Q235钢单层板对平头刚性弹抗穿甲特性研究
2015-05-16邓云飞张伟孟凡柱曹宗盛郝鹏
邓云飞,张伟,孟凡柱,曹宗盛,郝鹏
(1.中国民航大学航空工程学院,天津 300300;2.哈尔滨工业大学空间碎片高速撞击研究中心,哈尔滨 150080)
Q235钢单层板对平头刚性弹抗穿甲特性研究
邓云飞1,张伟2,孟凡柱1,曹宗盛2,郝鹏1
(1.中国民航大学航空工程学院,天津 300300;2.哈尔滨工业大学空间碎片高速撞击研究中心,哈尔滨 150080)
采用撞击实验和理论模型对单层金属板的抗侵彻性能进行了研究,分析了靶体厚度对抗侵彻性能的影响。通过对比撞击实验和理论模型计算结果,验证了理论模型和参数的有效性。结果表明,采用合适的理论模型能够有效地预测靶板在弹体撞击下的弹道极限。此外,分析了靶体在弹体撞击下的塑性变形总耗能,包括靶板局部变形和整体变形的耗能,同时考虑了靶体材料的应变率效应。在平头弹撞击厚靶的工况中,引入了一个修正函数对靶体厚度进行修正。
弹体;靶体;撞击;侵彻;弹道极限
弹靶撞击相互作用过程为典型的结构动态响应问题,严重依赖弹体、靶体的材料响应。延性金属靶板在刚性弹体正撞击下的变形包含整体结构响应及局部失效。随靶板厚度增加靶板的整体变形减小,直至可忽略,主要破坏模式由全局响应转变为局部响应,耗能机理也会发生改变。靶板不同的破坏模式伴随不同塑性变形及耗能机制,因此应按耗能机制对弹体撞击的金属板穿透模式进行研究[1]。
Woodward等[2-4]通过建立金属靶板穿透模型,分析靶板破坏模式间联系及靶板发生不同破坏模式对应的耗能方式,进行定量描述;总结出刚性尖头弹击穿金属靶板的3种基本穿孔模式,即延性扩孔型、扩孔冲塞型及扩孔冲碟型;基于梁的弯曲理论,考虑贯穿过程中剪力、弯曲、膜力拉伸及弯曲、膜力拉伸耦合,但失效准则与靶板材料性能未联系。Forrestal等[5-6]假定侵彻贯穿过程为单一延性扩孔过程,用空腔膨胀理论研究刚性尖头弹侵彻、贯穿铝合金靶板问题,但未考虑靶板背面自由边界对穿孔后期影响。Wen等[7-9]通过大量的实验、理论研究软钢及铝合金圆板在固支边界条件下受低速刚性平头弹正撞击的响应及穿透,提出金属靶板在弹体正撞击下的半经验公式及理论公式。Jones等[10-11]认为高速撞击下贯穿的理论分析往往忽略整体结构变形,而结构变形会引起膜力,但膜力在低速冲击时为重要能量吸收方式;并利用能量平衡考虑横向剪切、径向及环向弯曲、膜力,给出圆板在钝头弹撞击下的响应。Chen等[12]提出剪切、弯曲耦合的理论分析模型,给出弹道极限及剩余速度的显式解答。潘建华等[13]研究简单剪切、绝热剪切破坏的转变条件。
本文利用带总体变形的局部简单剪切破坏Wen-Jones[14]模型研究单层靶的抗撞击特性,通过对比撞击实验及理论模型计算结果,验证理论模型的可靠性及精度。此外,基于实验数据,据靶板失效机理对平头弹撞击下延性金属板的穿透模式进行研究。
1 撞击实验
实验在哈尔滨工业大学高速撞击研究中心一级气炮上进行。测试设备主要包括气室、口径12.7 mm长2 m发射管、靶舱、激光测速系统、高速摄像机系统等[1]。弹体为平头杆弹,由经特殊热处理的38CrSi合金钢加工而成,热处理硬度约53 HRC,直径12.62 mm,名义质量34.5 g,弹体形状及尺寸见图1。靶体为单层Q235钢板,正方形靶板尺寸250 mm×250 mm,靶板四周加工螺栓孔,通过8个M8螺栓与靶架固定,靶板自由跨度210 mm×210 mm。厚度分别为1 mm、2 mm、6 mm,靶板对应记为T2,T4,T12。材料性能参数见文献[16]。

图1 弹体形状及尺寸(mm)Fig.1 Geometry of the projectiles
图2为平头弹撞击单层薄板的典型过程图像,追踪弹体撞击靶体全过程。金属弹体在侵彻过程中保持刚性,而靶体在撞击过程中常发生较大整体结构变形及局部化变形,如延性扩孔、冲塞、盘式凹陷及冲碟等,且产生圆形帽状冲塞。
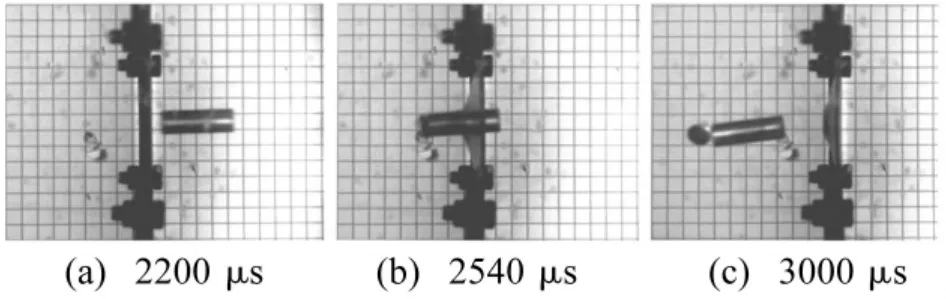
图2 平头弹体对薄靶的典型撞击工况: T4,vi=145.61 m/s,vr=87.54 m/sFig.2 Selection of high-speed camera images showing perforation process of the plates
表1为通过实验获得的初始-剩余速度数据,其中Vi,Vr分别表示弹体初始撞击速度及贯穿靶体后剩余速度。
用R-I公式[17]处理弹体的初始速度-剩余速度关系,所得靶体弹道极限表达式为
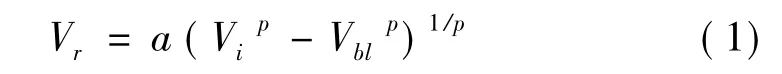
式中:Vi为弹体初始撞击速度;Vr为弹体贯穿靶板后剩余速度;Vbl为弹道极限速度;a,p为待定常数,可通过实验所得弹体初始-剩余速度数据进行最小二乘拟合获得,a=mp/(mp+mpl),mp、mpl分别为子弹及冲塞质量。

表1 Q235钢靶侵彻实验结果Tab.1 Penetration test results of Q235 steel targes
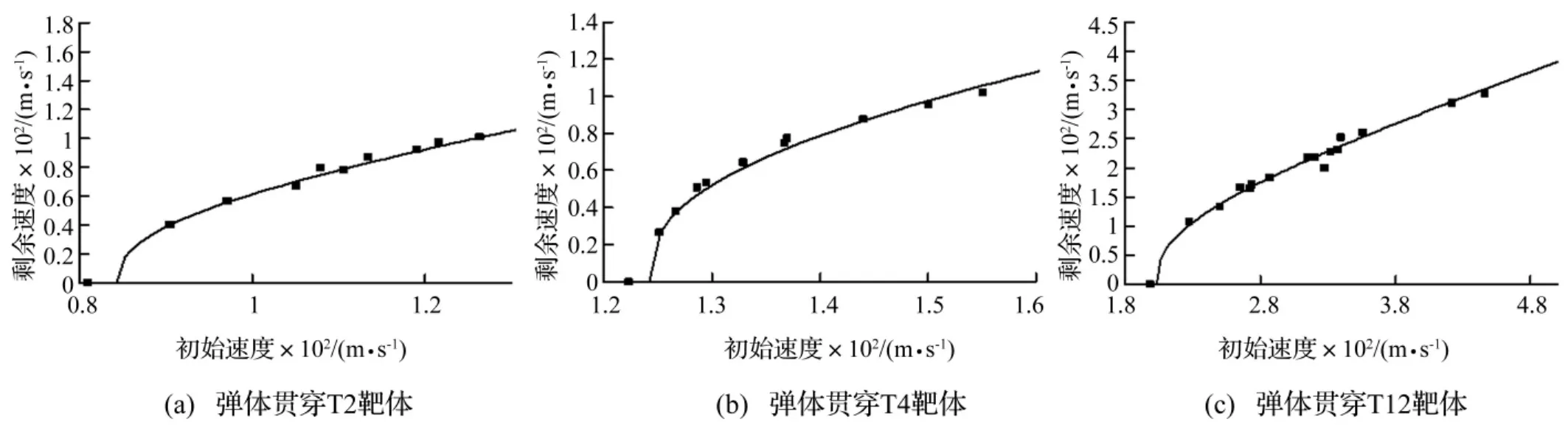
图3 弹体贯穿靶体初始-剩余速度Fig.3 Residual vs.initial velocities for targets
表2为据式(1)拟合所得模型参数,其中a<1说明弹体撞击靶体会产生冲塞。此外,弹道极限Vbl及参数a随靶体厚度增加而减小,而p则无变化规律。

表2 Q235钢靶弹道极限及模型参数Tab.2 Ballistic limits and model constants of Q235 targets
图3为弹体侵彻靶板初始-剩余速度实验数据及利用式(1)拟合的初始-剩余速度曲线。
2 理论模型
由实验结果知,随板厚变化在刚性平头弹正撞击下延性金属板破坏模式可分两种,即带总体变形的拉伸破坏及局部化剪切冲塞破坏[18]。靶板越厚靶体变形越局部化,整体变形可忽略不计[13]。
Wen等[19]据虚功原理,基于延性金属板准静态理论建立的平头弹低速冲击下金属板冲塞破坏模型适用于靶体无绝热剪切破坏情况。金属靶板在刚性平头弹撞击下发生冲塞破坏,见图4。
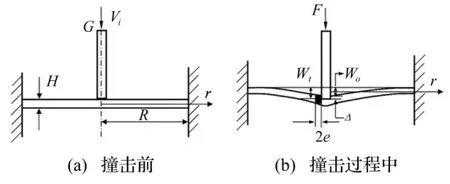
图4 平头弹撞击金属靶板示意图Fig.4 Schematic of metal targets impacted by blunt-nosed projectiles
设靶体材料为理想塑性材料,且据假设的横向变形速度场获得靶体变形位移场为
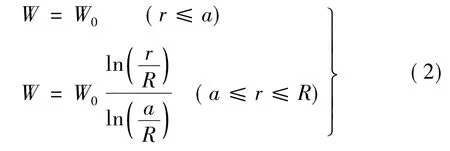
式中:W0为弹靶接触区域横向位移;W为半径r处横向位移;R为靶体固支半径;a为弹体半径;H为圆形金属靶板厚度。



给定等效塑性应变为0,据不同应变率下屈服应力利用式(14)进行拟合,得p=1400,q=1.5。不同应变率下屈服强度实验值与理论值对比见图5。

图5 不同应变率下屈服强度实验值与理论值对比Fig.5 Comparisons of yield strengths between theoretical predictions and tests for various strain rates
3 结果与讨论
利用式(18)对T2、T4、T12实验工况进行计算,对比实验、理论计算的弹道极限发现,在薄板情况下两者吻合较好(表2);但在厚板情况T12时,弹道极限理论值257.4 m/s较实验值203 m/s大。原因为靶体有效厚度小于实际厚度。图6为弹孔全局及剖面放大图,其中图6(b)弹孔剖面放大倍数为50、100。在侵彻方向,弹孔前部分较光滑,后部分较粗糙(裂纹区域),原因为延性金属板在平头弹撞击下靶体内在弹体前面产生裂纹,且裂纹扩展速度高于弹体速度,造成靶体有效厚度下降。

图6 平头弹撞击单层中厚板回收样件(vi=314.69 m/s,vr=218.18 m/s)Fig.6 Deformed plates and plugs after impacted by blunt-nosed projectiles
因此,引入修正函数ω(H)对靶板厚度进行修正。有效厚度He表述为

式中:ω(H)为与靶体厚度相关的函数,写成幂级数形式为
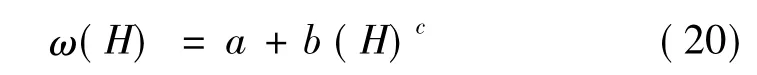
式中:a,b,c为待定常数。
利用不同厚度靶体的实验结果对ω(H)进行拟合,得

计算T12弹道极限时利用式(20)估算弹体侵入靶体有效厚度,再将估算值代入式(18),得T12弹道极限速度为198.7 m/s,与实验值203 m/s较接近,见表3。由分析知,该模型能较好预测延性金属板对平头弹的弹道极限。
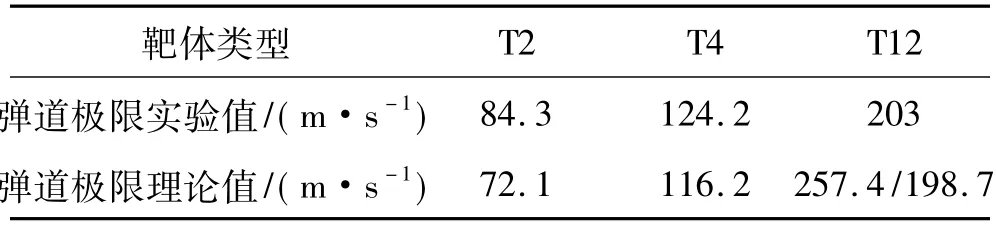
表3 单层板对平头弹弹道极限理论值与实验值对比Tab.2 Comparisons of the experimental and theoretical results for blunt-nosed projectiles
4 结论
(1)本文通过撞击实验与理论模型研究刚性平头弹体正撞击下金属靶板失效机理及耗能机制,采用合适理论模型计算所得靶体弹道极限值与实验值一致。
(2)分析靶体在弹体撞击下总耗能,包括靶板局部变形及整体变形的总耗能,并考虑靶体材料的应变率效应。
(3)厚金属板在平头弹撞击下靶体在运动弹体前面会产生微裂纹,造成弹体的有效侵入厚度小于靶体厚度。需引入修正函数对靶体厚度进行修正。
[1]孙炜海.锥形弹丸正撞击下金属靶板破坏模式的理论和数值模拟研究[D].合肥:中国科学技术大学,2009.
[2]Woodward R L.The interrelation of failure modes observed in the penetration of metallic targets[J].International Journal of Impact Engineering,1984,2(2):121-129.
[3]Woodward R L.A structural model for thin plate perforation by normal impact of blunt projectiles[J].International Journal of Impact Engineering,1987,6:4129-4140.
[4]Woodward R L,Cimpoeru S J.A study of the perforation of aluminium laminate targers[J].International Journal of Impact Engineering,1998,21(3):117-131.
[5]Forrestal M J,Rosenberg Z,Luk V K.Perforation of aluminum plates with conical-nosed rods[J].Appl.Mech. Trans.ASME,1987,54:230-232.
[6]Rosenberg Z,Forrestal M J.Perforation of aluminum plates with conical-nosed rods-additional data and discussion[J]. Appl.Mech.Trans.ASME,1988,55:236-238.
[7]Wen H M,Jones N.Semi-empirical equations for the perforation of plates struck by a mass[A].Bulson P S. Structure under shock and impact(SUSI)Ⅱ,computational mechanics publications[C].Southhampton,Bos-ton and Thomas telford,London,1992:369-380.
[8]Wen H M,Jones N.Experimental investigation into the dynamic plastic response and perforation of a clamped circular plate struck transversely by a mass[J].Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers,Part C:Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science,1994,208(C2):113-117.
[9]Wen H M,Jones N.Experimental investigation of the scaling laws for metal plates struck by large mass[J].Journal of Impact Eng.,1993,13(3):485-505.
[10]Jones N,Kim S B,Li Q M.Response and failure of ductile circular plates struck by a mass[J].Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology,1997,119:332-342.
[11]Jones N.Structural impact[M].Cambridge,U.K.: Cambridge University Press,1989.
[12]Chen X W,Li Q M.Shear plugging and perforation of ductile circular plates struck by a blunt projectile[J].International Journal of Impact Engineering,2003,28:513-536.
[13]潘建华,文鹤鸣.平头弹丸正撞击下延性金属靶板的破坏模式[J].高压物理学报,2007,21(2):157-164.
PAN Jian-hua,WEN He-ming.Failure modes of ductile metal plates under normal impact by flat-ended projectiles[J].Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics,2007,21(2):157-164.
[14]Wen H M,Jones N.Low-velocity perforation of punchimpact-loaded-metal plates[J].Trans ASME,J Pressure Vessel Technol,1996,118(2):181-187.
[15]邓云飞,张伟,曹宗胜.间隙对A3钢薄板抗卵形头弹侵彻性能影响的实验研究[J].振动与冲击,2013,32(12):95-99.
DENG Yun-fei,ZHANG Wei,CAO Zong-sheng.Effect of gap on bevavior of a double-layered A3 steel shield against penetration of ogival rigid projectiles[J].Journal of Vibration and Shock,2013,32(12):95-99.
[16]郭子涛.弹体入水特性及不同介质条件金属靶的抗侵彻性能研究[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2012.
[17]Recht R F,Ipson T W.Ballistic perforation dynamics[J].J. Appl.Mech.,1963,30:384-390.
[18]ZhangWei,DengYun-fei,CaoZong-sheng,etal. Experimental investigations on the ballistic performance of monolithic and layered metal plates subjected to impact by blunt rigid projectiles[J].International Journal of Impact Engineering,2012,49:115-129.
[19]Langseth M,Larsen P K.The behaviour of square steel plates subjected to a circular blunt ended load[J].Int.J.Impact Eng.,1992,12(4):617-638.
[20]Symonds P S.Survey of methods of analysis for plastic deformation of struetures under dynamic loading[R].Brown University,Division of Engineering Report BU/NSRDC/l-67,1967.
[21]Jones N.Structural impact[M].Cambridge,U.K.: Cambridge University Press,1989.
Ballistic resistance of Q235 steel monolithic plates impacted by rigid blunt-nosed projectiles
DENG Yun-fei1,ZHANG Wei2,MENG Fan-zhu1,CAO Zong-sheng2,HAO Peng1
(1.College of aeronautical Engineering,Civil Aviation University of China,Tianjin 300300,China; 2.Hypervelocity Impact Research Center,Harbin Institute of Technology,Harbin 150080,China)
Impact tests and theoretical analysis were carried out to study the ballistic performance of monolithic steel plates,and the influence of thickness of plates on ballistic performance was revealed.In general,good agreement was obtained between the predictions from analytical model and the experimental results.The results show that the theoretical model can be used to predict the limit ballistic velocities of plates under the impact of projectiles.Moreover,the energy absorption due to plastic deformation of plates was discussed and accounted,including local and global deformation energy absorption,and the effect of strain rate of plate material was also taken into account.An amendment function was used to correct the thickness of plate in the case of plate impacted by blunt-nosed projectile.
projectile;target;impact;penetration;ballistic resistance
O347;O385
A
10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2015.02.013
中国民航大学科研启动资金资助项目(2013QD03X);中央财经高校项目(3122014D018)
2013-11-08修改稿收到日期:2014-01-02
邓云飞男,讲师,1982年生
张伟男,教授,博士生导师,1964年生邮箱:zhdawei@hit.edu.cn
