光学相干断层扫描仪在多发性硬化患者中的初步应用
2014-04-13胡赛静厉向游逸安
胡赛静 厉向 游逸安
光学相干断层扫描仪在多发性硬化患者中的初步应用
胡赛静 厉向 游逸安
目的 利用光学相干断层扫描仪(OCT)评估多发性硬化(MS)患者与正常人眼视网膜神经纤维层(RNFL)厚度和黄斑中心凹厚度及体积的差异,评估OCT监测MS患者病程中轴突缺失的意义。 方法 选取MS患者30例(60眼),根据有无视神经炎(ON)发作史分为MS-ON组(41眼)和MS-NON组(19眼),同时选择年龄和性别相匹配的健康体检者30例(60眼)为对照组。对3组受试者均进行详细的眼科检查,并使用OCT测定RNFL厚度和黄斑参数。采用单因素方差分析对3组的RNFL厚度、黄斑中心凹厚度和体积的差异进行分析。 结果 两组MS患者的RNFL厚度和黄斑参数与对照组均有统计学差异,MS-ON组和MS-NON组之间的RNFL厚度和黄斑参数也有差异(均P<0.05)。 结论 OCT可作为MS诊断的辅助检查手段。
多发性硬化 视网膜神经纤维层厚度 黄斑体积 黄斑中心凹厚度 光学相干断层扫描
光学相干断层扫描仪(optical coherence tomography,OCT)是一种新兴的非接触式、非侵入性、高敏感性的眼科影像诊断技术,它能以快速、重现的方式对视网膜解剖结构提供高分辨率的重建,是一种主要针对眼视网膜神经纤维层(retinal nerve fiber layer thickness,RNFL)厚度的测量技术[1-2],在黄斑部疾病的诊断中有突出的优势[3-5],国内外研究显示,用OCT测量RNFL厚度可重复性较好,其准确性已经得到业内人士的认可[4]。
多发性硬化症(multiple sclerosis,MS)是一种中枢神经系统(central nervous system,CNS)脱髓鞘疾病,以神经退行性病变为特点。视神经是MS的常见受累部位之一,约50%的MS患者病程中发生视神经炎(optic neuritis,ON),约20%患者以ON起病。视网膜缺乏髓鞘但包含神经节细胞及其相关的神经轴突[6],因此可以作为研究神经退行性变、视神经保护,甚至潜在的视神经再生的理想可视化结构。本研究应用OCT观察MS患者的RNFL厚度改变,拟探讨OCT对MS诊断的辅助作用。
1 对象和方法
1.1 对象 回顾性研究2009-01—2012-12经我院神经内科确诊的MS患者30例(60眼),所有患者均符合2005年修订版McDonald诊断标准[7]。其中男11例,女19例,年龄38~59岁,平均(43.00±2.10)岁。病程2~18年,平均8.09年。根据有无ON发作史将患者分为MSON组(41眼)和MS-NON组(19眼)。MS患者60眼经眼科常规检查,6眼有轻度屈光不正,余均无其他眼疾。矫正视力>1.0的2眼,0.3~1.0的21眼,0.05~0.3的23眼,<0.05的17眼。选择年龄、性别相匹配的健康体检者30例(60眼)为对照组,矫正视力≥0.8,均排除眼科及神经系统疾病。
1.2 检查方法
1.2.1 常规检查 所有受试者均完善眼科检查,包括眼压测量,自动电脑验光仪验光,眼前段裂隙灯检查,前房角镜和眼底检查(+90D)等。
1.2.2 OCT扫描 将受试眼以1%托吡卡胺散瞳至直径约5mm,使用Carl Zeiss公司生产的Humphrey OCT-3000型,选择RNFL地形图扫描模式,其中包括6个递增的同心圆扫描,图像经计算机分析程序整合出RNFL厚度,提供内侧扇形(2.9mm)和外侧扇形(6.8mm)区域共16个区域的平均RNFL厚度。黄斑体积测量以黄斑中心凹为中心,采用快速黄斑厚度地形图扫描模式,行直径分别为1、3、6mm的线性扫描,扫描深度为300μm。放射状线性扫描6条,每条线之间的夹角为30°。每眼以黄斑中心凹为中心进行相同参数的扫描,由视网膜厚度和视网膜厚度/体积分析软件自动显示测量结果。所有受试眼均由同一测量者完成OCT扫描。
1.3 统计学处理 应用SPSS 17.0统计软件,计量资料以表示,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析。
2 结果
2.1 3组受试眼各区域RNFL厚度比较 与MS-NON组及对照组比较,MS-ON组受试眼16个区域的平均RNFL厚度均存在统计学差异(均P<0.05)。与对照组比较,MS-NON组受试眼下方内环和鼻侧外环的RNFL厚度较薄(均P<0.05),见表1。
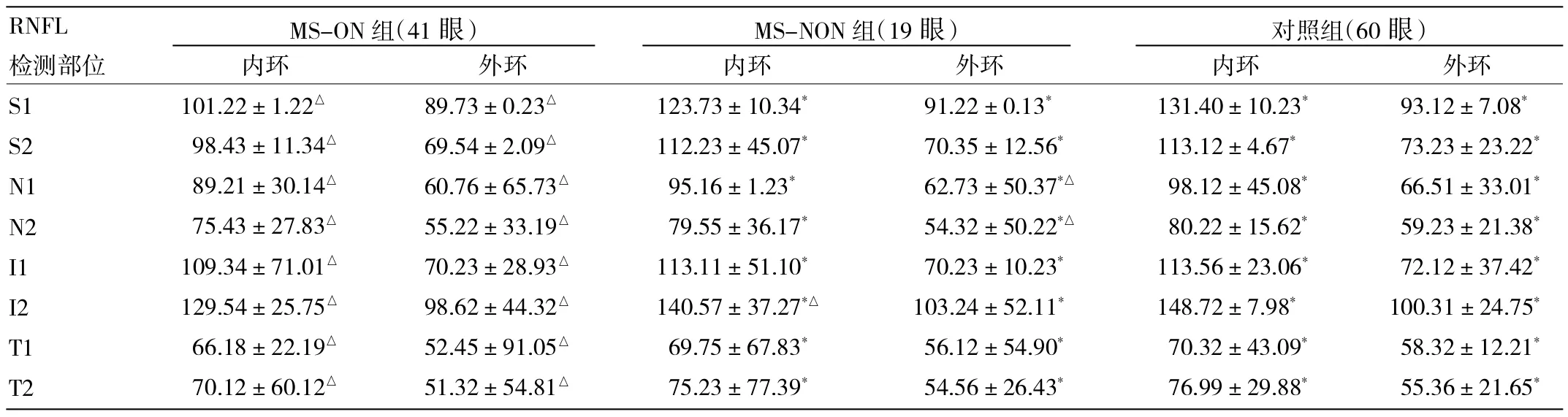
表1 3组受试眼各区域RNFL厚度比较(μm)
2.2 3组受试眼黄斑体积和黄斑中心凹厚度比较 MSNON组、MS-ON组及对照组受试眼黄斑体积分别为(7.02±0.02)、(6.91±0.11)和(6.99±1.00)mm3,3组黄斑中心凹厚度分别为(180.24±2.19)、(173.30±1.23)和(195.38±48.30)μm,组间比较均存在统计学差异(均P<0.05)。
3 讨论
MS是CNS白质和灰质通路轴突和神经元的慢性炎症及退行性疾病,其临床表现多样化,包括视神经、运动神经、感觉器官、认知力和情感方面的改变。目前磁共振成像(MRI)是检测MS神经轴突缺失的首要方法,但MRI在视神经脱髓鞘疾病的诊断及病程监测上有一定的限制[6]。在MS的病程进展中,对RNFL变化的观察是很重要的。因为在伴发ON的MS患者中,视神经纤维也同样可以发生脱髓鞘改变,所以利用OCT扫描MS患者的RNFL厚度和黄斑容积,能够对患者的诊断和病情评估作出新的补充。OCT是目前最理想的测量RNFL厚度和黄斑体积的仪器,作为一种能从组织结构上识别视网膜的技术,OCT识别RNFL厚度能精确到<10μm[4]。Costello等[8]的研究已证实OCT明确发现青光眼患者的RNFL明显变薄。OCT也可用于神经系统疾病,特别是对MS所致视神经损伤的RNFL厚度改变进行评价。Polman等[7]观察发现在MS早期即有RNFL的缺损,甚至比视力色觉和视盘变化更早,所以笔者认为OCT可以作为MS诊断和病情评估的一种辅助手段。
在本研究中,采用RNFL厚度地形图扫描分析模式,这种模式能分析视乳头周围较大范围和较多方位的平均RNFL,较传统扫描模式范围广,有助于发现RNFL损害的敏感区域。本研究中MS-NON组与对照组的RNFL相比,仅下方内环和鼻侧外环的RNFL厚度较薄,这说明虽然MS患者眼部尚未出现临床症状,但OCT检查已发现损伤,提示当MS累及视神经时,OCT能灵敏地反映视神经的损伤。至于病变主要在两个方位出现是否说明这两个区域的神经纤维更容易受损,还有待于更深入的研究。RNFL损伤阈值约为75μm,如果轴突缺失达到一定程度即RNFL厚度损伤>75μm,才会出现视功能降低[9]。国外研究发现有ON病史的MS患者RNFL厚度明显变薄,而无ON病史的MS的患者同样也有RNFL厚度的异常减少,这说明轴突损伤可发生在缺乏临床症状的时期,很有可能是MS的早期表现[10],本研究结果再次证实了这些可能性。
黄斑体积反映了视网膜神经节细胞的完整性,Pulicken等[11]研究发现11%的伴有ON的MS患者与正常眼相比黄斑体积减少,本研究中MS-ON组和MSNON组的黄斑中心厚度和黄斑体积较对照组减少,MS-ON组比MS-NON组也有减少,而且这两组患者的黄斑参数皆有差异,说明黄斑参数的灵敏性并不亚于RNFL,两者可以互相佐证MS患者的轴突损伤。
国外学者已经发现用OCT衡量RNFL变薄的严重程度可以分离MS的各种亚型[11-13],特别是用于检测患者进一步的病程变化。OCT在更多实质性的视网膜病理改变中起着积极的作用,有望成为RNFL轴突缺失的衡量标准[14]。在未来的工作中,笔者还将设计大样本的长期随访病例,研究OCT在MS诊断和随访监测过程中的临床意义。
[1]Schuman J S,Pedut-Kloizman T,Hertzmark E,et al.Reproducibility of nerve fiber layer thickness measurements using optical coherence tomography[J].Ophthalmology,1996,103(11): 1889-1898.
[2]Mok K H,Lee V W,So K F.Retinal nerve fiber layer measurement of the Hong Kong chinese population by optical coherence tomography[J].J Glaucoma,2002,11(6):481-483.
[3]Paunescu L A,Schuman J S,Price L L,et al.Reproducibility of nerve fiber thickness,macular thickness,and optic nerve head measurements using StratusOCT[J].Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2004,45(7):1716-1724.
[4]Hess D B,Asrani S G,Bhide M G,et al.Macular and retinal nerve fiber layer analysis of normal and glaucomatous eyes in children using optical coherence tomography[J].Am J Ophthalmol,2005,139(3):509-517.
[5]Medeiros F A,Zangwill L M,Bowd C,et al.Comparison of the GDx VCC scanning laser polarimeter,HRT II confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope,and stratus OCT optical coherence tomograph for the detection of glaucoma[J].Arch Ophthalmol,2004, 122(6):827-837.
[6]De Stefano N,Matthews P M,Antel J P,et al.Chemical pathology of acute demyelinating lesions and its correlation with disability [J].Ann Neurol,1995,38(6):901-909.
[7]Polman C H,Reingold S C,Banwell B,et al.Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis:2010 revisions to the McDonald criteria[J].Ann Neurol,2011,69(2):292-302.
[8]Costello F,Coupland S,Hodge W,et al.Quantifying axonal loss after optic neuritis with optic coherence tomography[J].Ann Neurol,2006,59(6):963-969.
[9]Pro M J,Pons M E,Liebmann J M,et al.Imaging of the optic disc and retinal nerve fiber layer in acute optic neuritis[J].Neurol Sci,2006,250(1-2):114-119.
[10]Jiao S,Knighton R,Huang X,et al.Simultaneous acquisition of sectional and fundus ophthalmic images with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography[J].Opt Express,2005,13(2):444-452.
[11]Pulicken M,Gordon-Lipkin E,Balcer L J,et al.Optical coherence tomography and disease subtype in multiple sclerosis[J].Neurology,2007,69(22):2085-2092.
[12]Henderson A P,Trip S A,Schlottmann P G,et al.An investigation of the retinal nerve fibre layer in progressive multiple sclerosis using optical coherence tomography[J].Brain,2008,131 (Pt1):277-287.
[13]Gordon-Lipkin E,Chodkowski B,Reich D S,et al.Retinal nerve fiber layer is associated with brain atrophy in multiple sclerosis [J].Neurology,2007,69(16):1603-1609.
[14]Grazioli E,Zivadinov R,Weinstock-Guttman B,et al.Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness is associated with brain MRI outcomesin multiple sclerosis[J].NeurolSci,2008,268(1-2):12-17.
Optical coherence tomography in evaluation of retinal parameters for patients with multiple sclerosis
ObjectiveTo evaluate the retinal nerve fiber layer(RNFL)thickness and macular fovea thickness/volume in multiple sclerosis patients and healthy individuals with optical coherence tomography(OCT).Methods Thirty consecutive multiple sclerosis patients(60 eyes)and 30 healthy individuals(60 eyes)were recruited in this prospective study.Multiple sclerosis patients were classified as MS patients with a history of optic neuritis(41 eyes,MS-ON group)and MS patients without history of optic neuritis(19 eyes,MS-NON group).Comprehensive ophthalmic examinations,including RNFL thickness and macular fovea thickness/volume were performed using Humphrey OCT.Mean values for the thickness of the peripapillary RNFL and macular volume were calculated.Results The RNFL thicknesses in each quadrant in MS patients were all thinner than those in healthy controls(P<0.05).The average macular thickness and macular volume were both thinner in MS patients.The RNFL thickness and macular fovea thickness/volume in each quadrant were all thicker in eyes without optic neuritis than those in eyes with optic neuritis.Conclusion OCT measurements can effectively identify the nerve changes in MS patients,which is of value in diagnosis of MS.
Multiple sclerosis Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness Macular volume Macular fovea thickness Optical coherence tomography

2013-10-25)
(本文编辑:胥昀)
温州市科技局课题基金资助项目(Y20110229)
325000 温州医科大学附属第一医院眼科
