桔皮素对人非小细胞肺癌细胞生长及侵袭的影响
2015-04-17石歆
石 歆
(河南中医学院第一附属医院内科,河南 郑州 450000)
桔皮素对人非小细胞肺癌细胞生长及侵袭的影响
石 歆△
(河南中医学院第一附属医院内科,河南 郑州 450000)
目的: 探讨桔皮素(TGN)对非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)细胞生长和侵袭的影响及其分子机制。方法: 体外培养非小细胞肺癌A549细胞,分别用不同浓度的TGN处理,MTT比色法检测细胞活性,Annexin V-FITC/PI染色及流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡率,Transwell检测细胞侵袭,RT-PCR分析MMP-2和MMP-9 的mRNA表达水平,Western blotting检测Ki67、Cyt C、caspase-3、cleaved caspase-3、MMP-2、MMP-9、Akt、p-Akt以及p-PI3K表达水平。结果: 桔皮素剂量依赖性地抑制A549细胞增殖(P<0.05),同时伴随有增殖标记分子Ki67表达水平的下调。分析发现,桔皮素诱导细胞中Cyt C、caspase-3和cleaved caspase-3的表达上调(P<0.01),加速A549细胞的凋亡。此外,桔皮素作用后,A549细胞中侵袭相关蛋白MMP-2和MMP-9的表达量下降,且侵袭数目随桔皮素浓度增加而减少。进一步研究表明,桔皮素作用后A549细胞中p-Akt和p-PI3K表达水平降低(P<0.05),阻断PI3K/Akt信号通路后,不同浓度TGN对细胞活性影响没有变化。结论: 桔皮素能抑制A549细胞生长及侵袭,促进细胞凋亡,可能通过抑制PI3K/Akt信号通路的激活起作用。因此,本研究将为非小细胞肺癌的防治提供新的研究方向。
桔皮素; 非小细胞肺癌; 细胞侵袭; PI3K/Akt信号通路
非小细胞肺癌(non-small-cell lung cancer, NSCLC)是一种极为常见的恶性肿瘤,占肺癌的80%,有致死率高、预后较差的特点[1]。因此,临床上寻找对非小细胞肺癌有明显抑制作用的药物有非常重要的意义。桔皮素(tangeretin, TGN)属黄酮类化合物,来源于芸香科川橘果皮、酸橙果皮和柑橘茎叶等,具有抗真菌作用。近年来,体外研究证实桔皮素对结肠癌和乳腺癌细胞发生发展有明显抑制作用[2-3],但是桔皮素对非小细胞肺癌的作用及其机制尚不清楚。因此,本文拟探究桔皮素对非小细胞肺癌A549生长、侵袭的影响,并分析潜在的作用机制,从而为非小细胞肺癌的防治提供新的研究靶向。
材 料 和 方 法
1 材料与试剂
A549细胞株由本实验室提供;桔皮素购于天津化标生物技术有限公司,DMSO、MTT和SDS、Annexin V-FITC凋亡检测试剂盒均购于Sigma;RPMI-1640培养基、胎牛血清和胰蛋白酶购于Gibco;DMEM高糖培养基购于Hyclone;蛋白激酶B(protein B, Akt)、磷酸化Akt(p-Akt)和磷酸化磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(phosphorylated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase,p-PI3K)多克隆抗体购于Santa Cruz;鼠抗人基质金属蛋白酶(matrix metalloproteinase, MMP)-2和MMP-9单克隆抗体购于福州迈新生物;兔抗人Ki67单克隆抗体购于LabVision;caspase-3和cleaved caspase-3抗体购于Cell Signaling;鼠抗人β-actin单克隆抗体购于Ambion;LY294002购于Sigma;RNA各提取试剂及PCR引物购于上海生工生物;PCR反应体系产品购于Promega。
2 方法
2.1 MTT实验 取0.25%胰蛋白酶消化对数期A549细胞株,单细胞悬液接种于96孔培养板(每孔1×105个),5% CO2、37℃条件下培养24 h后加入TGN(终浓度分别为0、20、40和60 μmol/L),再培养72 h后每孔加入5 g/L的MTT 20 μL,相同条件继续培养4 h后终止实验。弃上清液,每孔加100 μL DMSO,混匀后10 min内在酶标仪上测490 nm波长处A值,重复实验3次。相对细胞活性(%)=实验组A值/对照组A值×100%。
2.2 Annexin V-FITC/PI染色及流式细胞术分析 取A549细胞接种于培养板,每孔含1×106个细胞,加入TGN(终浓度分别为0、20、40和60 μmol/L),5% CO2、37 ℃条件下培养24 h,按照Annexin V-FITC/PI检测试剂盒说明书严格操作,用流式细胞术测定凋亡率。
2.3 Western blotting实验 取TGN(60 μmol/L)处理A549细胞48 h,冷冻离心法提取总蛋白,BCA法检测其浓度。Western blotting 检测Ki67、细胞色素C(cytochrome C,Cyt C)、caspase-3、cleaved caspase-3、MMP-2、MMP-9、Akt、p-Akt及p-PI3K的表达。
2.4 Transwell实验 取4组A549细胞消化成单细胞悬液后接种于培养板,加入TGN(终浓度分别为0、20、40和60 μmol/L),5% CO2、37 ℃条件下培养24 h,8 000 r/min离心5 min后置于无血清培养基中重悬细胞。取200 μL细胞悬液接种于24 孔板的Transwell小室中(含2×105个细胞),小室中置8 μm PET膜,外室加DMEM高糖培养基(含10%胎牛血清),孵育8 h后用中性甲醇固定30 min,除去未迁移细胞,瑞氏染色后观察细胞迁移数目。
2.5 RT-PCR实验 取对照组A549细胞和TGN(60 μmol/L)处理48 h的A549细胞,按说明书分别提取各组总RNA,逆转录为cDNA。MMP-2引物上游序列为5’-GCG ATG GAT ACC CCT TTG ACG-3’,下游序列为5’-CCC TGG AAG CGG AAT GGA A-3’;MMP-9引物上游序列为5’-GGT CCC CCC ACT GCT GGC CCT TCT ACG GCC-3’,下游序列为5’-GTC CTC AGG GCA CTG GAG GAT GTC ATA GGT-3’;内参照β-actin引物上游序列为5’-GGG AAA TCG TGC GTG ACA-3’,下游序列为5’-TCA GGA GGA GCA ATG ATC-3’。PCR 产物进行1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳,利用Quantity One分析各电泳条带的灰度值,用目的条带的灰度值与对照条带的灰度值的比值表示目的基因MMP-2 mRNA的相对表达量。实验重复3次。
3 统计学处理
数据用均数±标准差(mean±SD)表示,采用SPSS 13.0软件分析,用t检验及单因素方差分析比较样本间结果,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
结 果
1 桔皮素对A549细胞增殖的影响
桔皮素对A549的细胞增殖具有显著的抑制作用,且与桔皮素浓度呈正比,0、20、40和60 μmol/L的TGN处理后相对细胞活性依次是(99.9±5.2)%、(86.7±7.1)%、(66.8±11.1)%和(48.9±9.9)%,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。随着TGN浓度的增加,增殖标记分子Ki67表达水平逐渐下降(P<0.05),见图1。
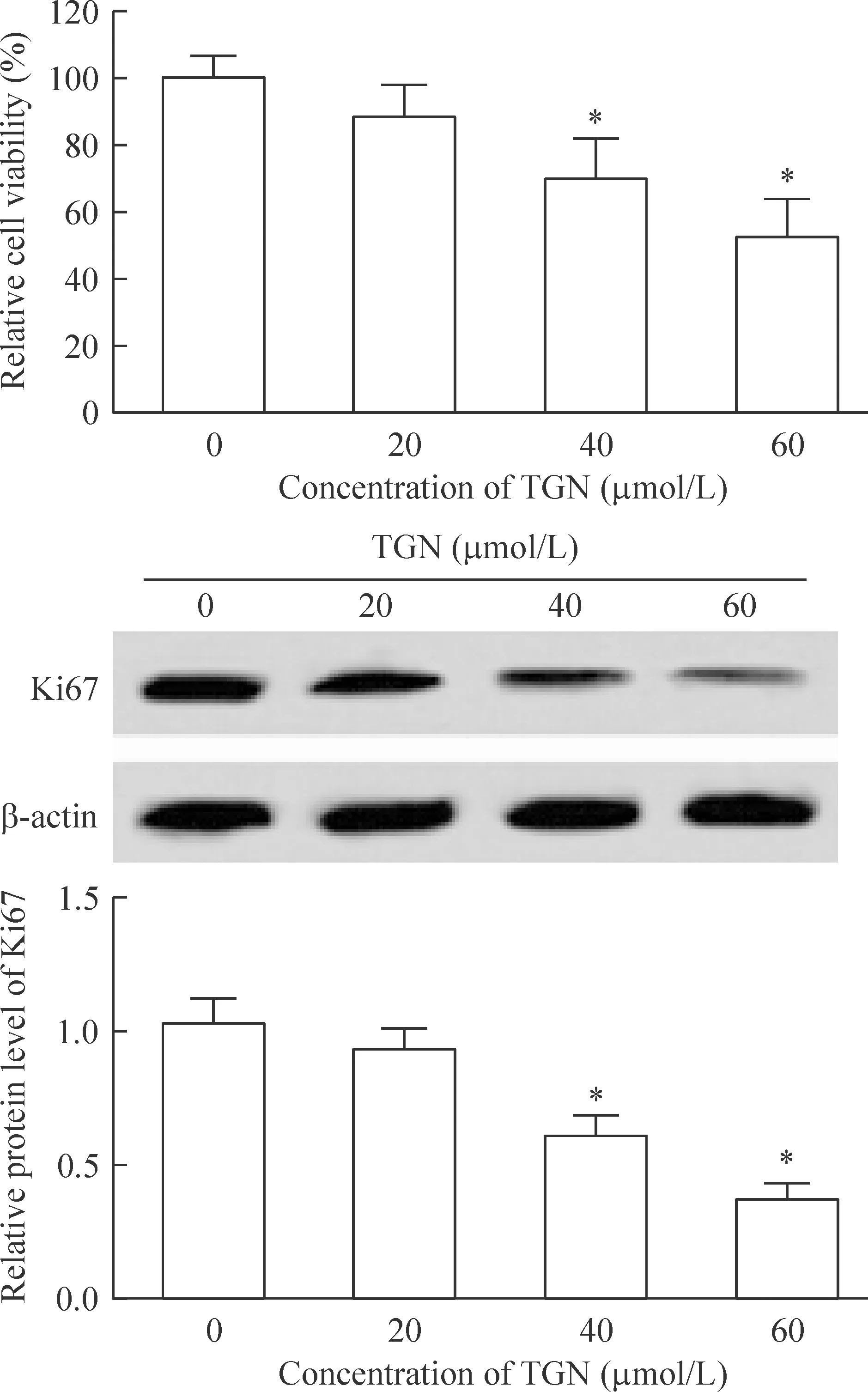
Figure 1.Effects of TGN on cell proliferation. Mean±SD. n=3. *P<0.05 vs 0 μmol/L.
2 桔皮素对A549细胞凋亡的影响
Annexin V-FITC/PI染色及流式细胞术结果显示,浓度越高的桔皮素促进A549细胞凋亡作用越显著,与对照组相比,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。当TGN的浓度为60 μmol/L时,凋亡率升至(72.6±6.9)%,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),表明桔皮素对A549的凋亡作用呈剂量依赖性,见图2。
3 桔皮素对凋亡相关分子细胞色素C和caspase-3水平的影响
Western blotting实验分析显示,桔皮素对A549细胞的Cyt C和caspase-3的表达水平影响显著,与对照组相比,TGN处理后细胞中Cyt C和cleaved caspase-3的含量明显增加(P<0.01),从分子水平验证了一定浓度的TGN对A549细胞的促凋亡作用,见图3。
4 桔皮素对细胞侵袭的影响
Transwell侵袭实验分析表明,随着TGN浓度的增加,A549侵袭细胞的数目明显降低,当用60 μmol/L的TGN处理时,侵袭细胞的数目降至56.9±8.3,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),表明TGN剂量依赖性地抑制了A549细胞的侵袭,见图4。
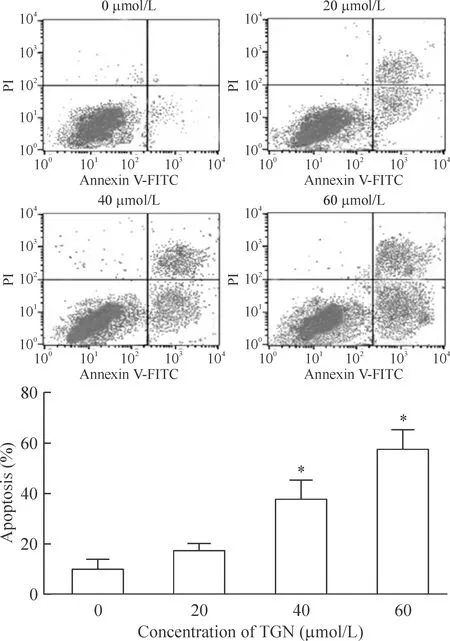
Figure 2.The effects of TGN on apoptosis of A549 cells. Mean±SD. n=3. *P<0.05 vs 0 μmol/L.
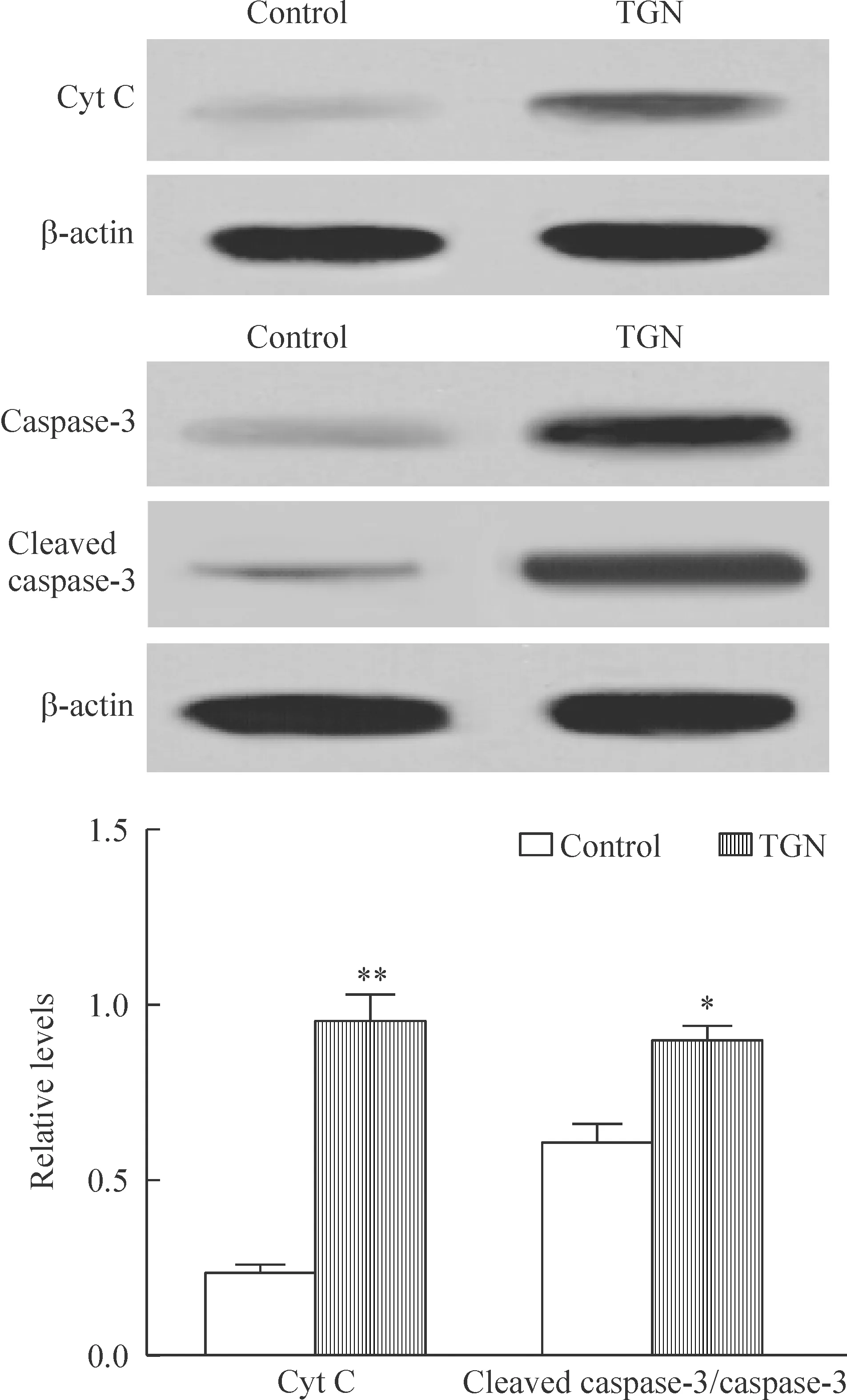
Figure 3.The effects of TGN (60 μmol/L) on apoptosis-related protein expression. Mean±SD. n=3. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs control.
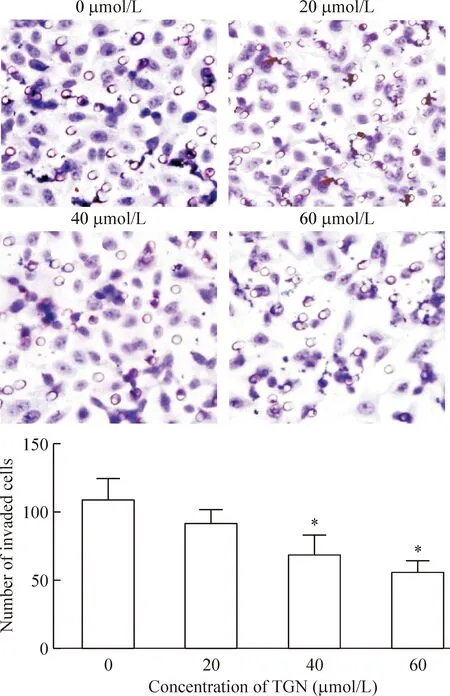
Figure 4.The effects of different concentrations of TGN on the number of invasive A549 cells. Mean±SD. n=3. *P<0.05 vs 0 μmol/L.
TGN处理组中MMP-2 和MMP-9 mRNA水平明显低于对照组(P<0.05)。此外,Western blotting实验结果显示,TGN处理组MMP-2与MMP-9蛋白表达水平比对照组显著降低(P<0.05),表明TGN通过MMPs蛋白来调节细胞侵袭,见图5。
6 桔皮素通过PI3K/Akt调控A549细胞的增殖及侵袭
Western blotting实验分析显示,TGN处理后A549中p-Akt和p-PI3K的蛋白水平比对照组显著降低(P<0.05),表明桔皮素与A549中PI3K/Akt信号通路有相关性。不同浓度TGN处理A549细胞后,细胞相对活性逐渐降低(P<0.05);当5 μmol/L Akt选择性抑制剂LY294002处理A549细胞4 h后,再对细胞进行不同浓度的TGN处理,细胞活性彼此无变化,表明TGN通过PI3K/Akt信号通路影响A549细胞,见图6。
讨 论
桔皮素是一种天然多甲氧基黄酮,具有潜在的抗炎、抗氧化功效,且对乳腺癌、结肠癌、肺癌和胃癌等有抑制作用[4-5]。本实验检测到A549细胞经桔皮素处理后细胞增殖相关蛋白Ki67[6]表达水平下降,细胞活性随着桔皮素的浓度增加而降低,证实桔皮素能够有效抑制A549细胞增殖。此外,实验表明桔皮素能明显促进A549细胞凋亡和抑制细胞侵袭,与桔皮素在人肝癌细胞株SMMC-7721的作用结果一致[7]。桔皮素抗肿瘤作用的具体机制尚不清楚,可能与抑制瘤细胞DNA合成、加速细胞凋亡和影响细胞信号通路相关。
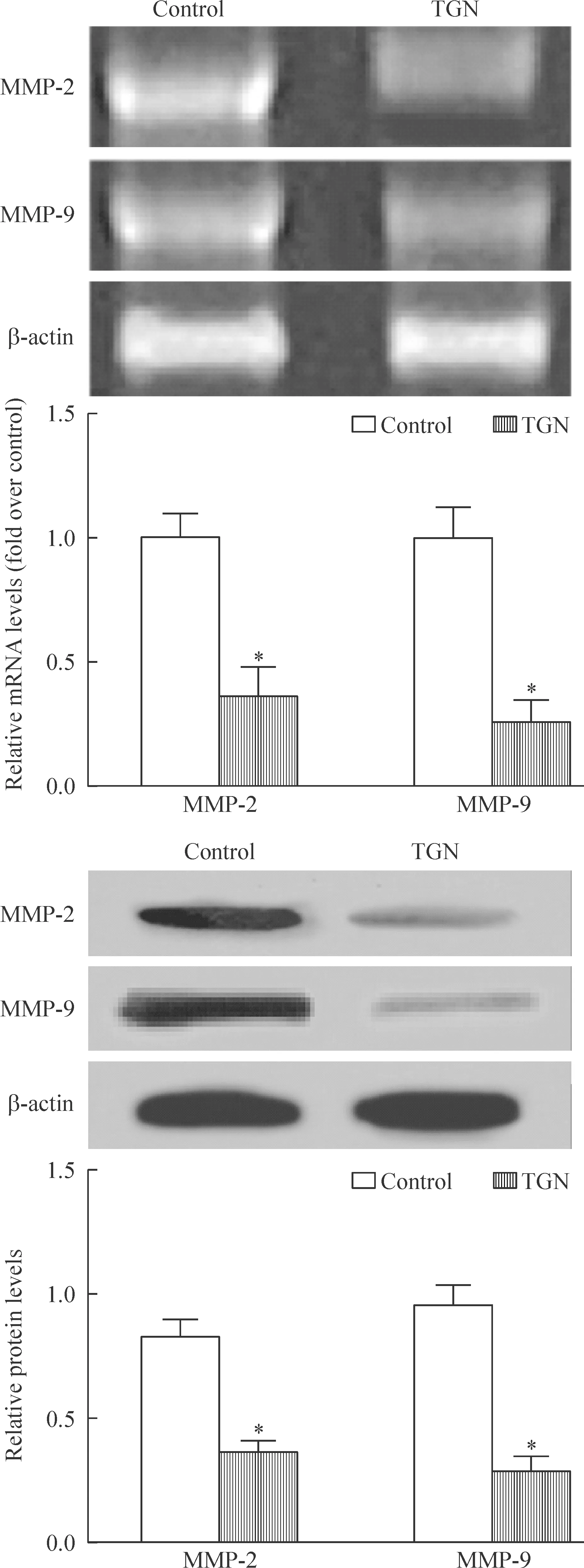
Figure 5.The effects of TGN (60 μmol/L) on the expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9. Mean±SD. n=3. *P<0.05 vs control.
既往研究表明,Akt经PI3K的调节后磷酸化成p-Akt,这时PI3K/Akt信号通路激活。PI3K/Akt信号通路与细胞增殖和凋亡紧密相关,很多报道证实了PI3K/Akt信号通路在瘤细胞中处于激活状态[8]。Sukawa等[9]证实p-Akt的大量活化与胃癌患者的预后不良有关,表明PI3K/Akt通路在胃癌的发展进程中起重要调控作用。为进一步分析桔皮素影响小细胞肺癌细胞增殖和侵袭的作用机制,本研究分析桔皮素对PI3K/Akt通路的影响。结果表明,TGN处理后,细胞中Akt的磷酸化水平明显降低。蔡勇等[10]研究了醉茄素A影响A549细胞增殖和凋亡的机制,揭示一定浓度的醉茄素A作用A549细胞48 h后,p-Akt/Akt降低,PI3K/Akt信号通路被抑制,caspase-3等促凋亡蛋白表达量增加,A549细胞增殖得到抑制。另外,从皂荚中分离的有效成分gleditsioside B能够抑制PI3K/Akt信号通路而降低MPP-2活性,从而减弱内皮细胞侵袭[11]。上述结果表明桔皮素可能通过抑制PI3K/Akt信号通路来调控A549癌细胞的增殖及侵袭。本实验中与瘤细胞侵袭相关蛋白MMP[12]表达水平明显降低,促细胞凋亡因子Cyt C和caspase-3[13-14]表达水平显著升高,表明桔皮素通过影响PI3K/Akt信号通路介导的MMP、Cyt C和caspase-3水平对A549细胞起作用。
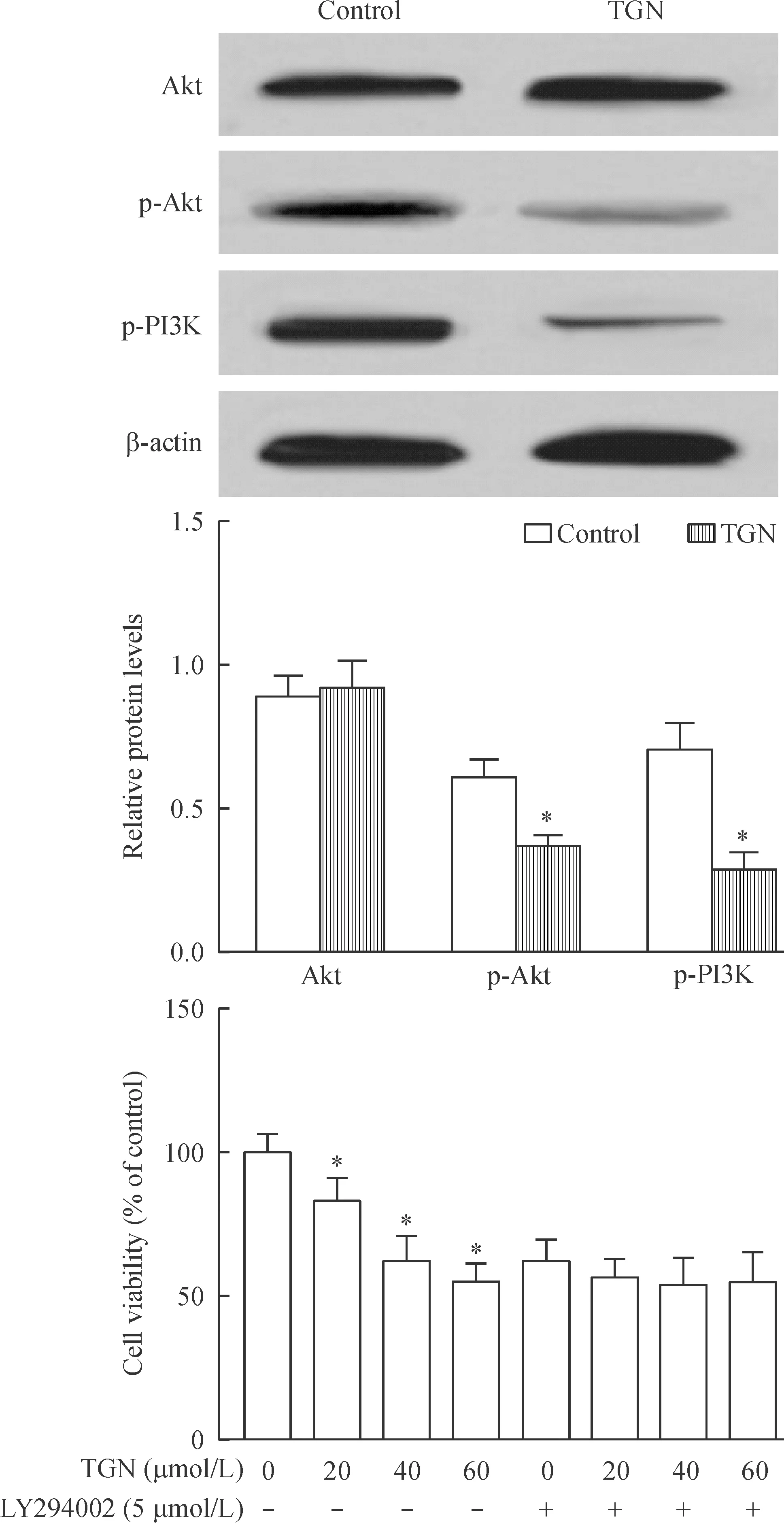
Figure 6.The effects of TGN on the molecular levels of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Mean±SD. n=3. *P<0.05 vs control.
综上,桔皮素能够抑制A549细胞的生长和侵袭,加速细胞凋亡,该过程有可能通过抑制PI3K/Akt信号通路起作用。因此,利用桔皮素治疗NSCLC在临床上具有巨大的潜在价值。
[1] Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, et al. Cancer statistics, 2010[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2010, 60(5):277-300.
[2] Morley KL, Ferguson PJ, Koropatnick J. Tangeretin and nobiletin induce G1 cell cycle arrest but not apoptosis in human breast and colon cancer cells[J]. Cancer Lett, 2007, 251(1):168-178.
[3] Bracke M, Bruyneel E, Vermeulen SJ, et al. Citrus flavonoid effect on tumor invasion and metasis[J]. Food Technol, 1994, 48(11):121-124.
[4] Arivazhagan L, Pillai SS. Tangeretin, a citrus pentamethoxyflavone, exerts cytostatic effect via p53/p21 up-regulation and suppresses metastasis in 7, 12-dimethylbenz (α)anthracene-induced rat mammary carcinoma[J]. J Nutr Biochem, 2014, 25(11):1140-1153.
[5] Dong Y, Cao A, Shi J, et al. Tangeretin, a citrus polymethoxyflavonoid, induces apoptosis of human gastric cancer AGS cells through extrinsic and intrinsic signaling pathways[J]. Oncol Rep, 2014, 31(4):1788-1794.
[6] Gurda GT, Baras AS, Kurman RJ. Ki-67 index as an ancillary tool in the differential diagnosis of proliferative endometrial lesions with secretory change[J]. Int J Gynecol Pathol, 2014, 33(2):114-119.
[7] 何蕊伶, 张娟娟, 伍怡颖, 等. 桔皮素对人肝癌细胞株SMMC-7721抑制作用的初步研究[J]. 四川生理科学杂志, 2008, 30(4):150-151.
[8] Chang F, Lee JT, Navolanic PM, et al. Involvement of PI3K/Akt pathway in cell cycle progression, apoptosis, and neoplastic transformation: a target for cancer chemotherapy[J]. Leukemia, 2003, 17(3):590-603.
[9] Sukawa Y, Yamamoto H, Nosho K, et al. HER2 expression and PI3K-Akt pathway alterations in gastric cancer[J]. Digestion, 2014, 89(1):12-17.
[10]蔡 勇, 王季颖. 醉茄素A对非小细胞肺癌A549细胞增殖、凋亡及PI3K/Akt信号通路的影响[J]. 临床肿瘤学杂志, 2014, 19(2):107-111.
[11]Tong B, Lu D, Wei Z, et al. Gleditsioside B, a triterpene saponin isolated from the anomalous fruits ofGleditsiasinensisLam., abrogates bFGF-induced endothelial cell migration through preventing the activation of MMP-2 and FAKviainhibiting ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways[J]. Vascul Pharmacol, 2013, 58(1-2):118-126.
[12]郭晓鹤, 张彩凤, 夏永华, 等. CADM1过表达对人胃癌MKN-45细胞增殖和侵袭的影响及其分子机制[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2013, 28(12):2283-2287.
[13]Faccenda D, Tan CH, Duchen MR, et al. Mitochondrial IF1preserves cristae structure to limit apoptotic cell death signaling[J]. Cell Cycle, 2013, 12(16):2530-2532.
[14]逯 丹, 舒晓明, 张婵娟, 等. 人参皂苷Rg1抑制叔丁基过氧化氢诱导的原代大鼠皮层神经元损伤[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2014, 30(3):479-485.
Effects of tangeretin on growth and invasion of human non-small-cell lung cancer cells
SHI Xin
(Department of Internal Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, China. E-mail: shixin_tcm@163.com)
AIM: To study the influences of tangeretin (TGN) on the growth and invasion of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells, and to explore the molecular mechanisms. METHODS: The A549 cells were treated with different concentrations of TGNinvitro. The relative cell activity was determined by MTT assay. The apoptotic rate was analyzed by flow cytometry with Annexin V-FITC/PI staining. The number of the invasive cells was measured by Transwell assay. The mRNA expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 was detected by RT-PCR, and the protein levels of Ki67, Cyt C, caspase-3, cleaved caspase-3, MMP-2, MMP-9, Akt, p-Akt and p-PI3K were determined by Western blotting analysis. RESULTS: TGN inhibited the proliferation of A549 cells in a dose-dependent manner (P<0.05) along with the low expression level of proliferation biomarker Ki67. TGN up-regulated the protein levels of Cyt C, caspase-3 and cleaved caspase-3 (P<0.01) and promoted the apoptosis of A549 cells in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, TGN down-regulated the invasion-related molecules MMP-2 and MMP-9 at the mRNA and protein levels, and the number of invasive cells reduced with the increase in the concentration of TGN. The protein levels of p-Akt and p-PI3K in the A549 cells was reduced (P<0.05), and no difference of the cell viability in the cells treated with different concentrations of TGN was observed after blocking PI3K/Akt signaling pathway using LY294002. CONCLUSION: TGN inhibits the growth and invasion of A549 cells and promotes the cell apoptosis by potentially inhibiting PI3K/Akt signaling pathway activation. Therefore, this study will provide a new target for the prevention and control of NSCLC.
Tangeretin; Non-small-cell lung cancer; Cell invasion; PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
1000- 4718(2015)03- 0452- 05
2014- 08- 11
2015- 01- 08
△通讯作者 Tel: 0371-66232471; E-mail: shixin_tcm@163.com
R730.23
A
10.3969/j.issn.1000- 4718.2015.03.012
