线粒体DNA D-loop区多态性与肝癌预后的研究
2016-07-14张风宾郭占军吴忱思张瑞星
张风宾,郭占军,吴忱思,张瑞星
(河北医科大学第四医院消化内科,石家庄 050011)
线粒体DNA D-loop区多态性与肝癌预后的研究
张风宾,郭占军,吴忱思,张瑞星
(河北医科大学第四医院消化内科,石家庄 050011)
【摘要】目的 通过对线粒体DNA D-loop区的碱基测序,了解其多态性及突变情况,并探讨其与肝癌发病机率及预后的关系。方法 提取49个乙型肝炎后肝癌病人的肝癌组织,癌旁组织和血液中的线粒体DNA,用测序法测定线粒体DNA D-loop区的碱基序列,了解其单核苷酸多态性和变异情况,并分析其与肝癌发病率及2年生存率的关系。结果 通过观察发现,肝癌病mtDNA突变情况与肝癌预后无明确相关,而1个SNP位点(核苷酸150 C/T)与肝癌的生存期之间存在统计学上的显著差异。经COX回归分析,发现150位点为肝癌预后的独立危险因素;150C的患者生存期显著短于150T的生存期(相对危险度,0.246;95%CI,0.070-0.861;P=0.028)。结论通过分析在线粒体DNAD-loop区的多态性,可以帮助筛别预后不良的肝癌患者。
【关键词】肝细胞肝癌;线粒体DNA D-loop;突变;单核苷酸多态性
肝细胞肝癌是常见恶性肿瘤之一,在世界范围内,是男性第五大好发肿瘤,是女性第七常见肿瘤[1],是第二常见的死亡病因[2],每年有将近50万的病人死于肝癌[2]。肝癌在中国也是常见肿瘤,中国每年肝癌的发病率和死亡率分别为29.9/100 000 和27.7/100 000[3]。危险因素包括B型、C型肝炎病毒和酒精滥用[4]。乙型肝炎病毒感染在我国是一非常严重的问题,因我国有9千3百万的乙型肝炎病毒携带者,2千万的慢性乙型肝炎患者[5]。酒精滥用在中国也逐年上升,6.6%的男性和0.1%的女性诊断为酒精滥用[6]。许多患者进展为肝病,如酒精性肝炎和肝硬化,直至肝癌。虽然随着检查手段的改善,肝癌已能较早发现;但因其复发率较高,肝癌患者的预后仍然较差。虽然现在已明确许多因素,如肿瘤的数目、大小,数量,细胞分化程度,门脉瘤栓和肝脏炎症程度,都与肝癌的复发与预后相关,但对于过氧化损伤与肝癌的预后关系,则研究较少[7、8]。肝炎病毒感染和酒精滥用导致肝细胞内氧化损伤加重,进而导致DNA的变化包括线粒体DNA的不稳定性[9-11]。线粒体基因体是长16 kb闭环双链,含有37个基因,包括2个rRNA和22 tRNA[12]。因为线粒体 DNA产生 ROS并且缺少DNA修复功能,所以线粒体DNA比核DNA更容易损伤[13]。在许多癌症中,包括肝炎病毒导致的肝癌中,DNA突变频发于线粒体DNA的非编码区域,称作D-loop区[12、14、15],其包含有1122 bp(nucleotides 16,024-16,569 and 1-576;www.mitomap.org).因其含有复制的起始链和转录的主要启动子[16],所以它对线粒体基因组的复制和表达有着重要的调节作用。D-loop区的序列变化在多种肿瘤中被发现,但是因为没有测定血液标本的序列,所以这些序列变化代表体细胞变异还是单核苷酸多态性还是未知。虽然目前有一些研究通过测定血DNA发现了一些SNPs(single nucleotide polymorphism,下同)位点,但现在几乎没有SNPs被筛选出来以预测癌症的发病风险及预后[17-19]。本研究中,通过测定肝癌患者的外周血、癌旁及肝癌组织中的mtDNA D-loop 区DNA序列,发现了92个SNPs和25个突变位点,并通过与正常对照组比较,筛查出了与肝癌预后相关的SNPs位点[16],并证实了这些突变和SNPs与肝癌预后的预测强度。
1 材料和方法
1.1组织标本和线粒体DNA的提取
收集河北医科大学第四医院肝胆外科49例肝癌病人(所有患者的肝功能属Child-Pugh分级A或B,肝总胆红素水平<301 mol/L)的癌组织、癌旁组织和血液,立即放-70℃存放。所有病人标本的收集经过河北医科大学第四医院伦理委员会批准。用MitochondrialDNAExtractionKit(Genmed Scientific Inc,Shanghai,China)提取线粒体DNA,所有线粒体DNA放-20℃存放备用。
1.2PCR扩增和DNA测序
D-loop用正义引物 5'-CCCCATGCTTACAA GCAAGT-3‘和 反 义 引 物 5'-GCTTTGAGGAG GTAAGCTAC-3'扩增[31],PCR试剂盒采用 PCR Master Mix Kit(Promega,Madison,WI),通过 PCR System 9700 Thermocycle(Applied Biosystem,Foster City,CA)扩增。PCR 产品经净化处理后用Abiprism Genetic Analyzer 3100(Applied Biosystem)进行测序分析。如果同病人癌组织和血液及癌旁组织比较有序列变化,这种变化就定义为变异。
1.3统计学方法
应用Kaplan-Meier、log-rank test和 Cox回归分析对数据进行处理。所有的统计处理操作均应用SPSS 11.5软件(SPSS Company,Chicago,IL),P值小于0.05定义为有统计意义。
2 结果
49例患者中临床分期一期13人,二期36人;所有病人在肝癌切除术后均未接受放化疗等辅助治疗。我们对49例入组病人每3月进行一次随访,得到了2年生存情况。2年之内共27例患者死亡。收集的临床资料使用Kaplan-Meier和 log-rank处理。结果显示:患者的性别、年龄、Child分级和肿瘤数目与2年生存率无统计学意义;而肿瘤分期、肿瘤大小和门脉瘤栓则差异存在显著性(表1)。与预期相符,不同分期患者的2年生存率具有明显差别,肿瘤分期I期的为76.9%,而II期仅有33.3%;差异具有显著性(P<0.05);肿瘤直径>5 cm的生存期明显短于肿瘤直径<5 cm患者;合并有门脉瘤栓的患者均在随访期内死亡。以上数据表明,肿瘤分期、肿瘤大小和门脉瘤栓为影响肝癌预后的危险因素。
我们检测了92个SNPs与肝癌生存期之间的关系,在每个 SNP位点,49例患者被分为2组,经Kaplan-Meier生存分析发现,在150位点,存在2年生存率的显著差异,150C的生存期显著短于150T (P=0.028)(图1),我们发现此位点与肝癌预后相关。为了进一步分析150位点、肿瘤分期、肿瘤大小、门脉瘤栓这4个可能因素对患者预后的影响,我们将其引入COX比例风险模型,多因素分析显示,150位点和门脉瘤栓是影响预后的独立因素(表2)。150C基因型的患者2年生存期显著短于150T(相对危险度,0.246;95%CI,0.070-0.861;P= 0.028)。以上数据提示150位点的基因型对肝癌的生存期具有显著影响。
3 讨论
mtDNA D-loop区的SNPs和突变位点已经用来预测肝癌的发病情况[16]。本研究通过对 mtDNA(碱基16190-583)的测序进一步研究了SNPs和突变位点与肝癌术后生存期的关系,发现150(C/T)位点与2年生存率有关,多因素分析显示,150(C/ T)是影响预后的独立因素,D-loop区不同的SNPs在肝癌的发生发展过程中具有不同的作用,150位点位于高突变1区(HV2),而以前我们发现的与食管鳞状细胞癌相关的位点位于高变1区[19]。在这些突变热点区域,肿瘤和生殖细胞的mtDNA都极易发生突变,其中的原因还不得而知。但我们的研究提示其在肿瘤预后方面具有重要作用。150C患者的生存期明显较短且生存曲线下降迅速(图1),但其中的原因需要进一步研究。
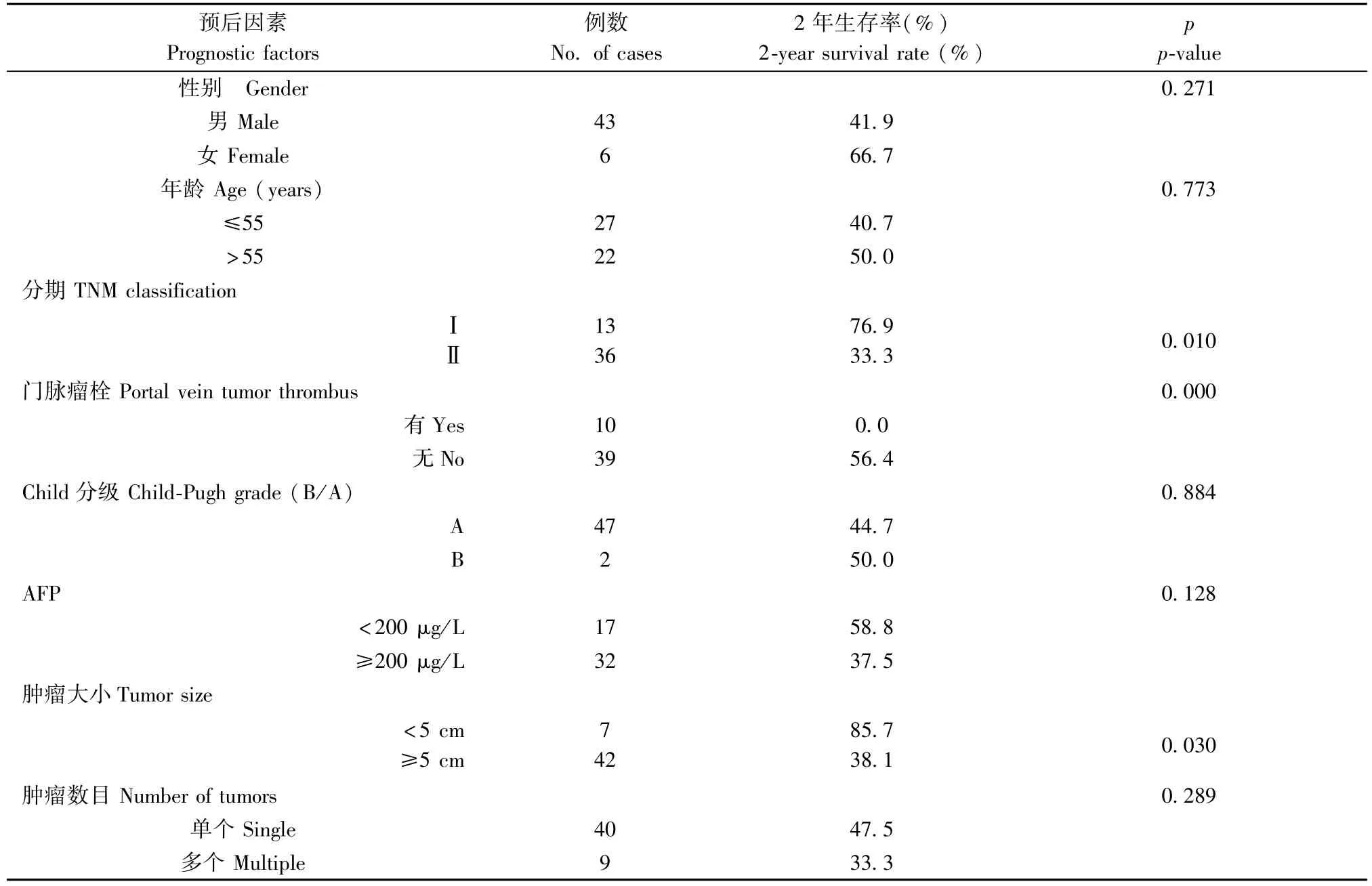
表1 患者基本临床资料Tab.1 Clinical data of the HBV-HCC patients
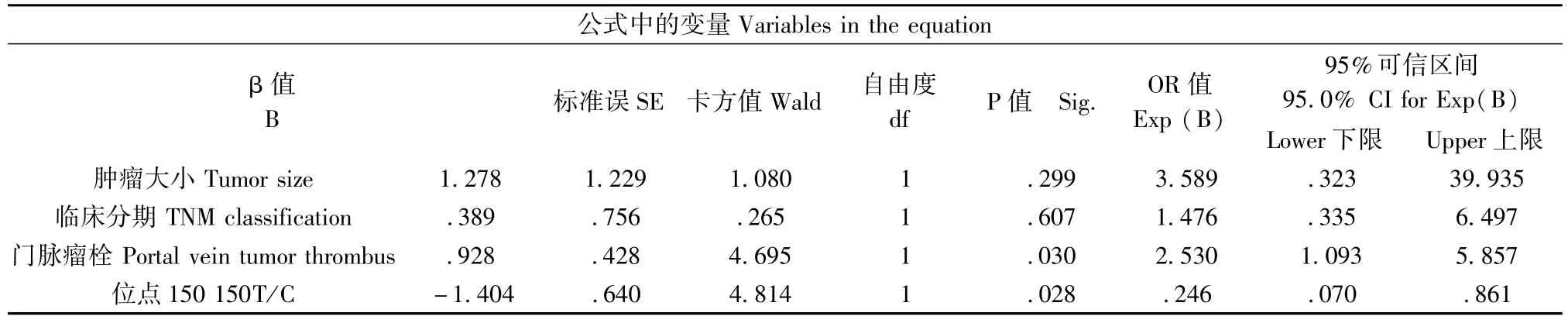
表2 预后相关资料多因素分析Tab.2 Multivariate analysis of the prognostic information
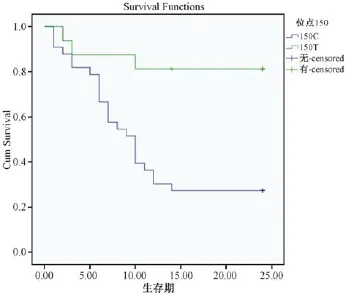
图1 150位点生存分析Fig.1 Cumulative survival of patients with 150 locus tumors
mtDNA D-loop区是线粒体基因组复制和表达的重要调控区,这一区域的SNPs可能影响mtDNA的复制,从而影响呼吸链的功能,使细胞能量供应发生障碍,产生大量的活性氧。活性氧可以对细胞核基因组产生损害从而导致肿瘤的发生[20]。线粒体单倍型类群H和U提供了杂合细胞体模型[21],已经证实这些人的遗传变异情况是由于氧化磷酸化功能不同而引起。与以前报道相符,本研究发现TNM分期、门静脉瘤栓、肿瘤大小和肝细胞肝癌的预后相关,依据2015 NCCN临床指南,直径<3 cm的肿瘤是适于手术切除的,但我们也切除较大直径的肿瘤,毕竟大多数患者就诊时肿瘤直径已超过3厘米。我们的数据显示,对于肿瘤直径<5 cm的患者,行肝癌切除2年生存率可以达到80%。
参考文献:
[1] Bosetti C,Turati F,La Vecchia C.Hepatocellular carcinoma epidemiology[J].Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol,2014,28 (5):753-770.
[2] Ferlay J,Soerjomataram I,Dikshit R,et al.Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide:sources,methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012[J].Int J Cancer,2015,136(5):E359 -E386.
[3] 王永川,魏丽娟,刘俊田,等.发达与发展中国家癌症发病率与死亡率的比较与分析 [J].中国肿瘤临床,2012,39:679-682.
[4] Caldwell S,Park SH.The epidemiology of hepatocellular cancer from the perspectives of public health problem to tumor biology [J].J Gastroenterol,2009,44(Suppl 19):96-101.
[5] Lu FM,Zhuang H.Management of hepatitis B in China[J]. Chin.Med,2009,122:3-4.
[6] Lu L,Wang X.Drug addition in China[J].Ann NY Acad Sci,2008,1141:304-317.
[7] Maki A,Kono H,Gupta M,et al.Predictive power of biomarkers of oxidative stress and inflammation in patients with hepatitis C virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Ann Surg Oncol,2007,14:1182-1190.
[8] 裴广军,付莉,崔亚玲,等.中国人群饮酒与原发性肝癌关系的Meta分析[J].现代预防医学,2008,35:2626-2627. [9] 邓敬桓,秦雪.原发性肝癌发生机制的研究进展 [J].环境与健康杂志,2007,24:924-926.
[10] Ribes J,Clèries R,Esteban L,et al.The influence of alcohol consumption and hepatitis B and C infections on the risk of liver cancer in Europe[J].J Hepatol,2008,49:233-242.
[11] Lin CW,Lin CC,Mo LR,et al.Heavy alcohol consumption increases the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B virus-related cirrhosis[J].J Hepatol,2013,58:730-735.
[12] Lee HC,Yin PH,Lin JC,et al.Mitochondrial genome instability and mt DNA depletion in human cancers[J].Ann New York Acad Sci,2005,1042:109-122.
[13] Taylor R,Wturnbull DM.Mitochondrial DNA mutations in human disease]J].Nat Rev Genet,2005,6(5):389-402.
[14] Nashikawa M,Nishiguchi S,Shiomi S,et al.Somatic mutation of mitochondrial DNA in cancerous and noncancerous liver tissue in individuals with hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Cancer Res,2001,61:1843-1845.
[15] Sanchez-Cespedes M,Parrella P,Nomoto S,et al.Identification of a mononucleotide repeat as a major target for mitochondrial DNA alterations in human tumors[J].Cancer Res,2001,61:7015-7019.
[16] Zhang RX,Zhang FB,Wang CJ,et al.Identification of sequence polymorphism in the D-loop region of mitochondrial DNA as a risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma with distinct etiology[J].J Exp Clin Cancer Res,2010,29(1):130.
[17] Navaglia F,Basso D,Fogar P,et al.Mitochondrial DNA D-loop in pancreatic cancer:somatic mutations are epiphenomena while the germline 16519 T variant worsens metabolism and outcome [J].Am J Clin Pathol,2006,126:593-601.
[18] Wang L,McDonnell SK,Hebbring SJ,et al.Polymorphisms in mitochondrial genes and prostate cancer risk[J].Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev,2008,17:3558-3566.
[19] Zhang R,WangR,ZhangF,etal.Singlenucleotide polymorphisms inthemitochondrialdisplacementloopand outcome of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].J Exp Clin Cancer Res,2010,29:155.
[20] Shigenaga MK,Hagen TM,Ames BN.Oxidative damage and mitochondrial decay in aging[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,1994,91:10771-10778.
[21] Gomez-Duran A,Pacheu-Grau D,Lopez-Gallardao E,et al. Unmasking thecauseofmultifactorialdisorders:OXPHOS differences between mitochondrial haplogroups[J],Hum Mol Genet,2010,19:3343-3353.
〔修回日期〕2016-02-24
Investigation of the association between mitochondrial D-loop polymorphisms and hepatocellular carcinoma outcome
ZHANG Feng-bin,GUO Zhan-jun,WU Chen-si,ZHANG Rui-xing
(Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology,The Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University,Shijiazhuang 050011,China)
【Abstract】Objective To investigate the accumulation of mutations and single nucleotide polymorphisms(SNPs)in the displacement loop(D-loop)of mitochondrial DNA(mtDNA)might be associated with cancer risk and disease outcome.Methods We obtained cancerous and noncancerous liver tissues from 49 HBV-related HCC patients at the Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University.mtDNA of the liver tissues was extracted with Mitochondrial DNA Extraction Kit.Mutation and polymorphism were confirmed by repeated analysis.We assessed the prediction power of D-loop SNPs in hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC)patients.Results No mutation in these HCC patients had prediction power for postoperational survival,whereas one SNP site(nucleotide 150 C/T)was identified by the log-rank test for statistically significant prediction of HCC survival.In an overall multivariate analysis,allele 150 was identified as an independent predictor of HCC outcome.The length of survival of patients with allele 150C was significantly shorter than that of patients with allele 150T(relative risk,0.246;95%CI,0.070-0.861;P=0.028).Conclusions The analysis of genetic polymorphisms in the mitochondrial D-loop helps to identify patient subgroups at high risk of a poor disease outcome.
【Key words】Hepatocellular carcinoma,HCC;Mitochondrial D-loop;Mutation;Single nucleotide polymorphisms,SNP;Survival analysis
【中图分类号】R-33
【文献标识码】A
【文章编号】1671-7856(2016)04-0058-04
doi:10.3969.j.issn.1671-7856.2016.04.010
[基金项目]河北省科技厅资助项目,项目编号:132777185。
[通讯作者]张风宾(1981-)男,主治医师,硕士研究生学历,主要研究方向为消化道肿瘤,Email:zhangfengbin1981@163.com
