Cx43、NMDA与大鼠肠易激综合征内脏敏化的关系研究
2015-06-28张静瑜黄裕新秦明高会军窦维佳王景杰
张静瑜,黄裕新,秦明,高会军,窦维佳,王景杰
·基础研究·
Cx43、NMDA与大鼠肠易激综合征内脏敏化的关系研究
张静瑜,黄裕新,秦明,高会军,窦维佳,王景杰
目的探讨大鼠间隙连接蛋白43(Cx43)和骶髓N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸(NMDA)受体与肠易激综合征(IBS)内脏敏化的关系。方法雄性SD大鼠50只,随机分为正常对照组、正常结肠扩张组、IBS组、IBS结肠扩张组及IBS结肠扩张+甲磺酸伊马替尼(STI-571)干预组,每组10只。IBS组、IBS结肠扩张组和IBS结肠扩张并干预组大鼠采用旋毛虫感染制作IBS模型。采用免疫荧光组织化学法观察各组大鼠结肠Cx43和骶髓NMDA受体的表达。结果正常组、正常结肠扩张组、IBS组的结肠Cx43和骶髓NMDA表达水平差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),IBS结肠扩张组结肠Cx43和骶髓NMDA表达水平与正常组、正常结肠扩张组、IBS组比较均显著增强(P<0.01),而STI-571干预后大鼠结肠Cx43和骶髓NMDA表达均有所下降(P<0.01)。结论Cx43和NMDA可能在IBS内脏敏化机制中起关键作用。
肠易激综合征;连接蛋白43;受体,N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸
近年来由于人们生活方式改变,肠易激综合征(irritable bowel syndrome,IBS)的发病率不断增加[1-2],但发病机制却并不十分清楚。近年研究发现,IBS与内脏神经敏化有密切关系[3-4]。间隙连接蛋白(connexin,Cx)在人体广泛分布,其中Cx43是组成细胞间缝隙连接的主要成分[5],其表达异常与多种疾病的发生有关[6-8]。N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸(NMDA)受体由NR1、NR2A-D及NR3A-B等7种亚单位组成,广泛分布于中枢神经系统,其中小鼠和人的NR2B同源基因已获克隆。近年来研究发现,NR2B受体亚型在学习、记忆、进食行为、疼痛的产生及中枢性痛觉敏化形成等方面与人类多种神经疾病相关[7,9-10]。本研究探讨了Cx43和NMDA的表达与IBS的关系。
1 材料与方法
1.1 主要实验材料及试剂 保虫昆明鼠(旋毛虫系云黑龙江株)购自河南省疾病预防控制中心,雄性SD大鼠购自第四军医大学实验动物中心。甲磺酸伊马替尼(STI-571,美国Abcam),兔抗NMDA血清(1:3000,Novus公司),兔抗Cx43血清(1:3000,CellSignaling公司),羊抗兔IgG(1:500,Sigma公司),ABC复合物(1:500,Sigma公司)。
1.2 实验分组 50只SD大鼠随机分为正常对照组、正常结肠扩张组、IBS组、IBS结肠扩张组及IBS结肠扩张+STI-571组,每组10只。结肠扩张条件选用本课题组既往实验的高峰值,即球囊注水1.0ml[11];STI-571采用腹腔注射(20mg/ml,0.5ml/kg)。
1.3 IBS动物模型制作 保虫昆明鼠种鼠3只,脊柱脱臼法处死,剔除皮毛、内脏及肌肉;将肌肉剪碎置于300ml含2.5%胃蛋白酶和0.5%盐酸的消化液中,37℃水浴消化12~20h;经筛过滤,用生理盐水反复沉淀洗涤3~5次,收集旋毛虫幼虫囊包并计数。取昆明鼠20只,体重25g左右,灌胃法给予0.1ml含250~300条幼虫的生理盐水悬液感染大鼠;将传代感染的昆明鼠以颈椎脱臼法处死,收集旋毛虫(方法同前),IBS组、IBS结肠扩张组及IBS结肠扩张+STI-571组大鼠采用灌胃法给予1ml含4000条幼虫囊包的生理盐水悬液,饲养8周后抽检测定感染情况,确立模型制作成功[12]。
1.4 组织冰冻切片制作 各组大鼠进行灌注内固定后立即剖腹,取乙状结肠处0.4cm×0.2cm大小组织以及长约1cm的完整骶髓组织,放入4%多聚甲醛中于4℃固定6h,取出标本移入30%蔗糖液,4℃放置24h,超低温切片机(美国Nuair公司)10μm切片待染。
1.5 双重荧光免疫组织化学法检测Cx43及NMDA表达 将标本置于0.3% H2O2-甲醇中浸泡30min封闭内源性过氧化物酶,0.1% Triton浸泡30min,PBS漂洗;加入免疫血清稀释的Cx43过夜(1:2000,约14h);将切片和铺片置于室温下复温1h,经PBS漂洗后入1:60稀释的四甲基异硫氰酸罗丹明(TMRITC)标记的抗兔IgG二抗及异硫氰酸荧光素(FITC)标记的抗小鼠IgG二抗,室温孵育3h;PBS漂洗后将铺片平置于载玻片上,与切片标本同时用60%缓冲甘油封片。NMDA制备方法同上。采用激光共聚焦显微镜采图分析,每张切片取4~6个视野,将数字化图像储存于LSCM系统计算机,实验结束后进行图像分析。
1.6 统计学处理 采用SPSS 16. 0软件进行统计分析。荧光半定量结果经Image J 1.43软件处理,所得到的荧光光度值差异采用Kruskal-WallisH检验及Nemenyi法检验进行比较。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
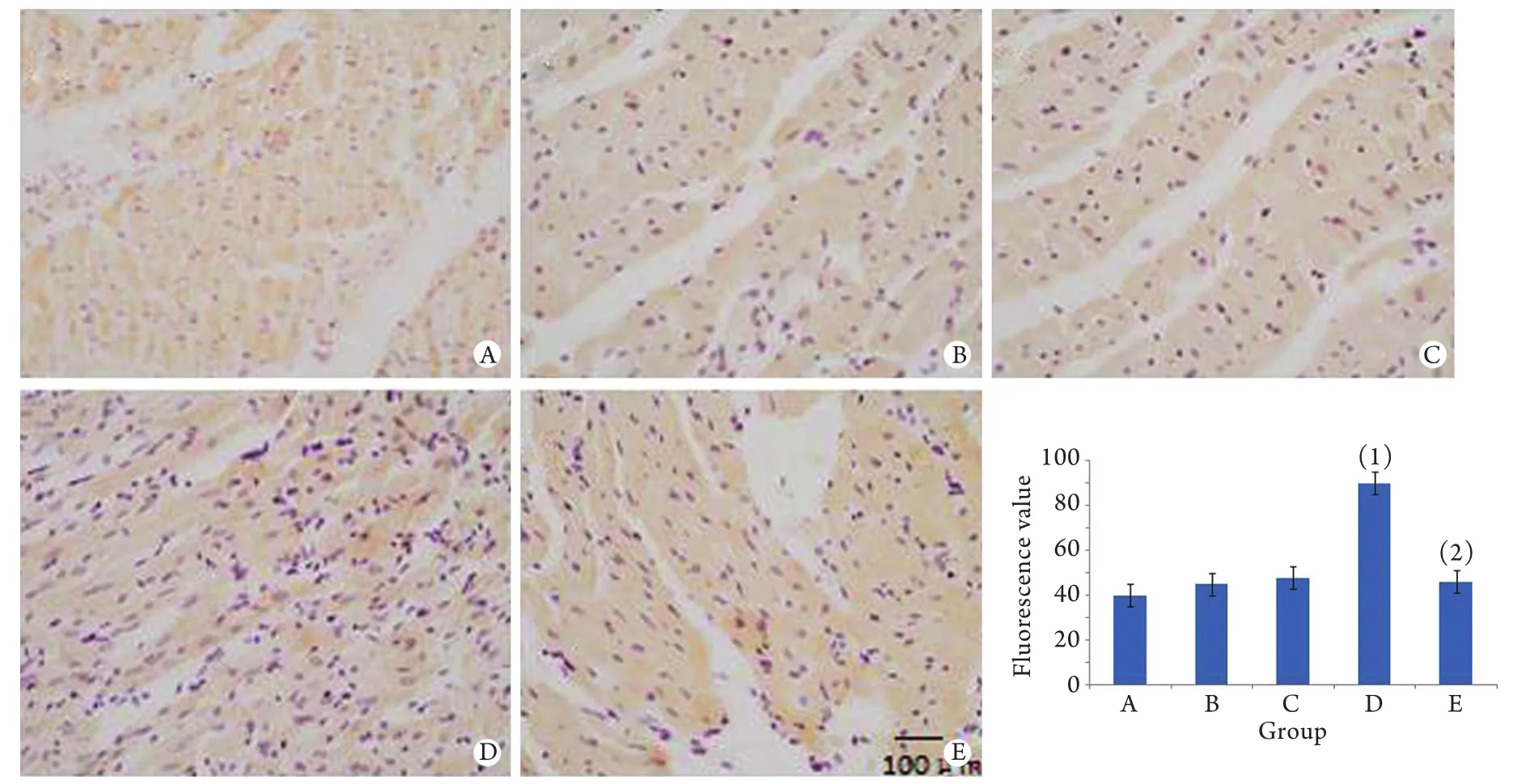
图1 各组大鼠结肠Cx43表达情况(免疫组化检测)Fig.1 Expression of Cx43 protein in colon of rats in each group (Immunohistochemistry)A. Normal group; B. Colon distension group; C. IBS group; D. IBS with colon distension group; E. STI-571 in IBS with colon distension group; (1)P<0.01 compared with normal group,colon distension group and IBS group; (2)P<0.01 compared with IBS with colon distension group
2 结 果
2.1 大鼠结肠Cx43表达情况 由图1可见,正常状态下大鼠结肠部位Cx43处于低水平表达,其荧光光度值为40±5。给予结肠插入球囊灌水扩张后,大鼠结肠部位Cx43表达水平有所增加,其荧光光度值为45±5,与正常对照组相比未见明显差异(P>0.05)。IBS组大鼠结肠部位Cx43表达水平(荧光光度值48±5)与正常对照组及正常扩张组相比均未见明显差异(P>0.05)。IBS组大鼠给予结肠扩张激后,其结肠部位Cx43表达水平显著增高,荧光光度值为90±5,与正常结肠扩张组比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.01),而给予STI-571腹腔注射干预的IBS大鼠结肠部位Cx43表达明显降低,其荧光光度值(46±5)与IBS结肠扩张组相比差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。
2.2 大鼠骶髓NMDA表达情况 正常状态下大鼠结肠部位骶髓NMDA处于低水平表达,其荧光光度值为59±5,给予结肠插入球囊灌水扩张后,大鼠结肠部位NMDA表达水平有所增加,其荧光光度值为64±5,与正常对照组相比未见明显差异(P>0.05)。IBS组大鼠结肠部位NMDA表达水平(荧光光度值68±5)与正常对照组及正常扩张组相比未见明显差异(P>0.05)。IBS组大鼠给予结肠扩张后,其结肠部位NMDA表达水平显著增高,荧光光度值为108±5,与正常扩张组比较有显著差异(P<0.01),而给予STI-571腹腔注射干预的IBS大鼠结肠部位NMDA表达明显降低,其荧光光度值(62±5)与IBS结肠扩张组相比差异有统计学意义(P<0.01,图2)。

图2 各组大鼠骶髓NMDA表达情况(激光共聚焦显微镜)Fig.2 Expression of sacral NMDA of rats in each group (Laser confocal microscopy)A. Normal group; B. Colon distension group; C. IBS group; D. IBS with colon distension group; E. STI-571 in IBS with colon distension group; (1)P<0.01 compared with normal group,colon distension group and IBS group; (2)P<0.01 compared with IBS with colon distension group
3 讨 论
IBS与肠道动力异常、内脏感觉异常、免疫异常、炎症反应、肠道菌群失调、遗传因素、食物因素、性别以及脑-肠相互作用、肠道神经内分泌网络调控失常等存在着密切关系[13]。研究提示,IBS患者以肠道动力异常和内脏感觉异常为主要表现,这些表现和变化均与神经作用存在密切联系[14]。
缝隙连接蛋白在人体广泛分布,Cx43是组成细胞间缝隙连接的主要成分。近年大量研究表明,胃肠运动受肠神经系统和Cajal间质细胞(interstitial cells of Cajal,ICC)共同调控,ICC连接平滑肌与神经细胞,三者之间广泛存在缝隙连接并形成网络样结构。通过缝隙连接,ICC为神经细胞和平滑肌细胞之间提供了重要的中介通道,从而更有效地传递电、神经信号以刺激平滑肌细胞,实现其起搏、舒缩功能[15]。本课题组前期实验发现IBS大鼠中ICC表达显著增高[16],本实验结果表明IBS扩张大鼠Cx43表达明显增高,推测IBS内脏敏化是通过ICC的过度敏化,而其间的缝隙连接蛋白发挥着重要作用。
近期研究发现,NMDA受体在内脏伤害性信息转导中具有重要作用,结肠炎恢复后脊髓背角NMDAR1和NMDAR2A/B的同步上调是导致内脏敏感性持续增高的原因[17]。正常NMDA受体被镁离子阻滞,外周神经损伤后,去极化导致镁离子从通道上移开,引起NMDA活化,进而促使大量钙离子内流,使突触后神经元兴奋性增高;细胞钙离子浓度增加引起转录因子c-fos、c-jun活化,最终活化许多下游基因;转录的改变最终引起细胞内和细胞表面受体蛋白表达的改变;蛋白激酶(包括PKC)在维持中枢敏化中发挥重要作用[18-21]。本研究采用旋毛虫感染制备大鼠IBS模型,给予结肠扩张刺激后可表现为IBS的内脏高敏化[12],本课题组曾采用STI-571阻断ICC,其后IBS的内脏敏化明显下降[16],而本实验的各项结果提示,IBS结肠扩张组的Cx43和NMDA表达与比正常对照组、正常结肠扩张组、IBS组和IBS结肠扩张+STI-571组比较均显著增强,表明Cx43和NMDA与IBS的内脏敏化可能有着密切联系。
[1]Yang J,Cai ST,Cui LH,et al. An epidemiological study and riskfactor analysis of irritable bowel syndrome in a Chinese naval force[J]. Med J Chin PLA,2013,38 (6): 453-456. [杨竞,蔡顺天,崔丽红,等. 海军某部官兵肠易激综合征流行病学调查及影响因素分析[J]. 解放军医学杂志,2013,38 (6): 453-456.]
[2]Shi Y,Liu LM,Zhang ZX. Current situation of irritable bowel syndrome in nursing and clinical medicine undergraduates[J]. J Zhengzhou Univ (Med Sci),2010,45 (5): 829-831. [史岩,刘腊梅,张振香. 护理及临床医学专业大学生肠易激综合征现状调查[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版),2010,45 (5): 829-831.]
[3]Qin HY,Xiao HT,Leung FP,et al. JCM-16021,a Chinese herbal formula,attenuated visceral hyperalgesia in TNBS-induced postinflammatory irritable bowel syndrome through reducing colonic EC cell hyperplasia and serotonin availability in rats[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med,2012,2012: 239638.
[4]Yang Y,Cui X,Chen Y,et al. Exendin-4,an analogue of glucagonlike peptide-1,attenuates hyperalgesia through serotonergic pathways in rats with neonatal colonic sensitivity[J]. J Physiol Pharmacol,2014,65(3): 349-357.
[5]Hu YM,Cheng HX,Cui YM,et al. Effects of ketamine on glutamate,NR2A and NR2B in hippocampus of rats with forced swimming[J]. Med J Chin PLA,2012,37 (5): 452-454. [胡益民,程慧娴,崔耀梅,等. 氯胺酮对强迫游泳大鼠海马谷氨酸、NR2A及NR2B的影响[J]. 解放军医学杂志,2012,37 (5): 452-454.]
[6]Tsuchida S,Arai Y,Kishida T,et al. Silencing the expression of connexin 43 decreases inflammation and joint destruction in experimental arthritis[J]. J Orthop Res,2013,31(4): 525-530.
[7]Ishido M,Kasuga N. Characteristics of the localization of connexin 43 in satellite cells during skeletal muscle regenerationin vivo[J]. Acta Histochem Cytochem,2015,48(2): 53-60.
[8]Zhang Y,Liu XH. Cx43 and Bcl-2 expressions in myocardial tissue during the developmental periods of human fetus[J]. Med J Chin PLA,2010,35 (2): 201-203. [张泳,刘学红. 人胚胎心肌组织发育过程中Cx43和Bcl-2蛋白表达的研究[J]. 解放军医学杂志,2010,35 (2): 201-203.]
[9]Mattison HA,Hayashi T,Barria A. Palmitoylation at two cysteine clusters on the C-terminus of GluN2A and GluN2B differentially control synaptic targeting of NMDA receptors[J]. PLoS One,2012,7(11): e49089.
[10] Li H,Fan YZ,Sun SA,et al. Cajal expression of interstitial cells and CX43 in the obstruction of renal pelvis and ureter obstruction[J]. J Zhengzhou Univ (Med Sci),2014,49 (1): 127-129. [李浩,范应中,孙生安,等. 肾盂输尿管连接部梗阻段Cajal间质细胞和CX43表达的检测[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版),2014,49 (1): 127-129.]
[11] Huang YX,Wang JJ,Jiang HL,et al. Rat colonic distention caused by changes of visceral activities experimental study[J]. Gastroenterol Hepatol J,2006,15(2): 119 - 122.[黄裕新,王景杰,姜惠玲,等. 大鼠结肠扩张刺激引起内脏活动变化的实验研究[J]. 胃肠病学和肝病学杂志,2006,15(2): 119-122.]
[12] Yang B,Zhou X,Lan C. Changes of cytokine levels in a mouse model of post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome[J]. BMC Gastroenterol,2015,15: 43.
[13] Matricon J,Meleine M,Gelot A,et al. Review article: associations between immune activation,intestinal permeability and the irritable bowel syndrome[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther,2012,36(11-12): 1009-1031.
[14] Qin HY,Xiao HT,Wu JC,et al. Key factors in developing the trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced post-inflammatory irritable bowel syndrome model in rats[J]. World J Gastroenterol,2012,18(20): 2481-2492.
[15] Yu W,Zeidel ML,Hill WG. Cellular expression profile for interstitial cells of cajal in bladder -a cell often misidentified as myocyte or myofibroblast[J]. PLoS One,2012,7(11): e48897.
[16] Zhang JY,Huang YX,Qin M,et al. SCF/c-kit excessive activation of visceral sensitization in the irritable bowel syndrome study[J]. J Shanxi Med Univ,2012,43(3): 177-181. [张静瑜,黄裕新,秦明,等. SCF/c-kit过度激活在肠易激综合征内脏敏化中的作用研究[J]. 山西医科大学学报,2012,43(3): 177-181.]
[17] Hu L,Jing XH,Cui CL,et al. NMDA receptors in the midbrain play a critical role in dopamine-mediated hippocampal synaptic potentiation caused by morphine[J]. Addict Biol,2014,19(3): 380-391.
[18] Chi YN,Zhang X,Cai J,et al. Formaldehyde increases intracellular calcium concentration in primary cultured hippocampal neurons partly through NMDA receptors and T-type calcium channels[J]. Neurosci Bull,2012,28(6): 715-722.
[19] Vullhorst D,Mitchell RM,Keating C,et al. A negative feedback loop controls NMDA receptor function incortical interneuronsvianeuregulin 2/ErbB4 signalling[J]. Nat Commun,2015,6: 7222.
[20] Tomita J,Ueno T,Mitsuyoshi M,et al. The NMDA receptor promotes sleep in the fruit fly,drosophila melanogaster[J]. PLoS One,2015,10(5): e0128101.
[21] Yang Y,Li W,Zhang H,et al. Association study of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit 2B (GRIN2B) polymorphisms and schizophrenia symptoms in the Han Chinese population[J]. PLoS One,2015,10(5): e0125925.
The relation of Cx43 and NMDA to visceral sensitization in rats with irritable bowel syndrome
ZHANG Jing-yu,HUANG Yu-xin,QIN Ming,GAO Hui-jun,DOU Wei-jia,WANG Jing-jie*
Department of Gastroenterology,Tangdu Hospital,Fourth Military Medical University,Xi’an 710038,China
*< class="emphasis_italic">Corresponding author,E-mail: jingyu1104@163.com
,E-mail: jingyu1104@163.com
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81070306)
ObjectiveTo study the relationship between connexin 43 (Cx43) and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors and visceral sensitization in the rats with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).MethodsThirty rats were gavaged withTriehinella spiralisto reproduce the IBS model. These rats were randomly divided into IBS group,IBS+colon distension group,and IBS+STI-571+colon distension group,and other groups of normal rats were randomized into normal group and normal+colon distension group,with 10 rats in each group. Immunofluorescent double staining were used to observe the expressions of intestine Cx43 and sacral NMDA receptors of rats in all the groups.ResultsThe Cx43 and sacral NMDA expressions in the normal group,normal+colon distension group and IBS group showed no significant changes (P>0.05),however,Cx43 and sacral NMDA expressions were significantly higher in IBS rats with colon distension as compared with those in normal group,normal+colon distension group,and IBS group (P<0.05),while they were significantly lower in the IBS+STI-571+colon distension group after STI-571 intervention (P<0.05).ConclusionCx43 and sacral NMDA may be the most important factor of visceral sensitization in IBS rats.
irritable bowel syndrome; connexin 43; receptors,N-methyl-D-aspartate
R574.4
A
0577-7402(2015)12-0946-04
10.11855/j.issn.0577-7402.2015.12.02
2015-06-28;
2015-09-05)
(责任编辑:熊晓然)
国家自然科学基金(81070306)
张静瑜,硕士研究生。主要从事胃肠道动力及机制方面的研究
710038 西安 第四军医大学唐都医院消化内科(张静瑜、黄裕新、秦明、高会军、窦维佳、王景杰)
王景杰,E-mail:jingyu1104@163.com
