CDK5与EMT相关蛋白在头颈部鳞状细胞癌中异常表达的相关性研究
2015-11-24赵明慧黄媛媛孙姗姗孔令平王宇郭文宇周旋王旭东张仑
赵明慧,黄媛媛,孙姗姗,孔令平,王宇,郭文宇,周旋,王旭东,张仑
CDK5与EMT相关蛋白在头颈部鳞状细胞癌中异常表达的相关性研究
赵明慧,黄媛媛,孙姗姗,孔令平,王宇,郭文宇,周旋,王旭东,张仑△
目的探讨头颈部鳞状细胞癌(HNSCC)中细胞周期素依赖蛋白激酶5(CDK5)及上皮间充质转化(EMT)相关蛋白N-钙黏蛋白(N-cadherin)、波形蛋白(Vimentin)及E-钙黏蛋白(E-cadherin)表达,以及CDK5的表达与患者预后的关系。方法免疫组化方法检测55例HNSCC患者癌组织中CDK5及EMT相关蛋白的表达情况;分析不同临床病理特征患者CDK5及EMT相关蛋白表达的差异,CDK5与EMT相关蛋白表达的相关性,以及CDK5表达与患者生存之间的关系。结果CDK5高表达率在有淋巴结转移患者中高于无淋巴结转移患者(91.67%vs 30.23%,P<0.05),在T3~T4期患者中高于T1~T2期患者(85%vs 20%,P<0.05);有淋巴结转移患者N-cadherin、Vimentin高表达率高于无淋巴结转移的患者(75.00%vs 6.98%;91.67%vs 27.91%,均P<0.05),E-cadherin高表达率低于无淋巴结转移的患者(8.33%vs 86.05%,P<0.05);CDK5与N-cadherin、Vimentin表达呈正相关,与E-cadherin表达呈负相关(rs分别为0.512、0.443、-0.363,均P<0.01);CDK5高表达患者3年生存率低于低表达患者(37.5%vs 87.0%,Logrankχ2=12.678,P<0.01)。结论CDK5及EMT相关蛋白在转移性HNSCC中异常表达;CDK5的表达状态对预测HNSCC患者的预后有一定价值。
头颈部肿瘤;癌,鳞状细胞;细胞周期蛋白依赖激酶5;钙黏着糖蛋白类;波形蛋白;淋巴转移
头颈部恶性肿瘤是目前全球第六高发恶性肿瘤,其中90%以上为鳞状细胞癌[1]。近几十年来,尽管采取了积极的治疗措施,头颈部恶性肿瘤患者的5年生存率仍仅为50%左右[1]。颈部淋巴结转移是头颈部鳞状细胞癌(HNSCC)患者预后不良的重要因素之一[2]。因此,阐明肿瘤转移的分子机制,寻找抑制肿瘤转移的新的治疗方案愈发重要。上皮间充质转化(EMT)是肿瘤细胞发生迁移和侵袭的重要机制之一[3]。研究表明,EMT在HNSCC转移过程中起到重要作用[4]。细胞周期素依赖蛋白激酶5(CDK5)能够调控前列腺癌细胞的迁移、甲状腺髓样癌细胞的增殖及胶质母细胞瘤的凋亡等[5]。抑制CDK5的活性可以逆转肿瘤EMT进程[6]。然而,迄今为止尚鲜见HNSCC中CDK5与EMT相关蛋白N-钙黏蛋白(N-cadherin)、波形蛋白(Vimentin)及E-钙黏蛋白(E-cadherin)表达方面的研究。本研究初步探讨了CDK5与EMT相关蛋白在HNSCC中表达的相关性及CDK5表达与预后的关系。
1.1 临床资料 资料来源于2015年5月-2018年6月参与江西省妇幼保健院开展的“关爱母亲公益活动”的3100例女性,所有女性均自愿接受宫颈HPV筛查。所有女性年龄范围25-65岁,平均年龄(39.08±10.21)岁,纳入标准包括:有性行为史;筛查时未怀孕;无宫颈上皮内瘤变、子宫颈癌和子宫切除史。以25-29岁开始,之后每5岁为一个年龄段,到≥50岁组,分为6个年龄组。
1 资料与方法
1.1 病例与组织标本来源收集天津医科大学肿瘤医院2008年1月—2012年1月外科手术切除的HNSCC患者的肿瘤标本55例,其中男50例,女5例,年龄20~77岁,平均(57.25±10.78)岁,有淋巴结转移HNSCC患者12例,无淋巴结转移患者43例。入选标准:(1)组织病理诊断为鳞癌。(2)能够按照2010年国际抗癌联盟UICC标准行TNM分期。(3)临床资料完整。随访时间为手术之日起至死亡或末次随访时间,截至2015年7月1日。总生存期定义为从疾病确诊时间至患者失去随访或死亡时间。所有组织标本去除坏死组织,用生理盐水洗去血污并经福尔马林固定后制作石蜡切片。
1.2 方法免疫组织化学法检测组织标本中CDK5及EMT相关蛋白表达。石蜡切片常规脱蜡水化,枸橼酸抗原修复(中杉金桥,北京),3%H2O2孵育,胎牛血清封闭,分别滴加CDK5、N-cadherin、Vimentin及E-cadherin一抗(CST,美国,1∶100稀释),4℃孵育24 h;PBS充分洗涤,加入生物素标记的二抗(1∶100稀释),37℃孵育30 min;PBS充分洗涤洗去二抗,加入辣根过氧化物酶标记的三抗(1∶100稀释),37℃孵育30 min;DAB显色剂显色,苏木素复染,梯度脱水,封片;DP-70倒置显微镜(Olympus,日本)采集图像。
蛋白表达水平根据染色水平进行分级。染色结果根据染色阳性细胞百分比及染色强度两个参数综合评价。每张切片随机观察10个视野,每个视野计数100个细胞,以10个视野中平均阳性细胞数计算阳性细胞率。CDK5、N-cadherin及Vimentin表达判定标准[7]:阳性细胞率≤10%评分0,11%~25%评分1,26%~50%评分2,51%~75%评分3,>75%评分4。染色强度评分:无染色评分0;黄色评分1;棕黄色评分2;棕褐色评分3。染色阳性细胞率评分及染色强度评分相乘即为最后评分:0~3分定义为低表达,4~12定义为高表达。E-cadherin表达判定标准[7]:阳性细胞率<10%为低表达,≥10%为高表达。
2.4 HNSCC中CDK5的表达与患者预后的关系55例HNSCC患者随访时间为3~60个月,中位随访时间49个月,失访1例。CDK5低表达患者和高表达患者的3年生存率分别为87.0%和37.5%,差异有统计学意义(Log-rank χ2=12.678,P<0.01),见图2。
2.2 EMT相关蛋白在HNSCC组织中的表达情况与无淋巴结转移的HNSCC相比,有淋巴结转移HNSCC中EMT相关蛋白N-cadherin、Vimentin表达水平升高,E-cadherin表达水平降低,见图1。有淋巴结转移的患者中N-cadherin、Vimentin高表达率高于无淋巴结转移的患者(75.00%vs 6.98%;91.67%vs 27.91%),E-cadherin高表达率低于无淋巴结转移的患者(8.33%vs 86.05%),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),不同性别、年龄、原发部位和T分期间EMT相关蛋白表达差异均无统计学意义,见表1。
2 结果
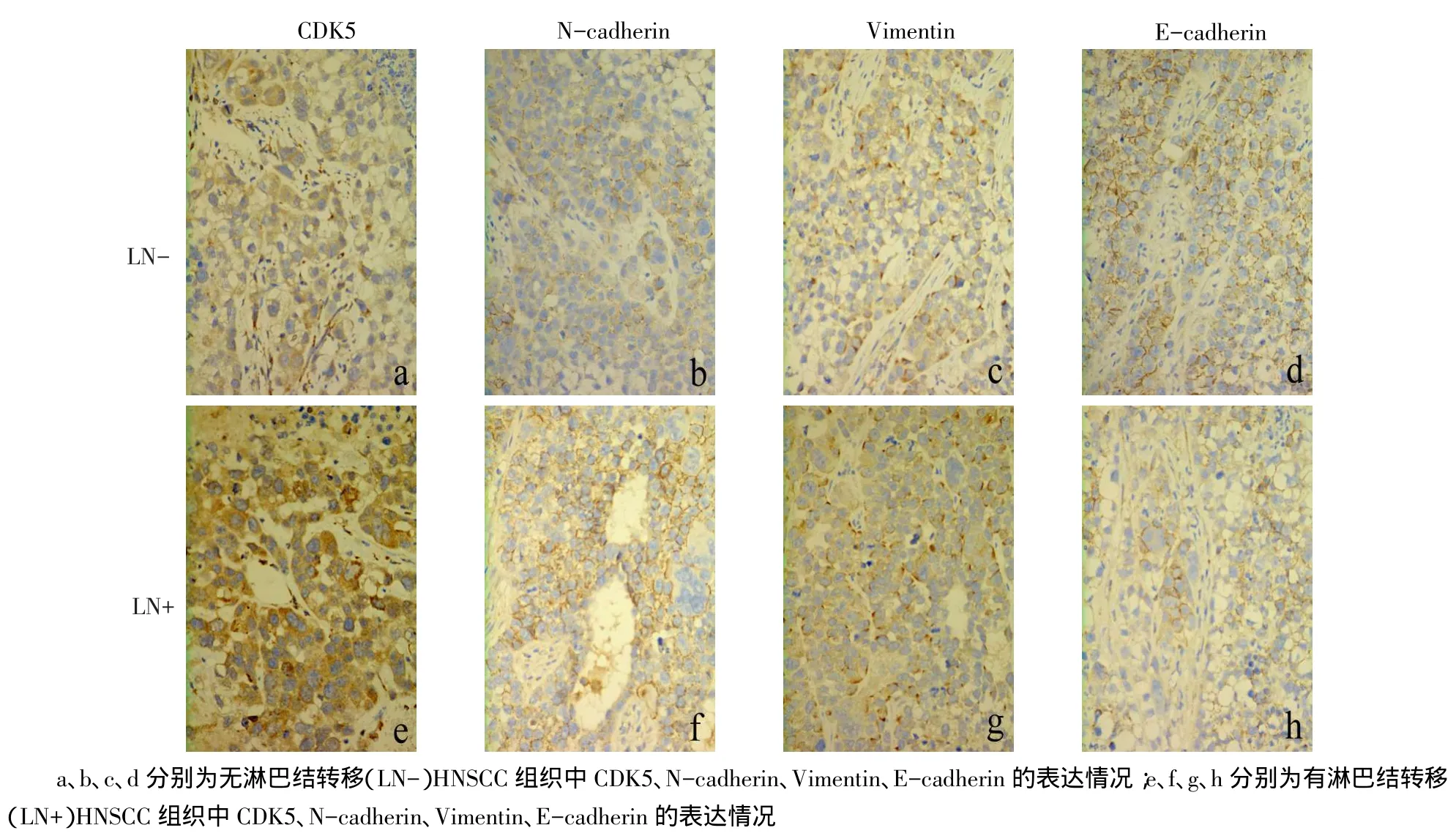
Fig.1Expressions of CDK5 and EMT related proteins were determined by immunohistochemistry in the groups of non-lymph node metastasis(LN-)and lymph node metastasis(LN+)图1 免疫组化法检测CDK5与EMT相关蛋白在无淋巴结转移及有淋巴结转移的HNSCC中的表达(SP,×400)
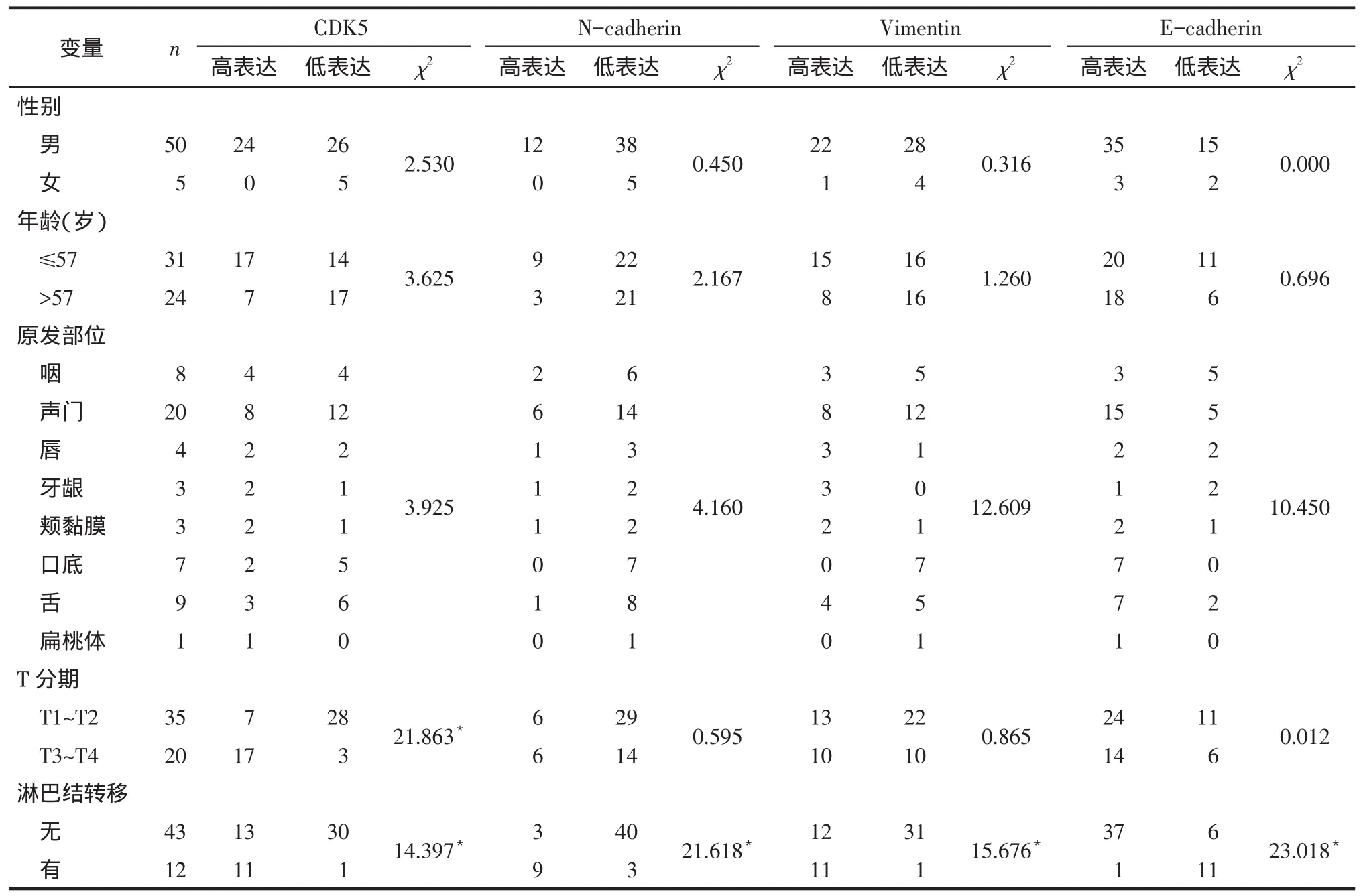
Tab.1Basic characteristics of the 55 HNSCC patients and the expressions of CDK5 and EMT related proteins were determined by immunohistochemistry表1 55例HNSCC患者的临床病理特征及免疫组化检测CDK5与EMT相关蛋白的表达(例)
EMT是肿瘤发生侵袭、转移的主要因素之一。在EMT过程中,肿瘤细胞由上皮表型向间充质表型转化,其特点为间充质标志相关蛋白如N-cadherin、Vimentin表达水平均升高,上皮标志相关蛋白如E-cadherin表达水平降低[3]。近年来研究发现在HNSCC[12]、食管癌[7]、乳腺癌[13]、前列腺癌[14]、膀胱癌[15]、肺癌[16-17]、肝癌[18]、胆管癌[19]等多种肿瘤侵袭、转移过程中均出现EMT过程。Zhang等[20]指出内皮细胞通过分泌表皮生长因子(EGF)诱导HNSCC细胞的EMT过程,从而促进肿瘤转移。Fujii等[12]发现在HNSCC中选择性环氧化酶2(COX-2)抑制剂可以恢复E-cadherin的表达,抑制EMT过程,发挥抗肿瘤转移的作用。本研究发现,与无淋巴结转移的HNSCC组织比较,有淋巴结转移的组织中N-cadherin、Vimentin的高表达率升高,E-cadherin的高表达率降低。本研究与相关研究结果均表明在HNSCC中EMT相关蛋白与转移有关。
率高于无淋巴结转移的患者(91.67%vs 30.23%,P<0.05);T3~T4期组织中CDK5高表达率高于T1~T2期组织(85%vs 20%,P<0.05);不同性别、年龄和原发部位间CDK5的表达差异均无统计学意义。
不久,渡口处又修了一座桥,渡口彻底废了。摆渡人无事可做,开始上岸活动,看村人播种收割。他喜欢秋天,他说秋天的田野一派金黄,有油画的美感。
看花却忆去年事,空堂听履声登登。 鼠姑万朵香烂漫,文梓双干阴清澄。 重寻古寺饯残暑,低葵疏蓼秋花凝。 惟有青松与红杏,摩挲画卷情难胜。 倚树老人捻须笑,龛中岁月传千灯。 吾侪衣鉢今有托,藉湜幸免韩门憎。 壮游山水我更羡,秀语寒饿人将惩。 闍黎有意工阅客,展卷苦道题名曾。[11]
2.3 HNSCC中CDK5与EMT相关蛋白表达的相关性55例HNSCC组织标本中,CDK5与N-cadherin、Vimentin表达呈正相关,与E-cadherin表达呈负相关(rs分别为0.512、0.443、-0.363,均P<0.01)。
1.3 统计学方法使用SPSS 18.0统计软件处理数据。分类资料组间比较采用χ2检验。Spearman等级相关分析CDK5与EMT相关蛋白表达的相关性。Kaplan-Meier法分析CDK5表达与患者生存之间的关系。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。

Fig.2CDK5 expression and Kaplan-Meier analysis图2 CDK5表达与生存期分析
3 讨论
CDK5作为脯氨酸介导的丝/苏氨酸蛋白激酶家族中的特殊一员,与p35或p39结合形成激活复合体,通过磷酸化黏着斑激酶(FAK)、踝蛋白(talin)、过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ(PPRAγ)及c-Myc等蛋白质,在神经细胞的发育和分化过程中发挥作用[8]。近来研究表明,CDK5在乳腺癌[8]、甲状腺髓样癌[9]、胰腺癌[10]、肝癌[5]、前列腺癌[11]等多种恶性肿瘤中高表达,在肿瘤的形成过程中起重要作用。Pozo等[9]在对甲状腺髓样癌的研究中发现,CDK5可以通过磷酸化视网膜母细胞瘤蛋白(Rb)促进肿瘤的发生和发展。Feldmann等[10]发现在胰腺癌中存在CDK5及其激活因子p35的高表达,下调CDK5表达能够抑制胰腺癌中的Ras-Ral信号通路,从而使肿瘤细胞迁移、侵袭能力下降,抑制肿瘤的发生和转移。上述结果均表明CDK5的高表达可能是多种肿瘤发生过程中的分子事件之一,抑制其表达可能成为多种肿瘤基因治疗的分子靶点。然而,CDK5在HNSCC中的作用尚不明确。本研究结果显示,在HNSCC组织中CDK5的高表达率在有淋巴结转移的组织中高于无淋巴结转移的组织,在T分期高的组织中高于T分期低的组织,CDK5低表达的患者3年生存率较高,CDK5可以作为HNSCC患者预后的预测因子之一。
2.1 CDK5在HNSCC组织中的表达情况见图1,表1。HNSCC组织中存在CDK5的表达,CDK5表达水平在有淋巴结转移的组织中高于无淋巴结转移的组织。在有淋巴结转移的患者中CDK5高表达
CDK5可以通过磷酸化FAK的丝氨酸732位点促进EMT进程[8]。在耐药性三阴乳腺癌中,CDK5能够提高Vimentin活性,进而诱导EMT过程[21]。本研究发现,HNSCC中CDK5的表达与EMT相关蛋白N-cadherin、Vimentin表达呈正相关,与E-cadherin表达呈负相关,表明CDK5可能通过某种机制促进HNSCC的EMT过程,进而提高肿瘤的侵袭、转移能力。目前已有研究发现选择性CDK抑制剂如Roscovitine(Seliciclib)能够有效抑制CDK5的活性[22]。
综上所述,在HNSCC中CDK5与EMT相关蛋白的表达具有高度相关性,CDK5可能是HNSCC侵袭、转移的重要分子标志,并可以作为预测患者生存的指标,而其影响EMT的具体机制是今后进一步研究的方向。CDK5有希望成为HNSCC基因治疗的
随访期内,12例(21.1%)患者出现硬膜下积液,硬膜下积液量平均(57.7±48.3) mL(12~167 mL)。其中,5例为少量硬膜下积液[(17±4.7)mL],4例为中等量硬膜下积液[(47.8±7.9)mL],3例为大量硬膜下积液[(128.3±40.1)mL]。
新靶点。
[1]Lee JM,Turini M,Botteman MF,et al.Economic burden of head and neck cancer[J].Eur J Health Econ,2004,5(1):70-80.doi: 10.1007/s10198-003-0204-3.
[2]Burusapat C,Jarungroongruangchai W,Charoenpitakchai M.Prognostic factors of cervical node status in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J].World J Surg Oncol,2015,13(1):51.doi:10.1186/ s12957-015-0460-6.
[3]Kim M,Lim J,Yang Y,et al.N-myc downstream-regulated gene 2(NDRG2)suppresses the epithelial–mesenchymal transition(EMT)in breast cancer cells via STAT3/Snail signaling[J].Cancer Lett,2014,354(1):33-42.doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2014.06.023.
[4]Smith A,Teknos TN,Pan Q.Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J].Oral Oncol,2013,49(4):287-292.doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2012.10.009.
[5]Ehrlich SM,Liebl J,Ardelt MA,et al.Targeting cyclin dependent kinase 5 in hepatocellular carcinoma-A novel therapeutic approach[J]. J Hepatol,2015,63(1):102-113.doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2015.01.031.
[6]Ren Y,Zhou X,Yang J,et al.AC1MMYR2 impairs high dose paclitaxel-induced tumor metastasis by targeting miR-21/CDK5 axis[J]. Cancer Lett,2015,362(2):174-182.doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2015.03.038.
[7]Yu HF,Zhang X,Xu ML,et al.Expression levels and clinical significance of FOXQ1 and E-cadherin in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Tianjin Med J,2015,43(2):170-174.[于海峰,张逊,徐美林,等.FOXQ1和E-cadherin在食管鳞状细胞癌中的表达及临床意义[J].天津医药,2015,43(2):170-174].doi:10.11958/j. issn.0253-9896.2015.02.015.
[8]Liang Q,Li L,Zhang J,et al.CDK5 is essential for TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and breast cancer progression[J].Sci Rep,2013,3:2932.doi:10.1038/srep02932.
[9]Pozo K,Castro-Rivera E,Tan C,et al.The role of Cdk5 in neuroendocrine thyroid cancer[J].Cancer Cell,2013,24(4):499-511.doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.08.027.
[10]Feldmann G,Mishra A,Hong SM,et al.Inhibiting the cyclin-dependent kinase cdk5 blocks pancreatic cancer formation and progression through the suppression of ras-ral signaling[J].Cancer Res,2010,70(11):4460-4469.doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1107.
[11]Hsu FN,Chen MC,Lin KC,et al.Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 modulates STAT3 and androgen receptor activation through phosphorylation of Ser727on STAT3 in prostate cancer cells[J].Am J Physiol EndocrinolMetab,2013,305(8):975-986.doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00615.2012.
[12]Fujii R,Imanishi Y,Shibata K,et al.Restoration of E-cadherin expression by selective Cox-2 inhibition and the clinical relevance of the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J].J Exp Clin Cancer Res,2014,33:40.doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-33-40.
[13]Yu J,Sun W,Hua F,et al.BCL6 induces EMT by promoting the ZEB1-mediated transcription repression of E-cadherin in breast cancer cells[J].Cancer Lett,2015,365(2):190-200.doi:10.1016/j. canlet.2015.05.029.
[14]Jadaan DY,Jadaan MM,McCabe JP.Cellular plasticity in prostate cancer bone metastasis[J].Prostate Cancer,2015,2015:651580.doi: 10.1155/2015/651580.
[15]Shan LP,Zhang M,Li B,et al.Clinicopathologic significance of EpCAM and E-cadherin expression in urothelial carcinoma of bladder[J]. Tianjin Med J,2013,41(6):527-530.[单立平,张墨,李波,等.EpCAM和E-cadherin在膀胱尿路上皮癌的表达及意义[J].天津医药,2013,41(6):527-530].doi:10.3969/j.issn.0253-9896.2013.06.005.
[16]Gu K,Li MM,Shen J,et al.Interleukin-17-induced EMT promotes lung cancer cell migration and invasion via NF-kappaB/ZEB1 signal pathway[J].Am J Cancer Res,2015,5(3):1169-1179.
[17]Tan YM,Zhang X,Xu ML,et al.The expression and clinical significance of RhoB and E-cadherin in non-small-cell lung cancer tissues[J].Tianjin Med J,2014,42(1):27-30.[谭祎媚,张逊,徐美林,等.RhoB和E-cadherin在非小细胞肺癌组织中的表达及临床意义[J].天津医药,2014,42(1):27-30].doi:10.3969/j.issn.0253-9896.2014.01.009.
[18]Li DL,Zhang ZQ,Chen SH,et al.Expression of T-cadherin in hepatocellular carcinoma and its relationship with relapse and metastasis of tumor[J].Med J Chin PLA,2015,40(4):315-318.[李东良,张志强,陈少华,等.T-cadherin在肝细胞癌中的表达及其与肿瘤复发转移的关系[J].解放军医学杂志,2015,40(4):315-318].doi: 10.11855/j.issn.0577-7402.2015.04.12.
[19]Yang JH,Dong ZH,Xiao FB,et al.Expression and significance of neural cadherin in perihilar cholangiocarcinoma[J].Tianjin Med J,2014,42(7):680-682.[杨景红,董祖海,肖福斌,等.神经型钙黏蛋白在肝门部胆管癌中的表达及意义[J].天津医药,2014,42(7): 680-682].doi:10.3969/j.issn.0253-9896.2014.07.016.
[20]Zhang Z,Dong Z,Lauxen IS,et al.Endothelial cell-secreted EGF induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition and endows head and neck cancer cells with stem-like phenotype[J].Cancer Res,2014,74(10):2869-2881.doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-2032.
[21]Deng X,Kohanfars M,Hsu HM,et al.Combined phosphoproteomics and bioinformatics strategy in deciphering drug resistant related pathways in triple negative breast cancer[J].Int J Proteomics,2014,2014:390781.doi:10.1155/2014/390781.
[22]Gallorini M,Cataldi A,di Giacomo V.Cyclin-dependent kinase modulators and cancer therapy[J].Bio Drugs,2012,26(6):377-391. doi:10.2165/11634060-000000000-00000.
(2015-08-05收稿 2015-08-26修回)
(本文编辑 李国琪)
CDK5 and epithelial-mesenchymal transition related proteins are abnormally expressed in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
ZHAO Minghui,HUANG Yuanyuan,SUN Shanshan,KONG Lingping,WANG Yu,GUO Wenyu,ZHOU Xuan,WANG Xudong,ZHANG Lun△
Department of Maxillofacial&E.N.T(ear,nose,and throat)Oncology,Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital;National Clinical Research Center of Cancer;Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Therapy,Tianjin 300060,China△
ObjectiveTo explore the expressions of Cyclin-dependent kinase 5(CDK5)and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition(EMT)related proteins including N-cadherin,Vimentin and E-cadherin in head and neck squamous cell carcino-
head and neck neoplasms;carcinoma,squamous cell;cyclin-dependent kinase 5;cadherins;vimentin;lymphatic metastasis
R739.6
A
10.11958/j.issn.0253-9896.2015.12.017
国家自然科学基金资助项目(81172573)
天津医科大学肿瘤医院颌面耳鼻咽喉肿瘤科,国家肿瘤临床医学研究中心,天津市肿瘤防治重点实验室(邮编300060)
赵明慧(1990),女,硕士在读,主要从事头颈部肿瘤的诊治研究
△通讯作者E-mail:Lun_zhang_jing@yahoo.com.cn
ma(HNSCC),and to determine the relationship between the expression of CDK5 and prognosis.MethodsThe expression levels of CDK5 and EMT related proteins were evaluated by immunohistochemistry in 55 patients who were diagnosed as HNSCC.They were also analyzed in different clinical pathological factors.The correlation of CDK5 and EMT related proteins as well as the relationship between the expression of CDK5 and prognosis were also analyzed.ResultsThe expression level of CDK5 was significantly higher in patients with lymph node metastasis than that in patients with non-lymph node metastasis(91.67%vs 30.23%,P<0.05).It’s also higher in T3-T4 stages than that in T1-T2 stages(85%vs 20%,P<0.05).The expression levels of N-cadherin and Vimentin were significantly higher in patients with lymph node metastasis than those in patients with non-lymph node metastasis(75.00%vs 6.98%;91.67%vs 27.91%,all P<0.05).However,the expression level of E-cadherin was significantly lower in patients with lymph node metastasis(8.33%vs 86.05%,P<0.05)compared to that in patients without.CDK5 was positively correlated with N-cadherin and Vimentin,but negatively correlated with E-cadherin(rs=0.512,0.443,-0.363,all P<0.01).The 3-year survival rates were significantly lower in patients with high expression of CDK5(37.5%)than that in patients with low expression of CDK5(87%,Log-rankχ2=12.678,P<0.01).Conclusion CDK5 and EMT related proteins were activated abnormally in HNSCC with lymph node metastasis.CDK5 may be a new biological marker for prognosis of HNSCC.
