厄洛替尼联合培美曲塞/顺铂治疗EGFR野生型或突变状态未知肺腺癌脑转移的疗效初探
2015-12-14张亚雷杨海虹何绮华邵文龙何建行
张亚雷 杨海虹 何绮华 邵文龙 何建行
·论著·
厄洛替尼联合培美曲塞/顺铂治疗EGFR野生型或突变状态未知肺腺癌脑转移的疗效初探
张亚雷 杨海虹 何绮华 邵文龙 何建行★
目的评价厄洛替尼联合培美曲塞/顺铂治疗EGFR野生型和突变状态未知肺腺癌脑转移的疗效和毒副作用。方法初治或复治的肺腺癌脑转移患者17例,其中9例患者为EGFR野生型,8例患者EGFR突变状态未明。培美曲塞(500 mg/m2)与顺铂(20 mg/m2)分别于第1天和第1~3天给药,厄洛替尼(150 mg/d)于第4~21天给药,21天为1周期。化疗结束后厄洛替尼维持治疗直至疾病进展或毒副作用不可耐受。结果对于颅内病灶,3例患者取得完全缓解(CR),9例患者部分缓解(PR),4例患者疾病稳定(SD),客观反应率(ORR)达到70.6%(12/17),疾病控制率(DCR)达到100%(17/17);对于颅外病灶,无CR患者,7例患者取得PR,9例患者取得SD,1例患者疾病进展(PD),客观反应率(ORR)达到41.2%(7/17),疾病控制率(DCR)达到94.1%(16/17);颅内和颅外疾病控制的无进展生存期的中位数11.1个月和10.7个月。结论厄洛替尼联合培美曲塞/顺铂治疗EGFR野生型或突变状态未知肺腺癌脑转移是有效的,而且耐受性好。但是,仍需要进一步的临床试验来证实。
培美曲塞;厄洛替尼;肺腺癌;脑转移癌
非小细胞肺癌(non-small cell lung cancer,NSCLC)是全世界癌症相关死亡的主要原因之一。脑转移瘤(brain metastases,BM)通常发生在肺腺癌患者,与患者的不良预后和生活质量差相关。大约有30%~50%的NSCLC患者在治疗前或治疗过程中发生脑转移[1]。目前肺癌脑转移的治疗方法有限,因此,通常脑转移患者预后很差[2]。
厄洛替尼和培美曲塞是治疗肺腺癌并脑转移患者的有效药物。厄洛替尼是表皮生长因子受体(epidermal grow th factor receptor,EGFR)酪氨酸激酶抑制剂(tyrosine kinase inhibitor,TKI),为一种小分子药物,能够穿越血脑屏障。研究表明厄洛替尼可以明显提高EGFR突变阳性肺腺癌脑转移瘤治疗的有效率和无症状脑转移患者的总生存率[3,4]。然而,对于EGFR野生型或突变状况未知的患者,厄洛替尼治疗脑转移的有效率较差,患者的生存期亦较短[5]。培美曲塞是胸苷酸合成酶(thymidylate synthase,TS)、二氢叶酸还原酶(dihydrofolate reductase,DHFR)和甲酰甘氨酰胺核苷酸转移酶的抑制剂(glycinam ide ribonicleotide formyltransferase,GARFT)[6]。培美曲塞的耐药可能主要归因于TS表达的增加[7]。
非小细胞肺癌具有很强的肿瘤的异质性,靶向药物和化疗联合可能发挥协同效应[8]。小样本的临床研究显示厄洛替尼联合培美曲塞在既往治疗过的晚期肺腺癌患者中具有较好的疗效[9],也具有很好的耐受性[10]。
因此我们推测,厄洛替尼联合培美曲塞/顺铂的方案可能对EGFR野生型和突变状态未知的肺腺癌脑转移患者的治疗更有效。
1 资料和方法
1.1 病例选择
17例患者均为广州医科大学附属第一医院胸胸外科胸部肿瘤专科于2010年12月~2013年10月收治的晚期NSCLC患者,均经细胞学或病理学证实为肺腺癌,脑部MRI证实有脑转移;伴或不伴其他部位转移;KPS评分≤2分;患者具体临床资料见表1。
1.2 EGFR基因突变分析
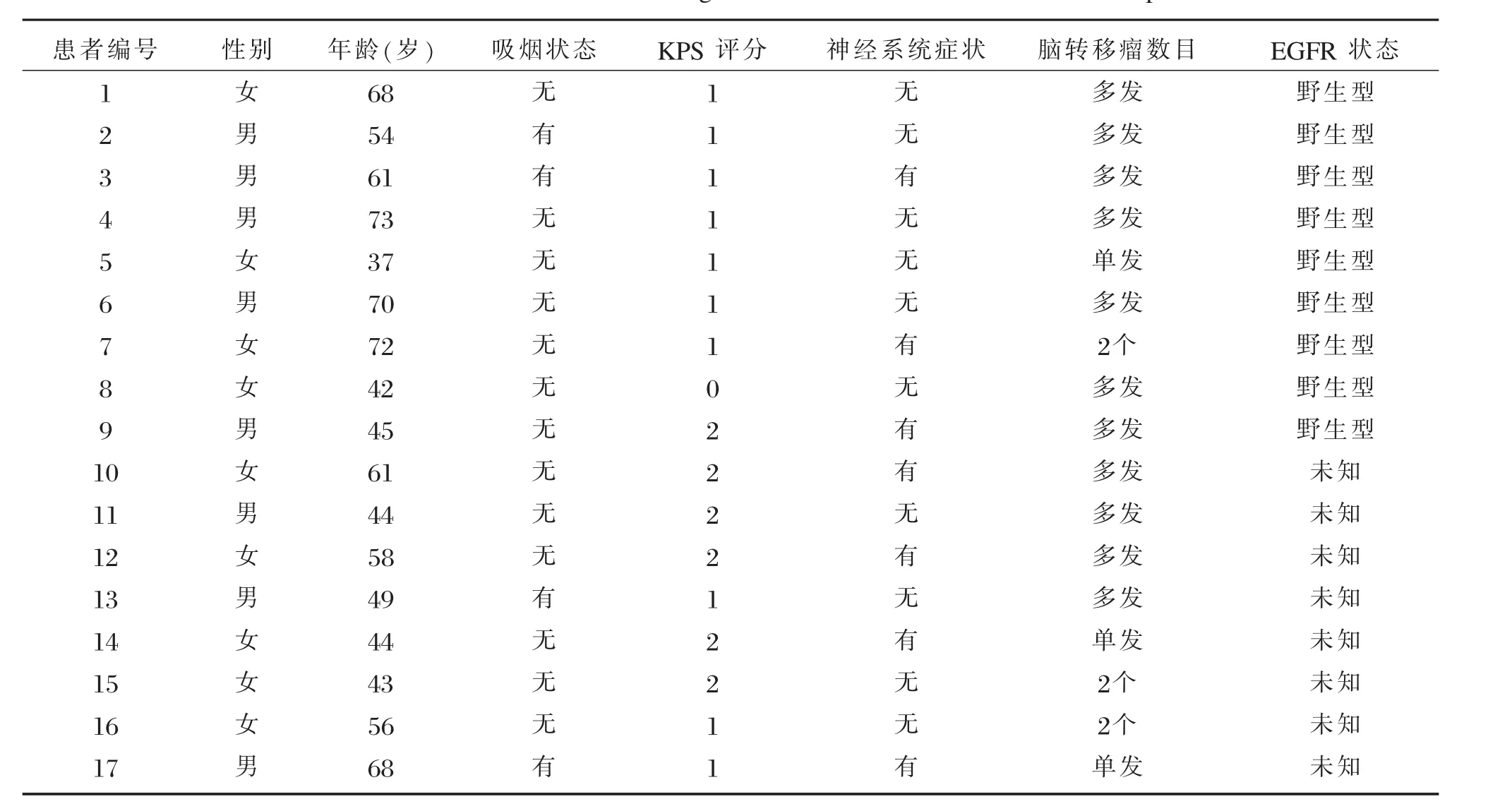
表1 17例肺腺癌脑转移患者临床资料Table 1 The characteristics of the 17 lung adenocarcinoma w ith brain metastases patients
从福尔马林固定石蜡组织中提取DNA,使用QIAamp DNA试剂盒(Qiagen,Hilden,Germany)进行检测。使用市售的amoydx®人类EGFR基因29种突变的荧光PCR诊断试剂盒检测EGFR突
变(厦门诊断技术有限公司,厦门,中国)。本试剂盒检测EGFR 18-21外显子29个位点的突变,包括T790M、L858R、L861Q、S768I、G719S、G719A、G719C,外显子20和19的插入及19外显子缺失突变。
1.3 治疗方法
给予患者培美曲塞500mg/m2,第1天进行静脉滴注;顺铂20mg/m2,第1~3天进行静脉滴注,每3周为1个周期。用药前1周开始给予患者口服叶酸400μg/天,持续到化疗结束;同时用药前1周给予VitB121mg肌注,每9周重复1次;患者用药前1天、当天和第2天口服地塞米松片3.75mg,每日2次。化疗开始后给予患者厄洛替尼每天150mg口服(化疗当日除外),直到疾病进展或毒性无法耐受。治疗过程中常规使用止吐药物及相关对症治疗。
1.4 疗效评价与随访
根据RECIST 1.0进行实体瘤近期疗效评价[11],分为完全缓解(CR),部分缓解(PR),疾病稳定(SD),疾病进展(PD)。以CR+PR计算有效率(ORR),以CR+PR+SD计算疾病控制率(DCR)。无进展生存期(PFS)是从患者开始接受化疗计算,直至患者因疾病进展为止。最后的随访时间是2014年8月。
1.5 毒副反应
按照美国NCI制定的毒副反应标准(CTC第3版)评价毒副反应,分为0~4级共5个等级。
1.6 统计学分析
数据以SPSS 10.0统计软件进行统计处理,用卡方检验比较不同因素在缓解率及疾病控制率方面有无差异。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 近期疗效
所有患者均接受2~8化疗周期(中位数,5个周期)。在最后一次随访时仍然有8例患者存活。颅内和颅外病灶的中位PFS分别为11.1个月和10.7个月,两者差异无显著性(P=0.876),其中11号患者的PFS时间达到45个月且目前仍然存活。对于颅内病灶,3例患者取得CR、9例患者PR、4例患者SD,客观反应率(ORR)达到70.6%(12/17),疾病控制率(DCR)达到100%(17/17);对于颅外病灶,无CR患者、7例患者取得PR、9例患者SD、1例患者PD,客观反应率(ORR)达到41.2%(7/17),疾病控制率(DCR)达到94.1%(16/17)(具体见表2和图1)。颅内病灶与颅外病灶的的ORR差异无显著性(P=0.084)。图2显示的是13号患者脑转移瘤在联合方案治疗3个疗程后完全消失(CR)。

图1 17例患者颅内病灶及颅外病灶的PFS时间Figure 1 Progression-free survival of 17 patients by extracranial or intracranial disease control

表2 17例肺腺癌脑转移患者治疗的疗效Table 2 The tumor response and disease control of the 17 lung adenocarcinomaw ith brainmetastases patients

图2 13号患者治疗前后效果对比Figure 2 The effectbefore and after treatmentof the patientNo.13
2.2 毒副作用
14例患者出现1~2度皮疹,1例患者出现3度皮疹,2度腹泻1例,2级口腔粘膜炎1例。患者对组合方案的耐受性良好,只有1~2级血液学毒性。
3 讨论
肺癌伴有脑转移的患者生存期短,生活质量差,预后不佳[12]。培美曲塞是一种新的多靶点抗叶
酸化疗药物,通过干扰细胞复制过程中叶酸代谢途径而发挥抗肿瘤作用。研究显示,培美曲塞能明显抑制重要的叶酸依赖性辅酶胸苷酸合成酶(TS)、二氢叶酸还原酶(DHFR)和甘氨酰胺核苷甲酰基转移酶(GARFT)的活性。培美曲塞通过对这些关键酶活性进行多靶点抑制,使得嘌呤和胸腺嘧啶核苷生物合成减少,从而影响肿瘤细胞DNA和RNA合成[13]。培美曲塞一线治疗的肺腺癌患者中46%的患者显效[14,15]。吴一龙等[16]研究结果显示对于中国的EGFR敏感突变的伴有无症状BM的肺腺癌患者,厄洛替尼作为二线治疗时的ORR可达到58.3%。而EGFR野生型的BM患者,对治疗的反应率及生存预后均差于EGFR突变的患者[5]。
我们前期使用厄洛替尼联合培美曲塞/顺铂方案治疗EGFR野生型的肺腺癌脑转移患者,取得了不错的疗效[17]。在本研究中厄洛替尼联合培美曲塞/顺铂治疗EGFR野生型或突变状态未知肺腺癌脑转移患者的的颅内治疗反应为70.6%(12/17),PFS达11.1个月,明显优于该方案对EGFR野生型的肺腺癌脑转移患者的疗效。原因(1)可能是由于厄洛替尼和培美曲塞的协同作用[18,19]。EGFRTKI可以降低TS酶的表达和活性[20,21],从而增强肿瘤对培美曲塞的敏感性,与此同时,TS的抑制剂5-氟尿嘧啶可能增加EGFR的磷酸化,从而有可能提高EGFR-TKI的活性[22]。(2)EGFR突变状态未知的患者中,部分患者因活检时肿瘤细胞量太少无法行EGFR检测,部分患者拒绝行基因检查,该类患者中可能有部分患者的EGFR突变状态是阳性,对TKI的治疗反应性好[3],从而使得本研究中患者的PFS时间延长。
本研究中,我们观察到该联合方案对于颅内和颅外病灶的ORR分别为70.6%和41.2%,颅内疾病控制的表现有优于颅外疾病控制的趋势(PFS分别为11.1月vs 10.7月)。颅内病灶和颅外病灶的效果不完全一致,这可能是EGFR突变状态在肺腺癌中分布是不均一的[23]。Weber等[24]用同位素11C标记的厄洛替尼作为PET-CT的示踪剂,结果显示,厄洛替尼能在非小细胞肺癌颅内转移灶中聚集,对原发灶和转移灶均有效。原发灶与转移灶EGFR突变状态可能存在着差异,从而影响到该联合方案对颅内和颅外病灶的效果。毒副作用方面,大多是1-2级反应,整体来说患者对该方案的耐受性良好,这和既往的研究结果相似[10]。
总之,通过本研究我们发现厄洛替尼联合培美曲塞/顺铂治疗EGFR野生型或突变状态未知肺腺癌脑转移是有效的,疗效优于我们既往该方案治疗EGFR野生型肺腺癌脑转移患者的疗效,而且耐受性好,有待于扩大样本量进一步研究。
[1]Hazard LJ,Jensen RL,Shrieve DC.Role of stereotactic radiosurgery in the treatment of brain metastases[J]. Am JClin Oncol,2005,28(4):403-410.
[2]Chi A,Komaki R.Treatment of brain metastasis from lung cancer[J].Cancers(Basel),2010,2(4):2100-2137.
[3]Kim JE,Lee DH,Choi Y,et al.Epidermal grow th factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors as a first-line therapy for never-smokers w ith adenocarcinoma of the lung having asymptomatic synchronous brain metastasis [J].Lung Cancer,2009,65(3):351-354.
[4]Porta R,Sánchez-Torres JM,Paz-Ares L,et al.Brain metastases from lung cancer responding to erlotinib:the importance of EGFR mutation[J].Eur Respir J,2011,37 (3):624-631.
[5]Hsiao SH,Lin HC,Chou YT,et al.Impact of epidermal grow th factor receptor mutations on intracranial treatment response and survival after brain metastases in lung adenocarcinoma patients[J].Lung Cancer,2013,81(3):455-461.
[6]Shih C,Chen VJ,Gossett LS,et al.LY231514,a pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine-based antifolate that inhibits multiple folate-requiring enzymes[J].Cancer Res,1997, 57(6):1116-1123.
[7]Sigmond J,Backus HH,Wouters D,et al.Induction of resistance to the multitargeted antifolate pemetrexed (ALIMTA)in W iDr human colon cancer cells is associated w ith thymidylate synthase overexpression[J]. Biochem Pharmacol,2003,66(3):431-438.
[8]Spicer J,Harper P.Targeted therapies for non-small cell lung cancer[J].Int JClin Pract,2005,59(9):1055-1062.
[9]M inami S,Kijima T,Takahashi R,et al.Combination chemotherapy w ith interm ittent erlotinib and pemetrexed for pretreated patients w ith advanced non-small cell lung cancer:a phase I dose-finding study[J].BMC
Cancer,2012,12:296.
[10]Ranson M,Reck M,Anthoney A,et al.Erlotinib in combination w ith pemetrexed for patients w ith advanced non-small-cell lung cancer(NSCLC):a phase I dose-finding study[J].Ann Oncol,2010,21(11): 2233-2239.
[11]Eisenhauer EA,Therasse P,Bogaerts J,et al.New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours:revised RECIST guideline(version 1.1)[J].Eur JCancer, 2009,45(2):228-247.
[12]白皓,韩宝惠.352例肺癌脑转移预后因素分析[J].中国肺癌杂志,2008,11(1):101-106.
[13]Calvert H.An overview of folatemetabolism:features relevant to the action and toxicities of antifolate anticancer agents[J].Sem iOncol,1999,26(Supp l):3-10.
[14]Li C,Sun Y,Fang Z,et al.Comprehensive analysis of epidermal grow th factor receptor gene status in lung adenocarcinoma[J].J Thorac Oncol,2011,6(6):1016-1021.
[15]Orlando M,Lee JS,Yang C,et al.Efficacy of pemetrexed-cisplatin(PC)in East Asian patients(pts): Subgroup analysis of a phaseⅢstudy comparing PC versus gemcitabine-cisplatin(GC)in first-line treatment of advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer(NSCLC)[J].J Clin Oncol,2009,27(15s):abstr 8045.
[16]Wu YL,Zhou C,Cheng Y,et al.Erlotinib as secondline treatment in patients w ith advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and asymptomatic brain metastases:a phase II study(CTONG-0803)[J].Ann Oncol,2013,24 (4):993-999.
[17]Zhang Y,Yang H,Yang X,et al.Erlotinib w ith pemetrexed/cisplatin for patients w ith EGFR w ild-type lung adenocarcinoma w ith brain metastases[J]. Molecular and Clinical Oncology,2014,2(3):449-453.
[18]Giovannetti E,Lemos C,Tekle C,et al.Molecular mechanisms underlying the synergistic interaction of erlotinib,an epidermal grow th factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor,w ith the multitargeted antifolate pemetrexed in non-small-cell lung cancer cells[J].Mol Pharmacol,2008,73(4):1290-1300.
[19]Li T,Ling YH,Goldman ID and Perez-Soler R. Schedule-dependent cytotoxic synergism of pemetrexed and erlotinib in human non-small cell lung cancer cells [J].Clin Cancer Res,2007,13(11):3413-3422.
[20]Magne N,Fischel JL,Dubreuil A,et al.ZD1839 (Iressa)modifies the activity of key enzymes linked to fluoropyrim idine activity:rational basis for a new combination therapy w ith capecitabine[J].Clin Cancer Res,2003,9(13):4735-4742.
[21]Budman DR,Soong R,Calabro A,et al.Identification of potentially useful combinations of epidermal grow th factor receptor tyrosine kinase antagonists w ith conventional cytotoxic agents using median effect analysis[J].Anticancer Drugs,2006,17(8):921-928.
[22]Van Schaeybroeck S,Karaiskou-M cCaul A,Kelly D,et al.Epidermal grow th factor receptor activity determ ines response of colorectal cancer cells to gefitinib alone and in combination w ith chemotherapy[J].Clin Cancer Res,2005,11(20):7480-7489.
[23]Yatabe Y,Matsuo K,M itsudom i T.Heterogeneous distribution of EGFR mutations is extremely rare in lung adenocarcinoma[J].J Clin Oncol,2011,29(22): 2972-2977.
[24]Weber B,Winterdahl M,Memon A,et a1.Erlotinib accumulation in brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer:visualization by positron emission tomography in a patient harboring a mutation in the epidermal grow th factor receptor[J].JThorac Oncol, 2011,6(7):1287-1289.
The effecacy of erlotinib w ith pemetrexed/cisplatin for brain metastases patients from EGFR w ild-type or unkown lung adenocarcinoma
ZHANG Yalei,YANG Haihong,HE Qihua,SHAO Wenlong,HE Jianxing★
(Department of Thoracic Surgery,State Key Laboratory of Respiratory Diseases,The First A ffiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University,Guangzhou,Guangdong,China,510120)
Objective To evaluate the efficacy and side effects of erlotinib and pemetrexed/ cisplatin in the patients w ith brain metastases of EGFR w ild-type or unkown lung adenocarcinoma.Methods Seventeen patients w ith brain metastases of lung adenocarcinoma were enrolled in this study.Among the 17 cases,9 cases were EGFR w ild-type and 8 cases were EGFR unknown.Pemetrexed(500 mg/ m2)and cisplatin(20 mg/m2)were adm inistered on day 1 and days 1~3,respectively.Erlotinib(150 mg) was adm inistered daily on days 4~20,21 days for 1 cycle.After the end of chemotherapy,erlotinib maintenance treatment until progressive disease or toxicity could not be tolerated.Results W ith regard to the BM,there were 3 cases w ith complete response(CR),9 cases had partial response(PR)and 4 had stable disease(SD).The objective response rate(ORR)was 70.6%(12/17).Disease control rate(DCR)was 100% (17/17).As regards the extracranial tumors,there was no case w ith CR,7 cases had PR,9 cases had SD and 1 case had progressive disease(PD).The ORR was 41.2%(7/17)and DCR was 94.1%(16/17).Themedian progression-free survival time for intracranial and extracranial disease control was 11.1 and 10.7 months, respectively.Conclusion Erlotinib with pemetrexed/cisplatin is effective and well tolerated for brain metastases of EGFR w ild-type or unkown lung adenocarcinoma.However,further clinical trials are required to confirm our conclusions.
Pemetrexed;Erlotinib;Lung adenocarcinoma;Brain metastases
广州市医药卫生科技项目(20131A011135)
广州医科大学附属第一医院胸外科,呼吸疾病国家重点实验室,广东,广州510120
★通讯作者:何建行,E-mail:hejx@vip.163.com
