考虑硬件损伤和非理想信道的鲁棒多小区多用户协同波束形成技术
2014-05-30何世文鲁照华黄永明杨绿溪
汪 汉 何世文 鲁照华 黄永明* 杨绿溪
考虑硬件损伤和非理想信道的鲁棒多小区多用户协同波束形成技术
汪 汉①何世文①鲁照华②黄永明*①杨绿溪①
①(东南大学信息科学与工程学院 南京 210096)②(中兴通讯股份有限公司 深圳 518000)

无线通信;信道误差;收发机损伤;鲁棒协同波束形成;凸优化
1 引言
多输入多输出(Multiple Input Multiple Output, MIMO)技术因其能够显著提高系统容量、改善通信质量而受到产业界和学术界的广泛关注。但是已有的文献主要集中在不考虑收发机损伤及信道误差的理想状况下的无线通信传输技术,比如多用户MIMO,线性波束形成技术等。

上述文献研究中通常只考虑信道误差或者硬件损伤,目前没有文献在算法设计中同时考虑这两个因素。本文将同时考虑信道不确定性和收发机损耗这两个非理想条件优化设计多小区多用户下行链路波束,在满足给定用户目标信干噪比要求下最小化发射功率。最后通过数值仿真对本文算法性能进行了验证与比较分析。
本文组织结构如下:第2节提出了下行多用户多小区的系统模型;第3节提出两种波束形成技术,并将它们进行对比;第4节给出仿真结果;第5节总结全文。
2 系统模型

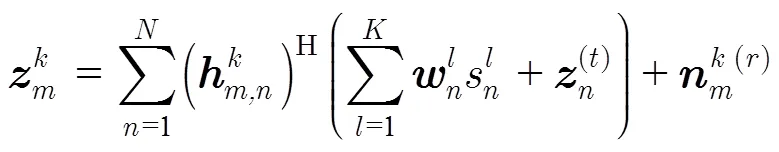
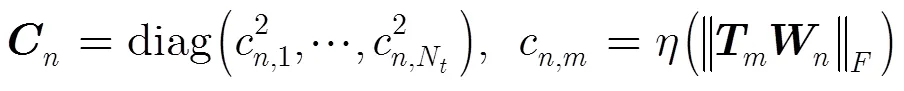
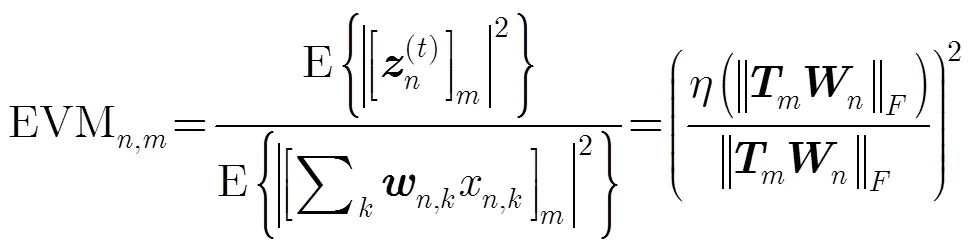


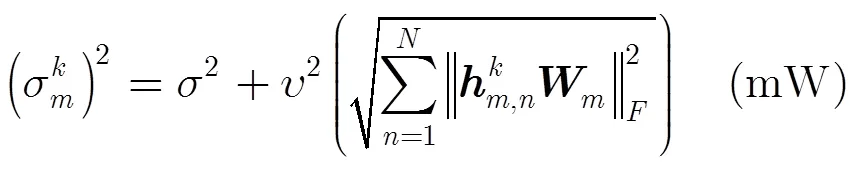
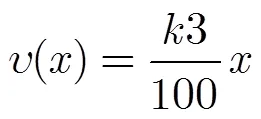
其中3表示接收端损伤系数,根据文献[15,20]的研究结果,3在[0,15]范围内比较合理。

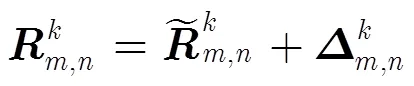
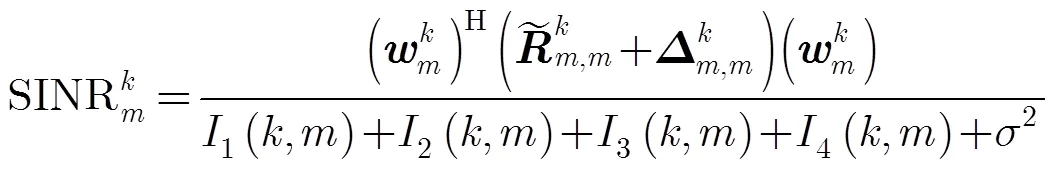
其中
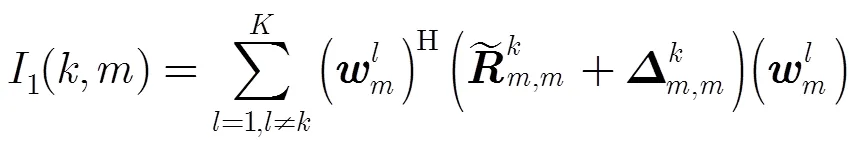
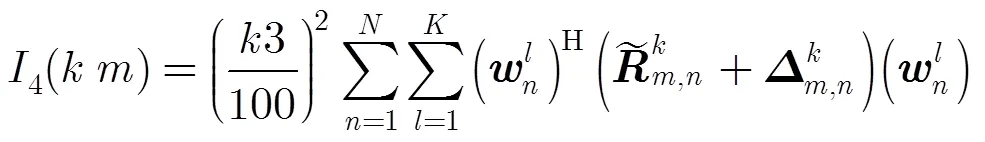
本文采用满足一定用户QoS要求的最小化总下行发射功率为优化目标;用数学表达式描述为以下两种形式:
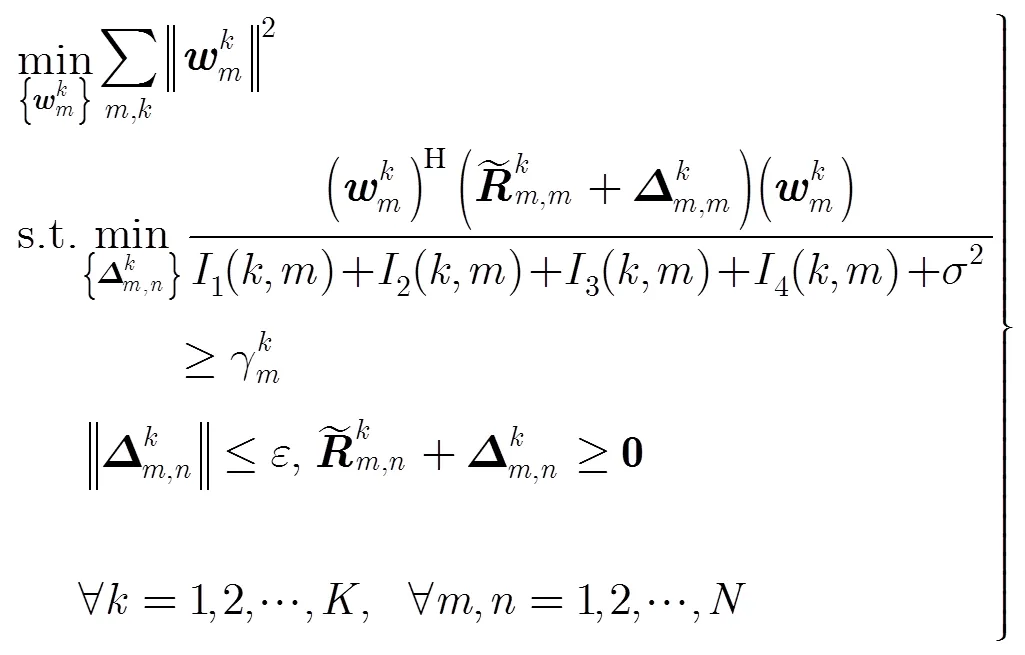
和

3 鲁棒的协同波束形成设计
优化问题式(9)和优化问题式(10)中的非凸鲁棒约束条件使这两个优化问题成为非凸优化问题,而且二者均是NP优化问题,通常很难获得其最优解。为了有效求解上述问题,下面先将上述两个优化问题中的非凸约束转换成凸约束,然后将原始优化问题转换成相对比较容易求解的形式。
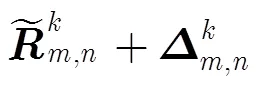

其中
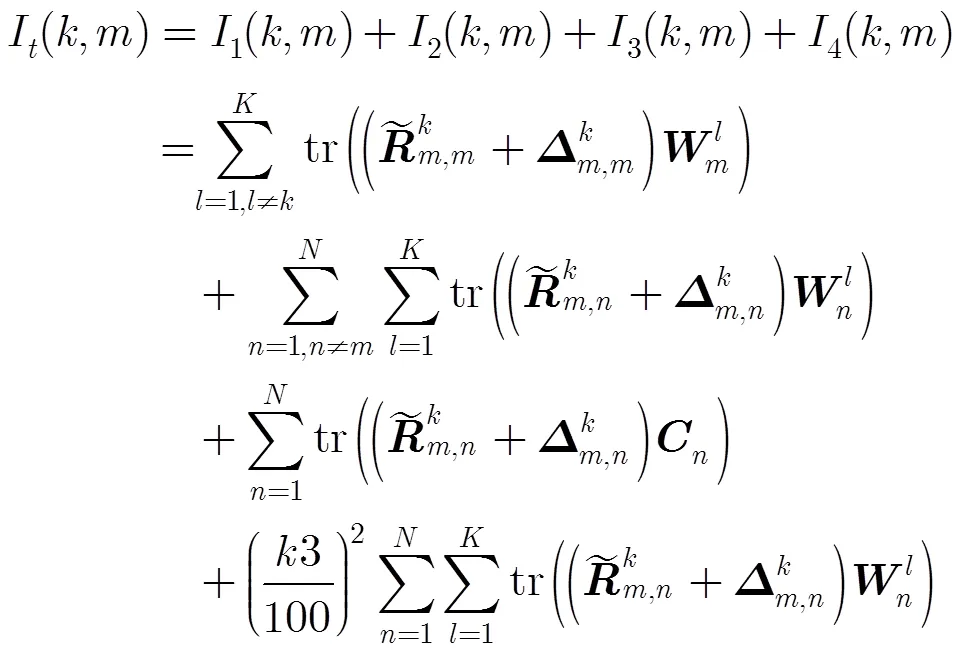
式(12)可以写成:
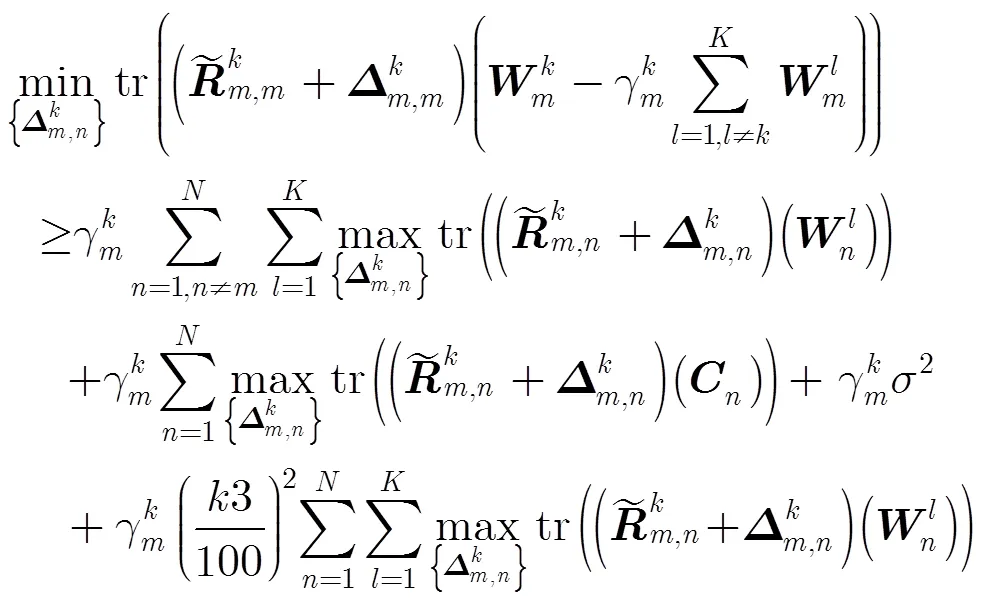
文献[11]的研究结果表明,式(13)可以等价为
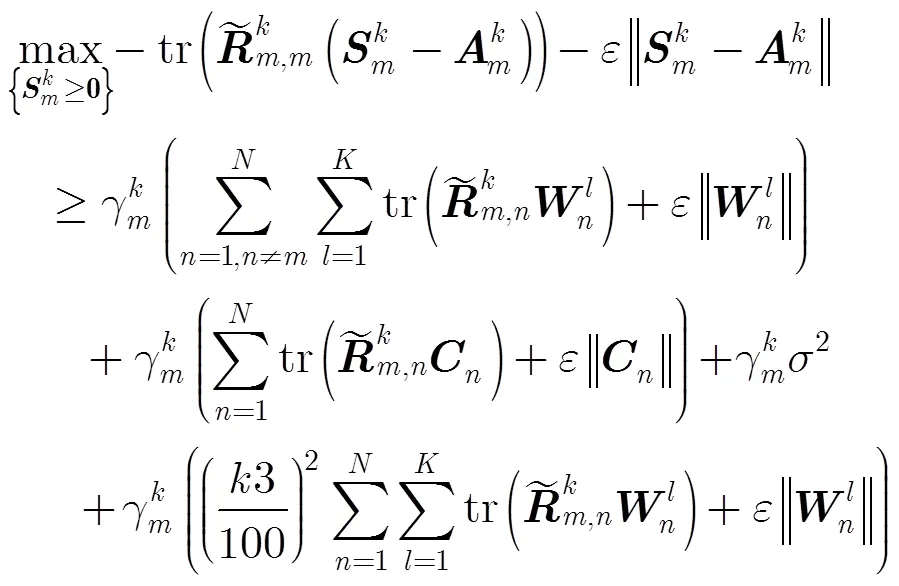
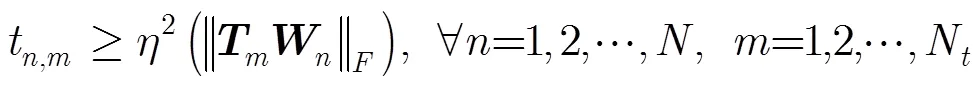
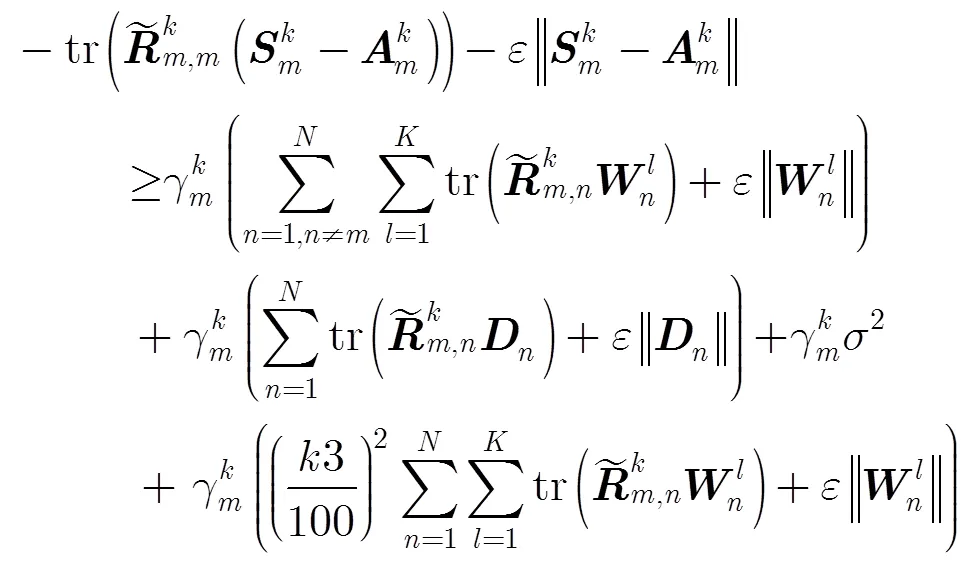
成立。
这样,非凸问题QoS约束可转换成凸约束式(16)和式(15),进而优化问题式(9)可以写成:
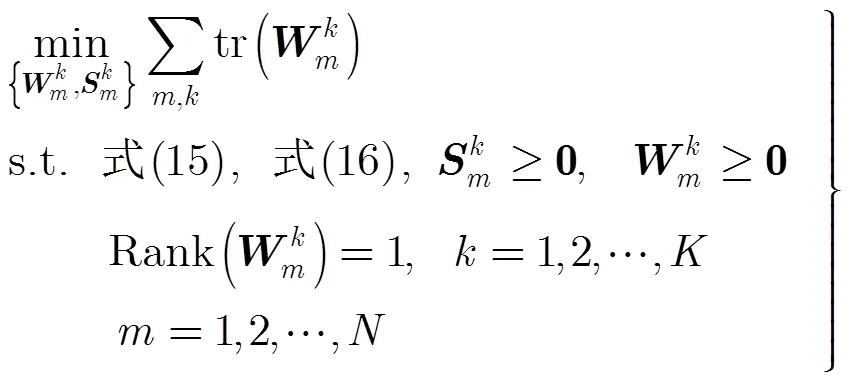
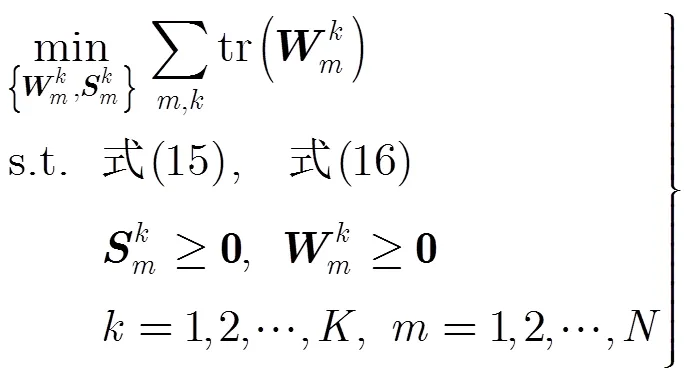

类似于优化问题式(9)中的QoS约束,优化问题式(10)中的QoS约束也是非凸约束,因此,也采用相似的思路将这个非凸约束转化成凸约束形式。式(10)可等价为
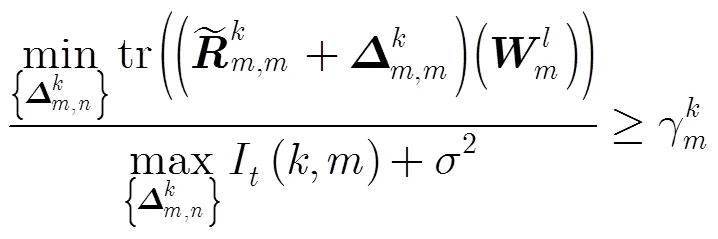

其中
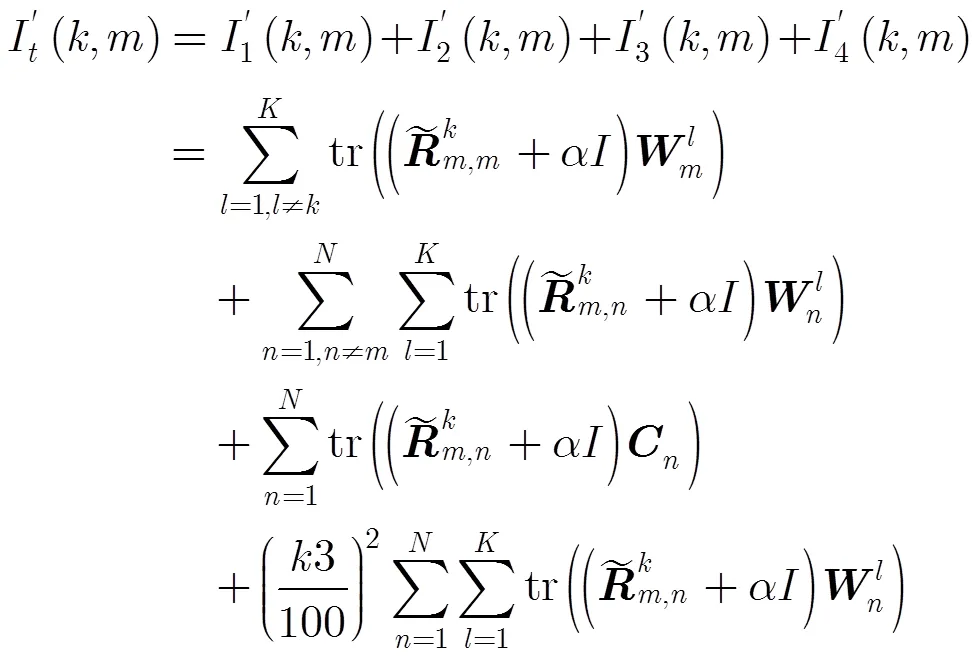
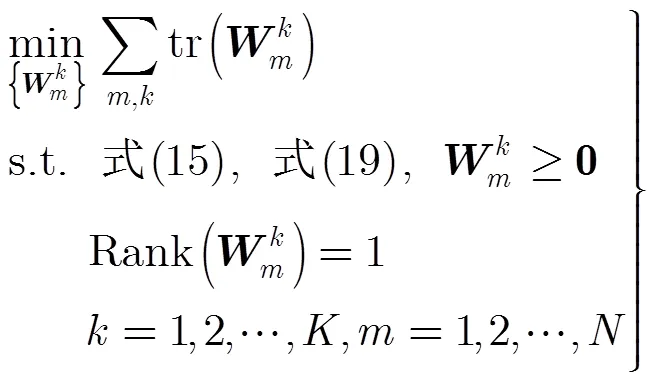
类似优化问题式(17),优化问题式(22)可以采用相似的方法求解,此求解方法称为算法2。
相对优化问题式(10)的鲁棒约束凸转化方法,在优化问题式(9)的鲁棒约束凸转化过程中多引入了正定矩阵变量,并且考虑了信道系数误差方差矩阵的半正定性,从SOCP算法复杂度分析可知算法1的复杂度要比算法2的复杂度高。由于算法1的优化问题是保证最差的情况满足目标SINR的要求,算法2的优化问题是系统性能的下界满足目标SINR的要求,所以算法2对系统条件要求更高。两种算法具体的差异可以在随后的仿真中看出,而在具体场景中选用哪种算法亦可根据实际情况和两种算法的特性来决定。
4 仿真分析


表1仿真参数[22]

参数数值参数数值 小尺度衰落阴影衰落的标准差8 dB 接收天线增益0 dB距离d的路损128.1+37.6lg(d)(km) 载频/下行带宽2 GHz /10 MHz穿入损失 (室内)20 dB 子载波数/带宽1/15 kHz噪声功率-127 dBm


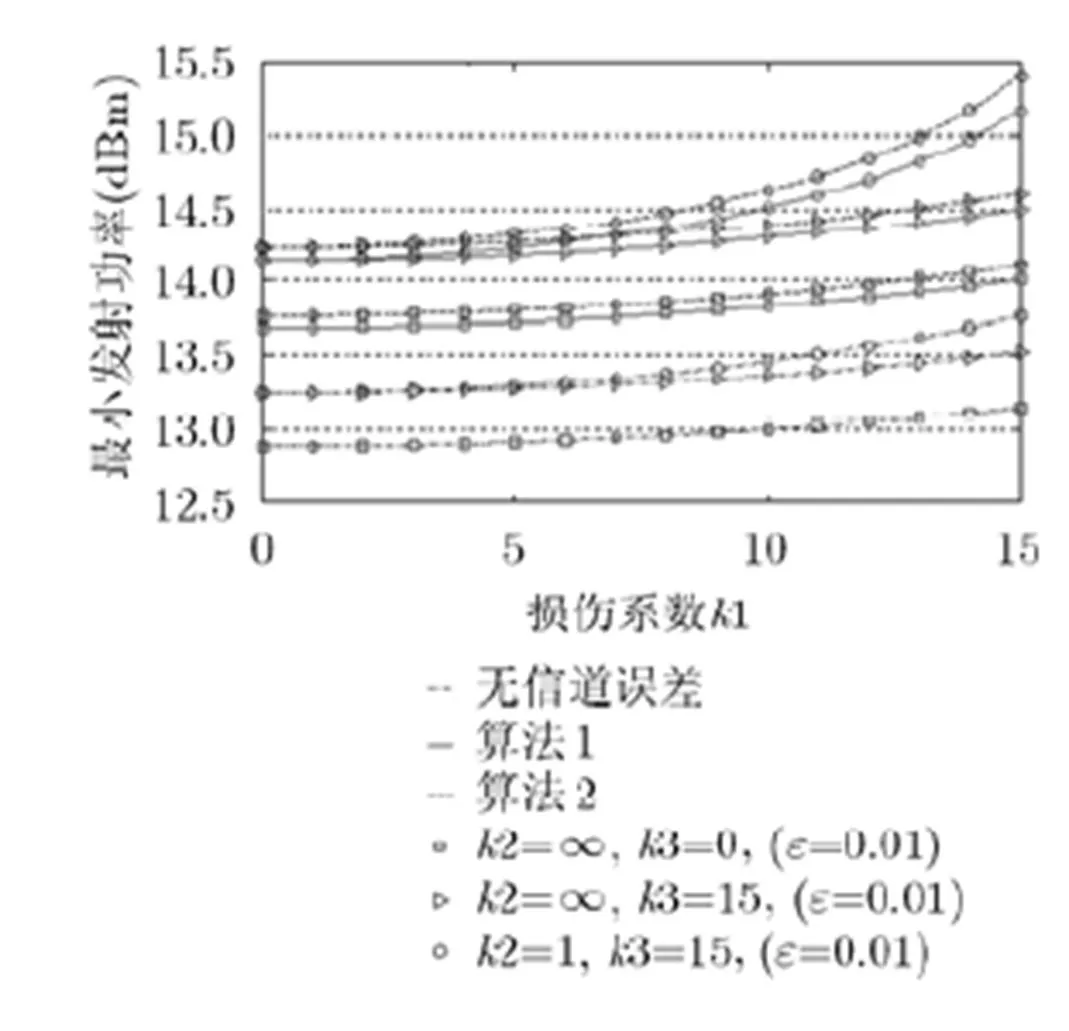
图1 损伤系数与最小发射功率对比图
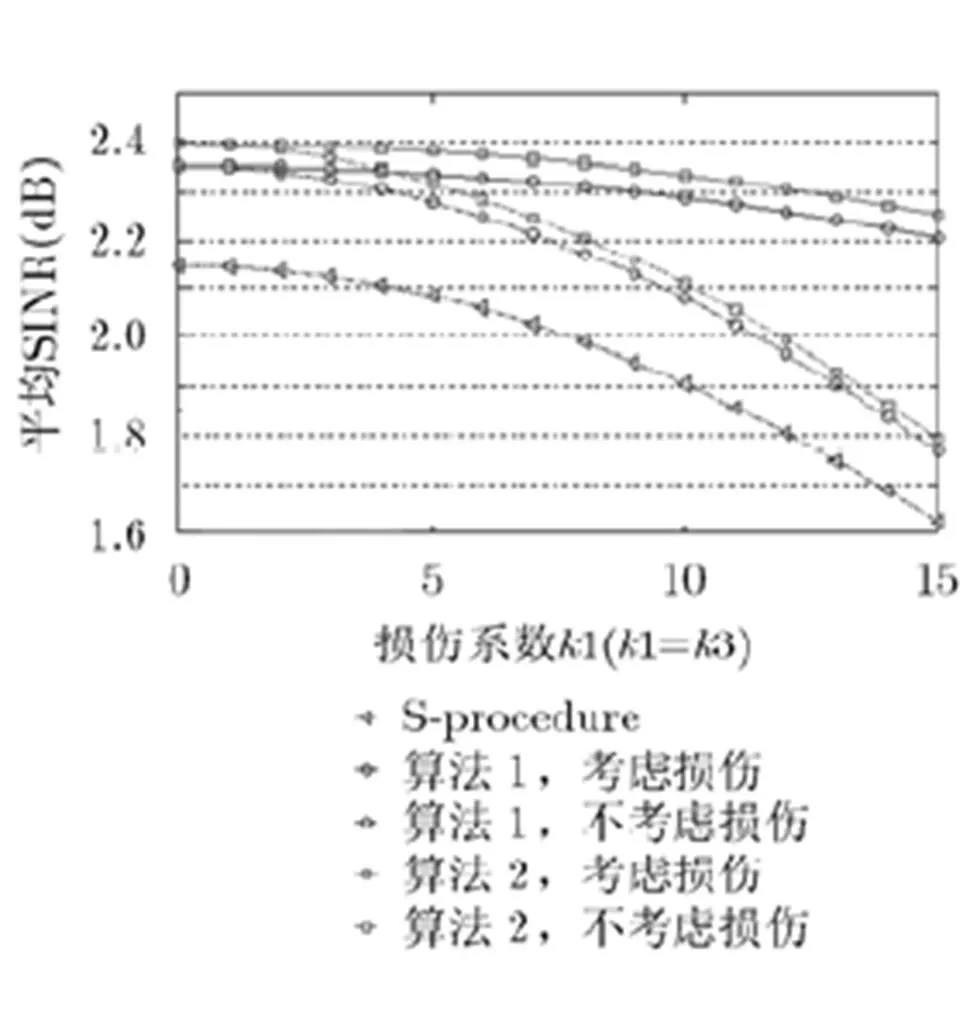
图2 损伤系数与实际SINR的对比图

图3 损伤系数与Worst-SINR的对比图
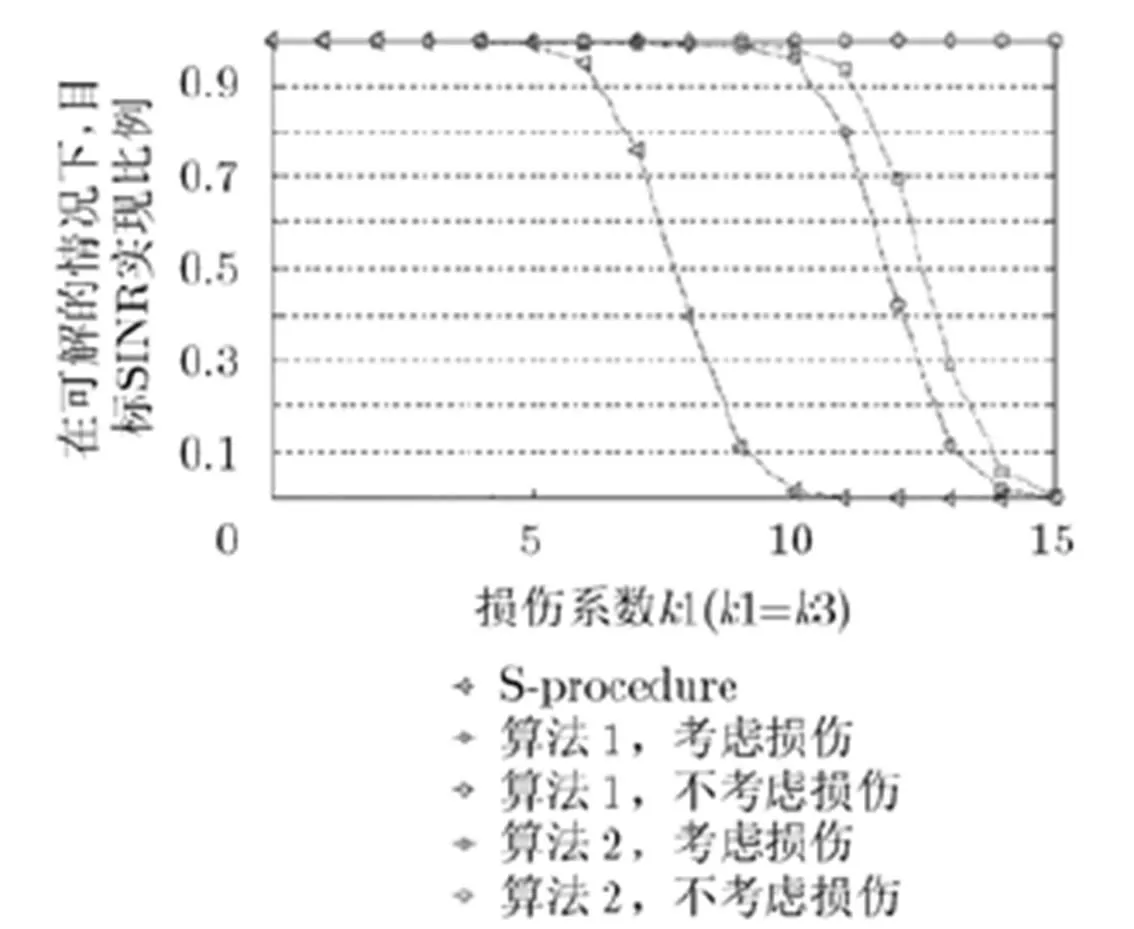
图4 损伤系数k1与目标SINR实现比例对比图
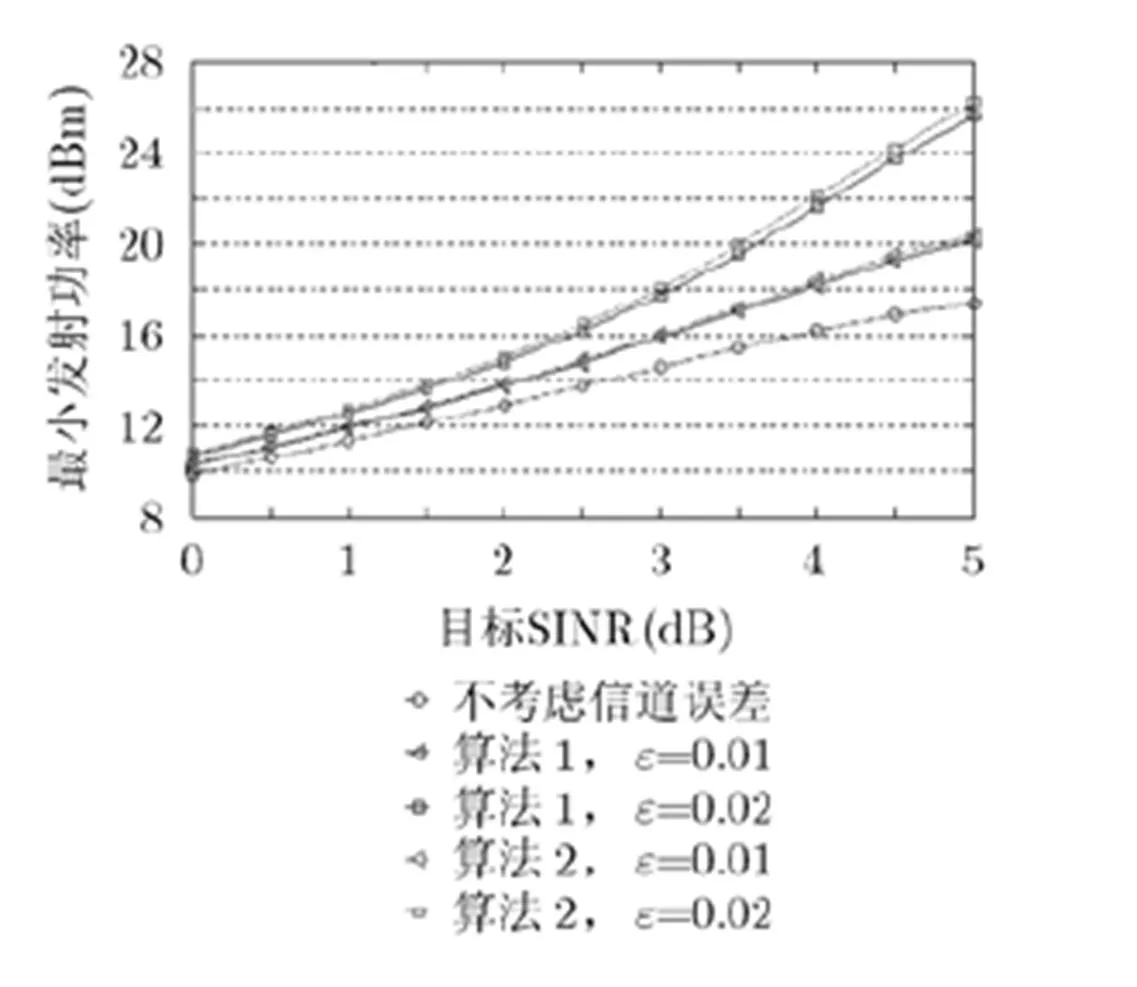
图5 目标SINR与最小发射功率的对比图
5 总结
针对多小区多用户多天线蜂窝系统,本文研究了同时考虑信道系数误差和收发机损伤的条件下两种不同鲁棒约束的最小化发射功率优化问题,进而采用了两种不同的方法将原始非凸约束转成了相应的凸约束,进而获得两个相对较容易的优化问题,接着利用秩释放方法求解原始优化问题,并获得两种优化算法。仿真分析表明,随着信道系数误差和收发机损伤的增加,所提出的两个优化算法所需要的最小发射功率也必须相应增加,用以克服误差和损伤带来的影响。算法2相对于算法1较为保守,所以后者相对前者所需的发射功率较小,可行解比例较大;但是算法复杂度高一些。
[1] Dahrouj H and Yu W. Coordinated beamforming for the multi-cell multi-antenna wireless system[J]., 2010, 9(5): 1748-1759.
[2] Huang Y, Yang L, and Liu J. A limited feedback SDMA for downlink of multiuser MIMO communication system[J]., DOI: 10. 1155/ 2008/ 947869.
[3] Huang Y, Yang L, Bengtsson M,. . Exploiting long-term channel correlation in limited feedback SDMA through channel phase codebook[J]., 2011, 59(3): 1217-1228.
[4] He S, Huang Y, Yang L,.. A multi-cell beamforming design by uplink-downlink max-min SINR duality[J]., 2012, 11(8): 2858-2867.
[5] Huang Y, Zheng G, Bengtsson M,.. Distributed multicell beamforming with limited intercell coordination[J]., 2011, 59(2): 728-738.
[6] Huang Y, Zheng G, Bengtsson M,.. Distributed multicell beamforming design approaching pareto boundary with max-min fairness[J]., 2012, 11(8): 2921-2933.
[7] Kim D, Vincent H, Park J,.. Outage probability and outage-based robust beamforming for MIMO interference channels with imperfect channel state information[J]., 2012, 11(10):3561-3573.
[8] Ma S and Sun D. Chance constrained robust beamforming in cognitive radio networks[J]., 2013, 17(1): 67-70.
[9] Yang J and Bengtsson M. Robust receive beamforming with interference and channel uncertainty[C]. IEEE Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications Conference, Sydney, 2012: 2231-2236.
[10] Shen C, Wang K, Chang T,.. Worst-case SINR constrained robust coordinated beamforming for multicell wireless systems[C]. IEEE International Conference, Kyoto, 2011: 1-5.
[11] Ponukumati D, Gao F, and Bode M. Robust multicell downlink beamforming based on second order statistics of channel state information[C]. Global Communications Conference, Houston, 2011: 1-5.
[12] Wajid I, Eldar Y, and Gershman A. Robust downlink beamforming for cognitive radio networks[C]. Global Communications Conference, Miami, 2010: 1-5.
[13] Moghadam N, Zetterberg P, Handel P,.. Correlation of distortion noise between the branches of MIMO transmit antennas[C]. IEEE Personal, Indoor, Mobile and Radio Communications Conference, Sydney, 2012:2079-2084.
[14] Bjornson E, Zetterberg P, Bengtsson M,.. Capacity limits and multiplexing gains of MIMO channels with transceiver impairments[J].2013, 17(1): 91-94.
[15] Ottersten B, Zetterberg P, and Bengtsson M. Optimal coordinated beamforming in the multi-cell downlink with transceiver impairments[C]. Global Communications Conference, Anaheim, 2012: 4775-4780.
[16] Holma H and Toskala A. LTE for UMTS: Evolution to LTE-advanced, 2nd[M]. Chicago, Wiley, 2011: 290-294.
[17] Dardari D, Tralli V, and Vaccari A. A theoretical characterization of nonlinear distortion effects in OFDM systems[J]., 2000, 48(10): 1755-1764.
[18] Studer C, Wenk M, and Burg A. System-level implications of residual transmit-RF impairments in MIMO systems[C]. European Conference on Antennas and Propagation, Rome, 2011: 2686-2689.
[19] Studer C, Wenk M, and Burg A. MIMO transmission with residual transmit-RF impairments[C]. The International ITG/IEEE Workshop on Smart Antennas, Bremen, 2010: 189-196.
[20] LTE performance vs. output power, model: HXG-122+. mini-circuits[OL]. http://www.minicircuits.com/app/ AN60- 050.pdf, 2011.
[21] Zhang S. Quadratic maximization and semidefinite relaxation [J]., 2000, 87(3): 453-465.
[22] 3GPP, Further advancements for E-UTRA physical layer aspects (Release 9)[S]. 2010.
汪 汉: 男,1990年生,硕士生,研究方向为下一代移动通信中协同MIMO技术.
何世文: 男,1978年生,博士后,主要研究方向为多点协作、中继协作通信和异构多点协作.
鲁照华: 男,1979年生,高级工程师,主要研究方向为无线通信信号处理.
黄永明: 男,1977年生,教授,博士生导师,主要研究方向为无线通信信号处理和优化理论.
杨绿溪: 男,1964年生,教授,博士生导师,主要研究方向为移动通信空时信号处理、协作通信和网络编码.
Robust Multi-cell Multi-user Cooperative Beamforming Technique Considering Transceiver Impairment and Imperfect Channel Information
Wang Han①He Shi-wen①Lu Zhao-hua②Huang Yong-ming①Yang Lü-xi①
①(,,210096,)②(,518000,)
In order to improve the robustness of the multi-cell multi-user multi-antenna downlink beamforming under the circumstance of considering the transceiver impairment and the imperfect channel information, two robust algorithms are proposed to solve the optimization issues considering two non-ideal factors. By releasing the non-convex constraints step by step, the original robust non-convex optimization issues are transformed to relatively easy-to-solve equivalent issues. The issues are effectively solved by using convex tool box, and the proposed algorithms are compared with traditional algorithms. Numerical simulations show that the proposed two algorithms can achieve better average-SINR and worst-SINR than the conventional algorithms without considering the two non-ideal factors.
Wireless communication; Channel imperfection; Transceiver impairment; Robust cooperative beamforming; Convex optimization
TN92
A
1009-5896(2014)05-1164-07
10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01054
黄永明 huangym@seu.edu.cn
2013-07-08收到,2014-02-14改回
国家科技重大专项(2013ZX03003006-02)国家自然科学基金(61271018, 61372101),江苏省自然科学基金(BK20130019, BK2011597)和工业支撑项目(BE2012167),教育部新世纪优秀人才资助计划(NCET-11-0088)和中兴通讯股份有限公司产学研项目(CON1211090001)资助课题
