市售DPP 4抑制剂类抗糖尿病药物的比较研究*
2014-08-06崔立迁
王 欣,崔立迁
(1.天津生物工程职业技术学院,天津 300462; 2.天津市产品质量监督检测技术研究院天津 300384)
随着人们饮食和生活化方式的改变,糖尿病患者数量在不断增加。全世界现有糖尿病患者约1.94亿,据世界卫生组织统计,预计到2030年,糖尿病患病人数将升至3.66亿。肠促胰岛素(GLP-1)因其有促进β-细胞分化、抑制胃排空等多种功能,被认为是治疗糖尿病很有前景的新药之一。但是DPP-4可以快速地使GLP-1失活,所以应用受到限制。近年来,研究发现DPP-4抑制剂可以成功抑制DPP-4活性,促进β-细胞再生,抑制β-细胞凋亡,DPP-4因此成为了治疗2型糖尿病新的靶点,DPP-4抑制剂成为治疗糖尿病的新药。自从2006年第一个DPP-4抑制剂西格列汀(sitagliptin)上市以来[1],越来越多的证据表明DPP-4抑制剂是糖尿病治疗的一个重大突破。目前,欧洲医药管理局已经批准西格列汀、维格列汀(vildagliptin)[2]、沙格列汀(saxagliptin)[3]和利格列汀(linagliptin)[4]四个DPP-4抑制剂用于2型糖尿病的临床治疗。在美国被批准上市的DDP-4抑制剂包括西格列汀、沙格列汀和利格列汀。2010年,阿格列汀(alogliptin)[5]在日本上市。次年,利格列汀也取得在日本的上市许可。目前这五种抑制剂均已在中国取得上市许可。另外,dutogliptin和gemigliptin等DPP-4抑制剂正在进行临床研究。不久的将来,会有更多的DPP-4抑制剂应用于2型糖尿病的临床治疗。因此,研究这些抑制剂之间的差别对于糖尿病治疗的临床用药显得格外重要。
1 结构差异
DPP-4抑制剂结构多样,根据其核心骨架将其分为肽类和非肽类两大类。肽类抑制剂包括西格列汀、沙格列汀和维格列汀,其中前者以β-丙氨酸为基本骨架,而后两者以α-甘氨酸为基本骨架(图1)。非肽类抑制剂包括利格列汀和阿格列汀,骨架分别为含氮杂环黄嘌呤和嘧啶二酮。其结构上的差别导致与DPP-4结合时有不同的结合方式。西格列汀、利格列汀和阿格列汀通过非共价键与DPP-4结合[6-8]。而维格列汀和沙格列汀则通过共价方式与DPP-4结合,即通过吡咯烷上的氰基与DPP-4形成一个可逆的共价络合物[9,10]。在体内,共价键的形成和解离过程是缓慢的,这导致有活性的和被抑制的DPP-4在体内缓慢达到平衡,并最终导致即使在抑制剂排空以后,DPP-4仍然会被抑制。这也就是沙格列汀和维格列汀对DPP-4的抑制时间超过了各自半衰期的原因。
2 药物动力学和药效差异
已上市的这五种抑制剂均是口服药物,可以被人体快速吸收。大部分DPP-4抑制剂在人体内的口服利用率均较高,其中西格列汀约为87%,维格列汀约为85%,沙格列汀约为67%,阿格列汀约为70%。利格列汀的口服利用率却偏低,只有约30%。在半衰期方面,也各不相同。维格列汀[11]和沙格列汀[12]半衰期较短,分别只有1.5 ~4.5 h和2 ~4 h,西格列汀、阿格列汀和利格列汀的半衰期则较长[13-15]。这导致各药在用药剂量和用药频率上有所差别,用药剂量从5~100 mg不等。除维格列汀外,大部分抑制剂每日只需1次给药,15 min内DPP-4抑制率超过90%,24 h内抑制率70% ~90%。而维格列汀每日1次用药,剂量为50 mg,24 h内DPP-4抑制率仅为50%。若每日给药2次,每次剂量为50 mg,24 h内抑制率则大于80%。
3 选择性
DPP-4是蛋白酶家族的一员,与之相似的有DPP-2、DPP-8以及DPP-9。尽管目前还没有一个抑制剂对一系列不同的酶均表现出很高的抑制活性,但是为了避免潜在的副作用,高选择性还是必要的。从表1可以看出,西格列汀对DPP-2、DPP-8以及DPP-9均有很高的选择性[6]。维格列汀虽然对DDP-2的选择性非常好,但是对DPP-8以及DPP-9的选择性却很低,分别为270和32[16]。沙格列汀也存在同样的问题,对DPP-2、DPP-8以及DPP-9的选择性分别为 >50 000、390和77[17]。相比之下,阿格列汀和利格列汀对DPP-2、DPP-8以及DPP-9的选择性都非常高[7,18]。
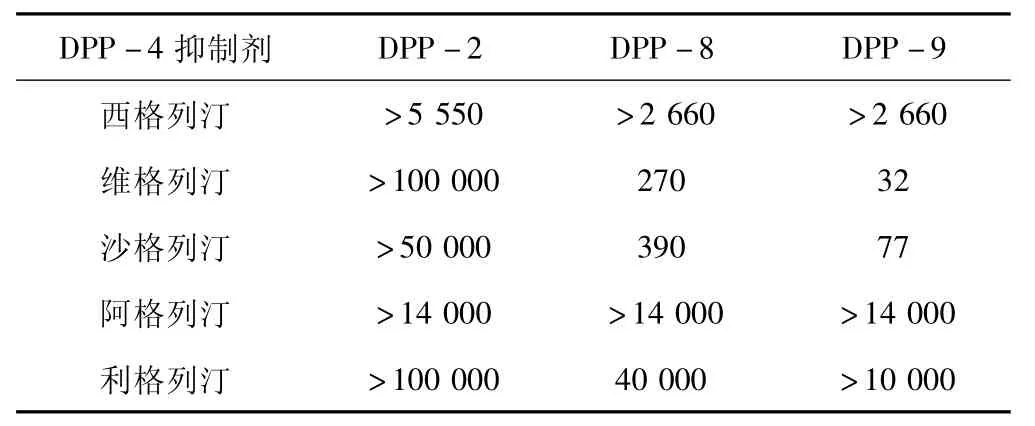
表1 DPP-4抑制剂的体外选择性
4 代谢与排泄
DPP-4抑制剂在人体内代谢和排泄方式不尽相同。如西格列汀、利格列汀和阿格列汀在人体内只有很小一部分进行代谢,约有79%的西格列汀以母体化合物形式通过尿液排出体外[19]。小于20%西格列汀在体内进行代谢生成6个代谢产物,其中三个是有活性的。但是由于这些代谢产物在血浆中的浓度过低,不会对西格列汀药物动力学产生影响。与西格列汀相似,阿格列汀也只有小于20%在体内进行代谢,80%左右的阿格列汀以母体化合物形式排出体外,其中60% ~70%通过尿液排泄[14]。利格列汀则有30%左右进行代谢,CD1790是其主要代谢产物,占18%左右[20]。利格列汀与前两个抑制剂的排泄方式有所不同,大约78%的利格列汀随粪便排出,只有小于5%部分随尿液排出。
维格列汀和沙格列汀在体内大部分会被降解,维格列汀的代谢途径主要是通过CYP450将其氰基水解为羧基(M20.7/LAY151)[21]。这种代谢产物占到维格列汀总量的55%。维格列汀主要由肾脏进行排泄,尿液中包含20%左右的母体化合物和50%左右的主要代谢产物。沙格列汀主要在肝脏内进行降解,被CYP 3A4/5氧化为5-羟基沙格列汀(BMS-510849),该代谢产物是一个可逆的DPP-4抑制剂,活性大约为母体化合物的50%。大约有22%沙格列汀和36%的BMS-510849最终通过肾脏排出体外[22]。
从上面的数据可以看出,除了利格列汀以外,其他抑制剂均要经肾脏进行排泄,因此肾功能不全必定会影响这些药物的使用。对于轻微肾功能不全的糖尿病患者,上述五种抑制剂可以按照常规剂量用药,不需要做出调整。但是对于中度或者严重的肾功能不全的糖尿病患者,剂量要相应的调整为常规用量的1/2或1/4。比如,沙格列汀在治疗伴有中度或者严重的肾功能不全的糖尿病患者时,用量要从5 mg/d降低为2.5 mg/d[22]。阿格列汀对于中度肾功能不全的糖尿病患者调整为正常用量的1/2(常规用量25 mg/d),对于严重肾功能不全的糖尿病患者则要进一步降低为正常用量的1/4[23]。如果使用利格列汀来治疗肾功能不全的糖尿病患者,用药剂量则不需要调整,这是由于利格列汀主要通过肝脏来代谢[24]。与之相反,在治疗轻微或中度肝功能不全的糖尿病患者时,西格列汀、沙格列汀和阿格列汀使用剂量不需要调整。而维格列汀则不推荐使用,原因为其可以升高转氨酶。利格列汀目前还需要更多的临床数据来确定其是否可以用于这类糖尿病患者。
5 药物相互作用
DPP-4抑制剂在大多数情况下不会与常见处方药发生相互作用。但维格列汀与硫脲合用时,为降低引发低血糖症的风险,维格列汀的用量要减为1/2。另外,在上文中提到CYP3A4/5可以降解沙格列汀,若其与CYP3A4/5抑制剂同时使用,如苯并二氢呋喃酮,其会提高沙格列汀在血浆中的浓度,所以若这两个药物同时使用,要降低沙格列汀的用量。虽然利格列汀也会被CYP3A4降解,但是由于利格列汀主要经肝脏进行代谢,抑制或刺激CYP3A4的药物不会影响利格列汀在血浆中的的浓度以及其对DPP-4的抑制活性[20]。
6 不良反应
6.1 头痛 已上市的DPP-4抑制剂都存在轻微增加头痛的副作用。临床数据显示使用维格列汀的糖尿病患者出现头痛的比率为 7.0%,而对照组为6.0%[25];使用沙格列汀的患者头痛比例为 6.5%,安慰剂组则为5.9%;接受利格列汀治疗的糖尿病患者头痛比例为5.7%,而接受glimepiride治疗的对照组为4.2%;使用阿格列汀的患者出现头痛的比例为5.6%,安慰剂组仅为3.0%[26]。同样,西格列汀的大量临床数据表明,使用西格列汀出现头痛的为5.8%,对照组为 5.6%[27]。
6.2 低血糖 低血糖症是很多口服降糖药的一个重要缺陷,尤其是硫脲类降糖药,其引起低血糖的风险是二甲双胍的3倍[28]。但是DPP-4抑制剂却与之相反,引起低血糖的风险非常低。一项为期2年、多中心、随机、双盲临床试验表明,使用维格列汀导致低血糖症的几率为 0.7%,低于甲磺双环脲(1.7%)[29]。西格列汀和二甲双胍联用疗法出现低血糖症状的几率(5%)远低于格列吡嗪与二甲双胍联用(32%)[30]。另一项沙格列汀和格列本脲的对照试验表明,在治疗中确认的低血糖症病例两者没有明显差别[31]。同样,阿格列汀与胰岛素联合治疗与使用安慰剂的对照组引起低血糖症的比例相似(24%vs27%)[32]。
6.3 急性胰腺炎 一项为期1年的调查表明,接受二甲双胍与接受西格列汀治疗的糖尿病患者中急性胰腺炎的住院率是相当的[33]。Garg等[35]总结2007年1月—2009年6月的数据也得到相似的结果,接受西格列汀治疗和非西格列汀的患者中患急性胰腺炎的几率相当。与之相反的是,Elashoff等[36]却发现使用西格列汀和GLP-1拮抗剂来治疗糖尿病与使用其他药物相比具有很高的患急性胰腺炎的几率。在利格列汀的临床试验中,患急性胰腺炎的比例为0.23%,而使用安慰剂的对照组没有出现[26]。
6.4 心血管病 心血管病是很多新药研发关注的重点,FDA目前已经要求药物公司必须证实其所研发的药物不会增加心血管病的风险。DPP-4抑制剂除了可以降低血糖和维持体重,还可以在一定程度上降低心脏收缩压。西格列汀能够连续24 h降低轻微高血压非糖尿病患者的血压2~3 mmHg,并且可以降低心脏收缩压[36]。最近研究还发现,DPP-4抑制剂可以改善餐后血脂水平。一项为期6周的临床试验表明,西格列汀有助于促进激素分泌,降低血液中脂肪酸浓度,改善β-细胞功能,从而降低餐后血浆中的甘油三酸酯的浓度[37]。另外一项为期4周的实验发现,在食用高脂肪食物后,维格列汀有助于改善甘油三酸酯和阿朴脂蛋白 B-48的代谢,从而实现降低餐后血脂[38]。但是DPP-4抑制剂促进餐后血脂代谢的作用机制还有待于进一步的研究。
自从2006年西格列汀上市以来,先后有5个不同的DPP-4抑制剂在不同地区上市用于治疗2型糖尿病。目前,已上市的DPP-4抑制剂除了在使用剂量和适用人群上有些差别,在抗糖尿病的效率和安全性等方面没有明显的差别。那么这些化合物在结构上的差异是否会造成其他的临床应用的不同,还需要更长期的临床数据的积累。
1 Dhillon S.Sitagliptin: a review of its use in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus[J].Drugs,2010,70(4): 489-512
2 Keating G M.Vildagliptin:a review of its use in type 2 diabetes mellitus[J].Drugs,2010,70(16): 2089-2112
3 Kania D S,Gonzalvo J D,Weber Z A.Saxagliptin:a clinical review in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus[J].Clin Ther,2011,33(8):1005-1022
4 Scott L J.Linagliptin: in type 2 diabetes mellitus[J].Drugs,2011,71(5):611-624
5 Scott L J.Alogliptin: a review of its use in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus[J].Drugs,2010,70(15): 2051-2072
6 Kim D,Wang L,Beconi M,et al.(2R)-4-Oxo-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-5,6-dihydro 1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazin-7(8H)-yl]-1-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butan-2-amine: a potent,orally active dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes[J].J Med Chem,2005,48(1):141-151
7 Feng J,Zhang Z,Wallace M B,et al.Discovery of alogliptin: a potent,selective,bioavailable,and efficacious inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase IV[J].J Med Chem,2007,50(10):2297-2300
8 Eckhardt M,Langkopf E,Mark M,et al.8-(3-(R)-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-7-but-2-ynyl-3-methyl-1-(4-methyl-quinazolin-2-ylmethyl)-3,7-dihydro-purine-2,6-dione(BI 1356),a highly potent,selective,long-acting,and orally bioavailable DPP-4 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes[J].J Med Chem,2007,50(26):6450-6453
9 Brandt I,Joossens J,Chen X,et al.Inhibition of dipeptidyl-peptidase IV catalyzed peptide truncation by Vildagliptin((2S)-{[(3-hydroxyadamantan-1-yl)amino]acetyl}-pyrrolidine-2-carbonitrile) [J].Biochem Pharmacol,2005,70(1): 134-143
10 Kim Y B,Kopcho L M,Kirby M S,et al.Mechanism of Gly-PropNA cleavage catalyzed by dipeptidyl peptidase-IV and its inhibition by saxagliptin(BMS-477118) [J].Arch Biochem Biophys,2006,445(1):9-18
11 He Y L,Wang Y,Bullock J M,et al.Pharmacodynamics of vildagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes during OGTT[J].J Clin Pharmacol,2007,47(5): 633-641
12 Boulton D W,Geraldes M.Safety,tolerability,pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of once daily oral doses of saxagliptin for 2 weeks in type 2 diabetic and healthy subjects(Poster 0606-P) [J].Diabetes,2007,56(s1):A161
13 Bergman A J,Stevens C,Zhou Y,et al.Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of multiple oral doses of sitagliptin,a dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitor: a double-blind,randomized,placebo-controlled study in healthy male volunteers[J].Clin Ther,2006,28(1):55-72
14 Covington P,Christopher R,Davenport M et al.Pharmacokinetic,pharmacodynamic,and tolerability profiles of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor alogliptin: a randomized,double-blind,placebo-controlled,multiple-dose study in adult patients with type 2 diabetes[J].Clin Ther,2008,30(3):499-512
15 Heise T,Graefe-Mody E U,H üttner S,et al.Pharmacokinetics,pharmacodynamics and tolerability of multiple oral doses of linagliptin,a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor in male type 2 diabetes patients[J].Diabetes Obes Metab,2009,11(8):786-794
16 Burkey B F,Hoffmann P K,Hassiepen U,et al.Adverse effects of dipeptidyl peptidases 8 and 9 inhibition in rodents revisited[J].Diabetes Obes Metab,2008,10(11):1057-1061
17 Kirby M S,Dorso C,Wang A,et al.In vitro enzymologic characteristics of saxagliptin,a highly potent and selective DPP4 inhibitor with“slow binding”characteristic(Abstract) [J].Clin Chem Lab Med,2008,46: A79.
18 Thomas L,Eckhardt M,Langkopf E,et al.(R)-8-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-7-but-2-ynyl-3-methyl-1-(4-methylquinazolin-2-ylmethyl)-3,7-dihydro-purine-2,6-dione(BI 1356),a novel xanthine-based dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor,has a superior potency and longer duration of action compared with other dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors[J].J Pharmacol Exp Ther,2008,325(1):175-182
19 Vincent S H,Reed J R,Bergman A J,et al.Metabolism and excretion of the dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor[14C]sitagliptin in humans[J].Drug Metab Dispos,2007,35(4): 533-538
20 Blech S,Ludwig-Schwellinger E,Gräfe-Mody E U,et al.The metabolism and disposition of the oral dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor,linagliptin,in humans[J].Drug Metab Dispos,2010,38(4):667-678
21 He H,Tran P,Yin H,et al.Absorption,metabolism,and excretion of[14C]vildagliptin,a novel dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor,in humans[J].Drug Metab Dispos,2009,37(3): 536-544
22 Fura A,Khanna A,Vyas V,et al.Pharmacokinetics of the dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor saxagliptin in rats,dogs,monkeys and clinical projections[J].Drug Metab Dispos,2009,37(6): 1164-1171
23 Karim A,Fleck P,Hetman L,et al.Single-dose pharmacokinetics of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor alogliptin in subjects with renal impairment[J].Diabetes,2008,57(s1): A160:538
24 Graefe-Mody U,Friedrich C,Port A,et al.Linagliptin,a novel DPP-4 inhibitor:no need for dose adjustment in patients with renal impairment(Abstract 822) [J].Diabetologia,2010,53(s 1): s326
25 Schweizer A,Dejager S,Foley J E,et al.Assessing the general safety and tolerability of vildagliptin:value of pooled analyses from a large safety database versus evaluation of individual studies[J].Vasc Health Risk Manag,2011,7:49-57
26 Mikhail N.Safety of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors for treatment for type 2 diabetes[J].Curr Drug Safety,2011,6(5): 304-309
27 Williams-Herman D,Engel S S,Round E,et al.Safety and tolerability of sitagliptin in clinical studies:a pooled analysis of data from 10246 patients with type 2 diabetes[J].BMC Endocr Disord,2010,10: 7
28 Bodmer M,Meier C,Krähenbühl S,et al.Metformin,sulfonylureas,or other antidiabetes drugs and the risk of lactic acidosis or hypoglycemia: a nested case-control analysis[J].Diabetes Care,2008,31(11):2086-2091
29 Foley J E,Sreenan S.Efficacy and safety comparison between the DPP-4 inhibitor vildagliptin and the sulfonylurea gliclazide after two years of monotherapy in drug-na?ve patients with type 2 diabetes[J].Horm Metab Res,2009,41(12): 905-909
30 Nauck M A,Meininger G,Sheng D,et al.Sitagliptin Study 024 Group.Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor,sitagliptin,compared with the sulfonylurea,glipizide,in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin alone:a randomized,double-blind,non-inferiority trial[J].Diabetes Obes Metab,2007,9(2):194-205
31 Chacra A R,Tan G H,Apanovitch A,et al.CV181-040 Investigators.Saxagliptin added to a submaximal dose of sulphonylurea improves glycaemic control compared with uptitration of sulphonylurea in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomised controlled trial[J].Int J Clin Pract,2009,63(9): 1395-1406
32 Rosenstock J,Rendell M S,Gross J L,et al.Alogliptin added to insulin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes reduces HbA1c without causing weight gain or increased hypoglycemia[J].Diabetes Obes Metab,2009,11(12):1145-1152
33 Dore D D,Seeger J D,Arnold Chan K.Use of a claims-based active drug safety surveillance system to assess the risk of acute pancreatitis with exenatide or sitagliptin compared to metformin or glyburide [J].Curr Med Res Opin,2009,25(4):1019-1027
34 Garg R,Chen W,Pendergrass M.Acute pancreatitis in type 2 diabetes treated with exenatide or sitagliptin:a retrospective observational pharmacy claims analysis[J].Diabetes Care,2010,33(11):2349-2354
35 Elashoff M,Matveyenko A V,Gier B,et al.Pancreatitis,pancreatic,and thyroid cancer with glucagon-like peptide-1 based therapies[J].Gastroenterology,2011,141(1): 150-156
36 Mistry G C,Maes A L,Lasseter K C,et al.Effect of sitagliptin,a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor,on blood pressure in nondiabetic patients with mild to moderate hypertension[J].J Clin Pharmacol,2008,48(5):592-598
37 Tremblay A J,Lamarche B,Deacon C F,et al.Effect of sitagliptin therapy on postprandial lipoprotein levels in patients with type 2 diabetes[J].Diabetes Obes Metab,2011,13(4):366-373
38 Matikainen N,Manttari S,Schweizer A,et al.Vildagliptin therapy reduces postprandial intestinal triglyceride-rich lipoprotein particles in patients with type 2 diabetes[J].Diabetologia,2006,49(9):2049-2057
