老山芹根中亲脂性化学成分的GC-MS分析
2014-11-02杨敏飞苏娅萍霍雅玉王欣芮尤晓娟张海龙西安交通大学药学院西安710061
高 阳,杨敏飞,苏娅萍,霍雅玉,米 洁,王欣芮,尤晓娟,张海龙(西安交通大学药学院,西安 710061)
老山芹(Heracleum dissectum)又名东北牛防风、山芹菜、土当归,为伞形科(Umbelliferae)独活属多年生草本植物,主要分布在黑龙江、吉林和新疆等地。它是一种药食两用的植物,其幼嫩茎叶是美味的蔬菜,具有特殊的香味,深受当地人的喜爱,茎叶中含有丰富的膳食纤维,可以促进胃肠蠕动,清理肠道垃圾。它具有显著的降血压作用以及降血脂、降血糖、祛风、除湿、止痛等作用[1-2],尤其是对高血压病人具有显著的降压作用,而对正常人的血压无任何影响。
独活属植物的分类及鉴定一直很混乱,其属间和属内的划分也一直是伞形科系统学研究的一大难题[3],因此本研究通过对老山芹的化学成分的分析不但对独活属植物的分类具有重要的参考意义,同时鉴于老山芹的多种药用活性,通过首次对老山芹根中亲脂性化学成分的GC-MS分析,为今后系统分离鉴定老山芹的化学成分及进一步阐明其活性成分具有一定的参考价值。
1 仪器与试药
1.1 仪 器 日 本 岛 津 (Shimadzu)公 司 GC-MS/QP2010气相色谱-质谱联用仪。
1.2 试药 老山芹的根于2011年9月采自黑龙江省北安市,经西安交通大学医学部药学院牛晓峰教授鉴定为伞形科独活属植物Heracleum dissectum Ledeb.的根。甲醇、石油醚、氯仿为分析纯,乙酸乙酯为色谱纯。
2 方法与结果
2.1 样品的制备 取老山芹的干燥根4.0kg,剪成1~2cm的小段,甲醇回流提取3次,每次2h,合并提取液并减压回收溶剂得到甲醇总提物,甲醇总提物分散于水中,先后用石油醚和氯仿分别萃取,得石油醚层68.3g,氯仿层85.1g。
2.2 GC-MS分析条件
2.2.1 石油醚部分 GC条件 RTX-5MS柱(30m×0.25mm,0.25μm);柱温:始温150℃(保持5min),以8℃·min-1升温至220℃,再以5℃·min-1升温至280℃(保持15min),气化温度为280℃;分流比5∶1。
石油醚部分MS条件 EI离子源,电离能量70eV;离子源温度200℃;接口温度280℃;质量扫描范围50~600 m/z;溶剂峰切除时间0.5s,起测时间3.00min,结束时间40.75min;NIST147质谱图计算机检索数据库。
2.2.2 氯仿部分GC条件 色谱柱型号与石油醚部位相同;柱温:始温150℃,20℃·min-1升温至230℃,1℃·min-1升温至240℃,5℃·min-1升温至250℃,最后8℃·min-1升温至280℃(保持5min);分流比10∶1。
氯仿部分MS条件 质谱检测起测时间3.00min,结束时间24.75min;其余条件均与石油醚部位相同。
2.3 结果 对老山芹的石油醚部分和氯仿部分的总离子流图中各峰分别经质谱扫描后得到质谱图,通过NIST147质谱图计算机检索数据库进行检索,鉴定出石油醚部分19个化合物,氯仿部分14个化合物,按面积归一化法计算各化合物的相对百分含量。结果分别见图1和图2及表1和表2。

图1 石油醚层的总离子流图Fig.1 Total ion chromatogram of petroleum ether fraction

图2 氯仿层的总离子流图Fig.2 Total ion chromatogram of chloroform fraction

表1 石油醚层亲脂性化学成分分析结果Tab.1 Results of the petroleum ether fraction in the roots of Heracleum dissectum
3 讨论
老山芹根的GC-MS分析结果表明,石油醚层中甾体类(谷甾醇,豆甾醇及其衍生物及6β,6β-二溴-6,7-亚甲基睾丸激素)化合物的含量为主要成分,占52.86%,香豆素类化合物为第二大成分,含量共32.78%,其他的长链烷醇、烯、烯醇及酯含量共9.75%,此外还有0.84%的薁类化合物以及1.99%的三环衍生物等。氯仿部分的14个化合物中绝大多数为香豆素类化合物,其含量高达54.14%。从两部分的分析结果可以看出,老山芹根中尤其是氯仿层的亲脂性成分主要是香豆素类化合物。
香豆素类化合物具有多种多样的生物活性,如:抗 病 毒 及 抗 HIV 活 性[4-7],抗 菌 和 抗 寄 生 虫 活性[8-11],抗癌活性[12-15],抗炎和抗氧化活性[16-18],以及抗糖尿病和抗高血压活性[19-21]等。老山芹发挥降压作用的物质基础可能就是其中所含有的香豆素类化合物,为验证这一推测和阐明其中的降压活性成分,系统的化学成分研究和降压活性研究正在进行。
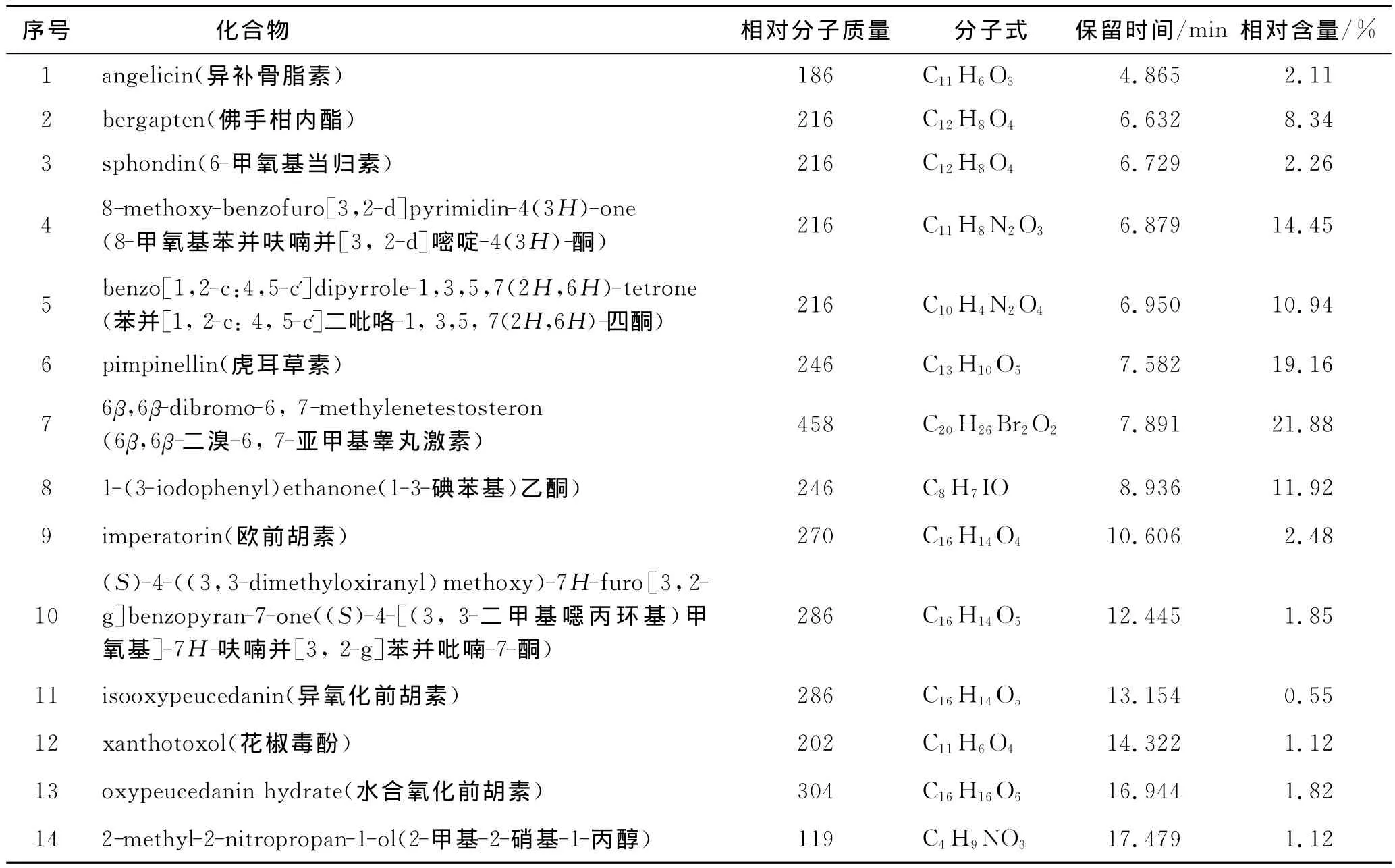
表2 氯仿部分化学成分分析结果Tab.2 Results of the chloroform fraction in the roots of Heracleum dissectum
市面上独活品种很多,主要来自伞形科当归属和独活属植物,而这2个属的主要化学成分为香豆素类,目前已经从不同品种的独活中分离得到的香豆素类化合物达70多种[22-23]。通过 GC-MS分析得知,老山芹根中的化学成分绝大多数为香豆素类化合物,这不仅为老山芹的归属提供了依据,同时也为老山芹的开发利用奠定了实验基础。
[1]刘继德,谭玉琴,姜诚,等.老山芹人工栽培及食用方法[J].中国农学通报,1997,13(2):46-47.
[2]张学政,崔文革,李洪贤,等.野生蔬菜——老山芹人工栽培技术[J].林业实用技术,2009,(2):39.
[3]刘瑾.西南地区独活属(HercleumL.)系统学研究[D].成都:四川大学.2007.
[4]Bourinbaiar A S,Tan X,Nagoruy R,et al.Effect of the oral anticoagulant,warfarin,on HIV-1replication and spread[J].AIDS,1993,7(1):129-130.
[5]Tummino P J,Fergusion D,Hupe D.Competitive inhibition of HIV-1protease by warfarin derivatives[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,1994,201(1):290-294.
[6]Romines K R,Chrusciel R A.4-Hydroxypyrones and related templates as nonpeptidic HIV protease inhibitors[J].Curr Med Chem,1995,2(4):825-838.
[7]Skulnick H I,Johnson P D,Aristoff P A,et al.Structure-based design of nonpeptidic HIV protease inhibitors:the sulfonamide-substituted cyclooctylpyramones[J].J Med Chem,1997,40(7):1149-1164.
[8]Kokubun T,Veitch N C,Bridge P D,et al.Dihydroisocoumarins and a tetralone fromCytospora eucalypticola[J].Phytochemistry,2003,62(5):779-782.
[9]Kwon Y S,Kobayashi A,Kajiyama S,et al,Antimicrobial constituents of Angelica dahurica roots[J].Phytochemistry,1997,44(5):887-889.
[10]Urdangarin C,Regente M C,Jorrin J,et al.Sunflower coumarin phytoalexins inhibit the growth of the virulent pathogen Sclerotinia sclerotiorum[J].J Phytophathol,1999,147(7):441-443.
[11]Tada Y,Shikishima Y,Takaishi Y,et al.Coumarins and gamma-pyrone derivatives fromPrangos pabularia:antibacterial activity and inhibition of cytokine release[J].Phytochemistry,2002,59(6):649-654.
[12]Mizuno A,Takata M,Okada Y,et al.Structures of new coumarins and antitumor-promoting activity of coumarins from Angelica edulis[J].Plata Medica,1994,60(4):333-336.
[13]Oikawa T,Sasaki M,Inose M,et al.Effects of cytogenin,a novel microbial product,on embryonic and tumor cell-induced angiogenic responses in vivo[J].Anticancer Res,1997,17(3C):1881-1886.
[14]张庆林,赵精华,毕建进,等.蛇床子中3种逆转肿瘤细胞多药耐药活性香豆素[J].中草药,2003,34(2):104-106.
[15]Morita H,Dota T,Kobayashi J.Antimitotic activity of glaupalol-related coumarins from Glaucidium palmatum[J].Bioorg Med Chem Lett,2004,14(14):3665-3668.
[16]Kummala T,Vuorela P,Johansson S,et al.Inhibitory activity of a series of coumarins on neutrophil eleastase secretion induced by platelet activating factor(PAF)and the chemotactic peptide fMLP[J].Pharm Pharmacol Lett,1998,8(3):144-147.
[17]Fernandez-Puntero B,Barroso I,Iglesias I,et al.Antioxidant activity of fraxetin:in vivo and ex vivo parameters in normal situation versus induced stress[J].Biol Pharm Bull,2001,24(7):777-784.
[18]Yun B S,Lee I K,Ryoo I J,et al.Coumarins with monoamine oxidase inhibitory activity and antioxidative coumarino-lignans from Hibiscus syriacus[J].J Nat Prod,2001,64(9):1238-1240.
[19]Nguelefack-Mbuyo P E,Nguelefack T B,Dongmo A B,et al.Anti-hypertensive effects of the methanol/methylene chloride stem bark extract of Mammea africana in l-NAME-induced hypertensive rats [J].J Ethnopharmacol,2008,117(3):446-450.
[20]Tchamadeu M C,Dzeufiet P D D,Nouga C C K,et al.Hypoglycaemic effects of Mammea africana (Guttiferae)in diabetic rats[J].J Ethnopharmacol,2010,127(2):368-372.
[21]Fort D M,Rao K,Jolad S D,et al.Antihyperglycemic activity of Teramnus labialis(Fabaceae)[J].Phytomedicine,2000,6(6):465-467.
[22]王长岱,乔博灵,赵晓文,等.香独活化学成分的研究[J].西北药学杂志,1989,4(4):17-19.
[23]柳江华,徐绥绪,姚新生.独活的化学成分与药理研究进展[J].沈阳药学院学报,1994,59(2):143-150.
