薄荷属植物挥发性成分及药理作用研究进展
2013-12-23陈智坤梁呈元任冰如李维林
陈智坤,梁呈元,任冰如,于 盱,李维林
江苏省中国科学院植物研究所,南京210014
目前,世界上已发现薄荷属植物(Mentha L.)25种以上[1],其作为重要的芳香植物广泛分布于北半球的温带地区,少数种见于南半球,我国有薄荷属植物12 种,主要分布于东北、华东、新疆等地区[2]。其中,薄荷属植物中薄荷(M. canadensis L.)、辣薄荷(M. ×piperita L.)、留兰香(M.spicata L.)等被广泛地应用于食品、医药、化妆品、香料、烟草等工业[3],当前,对该属植物的研究主要集中在挥发性成分,也就是俗称的“薄荷油”。薄荷挥发性成分主要为多种单萜类化合物,现代药理学研究表明其具有抗氧化、抗菌、抗辐射、抗癌、降血压等生物活性。本文对近年来国内外关于该属植物挥发性成分及活性研究现状进行综述,以期为进一步开发和利用该属植物提供科学参考。
1 薄荷属植物主要挥发性成分

表1 薄荷属植物主要挥发性成分Table 1 Main compounds of volatile components from Mentha L.
表1 为,近二十年来世界各地薄荷属植物所含主要挥发性成分的总结。由表1 可见,薄荷属植物挥发性相对比较规律,依据主成分大体可以分为四大类:一、薄荷醇(menthol)类保持不了主要植物有M.arvensis ,M. canadensis,M. × piperita,M. requienii;二、胡薄荷酮(pulegone)类,M. cervina,M. pulegium,M. ×dumetorum,M.requienii;三、胡椒酮(piperitone)类,M. aquatic,M. longifolia,M. rotundifolia,M. ×villosa;四、香芹酮类(carvone),M. spicata。然而,研究表明薄荷属植物因生境及生长阶段不同其挥发性成分也会存在显著差异。
2 薄荷属植物挥发性成分生物合成途径
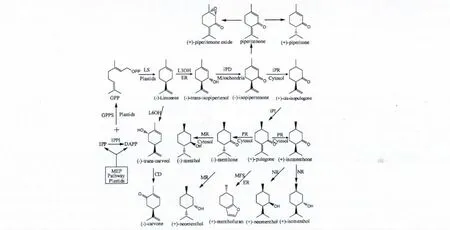
图1 薄荷属主挥发性成分生物合成途径Fig.1 The biosynthesis pathway of volatile components from Mentha L.
如图1 所示,目前国内外关于薄荷属植物的主要挥发性成分的生物合成途径已基本清晰。研究显示,薄荷属植物并非以MVA(mevalonic acid)为C5原料的传统单萜生物合成途径,而是以MEP 为主要C5 原料[40-44]。MEP 经多步反应转化成IPP 和DAPP,其中IPP 在IPPi 的作用下生成DAPP;DAPP和IPP 在GPPS 的作用下则产生C10 基本结构GPP;最后GPP 再在不同酶的作用下,经多步反应最终得到相应的单萜类成分。目前已通过分子手段寻找并克隆出调控薄荷属植物中萜类合成酶所对应的基因,并采用细胞悬浮培养等方式,进行相应萜类代谢产物的生物合成。
3 薄荷属植物精油相关药理作用
在世界各地,薄荷属植物有悠久的种植和使用史,在中国,该属植物已有2000 多年药食两用史[45]。目前,多个发达及发展中国家已将“薄荷油”列入药典范围。现代研究表明,薄荷属挥发性成分具有丰富的生物活性,除传统用于解热镇痛、胃肠道紊乱等疾病治疗的药理活性被验证,抗氧化、抗菌、抗辐射、抗癌、降血压等活性及对应作用机理也被逐渐发现。
3.1 抗氧化活性
目前,对于薄荷属植物的抗氧化活性研究比较热门,其中薄荷属的挥发性和非挥发性成分都显示出良好的抗氧化活性。Hussain[32]通过DPPH 自由基、亚油酸系统以及含有β-胡萝卜素的亚油酸系统进行抗氧化活性评价显示,M. spicata 精油对DPPH自由基和亚油酸体系有良好清除活性,其中DPPH对自由基IC50值为13.3 ±0.6 μg/mL,对亚油酸体系清除率可达61.5%,并发现其抗氧化活性与其主成分香芹酮有密切联系;Schmidt[46]研究表明M. ×piperita 精油同样对DPPH 自由基和OH 基自由基均有清除作用,其IC50值分别为860 μg/mL,0.26 μg/mL;Gulluce[47]研究表明M. longifolia 精油对DPPH自由基和亚油酸体系有一定抗氧化活性,其中对DPPH 自由基IC50值为10700 μg/mL,但对亚油酸体系在2 mg/mL 时仅达到36%的清除率。
3.2 对病原微生物及昆虫的作用
现代研究表明,薄荷属植物挥发性成分对多种病原微生物抑制作用。周露等[8]研究表明M.arvensis 精油对对大肠杆菌、金黄葡萄球菌、白念珠菌有明显的抗菌活性,其最小抑菌浓度(MIC)分别为0.16,1.25,2.5 v/v,其最小杀菌浓度(MBC)分别为0.31,5,2.5 v/v;李慧等[48]研究表明M.canadensis,M. ×piperita,M. × gentilis 精油对绿脓杆菌有抑制作用,通过与抗生素联用其抗菌范围和强度均有所变化;王微等[49]研究表明M.canadensis 精油对所选的包括表皮葡萄球菌等8 种病原菌都有很好的抗菌活性,枯草芽孢杆菌及变形杆菌出现最大的抑菌环,MIC 实验中,薄荷精油的浓度范围为5. 00%~0.039%,变形杆菌的MIC 及MBC 值最低,分别为0.625%及1.25%;Rodrigues[50]研究表明M.cervina 精油对23 种细菌具有抑制效果,其中精油对细菌的抑制是由于多种成分的相互协同作用,并非单一成分发挥作用;Goncalves[12]的研究结果显示M. cervina精油对三种真菌具有很好的抑制作用,其中对表皮寄生菌的MIC 值为0.63 mL/mL,可作为治疗脚气等真菌类疾病替代药品。Hafedh 等[51]研究显示M.longifolia 精油对四种革兰氏阴性菌和革兰氏阳性菌均有抑制作用;Bassole[52,53]研究表明M. × piperita精油对多种病原微生物具有抑制作用,而对人类病原体只有适度抑制;Sokovic[17,54]研究表明M. ×piperita 精油对匍枝根霉、灰霉病、黑曲霉和红色毛癣菌具有抑制效果;Mario[26]研究显示M. requienii 精油对镰刀菌等7 种微生物具有体外抑制活性;Sarer[31,32,55,56]等研究表明M. spicata 精油对多种病原微生物具有抑制作用,并以香芹酮为例验证单萜的对应异构体结构与抗菌活性有关,其中(R)(+)-limonene 抗菌活性大于(S)(-)-limonene;Rasooli[57]通过M.spicata 精油体内外生物膜研究实验为薄荷牙膏抗菌保护口腔黏膜提供临床依据,并通过与桉树精油联用发现一种新型预防和治疗龋齿的方法;Sutour[36,37]研究发现M. suaveolens 精油对病原微生物具有抑制作用,其主成分piperitone 对测试的微生物抑制作用最强,其次是piperitenone oxide 和piperitone oxide。除此而外,Walker[58-60]等研究表明M.longifolia,M. ×piperita,M.spicata 精油对玉米象、根结线虫、螨虫、蚊子等具有杀灭或趋避作用。因此,人们可利用薄荷属植物挥发性成分对病原微生物的抑制作用,将薄荷精油广泛用于喉咙、口腔等炎症治疗,食品储存,植物保护等领域。目前留兰香精油已作为重要的添加剂在牙膏中广泛使用,薄荷属其它植物也将在人们日常生活中发挥着巨大的作用。
3.3 抗辐射活性
Haksar[61]通过雄性大鼠实验表明M. spicata 精油对辐射造成的条件性味觉厌恶有改善作用;Samarth[62-71]研究表明M. ×piperita 精油对辐射诱导的瑞士白化小鼠睾丸损伤、小鼠肝脏抗氧化状态和脂质过氧化、骨髓染色体、脾脏、肠道损伤均具有保护作用,对小鼠血清磷酸酶具有降低作用,其作用机制可能与增加NO 的释放、自由基清除活性有关。由此可见,薄荷属植物精油具有应对电离辐射,可用于宇航员或核环境中的辐射的预防治疗。
3.4 抗癌活性
在伊朗M.Pulegium 被用于防腐、驱风、抗痉挛、治疗宫颈瘤等疾病。Shirazi[72]研究显示M. Pulegium 精油对人卵巢腺癌SK-OV-3,人恶性子宫颈细胞株Hela 和人肺癌A549 细胞系均表现出一定的抑制作用,其IC50值分别为14.10,59.10 和18.76 μg/mL,可作为治疗人类癌症的候选药物。
3.5 解热镇痛作用
Sousa[38]通过对服用M. ×villosa 精油及其主成分胡椒烯酮对经醋酸处理的疼痛小鼠模型,结果显示两者均具有镇痛效果,且这种影响不涉及中枢系统。
3.6 降压及对心血管的影响
Lahlou[73,74]研究表明静脉注射M. × villosa 油对采用醋酸去氧皮质酮作用的高血压小鼠模型,结果显示具有显著地降压和调节心律的作用,其主要作用机理是刺激释放NO 诱导血管平滑肌松弛。
3.7 抗组胺抗过敏作用
林月彬[75]通过三种过敏模型研究显示,薄荷醇高、中、低剂量组30 min 内在搔抓次数与空白模型组相比显著减少,高剂量组搔抓潜伏期与空白模型组相比显著延长;薄荷醇高剂量组能明显抑制组胺引起的回肠平滑肌张力收缩;薄荷醇高剂量组能抑制豚鼠腹腔细胞组胺释放作用。研究表明,薄荷醇具明显的止痒作用,其止痒作用与对抗组胺的作用和抑制组胺释放有关。
3.8 对皮肤的作用
薄荷属植物的重要精油成分薄荷醇表现出良好的透皮吸收作用,其在药品、化妆品、花露水等商品中得到广泛应用,但薄荷醇透皮吸收机理至今没有阐明。王晖[76]研究表明薄荷醇对家兔皮肤无急性刺激性。在临床常用浓度(1%)下,薄荷醇多次给药对家兔皮肤没有刺激性,但在2%浓度以上的薄荷醇在多次给药后会引起家兔皮肤结构不同程度的改变,但薄荷醇对豚鼠皮肤无致敏性。
3.9 毒副作用
尽管Mentha L.属植物精油有很长久的药食两用史,且被多个国家的FDA 列入药典范围,但其毒副作用也不容忽视。刘红杰[77]等研究表明过量使用M.canadensis 精油会造成肝脏损伤,其致病剂量为2.4 mL/kg。Odeyemi[78]研究同样显示过量使用M.longifolia 精油造成肝肾负担。因此,无论是个体差异还是薄荷属植物潜在的毒副作用,在使用剂量及未来研究中可能存在的毒副作用也都必须引起我们的高度重视。
4 展望
目前有关薄荷属植物挥发性成分的化学成分及药理活性研究已有大量研究报道,无论是抗氧化、抗菌、抗癌以及传统的解热镇痛等药理活性研究都不够深入,除个别研究系统阐述了药理学作用机理,大部分研究缺乏作用机制的深入探讨,未来可利用多种筛选模型,探究其生物作用,扩大薄荷属挥发性成分资源开发利用力度和前景。
笔者课题组已从事研究薄荷属植物10 多年,对我国薄荷原料药的质量甚为担忧,市场销售的薄荷鱼龙混杂,直接导致薄荷油成分参差不齐。虽然陈在敏等[77]通过GC-MS,HPLC 建立了薄荷素油及薄荷的指纹图谱,但指标性成分与活性有待商榷。因此加强原料药的品种选育及GAP 的研究控制,制定更加科学的质量标准,可在一定程度上保证药材质量。
薄荷属植物杂交严重,形态结构差异性低,鉴别难度大,许多研究存在植物基原混乱等显现,本文所总结的薄荷属植物均以种国际种接受名为准,对种以下如变种或变种接受名依据the plant list 数据库划归为种接受名。除此之外,薄荷属植物目前接受的种名有38 种,然而国内外研究薄荷属挥发性成分却始终集中在该属某几种,且没有进行同属的精油成分及相关活性比较。未来可对冷门的薄荷属植物挥发性物质成分及药理活性的研究,扩大该属植物的资源利用范围。
1 Harley RBC.Chromosme numbers in the genus Mentha..Bot J Linn Soc,1977,74:71-96.
2 The Editorial Board of Flora of China,Chinese Academy of Science. Flora of China. Vol. 17. Beijing:Science Press,1994.236-239.
3 Mimica DN,et al.Species (Lamiaceae)as promising sources of bioactive secondary metabolites. Curr Pharm Design,2008,14:3141-3150.
4 Esmaeili A,et al.Composition of the essential oils of Mentha aquatica L.and Nepeta meyeri Benth.from Iran.J Essent Oil Res,2006,18:263-265.
5 Sutour STF,et al. Chemical composition of the essential oil from Corsican Mentha aquatica-combined analysis by GC(RI),GC-MS and13C NMR spectroscopy. Nat Prod Commun,2011,6:1479-1482.
6 Singh AK,et al.Essential oil composition and chemoarrays of menthol mint (Mentha arvensis L. f. piperascens Malinvaud ex.Holmes)cultivars.Flavour Frag J,2005,20:302-305.
7 Pandey AK,Chowdhury AR.GC-MS studies of Japanese mint(Mentha arvensis L.)oil. J Med Aromatic Plant Sci,2000,22:468-469.
8 Zhou L,Xie WS. Studies on chemical constituents and antimicrobial activity of Mentha arvensis oil of Yunnan. Flavour Fragrance Cosmetics,2011,5:1-3.
9 Jirovetz L,et al. Chemical composition,olfactory evaluation and antioxidant effects of essential oil from Mentha canadensis.Nat Prod Commun,2009,4:1011-1016.
10 Rodrigues L,et al.Morphology of secretory structures and essential oil composition in Mentha cervina L. from Portugal.Flavour Frag J,2008,23:340-347.
11 Rodrigues L,et al.Chemodiversity studies on Mentha cervina L.populations from Portugal.Planta Med,2008,74:1199.
12 Goncalves MJ,et al. Composition and antifungal activity of the essential oil of Mentha cervina from Portugal. Nat Prod Res,2007,21:867-871.
13 Baser KHC,et al.Essential oils of Mentha species from Marmara region of Turkey.J Essent Oil Res,2012,24:265-272.
14 Singh HP,et al.Constituents of Leaf Essential Oil of Mentha longifolia from India.Chem Nat Compd,2008,44:528-529.
15 Nori SD,et al.Volatile component of Mentha longifolia (L.)Huds.from Iran.J Essent Oil Res,2000,12:111-112.
16 Younis YMH,Beshir SM. Carvone-rich essential oils from Mentha longifolia (L.)Huds.ssp schimperi Briq.and Mentha spicata L. grown in Sudan. J Essent Oil Res,2004,16:539-541.
17 Behnam S,et al.Composition and antifungal activity of essential oils of Mentha piperita and Lavendula angustifolia on post-harvest phytopathogens. Commun Agric Appl Biol Sci,2006,71:1321-1326.
18 Pino JA,et al.Essential oil of Mentha piperita L.grown in Jalisco.J Essent Oil Res,2002,14:189-190.
19 Stojanova A,et al.A comparative investigation on the essential oil composition of two Bulgarian cultivars of Mentha piperita L..J Essent Oil Res,2000,12:438-440.
20 Shahi AK,et al.Essential oil composition of Mentha x piperita L.from different environments of north India.Flavour Frag J,1999,14:5-8.
21 Rohloff J.Monoterpene composition of essential oil from peppermint (Mentha x piperita L.)with regard to leaf position using solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry analysis. J Agr Food Chem,1999,47:3782-3786.
22 Zhang RX,et al. Cymbopogon Jwarancusa(Jones)Schult. A species new to Yunnan and its chemical components of volatile oil.Bull Botanical Res,1995,(2):213-214.
23 Burbott AJ,et al.Configuration of piperitone from oil of mentha-piperita.Phytochem,1983,22:2227-2230.
24 Hassanpouraghdam MB,et al.New menthone type of Mentha pulegium L. volatile oil from Northwest Iran. Czech J Food Sci,2011,29:285-290.
25 Hajlaoui H,et al.Biological activities of the essential oils and methanol extract of tow cultivated mint species (Mentha longifolia and Mentha pulegium)used in the Tunisian folkloric medicine.World J Microb Biot,2009,25:2227-2238.
26 Chessa MSA,et al. Chemical composition and antibacterial activity of the essential oil from Mentha requienii Bentham.Nat Prod Res,2012,Epub ahead of print.
27 Schnelle FJ,Horster H.Glc Analysis of Essential Oil of Mentha Requienii.Planta Med,1968,16:48-53.
28 Brada M,et al. Variability of the chemical composition of Mentha rotundifolia from Northern Algeria. Biotechnologie Agronomie Societe et Environnement,2007,11:3-7.
29 Brada M,et al.Chemical composition of the leaf oil of Mentha rotundifolia (L.)from Algeria. J Essent Oil Res,2006,18:663-665.
30 Liang CY,et al. Essential oil composition of Mentha spicata L..Northwest Pharm J,2011,3:159-160.
31 Sarer E,et al. Composition and antimicrobial activity of the essential oil from Mentha spicata L. subsp spicata. J Essent Oil Res,2011,23:105-108.
32 Hussain AI,et al.Chemical composition,and antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of essential oil of spearmint (Mentha spicata L.)from Pakistan.J Essential Oil Res,2010,22:78-84.
33 Chauhan RS,et al.Chemical composition of essential oils in Mentha spicata L.accession IIIM(J)26 from North-West Himalayan region,India.Ind Crop Prod,2009,29:654-656.
34 Liu SH.Studies on chemical constituents of the essential oil from“801”mentha spicata.Guihaia,1997,17:286-288.
35 Sutour S,et al.Composition and chemical variability of Mentha suaveolens ssp suaveolens and M.suaveolens ssp insularis from Corsica.Chem Biodivers,2010,7:1002-1008.
36 Sutour S,et al.Chemical composition and antibacterial activity of the essential oil from Mentha suaveolens ssp insularis(Req.)Greuter.Flavour Frag J,2008,23:107-114.
37 Oumzil H,et al. Antibacterial and antifungal activity of essential oils of Mentha suaveolens. Phytother Res,2002,16:727-731.
38 Sousa PJC,et al.Antinociceptive effects of the essential oil of Mentha x villosa leaf and its major constituent piperitenone oxide in mice.Braz J Med Biol Res,2009,42:655-659.
39 Martins AD,et al.Preparation and characterization of Mentha x villosa Hudson oil-beta-cyclodextrin complex.J Therm Anal Calorim,2007,88:363-371.
40 Wildung MCR. Genetic engineering of peppermint for improved essential oil composition and yield. Transgenic Res,2005,14:365-372.
41 Edward M,et al. Monoterpene metabolism. cloning,expression,and characterization of menthone reductases from peppermint.Plant Physiol Biochem,2005,135:873-881.
42 Croteau RDE,et al. Menthol biosynthesis and molecular genetics.Naturwissenschaften,2005,92562-77:562-577.
43 B Markus Lange,Rodney Croteau.Genetic engineering of essential oil production in mint.Current Opinion in Plant Biology,1999,2:139-144.
44 Bouwmeester H,et al.Biosynthesis of the monoterpenes limonene and carvone in the fruit of caraway. Plant Physiol,1998,117:901-912.
45 The Editorial Committee on the Chinese Materia Medica of the State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine.Chinese Materia Medica. Vol.7. Shanghai:Shanghai Science and Technology Press,1999.79-84.
46 Schmidt E,et al. Chemical composition,olfactory evaluation and antioxidant effects of essential oil from Mentha x piperita.Nat Prod Commun,2009,4:1107-1112.
47 Gulluce M,et al.Antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of the essential oils and methanol extract from Mentha longifolia L.ssp longifolia.Food Chem,2007,103:1449-1456.
48 Li H,et al.Chemical composition and antibacterial activities of the essential oils isolated from leaves of Mentha × piperita,M. haplocalyx and M. × gentilis. Chin Bull Botany,2011,1:37-43.
49 Wang W,et al.Antimicrobial activities of Mentha haplocalyx Briq.essential oil.Bull Botan Res,2007,27:626-629.
50 Rodrigues L,et al. Antibacterial and antifungal activity of Mentha cervina essential oils and their main components.Planta Med,2010,76:1307.
51 Hafedh H,et al.Effect of Mentha longifolia L.ssp longifolia essential oil on the morphology of four pathogenic bacteria visualized by atomic force microscopy. Afr J Microbiol Res,2010,4:1122-1127.
52 Bassole IHN,et al. Composition and antimicrobial activities of Lippia multiflora Moldenke,Mentha x piperita L.and Ocimum basilicum L.essential oils and their major monoterpene alcohols alone and in combination.Molecules,2010,15:7825-7839.
53 Tassou C,Drosinos E.Nychas G.Effects of essential oil from Mint (Mentha-Piperita)on salmonella-enteritidis and listeria-monocytogenes in model food systems at 4-degrees and 10-degrees-C.J Appl Bacteriol,1995,78:593-600.
54 Sokovic MD,et al. Antifungal activity of the essential oil of Mentha x piperita.Pharm Biol,2006,44:511-515.
55 Kartal M,et al.Antimicrobial activity and composition of essential oils of Mentha spicata cultivated under organic farming conditions in Turkey.Planta Med,2008,74:1202.
56 Aggarwal KK,et al.Antimicrobial activity profiles of the two enantiomers of limonene and carvone isolated from the oils of Mentha spicata and Anethum sowa.Flavour Frag J,2002,17:59-63.
57 Rasooli I. Dental biofilm prevention by Mentha spicata and Eucalyptus camaldulensis essential oils. Int J Infect Dis,2008,12:E167.
58 Walker JT,Melin JB. Mentha x piperita,Mentha spicata and effects of their essential oils on Meloidogyne in soil.J Nematol,1996,28:629-635.
59 Ansari MA,et al.Larvicidal and mosquito repellent action of peppermint (Mentha piperita) oil. Bioresource Technol,2000,71:267-271.
60 Walker J,Melin J.Resistance of Mentha X piperita and Mentha spicata lines to root-knot nematodes. J Nematol,1995,27:523-524.
61 Haksar A,et al.Mint oil (Mentha spicata Linn.)offers behavioral radioprotection:a radiation-induced conditioned taste aversion study.Phytother Res,2009,23:293-296.
62 Samarth RM,Samarth M.Protection against radiation-induced testicular damage in swiss albino mice by Mentha piperita(Linn.).Basic Clin Pharm,2009,104:329-334.
63 Samarth RM,et al. Radioprotective influence of Mentha piperita (Linn)against gamma irradiation in mice:antioxidant and radical scavenging activity.Int J Radiat Biol,2006,82:331-337.
64 Samarth RM,et al. Protection of swiss albino mice against whole-body gamma irradiation by Mentha piperita (Linn.).Phytother Res,2004,18:546-550.
65 Samarth RM,Kumar A.Mentha piperita (Linn.)leaf extract provides protection against radiation induced chromosomal damage in bone marrow of mice. Indian J Exp Biol,2003,41:229-237.
66 Samarth RM,Kumar A.Radioprotection of Swiss albino mice by plant extract Mentha piperita (Linn.). J Radiat Res,2003,44:101-109.
67 Samarth RM,et al.Mentha piperita (Linn)leaf extract provides protection against radiation induced alterations in intestinal mucosa of Swiss albino mice.Indian J Exp Biol,2002,40:1245-1249.
68 Samarth RM,et al.Modulation of serum phosphatases activity in Swiss albino mice against gamma irradiation by Mentha piperita Linn..Phytother Res,2002,16:586-589.
69 Kumar A,et al. Anticancer and radioprotective potentials of Mentha piperita.Biofactors,2004,22(4):87-91.
70 Samarth RM,et al. Modulatory effect of Mentha piperita(Linn.)on serum phosphatases activity in Swiss albino mice against gamma irradiation.Indian J Exp Biol,2001,39:479-482.
71 Samartha RM,Kumar A.Nitric oxide mediated immunomodulation by Mentha piperita in Swiss albino mice.Nitric Oxide-Biol Ch,2004,11:128.
72 Shirazi FH,et al.Evaluation of northern Iran Mentha pulegium L.cytotoxicity.Daru,2004,12:106-110.
73 Lahlou S,et al. Cardiovascular effects of the essential oil of Mentha x villosa in DOCA-salt-hypertensive rats.Phytomedicine,2002,9:715-720.
74 Lahlou S,et al.Involvement of nitric oxide in the mediation of the hypotensive action of the essential oil of Mentha x villosa in normotensive conscious rats. Planta Med,2002,68:694-699.
75 Lin YB,et al.Study on antipruritic effect of Menthol.Chinese archives of traditional Chinese Medicine,2009,7:1488-1490.
76 Wan H,et al.The evaluation of menthol on cutaneous safety.Pharm Clinics Chin Mater Med,2008,3:32-35.
77 Chen ZM.Study on specific chromatogram and determination of chemical components in peppermint oil. Chin J PharmAnal,2011,10:1957-1960.
78 Odeyemi OO,et al. Toxicological evaluation of the essential oil from Mentha longifolia L.subsp capensis leaves in rats.J Med Food,2009,12:669-674.
