双星星族合成及其研究进展
2013-08-16李忠木
李忠木
(大理学院天文与科技史研究所,云南大理 671003)
双星星族合成及其研究进展
李忠木
(大理学院天文与科技史研究所,云南大理 671003)
研究表明:大约一半以上的恒星是双星,而且大部分双星与单星的演化明显不同,所以在星族合成中考虑双星的演化(即双星星族合成)对天体物理研究有重要意义。它因此被列为未来几十年星族合成的六大挑战之一。从双星星族合成的提出、关键研究内容和近几年的主要研究进展三个方面对双星星族合成方法进行了概述,其中重点阐述双星星族与单星星族的差别以及双星星族模型对天体物理研究的影响。
双星;星族合成
1 演化星族合成与双星星族合成
星系和星团的光线主要来自其中的恒星,因此这些天体的光线包含了它们的恒星形成及演化信息。我们可以用星族合成方法对星系和星团的恒星成分进行分析,从而对它们的形成和演化等重要过程进行研究。最初人们采用的星族合成方法是一种试验分析的技术〔1-6〕。这种方法采用恒星光谱的线性组合来解释星系和星团的整体光谱,其弱点是这种方法包含非常多的不定参数,这使得人们经常难以得到确定的结果。1978年,科学家提出了一种新的星族合成方法——演化星族合成〔7-20〕。这种新方法仅含有很少的几个不定参数,如:初始质量函数、恒星形成率、金属丰度等。它通过不同年龄时恒星在赫罗图上的分布来确定星族的整体光谱。到现在演化星族合成方法已经成了人们用于研究星系光谱的标准工具〔21〕。
在演化星族合成方法提出之后,人们就一直采用单星演化理论来确定不同时间恒星在赫罗图上的分布。这在操作上非常方便,因为单星的演化比较简单。通常不同恒星的演化可以用一个恒星演化轨迹库来表示,人们在星族合成研究中只要对这样的轨迹库进行插值即可。但实际上这样的操作并不完全与观测到的情况相符合。观测研究发现其实大部分恒星是双星或处在多星系统中,因此它们的演化不是纯粹的单星演化,这必然会影响到星族中恒星在赫罗图上的分布。不过天文学家们一直觉得这些双星或多星系统的演化不会对基于单星演化的星族合成(单星星族合成)结果造成大的影响〔22〕。此外,双星演化的计算比单星演化复杂得多,这无形中增大了研究的难度,因此大部分人仍然坚持使用单星星族合成方法,直至今日。
尽管如此,也有一些学者对由双星构成的星族(双星星族)进行研究,这就是双星星族合成。这些研究大部分都采用了Hurley等人〔23〕2002年建立的快速恒星演化程序进行恒星演化参数的计算。因为这个程序是基于一些通过拟合双星的演化轨迹而得到的拟合公式来计算双星的演化,所以其计算速度非常快,能够满足星族合成这样的大样本恒星系统研究的需求。另外,这个程序考虑了大部分双星相互作用,比较适合用于研究双星作用造成的影响。
2 双星星族合成的研究内容
因为星族合成是希望通过天体的整体光线来研究那些恒星不可分辨的天体的恒星成分,所以双星星族合成也不例外。根据这个目的,双星星族合成需要合成天体的各种可观测特征,主要包括:赫罗图(或颜色-星等图)、光谱、颜色、谱指数等。因为这些特征是研究中用于分析天体中恒星成分的主要依据,因此仔细研究双星星族的上述特征对星系和星团的星族研究非常重要。
双星星族合成的主要任务是详细考察双星演化对天体整体特征量的影响,以及探索如何使用这种方法对星系和星团的物理性质、形成和演化历史等进行研究。
3 双星星族合成的主要进展
国际上有几个小组开展了双星星族合成方面的研究,其中韩占文小组、李忠木小组和Bruzual小组〔24〕等人的工作属于演化星族合成,Hurley小组〔25〕和Kroupa小组〔26〕等人的工作则属于动力学合成。在演化星族合成方面,韩占文小组和李忠木小组的工作比较全面,他们最先建立了完善的双星星族合成模型并广泛地使用该模型开展研究。Bruzual小组只做了一个测试性的工作〔24〕,他们的结果与韩占文小组和李忠木小组在此之前的工作相一致。因为本文的主要对象是演化星族合成,所以这里仅就李忠木小组和韩占文小组的结果进行介绍。
李忠木小组的一个主要进展是建立了完整的双星星族合成模型。该模型同时包含了双星简单星族和双星复合星族合成模型。它给出了7种金属丰度、151种不同年龄(0-15 Gyr)的星族的高(0.3埃)、低(约20埃)分辨率光谱,以及谱指数、星等和颜色。其中高分辨率光谱的范围仅为可见光波段,而低分辨率的光谱则覆盖了紫外到近红外的整个波段〔27〕。因此,这个模型可以方便地用于星团和星系的颜色-星等图分析、光谱拟合、谱指数拟合等研究。为了方便和单星星族模型进行比较,李忠木小组的双星星族模型还采用完全相同的方法给出了与双星星族模型相对应的单星星族模型。大家可以通过相关的文章〔27-29〕来了解更多的信息。
基于上述的双星星族合成模型,我们仔细研究了双星作用对简单星族(一次星暴形成的星族)的颜色-星等图、能谱分布、谱指数和颜色等造成的影响,以及对简单星族年龄和金属丰度确定造成的影响〔30〕。结果表明,双星星族中会产生很多单星星族中难以出现的特殊恒星,如蓝离散星、黄离散星、红离散星、热亚矮星等。通常情况下,这些天体会使得相同金属丰度和年龄的双星星族会比单星星族蓝。另外,双星作用会使星族的光谱流量发生改变,通常对固定的金属丰度和较大的年龄,双星星族比单星星族在紫外波段上看起来亮很多(即紫外能流反转,见图1)。研究还表明,当使用双星星族和单星星族进行研究时,二者会得到不同的简单星族年龄和金属丰度。其中年龄的最大差异可达到8 Gyr。

图1 双星简单星族的紫外反转能谱
此外,由于很多研究都表明即使是星族成分比较简单的早型星系和球状星团,它们中的恒星也很可能不是一次形成的。因此,大部分星系和星团中的星族不是简单星族,而是复合星族。根据这种推论,2012年我们研究了双星星族对复合星族参数确定的影响〔31〕。结果发现,理论星族是否包含双星演化对复合星族中年轻成分的年龄测量造成了非常显著的影响。可以说,用双星星族和单星星族两类模型将会得到几乎完全不同的年轻恒星年龄。因此,星族模型中双星作用的加入有可能完全改变此前人们关于星系恒星形成历史的研究。另外,双星星族模型的使用可以改变此前关于星系中尘埃消光的研究结果:双星星族研究不再像单星星族研究那样需要负的消光值而且通常会得到更大的消光值。这些结果很可能会对将来的星系研究造成显著的影响。
当我们将双星星族模型用于具体星系和星团的研究时,我们同样取得了意想不到的成功。具体地,我们关于80个椭圆星系的谱指数研究给出了对星系等级成团并合形成模型的支持〔32〕。这与其它很多观测和动力学的研究相一致〔33〕。此外,同时考虑了双星作用和恒星转动的简单星族模型成功地解释了大麦哲伦云中中等年龄星团的奇异颜色-星等图〔34〕。星团中的蓝离散星、红离散星、主序和拐点展宽、扩展的红团簇等均被完美地重现。见图2。因为双星和恒星转动普遍存在于恒星之中,所以我们的模型是目前最自然的模型。
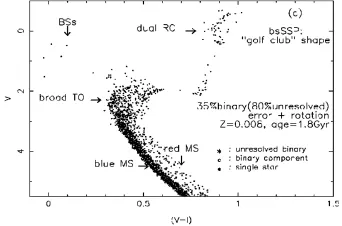
图2 金属丰度为0.008、年龄为1.8 Gyr的双星简单星族的颜色-星等图
除了上述结果外,韩占文小组的研究显示双星星族模型能够对星系测光红移的测定产生明显的影响〔35〕。他们还尝试着研究了双星作用对恒星形成率研究的影响,但结果表明双星作用似乎并不重要〔36〕。
4 讨论
双星是恒星存在的基本形式之一,其演化与单星有明显不同。双星演化对白矮星、脉冲星、Ia型超新星、引力波、伽马射线暴、演化星族合成等研究均有重要的意义。双星在星族合成研究中的作用被列入了未来几十年星族合成领域的六大挑战之一。目前有越来越多的学者正投入这方面的工作之中,相信双星星族合成会在天文和天体物理研究中独放异彩。虽然已经取得了明显的进展,但是双星星族合成还有很多地方有待提高。首先,大家几乎都采用Hurley等人的快速恒星演化程序进行双星演化计算。因为程序本身含有很大不确定性,所以基于这个程序得到的结果也难以精确。第二,我们的金属丰度(Z)上限值仅为0.03,这对很多天体显然太低(单星星族研究中一般取到0.05以上)。第三,不管是双星演化还是单星演化,都有很多演化阶段(图TP-AGB)的处理并不确定。最后,星族合成研究中的很多物理参量对其观测量的影响是简并的,这使得我们的很多结果都不确定。因此,双星星族合成还有很长的路要走,其发展不仅要依赖于更多、更全面的理论模拟,也需要更完善的观测限制。
〔1〕Spinrad H,Taylor B J.The Stellar Content of the Nuclei of Nearby Galaxies.I.M31,M32,and M81〔J〕.Astrophysical Journal Supplement,1971,22:445-484.
〔2〕Faber S M.Variations in Spectral-Energy Distributions and Absorption-Line Strengths among Elliptical Galaxies〔J〕. Astrophysical Journal,1973,179:731-754.
〔3〕O'Connell R W.Galaxy spectral synthesis.I- Stellar populations in the nuclei of giant ellipticals〔J〕.Astrophysical Journal,1976,206:370-390.
〔4〕Turnrose B E.The stellar content of the nuclear regions of SC galaxies〔J〕.Astrophysical Journal,1976,210:33-37.
〔5〕Pritchet C.Stellar population synthesis of galactic nuclei〔J〕.Astrophysical Journal Supplement,1977,35:397-418.
〔6〕Pickles A J.Differential population synthesis of early-type galaxies.III-Synthesis results〔J〕.Astrophysical Journal,1985,296:340-369.
〔7〕Tinsley B M.Evolutionary synthesis of the stellar population in elliptical galaxies.II-Late M giants and composition effects〔J〕.Astrophysical Journal,1978,222:14-22.
〔8〕Bruzual A G.Spectral evolution of galaxies.I-Early-type systems〔J〕.Astrophysical Journal,1983,273:105-127.
〔9〕Arimoto N,Yoshii Y.Chemical and photometric properties of a galactic wind model for elliptical galaxies〔J〕.Astronomy and Astrophysics,1987,173(1):23-38.
〔10〕Guiderdoni B,Rocca-Volmerange B.A model of spectrophotometric evolution for high-redshift galaxies〔J〕.Astronomy and Astrophysics,1987,186(1-2):1-21.
〔11〕Buzzoni A.Evolutionary population synthesis in stellar systems.I-A global approach〔J〕.Astrophysical JournalSupplement,1989,71:817-869.
〔12〕Bruzual A G,Charlot S.Spectral evolution of stellar populations using isochrone synthesis〔J〕.Astrophysical Journal,1993,405:538-553.
〔13〕Bressan A,Chiosi C,Fagotto F.Spectrophotometric evolution of elliptical galaxies.1:Ultraviolet excess and colormagnitude-redshift relations〔J〕.Astrophysical Journal Supplement,1994,94:63-115.
〔14〕Fritze V,Alvensleben U,Gerhard O E.Star formation in merging galaxies〔J〕.Astronomy and Astrophysics,1994,285:751-774.
〔15〕Worthey G,Faber S M,Gonzalez J Jesus,et al.Old stellar populations.5:Absorption feature indices for the complete LICK/IDS sample of stars〔J〕.Astrophysical Journal Supplement,1994,94(2):687-722.
〔16〕Leitherer C,Heckman T M.Synthetic properties of starburst galaxies〔J〕.Astrophysical Journal Supplement,1995,96(1):9-38.
〔17〕Fioc M,Rocca-Volmerange B.PEGASE:a UV to NIR spectral evolution model of galaxies.Application to the calibration of bright galaxy counts〔J〕.Astronomy and Astrophysics,1997,326:950-962.
〔18〕Maraston,C.Evolutionary synthesis of stellar populations:a modulartool〔J〕.MonthlyNoticesofthe Royal Astronomical Society,1998,300:872-892.
〔19〕Vazdekis A.Evolutionary Stellar Population Synthesis at 2 Å Spectral Resolution〔J〕.Astrophysical Journal,1998,513(1):224-241.
〔20〕Bruzual G,Charlot S.Stellar population synthesis at the resolution of 2003〔J〕.Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society,2003,344:1000-1028.
〔21〕Walcher J,Groves B,Budavári T,et al.Fitting the integrated spectral energy distributions of galaxies〔J〕.Astrophysics and Space Science,2011,331(1):1-51.
〔22〕Brinchmann J.Challenges in Stellar Population Studies〔J〕. IAUS,2010,262:3.
〔23〕Hurley J R,Tout C A,Pols O R.Evolution of binary stars and the effect of tides on binary populations〔J〕.Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society,2002,329(4):897-928.
〔24〕Hernández F C,Bruzual G.A Stellar Population Synthesis Model that Includes Binary Interaction〔J〕.Revista Mexicana de Astronomia y Astrofisica Conference Series,2011,40:277.
〔25〕Hurley J R,Shara M.A direct N-body model of corecollapse and core oscillations〔J〕.Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society,2012,425(4):2872-2879.
〔26〕Marks M,Kroupa P.Inverse dynamical population synthesis. Constraining the initial conditions of young stellar clusters by studying their binary populations〔J〕.Astronomy and Astrophysics,2012(543):A8.
〔27〕Li Z M,Han Z W.An isochrone data base and a rapid model for stellar population synthesis〔J〕.Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society,2008,387(1):105-114.
〔28〕Li Z M,Han Z W.Fitting formulae for the effects of binary interactions on lick indices and colors ofstellar populations〔J〕.Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics,2009,9(2):191-204.
〔29〕Li Z M,Zhang L Y,Liu J Z.Integrated spectral energy distributions of binary star composite stellar populations〔J〕.Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society,2012,424:874-883.
〔30〕Li Z,Han Z W.How Binary Interactions Affect Spectral Stellar Population Synthesis〔J〕.Astrophysical Journal,2008,685(1):225-234.
〔31〕Li Z M,et al.Importance of binary evolution for UV-opticalspectralfittingofearly-type galaxies〔J〕. Astrophysical Journal,submitted.
〔32〕Li Z M,Zhang F H,Zhan W H.A Study of Binary Stellar Population Synthesis of Elliptical Galaxies〔J〕.Chinese Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics,2006,6(6):669-679.
〔33〕Thomas D,Maraston C,Bender R,et al.The Epochs of Early-Type Galaxy Formation as a Function of Environment〔J〕.Astrophysical Journal,2005,621(2):673.
〔34〕Li Z M,Mao C Y,Li R H,et al.A binary study of colormagnitude diagrams of 12 globular clusters〔J〕.Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics,2010,10(2):135-141.
〔35〕Zhang F H,Han Z W,Li L F,et al.The effects of ultraviolet photometry and binary interactions on photometric redshift and galaxy morphology〔J〕.Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society,2010,408(2):1283-1306.
〔36〕Zhang F H,Li L F,Zhang Y,et al.Binary interactions on the calibrations of star formation rate〔J〕.Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society,2012,421(1):743-759.
Binary Star Stellar Population Synthesis
LI Zhongmu
(Institute for Astronomy and History of Science and Technology,Dali University,Dali,Yunnan 671003,China)
Observations showed that more than half stars are binaries,and the evolution of binaries is obviously different from single stars. Therefore,it is important to include binary evolution in stellar population synthesis.The importance of binaries for stellar population studies has been listed as one of six main challenges of stellar population synthesis in the next decades.This paper introduces the birth,main research content and progress of binary star stellar population synthesis.
binary star;stellar population synthesis
P153
A
1672-2345(2013)04-0029-04
云南省教育厅科研基金重点资助项目(2010Z004)
2012-12-27
2013-03-01
李忠木,教授,主要从事星族合成及星系研究.
(责任编辑 袁 霞)
10.3969/j.issn.1672-2345.2013.04.008
