新型尿苷肽类化合物Sansanmycin P的提取分离、结构鉴定及活性研究
2013-05-09王林林姚恩泰陈汝贤许鸿章解云英
王林林,蔡 强,何 宁,姚恩泰,陈汝贤,许鸿章,解云英
新型尿苷肽类化合物Sansanmycin P的提取分离、结构鉴定及活性研究
王林林,蔡 强,何 宁,姚恩泰,陈汝贤,许鸿章,解云英
目的 从放线菌 Streptomyces sp SS 发酵液中分离新型活性尿苷肽类似物。
抗生素类,抗结核; 假单胞菌,铜绿;Sansanmycin P
www.cmbp.net.cn 中国医药生物技术, 2013, 8(4):264-268
尿苷肽类抗生素是一类具有相同母核结构的化合物,主要包括 Sansanmycin、Mureidomycin、Pacidamycin 和 Napsamycin[1]。这类抗生素通过抑制 UDP-N-乙酰胞壁酸-五肽转位酶(MraY 转位酶)而抑制细菌细胞壁的合成。这种独特的机制使其与现有抗菌药物不会产生交叉耐药,从而成为寻找新型的低毒、窄谱抗菌药物的候选化合物或先导化合物[2-6]。本课题组在前期的抗菌药物筛选研究中,从放线菌 Streptomyces sp SS 的发酵液中分离到了一组具有抗铜绿假单胞菌和结核杆菌活性的尿苷肽类化合物 Sansanmycins[7-11],对其进一步研究,又分离到了一个新型的尿苷肽类化合物Sansanmycin P。本文对 Sansanmycin P 的分离纯化、结构鉴定和抗菌活性进行报道。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
1.1.1 菌株 放线菌 Streptomyces sp SS 从中国贵州土壤中分离得到;铜绿假单胞菌由本所菌种保藏中心提供。
1.1.2 培养基 斜面培养基为 ISP2 培养基;种子和发酵培养基由葡萄糖 3%、淀粉 0.5%、蛋白胨0.6%、(NH4)2SO40.7%、CaCO30.2% 组成;检定培养基为MH 培养基。
1.1.3 仪器及试剂 HPLC-1200 购自美国安捷伦公司;质谱数据用美国赛默飞世尔公司的 LTQ XT ion trap 型质谱仪采集;核磁数据用 Varian VNS-600采集;分析色谱柱 XBridge C18柱(4.6 mm × 150 mm,3.5 μm)及制备色谱柱 XBridge C18 OBD Prep 柱(19 mm × 150 mm,5 μm)均购自美国Waters 公司;大孔吸附树脂 D4006 和 X5 购自南开大学精细化工厂;离子交换树脂 DEAE-葡聚糖凝胶 A-25 购自上海化学试剂厂。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 发酵培养 菌种接种于斜面培养基上,28 ℃ 培养 7 d 后接种于种子培养基中,于 28 ℃、200 r/min 振荡培养 2 d,将生长良好的种子按10% 的接种量接入发酵培养基中,28 ℃、200 r/min发酵培养 5 d。
1.2.2 提取、分离和纯化 发酵液合并、离心,弃菌丝体,上清液上 D4006 大孔树脂柱,依次用水、10%、20%、30%、50% 丙酮各 12 L 洗脱,检测各组分抗铜绿假单胞菌活性,合并活性部分,旋转蒸发浓缩后真空冷冻干燥,得粗品。将粗品溶于 10 ml 0.02 mol/L Tris-HCl(pH 8.5)溶液中,上DEAE-葡聚糖凝胶柱 A-25,用 0.02 mol/L Tris-HCl加不同浓度的 NaCl 洗脱,分部收集,HPLC 检测,按组分合并,经 X5 大孔吸附树脂柱脱盐后,冷冻干燥,除得到已经报道的 Sansanmycin 外,还得一潜在的新组分 Sansanmycin P。将其溶于 2 ml 水中,用制备液相进行制备,流动相为 MeOH∶0.1% (NH4)2CO3= 32∶68,流速:5 ml/min。合并纯度大于 90% 的组分,脱盐后将洗脱液旋转蒸发、冷冻干燥。
1.2.3 抗菌活性 抗结核杆菌 H37Rv 活性以微孔板法(microplate alamar blue assay,MABA)[12]测定,以利福平和异烟肼为阳性药,并与 Sansanmycin家族已报道化合物抗结核活性对比。抗铜绿假单胞菌活性采用微量板液体稀释法测定。
2 结果
2.1 Sansanmycin P 的理化性质和结构鉴定
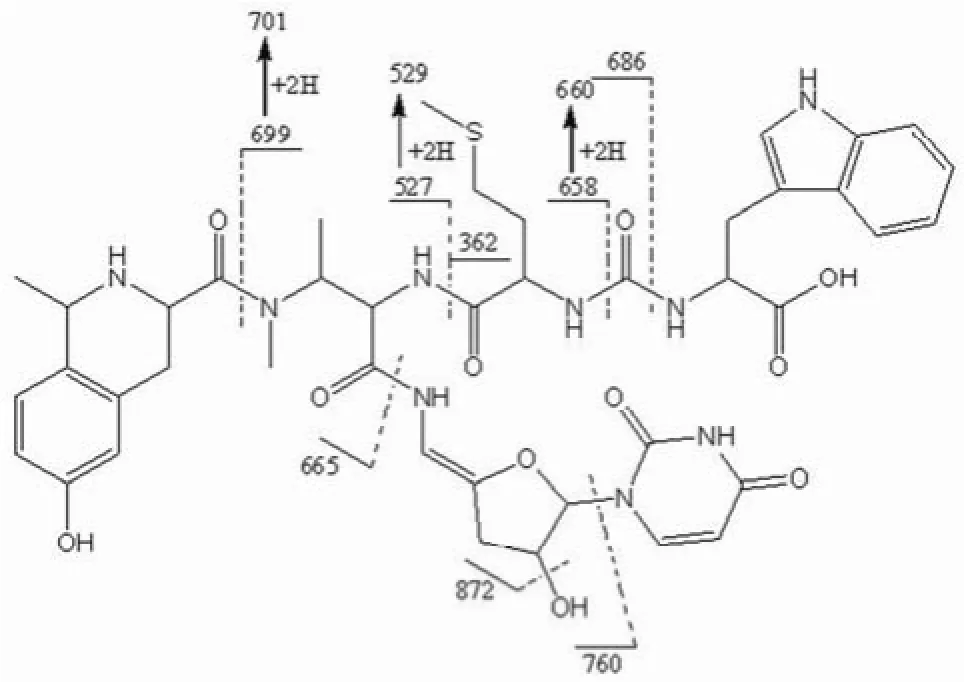
图1 Sansanmycin P 母离子(m/z 890)的 ESI-MS/MS 分析结果Figure1 ESI-MS/MS data of parent ion peak (m/z 890) of Sansanmycin P
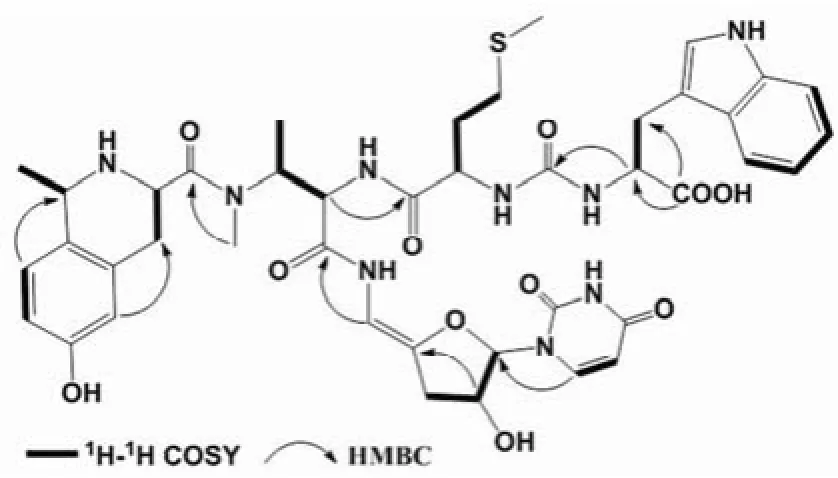
图2 Sansanmycin P 的部分 HMBC 和1H-1H COSY 数据Figure2 Selected HMBC and1H-1H COSY data for Sansanmycin P
2.2 抗菌活性
Sansanmycin P 对结核杆菌 H37Rv 和铜绿假单胞菌的抑制活性均较弱(MIC > 32 μg/ml),低于Sansanmycin A 的抗菌活性(表 2)。
3 讨论
2000 年,Bozzoli 等[15]通过固相合成法合成了一系列 Mureidomycin 类似物,证明中心模块AMBA 为活性必需基团。2001 年,Boojamra 等[4-5]全合成了二氢 Pacidamycin 及其衍生物,并阐明了其立体构型,表明其中所有氨基酸均为天然的S 构型,AMBA 为(2S,3S)构型,为活性必需构型;3'-脱氧尿苷可能与 MraY 转位酶的底物——UDP 竞争活性部位,也是活性所必需基团。Howard和 Bugg[16]对 Mureidomycin A 的氨基作用进行了研究,结果表明:肽链的氨基末端对酶的抑制活性是非常重要的,推测 Mureidomycin A 可能是通过末端铵离子与 MraY 转位酶活性中心的 Mg2+结
合位点结合而起到抑制作用。我们实验室前期通过半合成方法也对 N-末端进行了构效关系研究,结果表明,N 上连接的烷基空间位阻可能影响化合物与 MraY 转位酶间的相互作用[17]。这可能解释了Sansanmycin P 抗菌活性低的原因,Sansanmycin P的 N 末端四氢异喹啉结构上 1 位甲基的存在影响了铵离子与 MraY 转位酶活性中心的 Mg2+结合位点结合,从而影响了化合物的抗菌活性。

表1 Sansanmycin P 的1H-NMR(600 MHz)和13C-NMR(150 MHz)数据Table1 1H-NMR (600 MHz) and13C-NMR (150 MHz) data for Sansanmycin P

表2 Sansanmycin P 对铜绿假单胞菌和结核分枝杆菌 H37Rv 的 MIC 值(μg/ml)Table2 MIC values of Sansanmycin P against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv (μg/ml)
[1] Li QL, Xie YY, Chen RX, et al. Biosynthesis of uridyl peptide antibiotics: research advances. J Int Pharm Res, 2012, 39(1):17-25. (in Chinese)
李青连, 解云英, 陈汝贤, 等. 尿苷肽类抗生素生物合成研究进展.国际药学研究杂志, 2012, 39(1):17-25.
[2] Dini C. MraY inhibitors as novel antibacterial agents. Curr Top Med Chem, 2005, 5(13):1221-1236.
[3] Winn M, Goss RJ, Kimura K, et al. Antimicrobial nucleoside antibiotics targeting cell wall assembly: recent advances in structure-function studies and nucleoside biosynthesis. Nat Prod Rep, 2010, 27(2):279-304.
[4] Boojamra CG, Lemoine RC, Lee JC, et al. Stereochemical elucidation and total synthesis of dihydropacidamycin D, a semisynthetic pacidamycin. J Am Chem Soc, 2001, 123(5):870-874.
[5] Boojamra CG, Lemoine RC, Blais J, et al. Synthetic dihydropacidamycin antibiotics: a modified spectrum of activity for the pacidamycin class. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 2003, 13(19):3305-3309.
[6] Sun D, Jones V, Carson EI, et al. Solid-phase synthesis and biological evaluation of a uridyl branched peptide urea library. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 2007, 17(24):6899-6904.
[7] Xie Y, Chen R, Si S, et al. A new nucleosidyl-peptide antibiotic, sansanmycin. J Antibiot (Tokyo), 2007, 60(2):158-161.
[8] Xie Y, Xu H, Si S, et al. Sansanmycins B and C, new components of Sansanmycins. J Antibiot (Tokyo), 2008, 61(4):237-240.
[9] Xie YY, Xu HZ, Yu Y, et al. Isolation, purification and structure determination of uridylpeptide antibiotic Sansanmycin D with activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chin J Antibiotics, 2009, 34(1): 12-14, 44. (in Chinese)
解云英, 许鸿章, 俞莹, 等. 尿苷肽类抗生素Sansanmycin D的分离、纯化和结构鉴定. 中国抗生素杂志, 2009, 34(1):12-14, 44.
[10] Xie YY, Xu HZ, Yu Y, et al. Isolation, purification and structure determination of uridylpeptide antibiotic Sansanmycin E. Chin J Antibiotics, 2009, 34(6):326-328. (in Chinese)
解云英, 许鸿章, 俞莹, 等. 尿苷肽类抗生素Sansanmycin E的分离、纯化和结构鉴定. 中国抗生素杂志, 2009, 34(6):326-328.
[11] Xie Y, Xu H, Sun C, et al. Two novel nucleosidyl-peptide antibiotics: Sansanmycin F and G produced by Streptomyces sp SS. J Antibiot, 2010, 63(3):143-146.
[12] Collins L, Franzblau SG. Microplate alamar blue assay versus BACTEC 460 system for high-throughput screening of compounds against Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 1997, 41(5):1004-1009.
[13] Chatterjee S, Nadkarni SR, Vijayakumar EK, et al. Napsamycins, new Pseudomonas active antibiotics of the mureidomycin family from Streptomyces sp. HIL Y-82,11372. J Antibiot (Tokyo), 1994, 47(5): 595-598.
[14] Isono F, Sakaida Y, Takahashi S, et al. Mureidomycins E and F, minor components of mureidomycins. J Antibiot (Tokyo), 1993, 46(8):1203-1207.
[15] Bozzoli A, Kazmierski W, Kennedy G, et al. A solid-phase approach to analogues of the antibiotic mureidomycin. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 2000, 10(24):2759-2763.
[16] Howard NI, Bugg TD. Synthesis and activity of 5′-uridinyl dipeptide analogues mimicking the amino terminal peptide chain of nucleoside antibiotic Mureidomycin A. Bioorg Med Chem, 2003, 11(14):3083-3099.
[17] Li YB, Xie YY, Du NN, et al. Synthesis and in vitro antitubercular evaluation of novel sansanmycin derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 2011, 21(22):6804-6807.
Isolation, structural determinatio n and biological activity of novel uridyl peptide compound Sansanmycin P
WANG Lin-lin, CAI Qiang, HE Ning, YAO En-tai, CHEN Ru-xian, XU Hong-zhang, XIE Yun-ying
Objective To isolate new uridyl peptide components from the fermentation broth of Streptomyces sp. SS.Methods The new component was isolated and purified by various chromatography methods, such as macroporous adsorption resins, ion exchange resin and reversed-phase HPLC. Its structure was elucidated by spectroscopic analyses, such as UV, MS, MS/MS, 1D and 2D NMR.Results A novel uridyl peptide antibiotic, Sansanmycin P, with an N-terminal containing 1-methyl-6-hydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-3-isoquinoline carboxylic acid was obtained. Antibacterial activity in vitro, resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa MIC > 32 μg/ml, Mycobacterium tuberculosis MIC > 32 μg/ml.Conclusion Sansanmycin P is a novel Sansanmycin analogue with certain antimicrobial activities against Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Antibiotics, antitubercular; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Sansanmycin P
XIE Yun-ying, Email: xyying102@163.com
10.3969/cmba.j.issn.1673-713X.2013.04.005
国家自然科学基金面上项目(81273415);“重大新药创制”国家科技重大专项(2012ZX09301002-001-018)
100050 北京,中国医学科学院北京协和医学院医药生物技术研究所微生物化学室
解云英,Email:xyying102@163.com
2013-04-28
方法 发酵液经 D4006 大孔吸附树脂、DEAE-葡聚糖凝胶及制备液相分离纯化,获得单一化合物;根据 UV、MS、MS/MS、1D 和 2D NMR 确定化合物结构,并进行抗菌活性研究。
结果 分离纯化得到 1 个 N-末端含有1-甲基-6-羟基四氢异喹啉的尿苷肽类化合物 Sansanmycin P。初步体外抗菌活性,抗铜绿假单胞菌 MIC > 32 μg/ml,抗结核杆菌 MIC > 32 μg/ml。
结论 Sansanmycin P 为全新结构 Sansanmycins 类似物,具有一定抗结核杆菌和铜绿假单胞菌活性。
Author Affiliation: Microorganism and Chemistry Laboratory, Institute of Medicinal Biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100050, China
www.cmbp.net.cn Chin Med Biotechnol, 2013, 8(4):264-268
