GPC/SEC与激光光散射联用技术在食物蛋白分析中的应用研究进展
2014-02-25熊丽姬陈红兵高金燕
肖 娜,佟 平,熊丽姬,3,陈红兵,3,高金燕
(1.南昌大学食品科学与技术国家重点实验室,江西南昌330047;2.南昌大学生命科学与食品工程学院,江西南昌330047;3.南昌大学中德联合研究院,江西南昌330047)
GPC/SEC与激光光散射联用技术在食物蛋白分析中的应用研究进展
肖 娜1,2,佟 平1,熊丽姬1,3,陈红兵1,3,高金燕2,*
(1.南昌大学食品科学与技术国家重点实验室,江西南昌330047;2.南昌大学生命科学与食品工程学院,江西南昌330047;3.南昌大学中德联合研究院,江西南昌330047)
GPC/SEC与(LLS)联用技术在分离和测定大分子物质的分子量及其分布中发挥着越来越重要的作用。该方法所需样品少、快速、准确,而且可以同时测定出物质的重均分子量(Mw)、数均分子量(Mn)、Z均分子量(Mz)、Mw/Mn、第二维里系数(A2)以及均方根半径(Rg)。目前GPC/SEC与激光光散射联用技术主要用于测定蛋白质的分子量及其分布以及研究蛋白质的聚合状态,显示了其与众不同的性能,而且该技术在食物蛋白中的应用仍值得进一步研究。
GPC/SEC,激光光散射,分子量,食物蛋白
蛋白质是生命的体现者,是细胞的主要成分之一。它是由L型α-氨基酸通过酰胺键连接而成的肽链,再经过α或β折叠形成具有二级、三级、四级结构的生物大分子物质[1],同时它也是人类不可缺少的食物主要构成成分之一。当发现一种新的蛋白质或者多肽的时候,获得它的分子量的大小及其分子量分布,有助于对其其他方面的性质进行进一步的研究[2]。因此,构建出一种新的方法能够准确、快速地测定出蛋白质的分子量及其分布有着十分重要的意义。
光散射原理最早是在1972年由Wyatt[3]提出的。Wyatt指出通过光散射可以了解到散射粒子的浓度、取向、形状及大小等情况,并且可测定出物质的分子量。1983年Hjertberg[4]首次提出凝胶渗透色谱Gel Permeation Chromatography,GPC)低角度激光光散射联用技术可以连续地测定多聚物的绝对分子量。物质先通过凝胶色谱而被洗脱分离,再经过光散射检测器检测出物质的分子量,从而达到既可以分离物质的组分,又可以准确地测定出物质的分子量的效果。因此,凝胶渗透色谱/排阻色谱(Size exclusion Chromatography,SEC)与激光光散射(Laser Light Scattering,LLS)联用技术不仅具备了LLS技术可以测定蛋白质或者蛋白质聚合物的分子量以及蛋白在不同条件下的聚合情况的优点,还结合了GPC/SEC可以分离单一或混合的蛋白质组分,同时也能得知蛋白质纯度等情况的优点。而且GPC/SEC-LLS联用技术不需要标准物质校正凝胶柱系,可以直接测定出物质的分子量及其分布[5]。由于高聚物一般由不同分子量的同系物组成的混合物,因此它的分子量具有一定的分布。此外,该方法快速简单,测定误差一般不超过5%[6-7]。基于以上特点,GPC/SEC-LLS联用技术的应用非常广泛,例如,在食品[8]、医学[9]、聚橡胶工业[10]等领域都有相关研究报道。目前多用于测定多糖、蛋白质以及一些化学聚合物的分子量及其分布。
1 GPC/SEC-激光光散射技术原理
当GPC仪与激光光散射仪联用时,GPC仪可将溶液中的物质按分子量的大小从大到小洗脱出来[11-12]。再经过光散射检测器进行检测,当光束照射到高分子聚合物样品时,密度起伏和溶液浓度不均一可引起光散射现象,除入射光外的各个方向都会产生散射光[13]。各个方向所收集的散射光强度与分子量大小及溶液浓度成正比,与散射光角度的变化、分子的尺寸大小都有关。不同角度的激光光散射仪可以从多个角度对散射光的强度进行检测,这样就提高了检测的灵敏度,减少了误差[14]。目前用的较多的检测仪器是多角度激光光散射检测仪。以18角激光光散射仪为例,收集的散射光的强度来自于各个方向,高分子溶液的激光散射可用以下基本公式表示[15]。
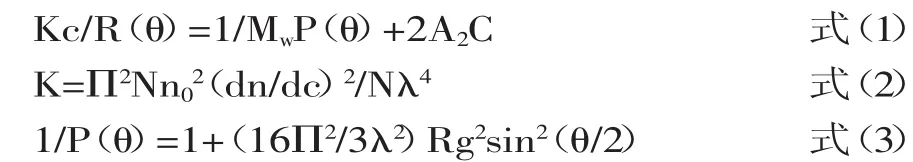
式中,K为与溶剂性质和入射光频率相关的常数;c为溶液浓度(g/mL);R(θ)为不同角度去除溶剂影响后的散射光强度;θ为散射光角度;Mw为重均分子量;P(θ)为散射光强度随角度变化的函数;A2为第二维里系数,A2是溶剂与溶质相互作用的度量,若溶液极稀时可忽略;n0为溶剂的折射率;dn/dc为折光指数增量,指聚合物溶液折光指数相对于溶质的浓度变化;N为阿佛加德罗常数;λ为入射光波长;Rg为高分子均方末端距,即链质量中心至各个链段距离平方的平均值。R(θ)为仪器测定量,K、c、n0、dn/dc、N、λ、θ均为常数或已知量,其中dn/dc值可通过折光仪测定,或通过折光仪的仪器常数与输入样品质量求得[16]。只有Mw、Rg和A2三个高分子链的基本参数为未知值,通过多个角度光散射强度的测定,即可推导求出。
随着条件的优化,陆续出现了GPC/SEC-动态光散射检测器(DLS)、GPC/SEC-静态光散射检测器(SLS)、GPC/SEC-多角度激光光散射检测器(MALLS)、GPC/SEC-低角度激光光散射检测器(LLLS)、GPC/ SEC-十八角激光光散射检测器等。目前常用的主要是前三种。表1对这三种常用检测器的特性及优劣进行了比较。
2 GPC/SEC-LLS在食物蛋白中的应用
目前测定蛋白质分子量的方法有很多,如渗透压法、光散射法、超速离心法、凝胶渗透色谱法、SDS-聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳(SDS-PAGE)以及质谱法等。常用的方法有凝胶渗透色谱法和SDS-PAGE。凝胶渗透色谱法(GPC)需要知道标准样品的分子量,测定出标准物质的相对分子质量标准曲线才能计算出待测组份的分子量的大小[17],而标准物质的价格较高,且需要多种联合使用,使得该方法在测定物质的分子量方面有一定的局限性。SDS-PAGE也是常用的测定蛋白质分子量的大小的方法之一,它还可以用于蛋白质样品的分离和鉴定,但是该方法测定的蛋白质分子量的偏差较高,约在10%以上[1],所以它对蛋白质的分子量大小的测定也只是一个估测。而GPC/ SEC-LLS联用技术,不仅可以快速准确的测定出物质的Mw、Mn、Mw/Mn、Mz、A2以及Rg[18],而且不需要测定标准物质的标定曲线。现将GPC/SEC-LLS联用技术在蛋白质中的应用作一概述。

表1 三种常用GPC/SEC-LLS检测仪的比较*Table.1 The comparison of the three common GPC/SEC-LLS detector
2.1 GPC/SEC-LLS用于分离和测定蛋白质的分子量
Ewa[19]用SEC-LLS技术检测了14种分子量在12~475ku之间的标准蛋白质的分子量,在实验中将蛋白质样品稀释到0.1mg/mL,进样量50ug就能满足仪器要求,还可以连续自动进样。样品先进样到GPC/SEC凝胶柱,再经过示差检测器测定出dn/dc,最后经过紫外检测器和光散射检测器检测,使用ASTRA软件对所得的峰进行分析,结果表明,对于分子量大于40ku的蛋白质,其误差范围都在5%以内,而且该方法快速、简单。Yan[20]用阴离子交换柱、SDS-PAGE和GPCMALLS这三种技术联合使用测定不同的大豆中大豆球蛋白及其亚群的差异。Emmanuelle[21]用GPC-LLS联用技术测定含有半光氨酸的蛋白质与聚已二酸乙二醇酯发生可逆加成的链式反应后所得到的复合物的分子量的大小,从而判断出二者的结合状态。此外,该技术不仅用于测定蛋白质的分子量,也常用于测定多糖、多糖衍生物以及一些化学聚合物的分子量及其分布。Raymond[22]用SEC-MALLS技术测定多种不同的溶剂中的醋酸琥珀羟丙甲纤维素(HPMCAS)的分子量及其分布,所测定的分子量的误差范围在3%~6%以内。由此可见,无论测定蛋白质和多糖,GPC/SEC-LLS联用技术都可以简单而直接地测定出其分子量及其分布,而且该方法快速,准确。所以GPC/SEC-LLS联用技术对于测定物质的分子量及其分布的优势很明显。
2.2 GPC/SEC-LLS用于检测蛋白质的纯度、分析蛋白质聚合物的状态
Qiang等[23]用SEC-DLS技术研究了挤压过程中不同的机械剪切力对大豆蛋白聚合物的影响,为大豆在挤压过程中的聚合情况的变化提供了有力的依据。他们发现大豆在挤压过程中随着挤压剪切力的加大,大豆蛋白的分子量会加大,说明大豆蛋白发生了聚合;然而,当挤压力度加大到一定程度之后,大豆蛋白的分子量减小,说明大豆蛋白发生了解聚。Yang[24]同时使用GPC-MALLS、zeta-电位法以及等温滴定量热法这三种方法研究β-乳球蛋白和甜菜果胶在不同的pH的情况下所形成的络合物的聚合情况以及结构的变化,并绘制出其结构变化曲线图。Yasushi[25]通过该方法测定了OmpF孔蛋白分子量及其分布,从而掌握了该蛋白的重叠和重组的情况。Matsumura[26]使用GPC-MALLS联用技术分别测定了在转谷氨酰胺酶和茂原链轮丝菌的催化作用下α-乳白蛋白交联形成的聚合物大小的情况。Matsumura指出转谷氨酰胺酶和茂原链轮丝菌都能够很快的催化α-乳白蛋白交联,通过测定α-乳白蛋白的分子量及其分布的变化可表征出α-乳白蛋白的单体快速的减少,以及大型聚合物的快速增长;而且茂原链轮丝菌所催化的α-乳白蛋白所形成的聚合物粒子的大小及其分子量都要比转谷氨酰胺酶所催化形成的聚合物粒子及其分子量要大,从而说明茂原链轮丝菌的催化作用要比转谷氨酰胺酶的催化作用要强;然而,在含有Ca2+存在的情况下,Ca2+会抑制α-乳白蛋白的交联,所形成的聚合物分子量也更小。不仅如此,GPC/SEC-LLS联用技术还可以从待测蛋白的出峰情况判断出待测蛋白的纯度,纯蛋白只会有一个峰,而杂蛋白则会有多个的峰值[27-28]。显然,使用GPC/SEC-LLS联用技术不仅可以测定蛋白质的纯度还可以判断出蛋白质在不同条件下的的聚合状态,从而可以判断出蛋白质的聚合是受哪些条件的影响。不言而喻,GPC/SECLLS联用技术是测定蛋白质纯度及聚合物的聚合情况的良好工具。
2.3 GPC/SEC-LLS用于研究不同条件对蛋白质性质的影响
Beaulieua等[29]用SEC-MALLS联用技术测定果胶对加热之后乳清蛋白的聚合的影响。在没有钙的情况下,果胶对乳清蛋白在加热时所形成的的聚合物的分子量大小及其分布没有太大影响;而在有钙的情况下,低甲氧基果胶会导致乳清蛋白加热时形成的聚合物的分子量变小,峰型也变小,分子量分布变窄,说明低甲氧基果胶会抑制加热时乳清蛋白的聚合。Mallika[30]应用GPC-DLS联用技术方法测定了GPC纯化的β-乳球蛋白的分子量及其分布,通过测定不同温度下处理β-乳球蛋白其分子量及其分布的变化,发现25℃时β-乳球蛋白以单体的形式存在;温度升到30℃的时候,β-乳球蛋白则同时以单体和二聚体的形式存在;温度再升高到45℃或更高时,β-乳球蛋白则会部分变性。众所周知,蛋白质具有多种性质和作用,如起泡性、溶解性、具有黏度、凝胶作用、乳化作用等,而且它也很容易受外界条件的影响,如pH、温度、表面活性剂等,因而,探索某一条件对蛋白质的性质的影响有重要意义。通过GPC/SEC-LLS联用技术测定蛋白质的分子量及其分布,可以得知某一因素对蛋白质的分子量及其性质的影响有多大[31-32],从而可以推导出蛋白质的性质与分子量的变化的关系。由此可见,GPC/SEC-LLS联用技术在食品研究与应用方面具有重要价值。
3 结论与展望
在进行蛋白质的分析中,GPC/SEC-LLS联用技术能够高效、快速、准确地测定出大分子物质的分子量及其分布、分散性、聚合情况等。然而,GPC/SECLLS联用技术只是单一的通过测定物质的分子量及其分布来反映物质的一些特性。如果能将其和其他仪器联合使用,如和黏度检测器连用,则不仅可以测定物质的分子量,还可以测定物质的黏度,这样,就为分子量的大小与黏度的关系提供更加有利的依据。国外已有相关文献报道了GPC/SEC-LLS联用技术与黏度检测器联用[33-34],国内则未见有相关的报道。而且目前国内应用GPC/SEC-LLS联用技术测定食物蛋白质的分子量及其的分子量分布、聚合情况等的相关应用也并不多见。随着技术的发展及需要,GPC/SEC-LLS联用技术将会在测定食物蛋白质纯度、分子量及其分子量的分布、聚合程度等研究领域中发挥越来越重要的作用。
[1]王克夷.蛋白质的导论[M].北京:中国科学出版社,2007:36-42.
[2]孔毅,吴梧桐,吴如金.蛋白质分子量测定方法的比较[J].分析仪器,2003(2):44-46.
[3]Wyatt P J.Light scattering in the microbial world[J].Polymer Testing,1983,3(4):267-289.
[4]Hjertberg T,Kulin L I,Sörvik E.Laser light scattering as GPC detector[J].Polymer Testing,1983,3(4):267-289.
[5]Capannoli G,Carinci V,D’Ascenzi S,et al.Dimensional analysis of saccharide conjugates with GPC and SEC-MALS:USA,US 08163296[P].2012-04-24.
[6]Rdalo J B,Medrano R,Saiz E,et al.A simple method to determine unperturbed dimensions ofpolymersusing size exclusion chromatography and multi-angle light scattering[J]. Polymer,2000,41:1615-1620.
[7]Hewa O G,Frank M,Peter K,et al.Molar mass characterization of cellulose acetates over a wide range of high DS by size exclusion chromatography with multi-angle laser light scattering detection[J].Carbohydrate Polymers,2012,88:96-102.
[8]Xu Mei,Li Dong Sheng,LI Bin,et al.Comparative study on molecular weight of konjac glucomannan by gel permeation chromatography-laser light scattering-refractive Index and laser light-scattering methods[J].Spectroscopy,2013,10:685-698.
[9]Se,Kazunori.Absolute molecular characterization of nonlinear block copolymers using GPC equipped with a low-angle laser light-scattering detector[J].Kobunshi Ronbunshu,2012,69(5):185-197.
[10]Kima C,Beuve J S,Guilbert S.Study of chain branching in natural rubber using size exclusion chromatography coupled with a multi-angle light scattering detector(SEC-MALS)[J].European Polymer,2009,45:2249-2259.
[11]Ritter A,Schmid M,Affolter S.Determination of molecular weights by size exclusion chromatography(SEC)-Results of round robin tests[J].Polymer Testing,2010,29:945-952.
[12]AnastasiosD.Applicability ofthe modfied universal calibration of gel permeation chromatography on proteins[J]. Journal of Chromatography A,2006,1127:183-186.
[13]Zainon O,Saphwan A A,Osman H.Molecular Characterisation of sago starch using gel permeation chromatography multi-angle Laser Light Scattering[J].Sains Malaysiana,2010,39(6):969-973.
[14]Morgan J T,Michael C S,Christian S.The influence of macromolecular architecture on the critical aggregation concentration of large amphiphilic starch derivatives[J].Food Hydrocolloids,2013,31(2):365-374.
[15]Liu Y G,Bo S Q,Zhu Y J.Determination of molecular weight and molecular sizes of polymers by high temperature gel permeation chromatography with a static and dynamic laser light scattering detector[J].Polymer,2003,44:7209-7220.
[16]Oliva A,Llabrés M,José B.Farina Estimation of uncertainty in size exclusion chromatography with a double detection system(light scattering and refractive index)[J].Talanta,2009,78:781-789.
[17]Leopold K K,Douglas M K,Archie E H.Size-exclusion chromatography-a review of calibration methodologies[J].Journal of biochemical and biophysical methods,2004,58:159-186.
[18]Chen T Q,ADILBEKOV J,WANG J,et al.Study on molecularcharacteristicsoffourcomponentscontained in HedysariRadixpolysaccharidebygelpermeation chromatographymultiangle laser light scattering technology(GPC-MALLS)[J].US National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health,2012,37(12):1798-1803.
[19]Ewa F S,Williams K R.Determination of molecular masses of proteins in solution:Implementation of an HPLC size exclusion chromatography and laser light scattering service in a core laboratory[J].Biomolecular Techniques,1999(10):51-63.
[20]Zhang G Y,Hayashi Y,Matsumoto S,et al.Molecular species of glycinin in some soybean cultivars[J].Phytochemistry,2002,60(7):675-681.
[21]Emmanuelle B,Lei Tao,Chen Wen Chang,et al.Synthesis of Semitelechelic Maleimide Poly(PEGA)for Protein Conjugation By RAFT Polymerization[J].Biomacromolecules,2009,10(7):1777-1781.
[22]Chen R,Ilasi N,Sekulica S S.Absolute molecular weight determination of hypromellose acetate succinate by size exclusion chromatography:Use of a multi-angle laser light scattering detector and a mixed solvent[J].Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis,2011,56:743-748.
[23]Fang Y Q,Zhang B,Wei Y M,et al.Effects of specific mechanical energy on soy protein aggregation during extrusion process studied by size exclusion chromatography coupled with multi-angle laser light scattering[J].Food Engineering,2012,115:220-225
[24]Li X Y,Fang Y P,Saphwan,et al.Complexation of Bovine Serum Albumin and Sugar Beet Pectin:Structural Transitions and Phase Diagram[J].Langmuir,2012,28(27):10164-10174.
[25]Yasushi W.Characterization of the refolding and reassembly of an integral membrane protein OmpF porin by low angle laser light scattering photometry coupled with high performance gel chromatography[J].Chromatography,2002,961:137-146.
[26]Matsumura Y,Lee D S,Mori T.Molecular weight distributions of α-lactalbumin polymers formed by mammalian and microbial transglutaminases[J].Food Hydrocolloids,2000,14(1):49-59.
[27]Hong P,Koza S,Bouvier ESP.A review size-exclusion chromatography forthe analysisofprotein biotherapeutics and theiraggregates[J].Liquid Chromatography & Related Technologies,2012,35(27):2923-2950.
[28]Hassan M I,Kumar V,Singh TP,et al.Purification and characterization of zinc alpha 2-glycoprotein-prolactin inducible protein complex from human seminal plasma[J].Separation Science,2008,31(12):2318-2324.
[29]Beaulieua M,Milena C,Sylvie L,et al.The formation of heat induced protein aggregates in whey protein/pectin mixtures studied by size exclusion chromatography coupled with multiangle laser light scattering detection[J].Food Hydrocolloids,2005,19:803-812.
[30]Mallika S,Zahur U H,William W Wilson.Association tendency of β-lactoglobulin AB purified by gel permeation chromatography as determined by dynamic light scattering under quiescent conditions[J].Food Hydrocolloids,1996,10(3):323-328.
[31]Bateman O A,Lubsen N H,Slingsby C.Association behaviour of human beta B1-crystallin and its truncated forms[J]. Experimental Eye Research,2001,73(3):321-331.
[32]Japp V D,Jam S.Size-exclusion chromatographymultiangle laser light scattering analysis of beta-lactoglobulin and bovine serum albumin in aqueous solution with added salt [J].Chromatography A,2000,867(1-2):105-112.
[33]Takashi M,Yasuo M,Tatsuya S.Characterization of polydihydrosilane by SEC-MALLS and viscometry[J].Polymer,2012,53:2973-2978.
[34]Christensena B E,Upset A S,Beer M U,et al. Macromolecularcharacterisation ofthree barley β-glucan standards by size exclusion chromatography combined with light scattering and viscometry:an inter laboratory study[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2001,45:11-22.
Application of GPC/SEC coupled with laser light scattering on food proteins
XIAO Na1,2,TONG Ping1,XIONG Li-ji1,3,CHEN Hong-bing1,3,GAO Jin-yan2,*
(1.State Key Laboratory of Food Science and Technology,Nanchang University,Nanchang 330047,China;2.College of Life Sciences and Food Engineering,Nanchang University,Nanchang 330047,China;3.Sino-German Joint Research Institute,Nanchang University,Nanchang 330047,China)
GPC/SEC and laser light scattering(LLS)combined technology play a more and more important role in the separation determination of molecular weight and its distribution of macromolecular substances.This method requires less samples,and also was fast and accurate,moreover it could also determine average molecular weight(Mw),the number average molecular weight(Mn),Z-average molecular weight(Mz),Mw/Mn,the second virial coefficient(A2)and root mean square radius(Rg)of the material.GPC/SEC and laser light scattering detection application in protein was summarized.At present,the technology mainly used for the determination of protein molecular weight and its distribution as well as the study of protein aggregation state,and showed its distinctive performance,however,its application in food protein deserved further study.
GPC/SEC;laser light scattering;molecular weight;food proteins
TS203
A
1002-0306(2014)04-0384-04
2013-07-08 *通讯联系人
肖娜(1991-),女,硕士研究生,研究方向:食品生物技术。
国家高技术研究发展计划(863计划)(2013AA102205);国家国际科技合作专项(2013DFG31380);国家自然科学基金(21162019);江西省科技计划项目(20122BBG70170-2)。
