例,阴性71例,PR阳性133例,阴性106例,分子分型Luminal A型32例,Luminal B型136例,HER-2过表达型33例,三阴性乳腺癌28例。
1.1.2排除标准非初诊乳腺癌患者,初诊乳腺癌分期为Ⅳ期者,未在本院进行完整治疗方案者,资料不完整者,原位癌,浸润性特殊癌,患其他恶性肿瘤者,心肝肾等功能衰竭者等。
1.2方法
1.2.1化疗方案本研究采用的化疗方案有TE方案(多西他赛75 mg/m2、表柔比星75 mg/m2,第一天静滴)、TEC方案(多西他赛75 mg/m2、表柔比星60 mg/m2、环磷酰胺500 mg/m2,第一天静滴)、EC方案(环磷酰胺600 mg/m2、表柔比星75 mg/m2,第一天静滴)、CEF方案(表柔比星75 mg/m2、环磷酰胺600 mg/m2、5-FU 600 mg/m2,第一天静滴)、TC方案(多西他赛75 mg/m2、环磷酰胺600 mg/m2,第一天静滴)等。每种化疗方案均21天为一个疗程,共3个疗程。患者化疗前30 min给予地塞米松、苯海拉明、异丙嗪、托烷司琼等对抗化疗引起的不良反应,每疗程化疗后检测血常规,白细胞过低给予重组人粒细胞刺激因子升白细胞治疗,新辅助化疗患者定期复查B超观察乳腺癌的变化情况。
1.2.2资料收集收集患者的年龄、体质量、身高、哺乳情况、月经情况、既往史和家族史等一般资料;B超等辅助检查结果;手术方式、肿瘤大小、病理类型、淋巴结转移等资料。
1.2.3病理完全缓解:指仅有原位癌残留,或者原发病灶、淋巴结均未发现肿瘤病灶。PR、ER阳性细胞比例<10%为阴性,阳性细胞比例≥10%为阳性;HER-2细胞膜无染色或者染色比例<10%为(-);染色比例≥10%,细胞膜微弱染色为(+),染色比例≥10%,细胞膜中度染色为(++);染色比例≥10%,细胞膜完全中度染色为(+++),HER-2(-)和(+)为HER-2阴性,HER-2(++)和(+++)为HER-2阳性,HER-2(+++)为HER-2过表达。分子分型:Luminal A型的HER-2阴性,ER和PR阳性,Ki67<14%;Luminal B型的HER-2阴性或者过表达,ER阳性,Ki67≥14%或者PR阴性或<20%;HER-2过表达型中HER-2过表达,PR、ER阴性;三阴型性乳腺癌中HER-2、PR、ER均阴性。
1.2.4随访随访至2015年6月,采用门诊随访或者电话随访。
1.3统计学方法
采用SPSS 20.0软件进行分析,均数之间比较采用t检验,率之间比较采用χ2检验,生存分析采用Kaplan-Meier法和Log rank法,多因素分析采用Logistic分析。以P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1临床因素和新辅助化疗病理完全缓解的关系
新辅助化疗病理完全缓解患者的体质量高于未病理完全缓解患者(P<0.05),病理完全缓解患者的哺乳时间短于未病理完全缓解患者(P<0.05),病理完全缓解患者的化疗周期长于未病理完全缓解患者(P<0.05),病理完全缓解肿瘤直径≥3 cm者所占比例低于未病理完全缓解患者(P<0.05);病理完全缓解和未病理完全缓解患者的身高、临床分期、腋窝淋巴结转移及绝经比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05,表1)。表明乳腺癌患者的体质量、哺乳时间、化疗周期和肿瘤大小影响新辅助化疗的病理完全缓解。
2.2病理指标和新辅助化疗病理完全缓解的关系
病理完全缓解患者ER和PR阴性比例高于未病理完全缓解患者(P<0.05),病理完全缓解患者HER-2阳性比例高于未病理完全缓解患者(P<0.05),病理完全缓解患者和未病理完全缓解患者的分子分型比较差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05),Ki-67比例和组织学分级比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05,表2)。表明乳腺癌患者的ER、PR、HER-2和分子分型影响新辅助化疗的病理完全缓解。
2.3新辅助化疗病理完全缓解的Logistic回归分析
乳腺癌患者的体质量、哺乳时间、化疗周期、肿瘤大小以及ER、PR、HER-2纳入Logistic回归分析,发现体质量和ER是乳腺癌患者新辅助化疗病理完全缓解的独立预测因素(P<0.05)。
2.4新辅助化疗病理完全缓解对生存的影响
239例乳腺癌新辅助化疗患者随访中位时间为32个月,其中20例死亡,45例出现远处转移或者局部复发,在36例达到病理完全缓解的患者中,无患者死亡,有6例发生远处转移,203例未达到病理完全缓解的患者中,21例死亡,39例远处转移或者局部复发。生存分析发现病理完全缓解患者和未病理完全缓解患者的无病生存期和总生存期比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05,表3)。
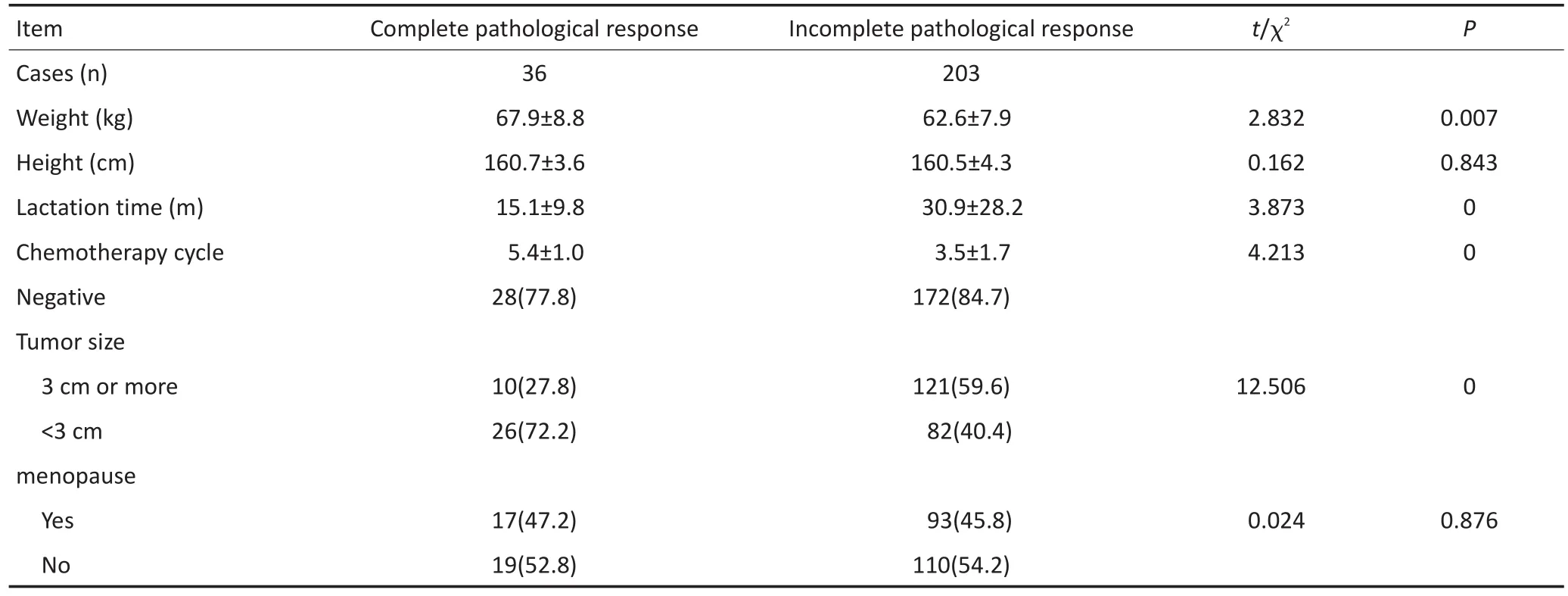
表1 临床因素和新辅助化疗病理完全缓解的关系Table 1Relationship between clinical factors and complete pathological response of neoadjuvant chemotherapy
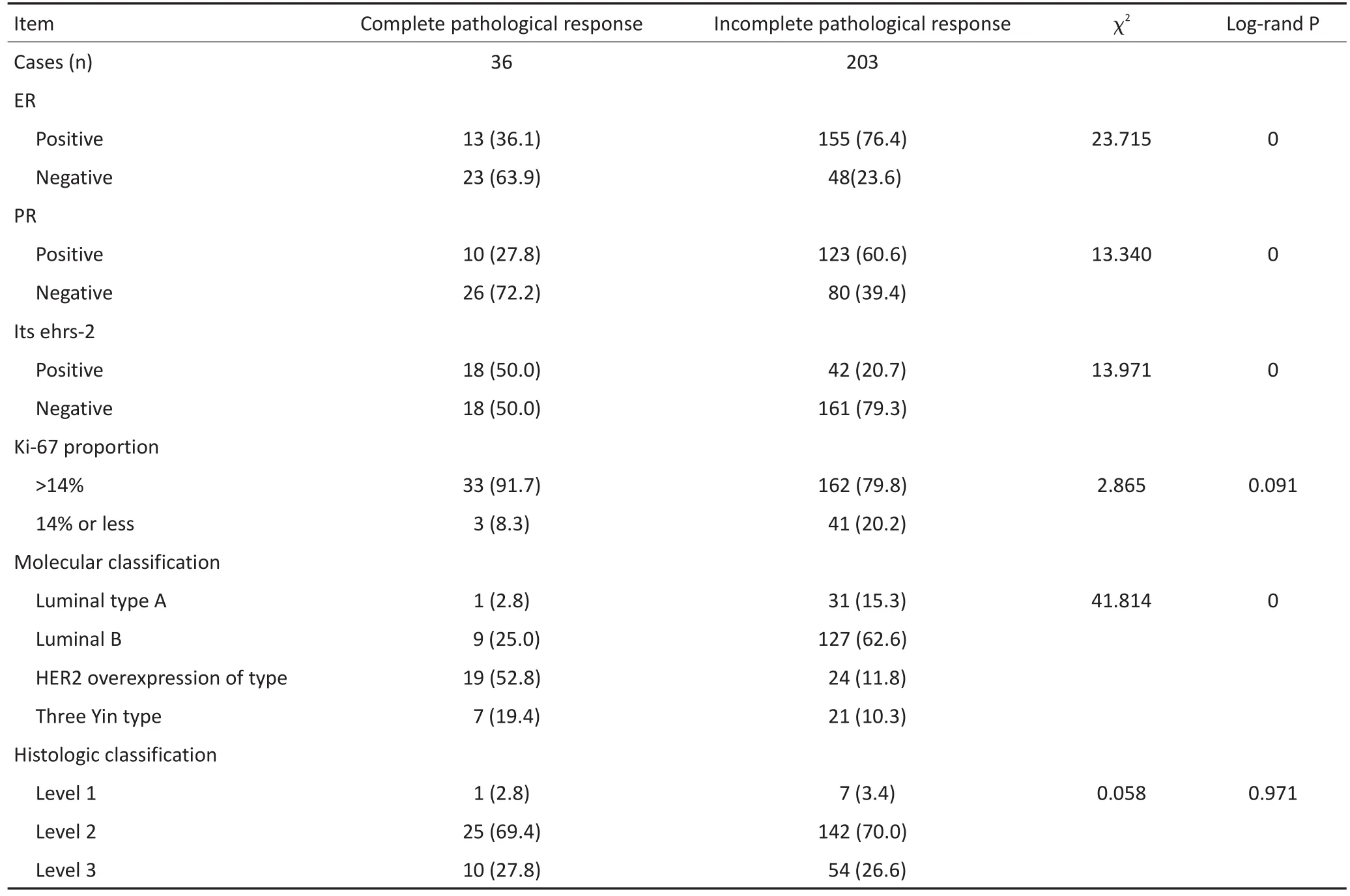
表2 病理指标和新辅助化疗病理完全缓解的关系Table 2Relationship between pathological parameters and complete pathological response of neoadjuvant chemotherapy
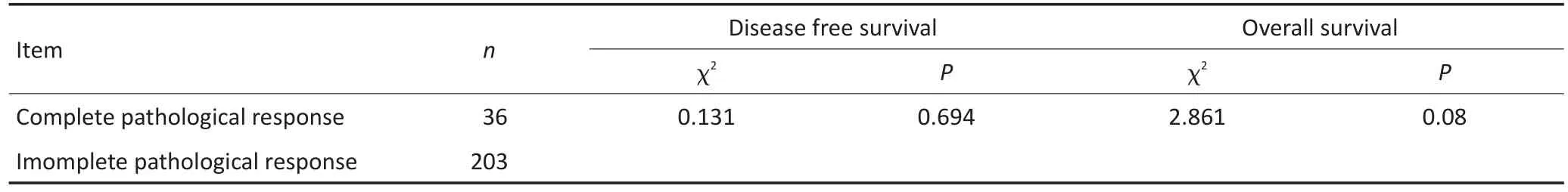
表3 新辅助化疗病理完全缓解对生存的影响Table 3Effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy complete pathological response on survival
3 讨论
乳腺癌新辅助化疗是根据乳腺癌的生物学理论提出,开始于乳腺癌局部治疗之前的辅助化学治疗,在乳腺癌手术或局部行放射治疗之前,以全身化疗为第一步治疗,然后再进行局部治疗的乳腺癌的治疗方法。新辅助化疗最初主要用于晚期乳腺癌患者,使无法进行手术的晚期乳腺癌患者获得局部放疗或者根治性手术的机会[7-8],新辅助化疗可以降低乳腺癌的临床分期、提高保乳率,减少或者消除转移病灶,选择比较敏感的化疗方案,防止乳腺癌远处转移等,提高乳腺癌患者的生存质量,随着对新辅助化疗研究的深入,新辅助化疗不只应用于晚期乳腺癌,在ⅡA期和ⅡB期乳腺癌患者中也有应用[9-10]。但新辅助化疗后乳腺癌患者的免疫力降低,手术风险增加;对新辅助化疗不敏感者进行新辅助化疗可能会延误患者的治疗,因此新辅助化疗在乳腺癌患者中的应用存在一些争议[11]。
病理完全缓解是指原发病灶和淋巴结均未见肿瘤病灶或者仅有原位癌残留。病理完全缓解是评价乳腺癌新辅助化疗预后的重要指标,有研究发现新辅助化疗后达到病理完全缓解患者具有更长的生存获益,然而新辅助化疗后获得病理完全缓解的只占少部分,有部分患者在新辅助化疗过程中病情继续进展,错过早期手术机会,也有部分患者出现化疗耐药,同时也有研究发现新辅助化疗患者的生存获益并没有显著延长[12-13],因此研究新辅助化疗病理完全缓解患者的生存获益是否提高以及病理完全缓解的影响因素具有重要意义[14]。李志华等[15]研究发现超重乳腺癌患者新辅助化疗的病理完全缓解比较差,超重乳腺癌患者的总生存率比较差;杨科等[16]研究发现ER、PR阴性的乳腺癌对新辅助化疗比较敏感。本研究结果发现新辅助化疗病理完全缓解患者的体质量、哺乳时间、化疗周期、肿瘤直径、ER、PR、HER-2和分子分型和未病理完全缓解患者比较差异均具有统计学意义;体质量和ER是乳腺癌患者新辅助化疗病理完全缓解的独立预测因素;病理完全缓解患者和未病理完全缓解患者的无病生存期和总生存期比较差异无统计学意义。本研究结果发现ER和PR阴性、HER-2阳性患者新辅助化疗后的病理完全缓解率比较高,体质量和ER是乳腺癌患者新辅助化疗病理完全缓解的独立预测因素。本研究结果同时发现病理完全缓解患者的预后较未病理完全缓解者好,但两者生存获益无明显差异。
[1]Thill M,Pisa G,Isbary G.Targets for Neoadjuvant Therapy-The Preferences of Patients with Early Breast Cancer[J].Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd,2016,76(5):551-556.
[2]Mutlu H,Eryılmaz MK,Musri FY,et al.Mean platelet volume as an independent predictive marker for pathologic complete response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with locally advanced breast cancer[J].Asian Pac J Cancer Prev,2016,17(4):2089-2092.
[3]Han YW,Wen SY,Liu W,et al.Clinical evaluation of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer[J].Chinese J Clin Oncol,2011,38(7):415-418.[韩芸蔚,温绍艳,刘伟,等.乳腺癌新辅助化疗的临床评价方法解析[J].中国肿瘤临床,2011,38(7):415-418.]
[4]Cao XS,Cong BB,Sun X,et al.A retrospective study of axillary and internal mammary sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer patients after neoadjuvant chemotherapy[J].China Oncology,2015,(8):608-613.[曹晓珊,丛斌斌,孙晓,等.乳腺癌新辅助化疗后腋窝及内乳前哨淋巴结活检研究[J].中国癌症杂志,2015,(8):608-613.
[5]Berruti A,Amoroso V,Gallo F,et al.Pathologic complete response as a potential surrogate for the clinical outcome in patients with breast cancer after neoadjuvant therapy:a meta-regression of 29 randomized prospective studies[J].J Clin Oncol,2014,32(34):3883-3891.
[6]Rastogi P,Anderson SJ,Bear HD,et al.Preoperative chemotherapy: updates of National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project Protocols B-18 and B-27[J].J Clin Oncol,2008,26(5):778-785.
[7]Zdenkowski N,Butow P,Hutchings E,et al.A decision aid for women considering neoadjuvant systemic therapy for operable invasivebreast cancer:development and protocol of a phaseⅡevaluation study(ANZ1301 DOMINO)[J].JMIR Res Protoc,2016,5(2):e88.
[8]Jiang PL,Ni J,Gu F,et al.Change of chemosensitivity of routine chemotherapy drugs in breast cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy[J].Chinese Journal of Experimental Surgery,2015,32(5):959-961.[姜鹏玲,尼杰,谷峰,等.乳腺癌新辅助化疗前后常用化疗药物敏感性的变化[J].中华实验外科杂志,2015,32(5):959-961.]
[9]Bouzón A,Acea B,García A,et al.Risk factors for positive margins in conservative surgery for breast cancer after neoadjuvantchemotherapy[J].Cir Esp,2016,94(7):379-384.
[10]Wang J,Sang D,Xu B,et al.Value of breast cancer molecular subtypes and Ki-67 expression for the prediction of efficacy and prognosis of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in a chinese population[J]. Medicine(Baltimore),2016,95(18):e3518.
[11]Liu ZY,Li BJ.Efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on breast cancer and dynamic changes of circulating tumor cells[J].Chin J Clin Oncol,2013,(23):1431-1435.[刘志勇,李宝江.乳腺癌新辅助化疗中循环肿瘤细胞的动态变化及疗效观察[J].中国肿瘤临床,2013,(23):1431-1435.]
[12]Shintia C,Endang H,Diani K.Assessment of pathological response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced breast cancer using the Miller-Payne system and TUNEL[J].Malays J Pathol,2016,38(1):25-32.
[13]Kuerer HM,Yang WT,Krishnamurthy S.Comment on Diagnosis of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy inbreast cancer by minimal invasive biopsy techniques[J].Br J Cancer,2016,114(10):e3.
[14]Wamer ET,Ballman KV,Strand C,et al.Impact of race,ethnicity,and BMI on achievement of pathologic complete response followingneoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer:a pooled analy-sis of four prospective Alliance clinical trials(A151426)[J].Breast Cancer Res Treat,2016,159(1):109-118.
[15]Li ZH,Luo YH,Wu XB,et al.Relationship between body mass index and eEfficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on progression breast cancer to[J].Guang Dong Medical Journal,2012,33(6):780-783.[李志华,罗永辉,吴晓波,等.体质指数与进展期乳腺癌新辅助化疗疗效的关系[J].广东医学,2012,33(6):780-783.]
[16]Yang,K,Cui SD,Li LF,et al.Relationship between expression of ER,PR,Ps2,Her-2 and neoadjuvant chemotherapy effect in breast cancer[J].SHANDONG MEDICAL JOURNAL,2011,51(6):18-19.[杨科,崔树德,李连方,等.乳腺癌组织中ER、PR、Ps2、C-erbB-2表达与新辅助化疗疗效的关系[J].山东医药,2011,51(6):18-19.]
(2016-07-11收稿)
(2016-08-18修回)

张恒伟专业方向为乳腺肿瘤的临床治疗。
E-mail:mrzhanghw54@126.com
Factors affecting complete pathological remission in neoadjuvant chemotherapy patients with breast cancer and survival analysis
Hengwei ZHANG,Juntao LI,Xuhui GUO,Minhao LV,Li QIN,Zhenduo LU,Lianfang LI,Shude CUI
Correspondence to:Hengwei ZHANG;E-mail:mrzhanghw54@126.com
Department of Breast Tumor,Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Zhengzhou University,Cancer Hospital of Henan Province,Zhengzhou 450003,China
This work was supported by the Henan Province Science and Technology Research Project in 2013(No.132102310405)
Objective:To investigate the factors affecting complete pathological remission in neoadjuvant chemotherapy patients with breast cancer and the influence of complete pathological remission on prognosis.Methods:A total of 267 cases of neoadjuvant chemotherapy patients with breast cancer were selected for this study from January 2008 to December 2014 in our hospital.The clinical and pathological data of the patients were collected.Moreover,the survival of the patients was followed up.Results:Univariate analysis showed that differences in weight,feeding time,cycles of chemotherapy,and tumor size between complete pathological remission and incomplete pathological remission patients subjected to neoadjuvant chemotherapy were statistically significant(P<0.05).The differences in ER,PR,HER 2,and molecular typing between complete pathological remission and incomplete pathological remission patients subjected to neoadjuvant chemotherapy were statistically significant(P<0.05).Multivariate analysis showed that the weight and ER were independent predictors of complete pathological remission in patients with breast cancer undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy(P<0.05).Survival analysis showed that differences in the disease-free survival and overall survival between complete pathological remission and incomplete pathological remission patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy were statistically insignificant(P>0.05).Conclusion:The weight and ER of breast cancer patients in neoadjuvant chemotherapy were independent predictors of complete pathological remission.The complete pathological remission due to neoadjuvant chemotherapy had an insignificant effect on survival.
breast cancer,neoadjuvant chemotherapy,complete pathological response,factor,prognosis
10.3969/j.issn.1000-8179.2016.18.814
郑州大学附属肿瘤医院,河南省肿瘤医院乳腺科(郑州市450003)
*本文课题受河南省2013年科技攻关计划项目基金(编号:132102310405)资助
刘真真liuzhenzhen73@163.com
