抗Ⅶ型胶原抗体ELISA辅助确诊一例获得性大疱性表皮松解症及文献复习
2014-12-18李志量王光平佘晓东李筱芳王宝玺冯素英
李志量 王光平 佘晓东 李筱芳 王宝玺 冯素英
抗Ⅶ型胶原抗体ELISA辅助确诊一例获得性大疱性表皮松解症及文献复习
李志量 王光平 佘晓东 李筱芳 王宝玺 冯素英
目的报道抗Ⅶ型胶原抗体酶联免疫吸附实验(ELISA)辅助确诊1例获得性大疱性表皮松解症(EBA)。同时复习文献,分析在大样本中该方法诊断EBA的敏感性和特异性。方法对1例临床表现、组织学特点、免疫学特点符合EBA的患者,应用抗Ⅶ型胶原抗体ELISA试剂盒检测其血清中Ⅶ型胶原抗体滴度;以4例健康人、5例大疱性类天疱疮和3例寻常型天疱疮患者为对照。查阅既往关于ELISA法诊断EBA的文献,总结各研究中患者入组标准、包被的抗原、敏感性、特异性,并与其他血清学方法对比。结果ELISA法检测该患者血清中抗Ⅶ型胶原抗体滴度为136 U/ml,对照组均为阴性。既往文献中,敏感性和特异性有区别,但总体而言,ELISA法诊断EBA的准确性高于免疫印迹。结论ELISA法诊断EBA简单快捷,具有较高准确性。
表皮松解,大疱性,获得性;酶联免疫吸附测定
获得性大疱性表皮松解症(epidermolysis bullosa acquisita,EBA)是一种以血清中出现Ⅶ型胶原抗体为特点的自身免疫性水疱病。该病通过临床表现、组织学及直接免疫荧光检查很难与其他表皮下水疱病鉴别。目前国内确诊该病主要依赖盐裂正常皮肤为底物的间接免疫荧光检查(salt-split indirect immunofluorescence,SSIIF)和免疫印迹检查。即使SSIIF在真皮侧发现抗体沉积,仍无法将EBA与P200类天疱疮及部分瘢痕性类天疱疮鉴别。免疫印迹检查操作繁琐,限制了其在临床的应用。我们在国内首次用酶联免疫吸附实验(ELISA)确诊了1例EBA患者。
病历资料
患者男,31岁,半年前无明显诱因于双胫前出现散在红斑,伴有瘙痒,随后出现黄豆至蚕豆大水疱,疱壁紧张,不易破,水疱逐渐累及至整个下肢、上肢、躯干,当地医院诊断为大疱性类天疱疮,给与甲泼尼龙60 mg/d口服,皮损控制后逐渐减量。减至35 mg/d时大疱再次泛发全身,来我院就诊。发病以来精神、睡眠尚可,大小便无明显异常。家庭中无类似疾病患者,发现乙肝表面抗原携带2个月。
体检:一般情况可,生命体征正常。全身浅表淋巴结未触及肿大。心肺腹部检查未见特殊。皮肤科情况:头皮、颈部、躯干、四肢密集分布米粒至鸡蛋大小红斑,前胸、后背散在蚕豆大糜烂面,结褐色痂(图1)。双手前臂可见粟丘疹。
皮损组织病理学检查:表皮下水疱形成,疱内可见纤维蛋白样物质及少许嗜酸性粒细胞,真皮浅层血管周围可见淋巴细胞及少许嗜酸性粒细胞为主的炎症细胞浸润(图2)。直接免疫荧光示IgG、C3基底膜带线状沉积。
实验室及辅助检查:血尿粪常规正常;肝肾功能、电解质正常;免疫球蛋白及补体均正常,可提取核抗原及抗核抗体均阴性,乳酸脱氢酶、血细胞沉降率及C反应蛋白均正常,结核菌素纯蛋白衍生物实验阴性;乙肝表面抗原、e抗原、核心抗体阳性。肿瘤标记物检查均阴性,心电图正常;腹部B超检查示肝脂肪浸润。SSIIF检查示患者血清IgG抗体在真皮侧沉积(图3);Ⅶ型胶原抗体ELISA(日本MBL,Nagoya公司)检测患者血清中抗体滴度为136 U/ml(参考值<6 U/ml)。同时用该试剂盒检测4例健康人、5例大疱性类天疱疮患者、3例寻常型天疱疮患者血清,结果均为阴性。
诊断:获得性大疱性表皮松解症。
治疗:考虑到该患者乙肝病毒处于活动期,为避免长期应用糖皮质激素引起病毒的进一步增殖,除给予甲泼尼龙40 mg/d静脉滴注外,还应用静脉注射免疫球蛋白(IVIg)2 g/kg分5天静脉泵入,口服四环素0.25 g日3次,烟酰胺0.9 g日3次,半个月后皮疹控制,甲泼尼龙逐渐减量。电话随访4个月,皮疹未复发。
讨 论
Ⅶ型胶原是位于致密板和致密板下带锚丝的主要成分。EBA患者血清中自身抗体针对的抗原表位主要位于Ⅶ型胶原的NC1域内[1]。针对NC1最末端227个氨基酸的软骨基质蛋白的血清抗体被证实具有致病性[2]。部分EBA患者血清中也可以检测到针对 NC2 域[3]和中间胶原区[4]的自身抗体,这类抗体的致病性及与EBA临床表现的关系尚待研究。
通过临床表现和组织病理学检查往往难以把EBA与大疱性类天疱疮、瘢痕性类天疱疮、线状IgA大疱性皮病、P200类天疱疮等其他表皮下水疱病鉴别开来,因此血清学检查有不可替代的作用。常用的血清学检测方法主要有三种:间接免疫荧光(IIF)、免疫印迹和ELISA。IIF仅能将线状IgA大疱性皮病与其他表皮下大疱病鉴别,即使进一步行SSIIF检查也仅能确诊大疱性类天疱疮,其他表皮下水疱病均表现为真皮侧抗体沉积。进一步行免疫印迹检查,理论上EBA患者血清抗体可以与真皮蛋白抗原在相对分子质量290 000处结合,但部分EBA血清中抗Ⅶ型胶原抗体是与Ⅶ型胶原NC1域的构象表位结合,在免疫印迹过程中这种构象表位受到破坏,会出现假阴性。
1997年,Chen等[5]首次以真核表达的具有完整空间构象的Ⅶ型胶原NC1段为底物对EBA患者血清进行ELISA检测,发现该方法具有极高的敏感性和特异性,可以检测到IIF和免疫印迹均阴性的患者血清中的抗体。随后多种包被不同抗原底物的ELISA检测方法以及商品化的Ⅶ型胶原抗体检测试剂盒都证实了该方法的可靠性[2,6-13];由于既往研究选择的入组患者和包被抗原底物的不同,ELISA检测的敏感性和特异性有一定差异,但总体而言该方法的准确性要优于免疫印迹(表1)。我们在本文中所用的商品化试剂盒除包被了NC1段外,也包被了NC2段,理论上可以进一步提高敏感性。也有研究表明,ELISA法检测到的抗体滴度与病情活动具有相关性,可用于临床指导治疗[5-7,9,11,13-15]。
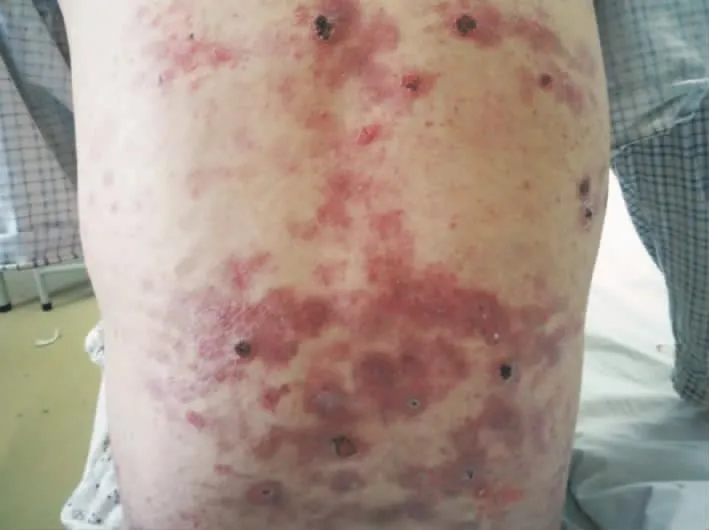
图1 患者背部散在红斑,部分皮疹结痂、破溃
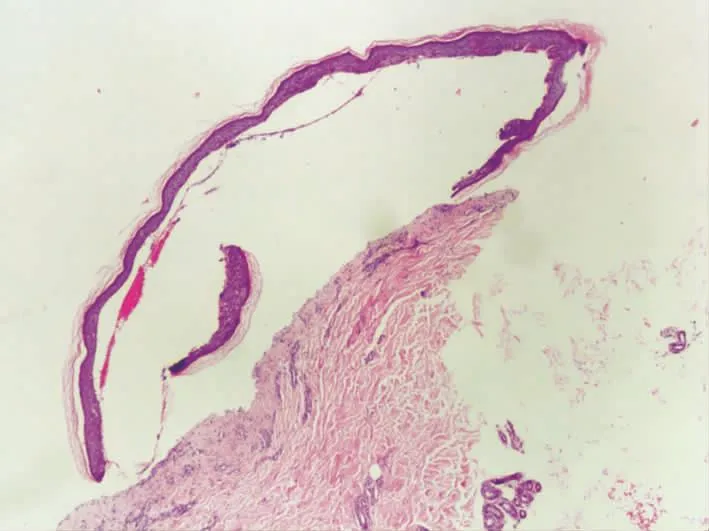
图2 皮损组织病理检查见表皮下疱,真皮浅层见炎细胞浸润(HE×40)
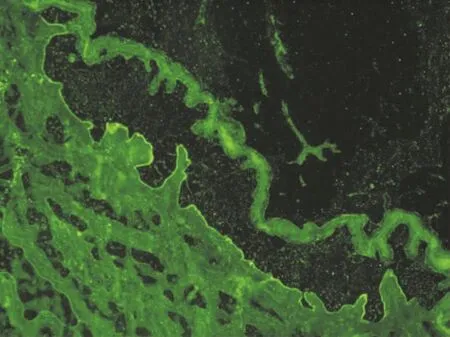
图3 盐裂正常皮肤为底物的间接免疫荧光检查示,患者血清IgG抗体沉积在盐裂皮肤真皮侧(×40)
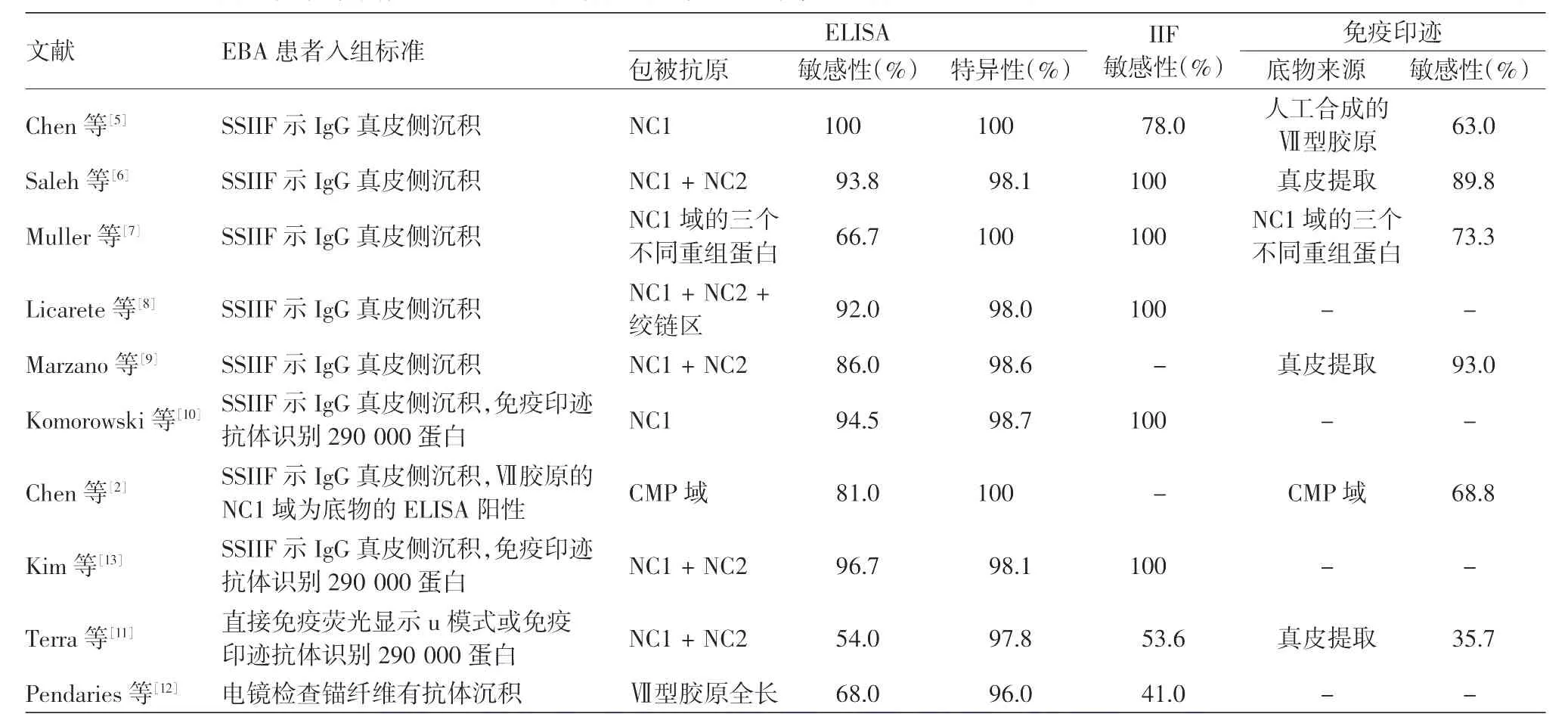
表1 既往应用酶联免疫吸附实验(ELISA)诊断获得性大疱性表皮松解症(EBA)的敏感度、特异度及与其他血清学方法的比较
ELISA法简便、快捷和无创的特点对EBA的诊断具有较高的应用价值。我们报道的这例患者,在没有进行免疫印迹检测的前提下,直接用ELISA方法确诊,说明该方法对EBA具有诊断价值。特别在现有技术条件下,大多数医疗机构无法常规开展SSIIF和免疫印迹这些步骤繁琐、技术要求高的检测方法,将Ⅶ型抗体检测试剂盒与BP180 NC16A抗体检测试剂盒结合起来,可以有效提高表皮下水疱病的诊断准确率。
[1]Lapiere JC,Woodley DT,Parente MG,et al.Epitope mapping of type VII collagen.Identification of discrete peptide sequences recognized by sera from patients with acquired epidermolysis bullosa[J].J Clin Invest,1993,92(4):1831-1839.
[2]Chen M,Doostan A,Bandyopadhyay P,et al.The cartilage matrix protein subdomain of type VII collagen is pathogenicfor epidermolysis bullosa acquisita[J].Am J Pathol,2007,170(6):2009-2018.
[3]Ishii N1,Yoshida M,Hisamatsu Y,et al.Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita sera react with distinct epitopes on the NC1 and NC2 domains of type VII collagen:study using immunoblotting of domain-specific recombinant proteins and postembedding immunoelectron microscopy [J].Br J Dermatol,2004,150(5):843-851.
[4]Ishii N,Yoshida M,Ishida-Yamamoto A,et al.Some epidermolysis bullosa acquisita sera react with epitopes within the triple-helical collagenous domain as indicated by immunoelectron microscopy[J].Br J Dermatol,2009,160(5):1090-1093.
[5]Chen M,Chan LS,Cai X,et al.Development of an ELISA for rapid detection of anti-type VII collagen autoantibodies in epidermolysis bullosa acquisita[J].J Invest Dermatol,1997,108(1):68-72.
[6]Saleh MA,Ishii K,Kim YJ,et al.Development of NC1 and NC2 domains of type VII collagen ELISA for the diagnosis and analysis of the time course of epidermolysis bullosa acquisita patients[J].J Dermatol Sci,2011,62(3):169-175.
[7]Müller R,Dahler C,Möbs C,et al.T and B cells target identical regions of the non-collagenous domain 1 of type VII collagen in epidermolysis bullosa acquisita[J].Clin Immunol,2010,135(1):99-107.
[8]Licarete E,Ganz S,Recknagel MJ,et al.Prevalence of collagen VII-specific autoantibodies in patients with autoimmune and inflammatory diseases[J].BMC Immunol,2012,13:16.
[9]Marzano AV,Cozzani E,Fanoni D,et al.Diagnosis and disease severity assessment of epidermolysis bullosa acquisita by ELISA for anti-type VII collagen autoantibodies:an Italian multicentre study[J].Br J Dermatol,2013,168(1):80-84.
[10]Komorowski L,Müller R,Vorobyev A,et al.Sensitive and specific assays for routine serological diagnosis of epidermolysis bullosa acquisita[J].J Am Acad Dermatol,2013,68(3):e89-e95.
[11]Terra JB,Jonkman MF,Diercks GF,et al.Low sensitivity of type VII collagen enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in epidermolysis bullosa acquisita:serration pattern analysis on skin biopsy is required for diagnosis[J].Br J Dermatol,2013,169(1):164-167.
[12]Pendaries V,Gasc G,Titeux M,et al.Immune reactivity to type VII collagen:implications for gene therapy of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa[J].Gene Ther,2010,17(7):930-937.
[13]Kim JH,Kim YH,Kim S,et al.Serum levels of anti-type VII collagen antibodies detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assayin patientswith epidermolysisbullosaacquisita are correlated with the severity of skin lesions [J].J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol,2013,27(2):e224-e230.
[14]Ito Y,Kasai H,Yoshida T,et al.Anti-type VII collagen autoantibodies,detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay,fluctuate in parallel with clinical severity in patients with epidermolysis bullosa acquisita[J].J Dermatol,2013,40(11):864-868.
[15]Sato M,Ishitsuka A,Shibuya Y,et al.Time-course of the change in titre of antibodies against type VII collagen in a patient with epidermolysis bullosa acquisita[J].Acta Derm Venereol,2012,92(6):693-694.
Detection of anti-type Ⅶ collagen antibodies using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in the auxiliary diagnosis of epidermolysis bullosa acquisita:a case report and literature review
Li Zhiliang,Wang Guangping,She Xiaodong,Li Xiaofang,Wang Baoxi,Feng Suying.Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology for Skin Diseases and STIs,Hospital of Dermatology,Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College,Nanjing 210042,China
s:Wang Baoxi,Email:wangbx@ncstdlc.org;Feng Suying,Email:fengsuying2010@aliyun.com
Objective To evaluate the performance of anti-type Ⅶ collagen antibody detection using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay(ELISA)in the auxiliary diagnosis of a case of epidermolysis bullosa acquisita(EBA),and to analyze its sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of EBA in large-scale studies by review of relevant literature.Methods Serum samples were collected from a patient with typical clinical,histological and immunological manifestations of EBA,4 healthy human controls,5 patients with bullous pemphigoid and 3 patients with pemphigus vulgaris.ELISA was performed to determine the serum levels of anti-typeⅦcollagen antibodies.Literature regarding the diagnosis of EBA using ELISA was reviewed with a summary of inclusion criteria for patient enrollment,coating antigens,sensitivity and specificity.A comparison was carried out between ELISA and the other serological methods.Results Anti-typeⅦcollagen antibodies were detected by ELISA in the serum of the patient with EBA(136 U/ml),but not in the other serum samples.The sensitivity and specificity of ELISA in the diagnosis of EBA differed in different studies,but in general,the accuracy of ELISA was higher than that of immunoblotting.Conclusion ELISA is a simple and convenient tool for the diagnosis of EBA with high accuracy.
Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita;Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
10.3760/cma.j.issn.0412-4030.2014.08.004
卫生公益性行业科研专项经费(201002016)
210042南京,中国医学科学院北京协和医学院皮肤病医院,江苏省皮肤病与性病学重点实验室
王宝玺,Email:wangbx@ncstdlc.org;冯素英,Email:fengsuying2010@aliyun.com
2013-12-26)
(本文编辑:颜艳)
