一类非线性脉冲免疫接种SIR传染病模型的周期解与分支*
2015-06-13赵文才刘雨林
赵文才,刘雨林
(山东科技大学数学与系统科学学院,山东 青岛 266590)
一类非线性脉冲免疫接种SIR传染病模型的周期解与分支*
赵文才,刘雨林
(山东科技大学数学与系统科学学院,山东 青岛 266590)
由于受到医疗资源的限制,疫苗的免疫接种率一般不是常数。采用非线性脉冲免疫接种函数,建立了一类具有终身免疫的脉冲预防接种SIR模型,利用频闪映射及差分方程的不动点,讨论了模型无病周期解的存在性;运用Floquet乘子理论和脉冲微分方程比较定理,证明了模型无病周期解的全局渐近稳定性;选取脉冲免疫接种周期为分支参数,利用分支定理,给出了系统存在正周期解的充分条件。
非线性脉冲接种;传染病模型;周期解;全局渐近稳定性;分支
传染病是人类的大敌,世界卫生组织2013年发布《世界卫生统计报告》(World health statistics 2013),现在每年新增艾滋病毒感染者约250万,这与二十年前的每年300万相比有所下降,但新增感染者仍比死于艾滋病的人数多8万,因此艾滋病人的绝对人数仍在增加。同时,艾滋病对高感染率国家成年人的死亡率产生了重要影响,比如在南非,该国的男性和女性平均预期寿命在1990年均为六十三岁,但到2011年下降为五十八岁,另一个非洲国家津巴布韦的人均寿命下降幅度更大,为六岁。近年来,由于人感染H7N9禽流感等新的传染病不断出现,全球范围内的传染病防控形势依然严峻。
为了对传染病进行预防和控制,人们常采用免疫接种策略,免疫接种有两种方式:连续接种和脉冲接种。麻疹、病毒性肝炎、脊髓灰质炎等人类长期面对的传染病,常采用连续接种策略。对于突发传染病,如重症急性呼吸综合征(SARS)、人感染高致病性禽流感、流行性感冒等,则适合采用脉冲免疫接种策略。脉冲免疫接种模型已有大量文献研究[1-7],文献[8]研究了一类具有饱和传染率的脉冲免疫接种SIRS模型
其中,p为免疫接种率,接种成功的比例为常数,即脉冲函数为线性函数
S(t+)=(1-p)S(t)
但是,免疫接种率一般不是常数。特别是对某些新发传染病,疫苗的研制和生产要受技术、人力、物力等条件的制约,疫苗接种要受到医院床位、医护人员等医疗资源的限制。医疗资源的限制会导致接种成功的比例具有饱和效应。因此,我们假设接种率为饱和函数
(2)
这里,p表示最大脉冲免疫接种率,θ为半饱和常数,即接种率为最大接种率的一半时所对应的易感者数量。从而脉冲接种函数为非线性函数
S(t+)=(1-p(t))S(t)
许多疾病治愈后会获得免疫力,随着时间的推移,有些疾病的免疫力会逐渐丧失,使得免疫人群重新成为易感者,也就是模型(1)中ω≠0的情况;有些疾病治愈后会获得长久免疫力,如麻疹、天花、白喉、流行性腮腺炎等病后终身免疫,也就是模型(1)中ω=0的情况。
综上分析,我们建立如下具有非线性脉冲免疫接种和终身免疫的SIR传染病模型
这里,S(t)、I(t)、R(t)分别表示t时刻易感者、染病者、移出者的数量。aA及(1-a)A分别表示单位时间内外来人口输入易感者和移出者的数量(0 对于非线性脉冲生态模型研究,目前文献较少。文献[9]研究了一类非线性脉冲状态依赖捕食被捕食模型,利用LambertW函数,研究了模型的阶1周期解。本文运用Floquet乘子理论和脉冲微分方程比较定理,讨论了模型(3)无病周期解的存在性和稳定性。利用分支定理,给出了系统存在正周期解的充分条件。 在系统(3)中,人口总数N(t)=S(t)+I(t)+R(t)满足 在系统(3)中,令I(t)=0,则 (4) 引理1 系统(4)存在唯一全局渐近稳定的正周期解(S*(t),R*(t))。 证明 由系统(4)的前两个方程,得 (5) 由(4)式的第三、四个方程, 于是 (6) (7) 记S(kT+)=Sk,构造频闪映射 Sk+1= f(Sk) (8) 其中 q1=e-μT-(1-p)e-2μT>0, 由(8)式可知 记R(kT+)=Rk,由(7)式可知 (9) 该映射有唯一的不动点 kT kT 由引理1,系统(3)存在无病周期解(S*(t),0,R*(t)),下面讨论该周期解的稳定性。 设(S(t),I(t),R(t))是系统(3)的任一正解,做变换x(t)=S(t)-S*(t),y(t)=I(t),z(t)=R(t)-R*(t),当t≠kT时,系统(3)关于无病周期解(S*(t),0,R*(t))的线性化系统为 (10) 设Φ(t)为该系统的基解矩阵,则 且Φ(0)=E,E为单位矩阵。于是 当t=kT时,脉冲条件变为 (11) 引入矩阵 则系统(10)的单值矩阵 于是, (λ+γ+μ)T 综上讨论,得 定理1 当R1<1时,系统(3)的无病周期解(S*(t),0,R*(t))局部渐近稳定。其中 下面证明无病周期解(S*(t),0,R*(t))的全局吸引性。 定理2 当R1<1时,系统(3)的无病周期解(S*(t),0,R*(t))全局吸引。 证明 由系统(3)得, 根据引理1,系统 存在正周期解 设(S(t),I(t),R(t))是系统(3)的任一解,由脉冲微分方程比较定理,对于任意正数ε,存在正整数N,当k>N时,有 S(t)≤x(t) (12) 根据模型(3)的第二个方程,当k>N时,有 (13) 由于R1<1,存在充分小的ε>0,使 综合定理1、2得, 定理3 当R1<1时,系统(3)的无病周期解(S*(t),0,R*(t))全局渐近稳定。 由于系统(3)的第一、二个方程不含移出者R(t),因而只需研究下面的子系统 (14) 下面利用分支定理[10]讨论系统(14)正周期解的存在性与分支。 考察阈值R1,不难发现,R1与脉冲免疫接种周期T成正比,若T过大,将导致R1≥1,无病周期解(S*(t),0,R*(t))不稳定。假设T=T0时R1=1,选取T为分支参数,并进行变量替换x1(t)=S(t),x2(t)=I(t),将系统(14)改写为 (15) 显然, 根据分支定理,若BC≠0,则系统(15)可由边界周期解分支出非平凡周期解。并且当BC<0时,分支是超临界的,当BC>0时,分支是次临界的。令 得到如下定理。 定理4 若条件(H)成立,则系统(15)在T0点存在超临界分支,即可由边界周期解(S*(t),0)分支出非平凡正周期解。这里,T0满足R1(T0)=1。 模型(3)采用饱和接种率 θ反映了接种率受医疗资源限制的程度,θ越大,对易感者的免疫接种率越低。阈值R1与模型(3)中所有参数有关,下面考察R1与医疗资源的限制程度θ及疫苗接种周期T之间的关系(如图1) 图1 R1与参数θ、T之间的关系Fig.1 The relationship of the R1 between the parameter θ and T 显然,若医疗资源的限制程度θ为定值,阈值R1与疫苗接种周期T成正比。同样,若疫苗接种周期T固定,R1随θ的增大而增大。因此,充实医疗资源、缩短疫苗接种周期,使阈值R1<1,则疾病灭绝。否则,疾病持续。 [1]D’ONOFRIOA.StabilitypropertiesofpulsevaccinationstrategyinSEIRepidemicmodel[J].MathematicalBiosciences, 2002, 179(1): 57-72. [2]ZHAOZ,CHENLS,SONGXY.ImpulsivevaccinationofSEIRepidemicmodelwithtimedelayandnonlinearincidencerate[J].MathematicsandComputersinSimulation, 2008, 79(3): 500-510. [3] 赵文才,孟新柱.具有垂直传染的SIR脉冲预防接种模型[J]. 应用数学,2009, 22(3): 676-682. [4]MENGXZ,CHENLS.GlobaldynamicalbehaviorsforanSIRepidemicmodelwithtimedelayandpulsevaccination[J].TaiwaneseJournalofMathematics, 2008, 12(5): 1107-1122. [5]MENGXZ,CHENLS,WUB.AdelaySIRepidemicmodelwithpulsevaccinationandincubationtimes[J].NonlinearAnalysis:RealWorldApplications, 2010, 11(1): 88-98. [6]ZHAOWC,ZHANGTQ,CHANGZB,etal.DynamicalanalysisofSIRepidemicmodelswithdistributeddelay[J].JournalofAppliedMathematics, 2013, 2013:ArticleID154387.doi:10.1155/2013/154387. [7]GAOSJ,LIUYJ,NIETOJJ,etal.Seasonalityandmixedvaccinationstrategyinanepidemicmodelwithverticaltransmission[J].MathematicsandComputersinSimulation, 2011, 81(9): 1855-1868. [8] 庞国萍,陈兰荪. 具饱和传染率的脉冲免疫接种SIRS模型[J]. 系统科学与数学, 2007, 27(4):563-572. [9] 王刚,唐三一. 非线性脉冲状态依赖捕食被捕食模型的定性分析[J]. 应用数学和力学,2013,34(5): 496-505. [10]LAKMECHEA,ARINOO.Bifurcationofnontrivialperiodicsolutionsofimpulsivedifferentialequationsarisingchemotherapeutictreatment[J].DynamicsofContinuousDiscreteandImpulsiveSystems, 2000, 7(2): 265-287. Periodic Solution and Bifurcation of an SIR Epidemic Model with Nonlinear Pulse Vaccination ZHAOWencai,LIUYulin (Shandong University of Science and Technology, College of Mathematics and Systems Science, Qingdao 266590, China) Due to limited medical resources, vaccine immunization rates are not often constant. To adapt nonlinear pulse vaccination function, an SIR epidemic model with lifelong immunity and pulse vaccination is stablished. By using stroboscopic map and fixed point of difference equations, the existence of disease free periodic solution in the model is discussed. The global asymptotically stability of disease free periodic solution is proved by applying Floquet multiplier theory and differential pulse comparison theorem. By choosing the pulse vaccination period as a bifurcation parameter, a sufficient condition under which the system has a positive periodic solution is obtained by using the bifurcation theorem. nonlinear pulse vaccination; epidemic model; periodic solution; global asymptotically stability; bifurcation 2014-05-13 国家自然科学基金资助项目(11371230);山东省自然科学基金资助项目(ZR2012AM012);山东省高等学校科技计划资助项目(J13LI05) 赵文才(1966年生),男;研究方向:生物数学;E-mail:wencaizhao@126.com 10.1347/j.cnki.acta.snus.2015.01.004 O A 0529-6579(2015)01-0013-061 无病周期解的存在性与稳定性
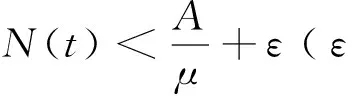
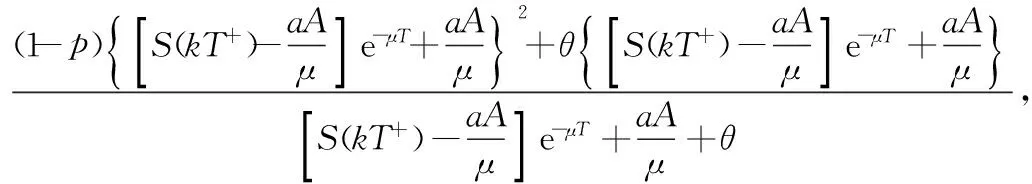
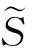
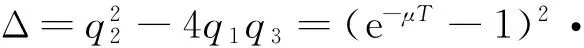



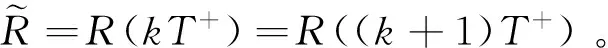
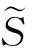
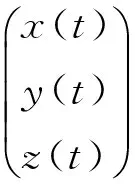
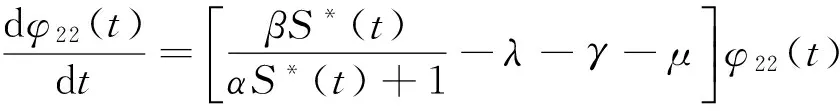
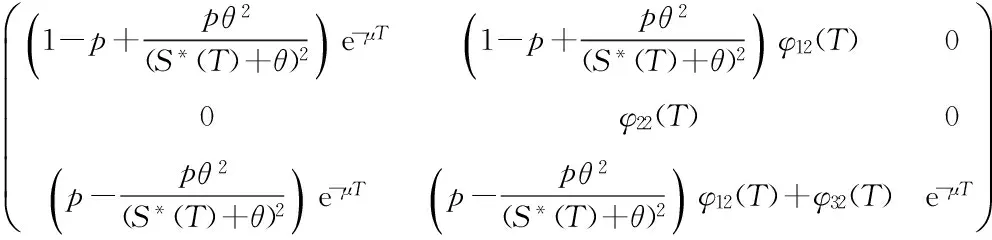
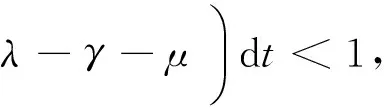

2 正周期解的存在性与分支

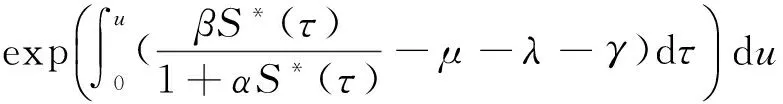
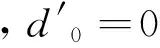
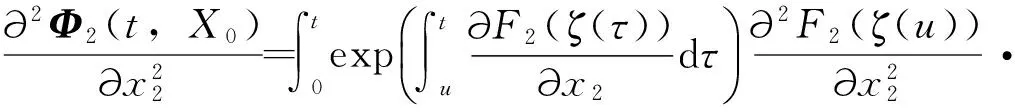
3 讨 论

