同源区段长度对In-Fusion技术连接效率的影响
2013-05-09李慧仙
李慧仙,朱 平
·论著·
同源区段长度对In-Fusion技术连接效率的影响
李慧仙,朱 平
目的 在目的基因原载体(DNA 模板)与克隆载体相同的条件下,探讨了 PCR 扩增片段(含目的基因)的末端与载体间同源区段长度对 In-Fusion 连接效率的影响,并建立以In-Fusion 技术为基础的高通量克隆方法。
定向分子进化; In-Fusion 技术; 同源区段; 高通量克隆
www.cmbp.net.cn 中国医药生物技术, 2013, 8(4):241-246
近年来发展起来的高通量克隆技术广泛应用于定向进化、结构基因组学等研究[1-2],它不依赖于酶切连接,克服了常规酶切连接法效率低下、载体自连程度高等因素的限制,尤其适用于较大基因片段的高效克隆[3]。根据连接方式的不同,又可分为以下两类:①依赖于 PCR 的连接,例如POE-PCR 技术(prolonged overlap extension PCR)[4]、MEGAWHOP 技术(megaprimer PCR of whole plasmid)[5]等。该类方法均基于 PCR 进行全长质粒扩增,阳性重组率可高达 100%,但是连接成功率取决于两片段能否成功退火,以及在第二轮 PCR中能否有效去除前一轮所用引物,通常技术要求高,不具有应用普遍性;②依赖于同源重组酶的连接,例如 Gateway 技术(Invitrogen)[6]、In-Fusion技术(Clontech)[7]等。Gateway 技术是基于 λ 噬菌体位点特异重组系统,由 BP 和 LR 两个反应构成,两个反应的阳性重组率均可高达 90% 以上,但会引入多余序列。该技术需要特殊含 attR 位点表达载体,Invitrogen 公司提供一系列常用 attR 位点修饰后的表达载体,此外,还可以将目的载体改造成为 Gateway 表达载体。该技术最大的优势在于通过 BP 反应构建入门载体后,通过 LR 反应就可以使插入片段在不同表达载体间快速准确穿梭,便于功能基因的分析和蛋白的表达。In-Fusion技术是依赖于 In-Fusion 酶 3' → 5' 外切酶活性,经短时间即可在插入片段与载体的同源区段(homologous or over-lapping sequence)上形成互补的单链黏端,继而在单链黏端之间自发退火形成重组质粒。In-Fusion 技术适用于任何载体,不需对载体进行改造,也不会引入多余序列,在设计基因片段的上、下游引物时,两引物的 5'-末端分别仅需要 15 个碱基与载体序列相同[8]。值得注意的是,与 Gateway 技术相比,In-Fusion 技术连接时只需要一步,在定向进化突变库构建应用中降低了多步骤连接带来的库容量与丰度的损失。
但在应用 In-Fusion 技术进行基因克隆时,15 bp 的同源区段长度对于大片段 DNA 的克隆还存在阳性重组率有所减低的问题[9-10]。Sleight 等[11]发现增加同源区段的长度可以提高阳性重组率,但同源区段增加多长为宜尚没有明确的答案。另外,无限制地增加同源区段长度也会因引物的加长而增加引物合成成本。能否在不增加引物长度的前提下,也能增加同源区段长度并大幅度提高阳性重组率?这一问题在进行定向进化研究时是可以解决的,条件是克隆前后所用的载体要相同,至少在克隆位点附近的序列要前后一致。即在应用易错 PCR(error-prone PCR)或 DNA 改组等技术进行 PCR扩增时,选取目的基因两侧的载体序列按常规方法设计出一般长度的引物,载体序列距离目的基因越远,则同源区段长度越长。我们在构建糖基水解酶Lxyl-p1-2 基因突变库时目的基因长度为 2412 bp,实验发现最适同源区段长度大约为 100 bp,此时的阳性重组率高达 90% 左右,远高于同源区段为15 ~ 50 bp 的阳性重组率。但若再继续增加同源区段长度则无明显的效果。本文对上述实验结果做重点介绍。
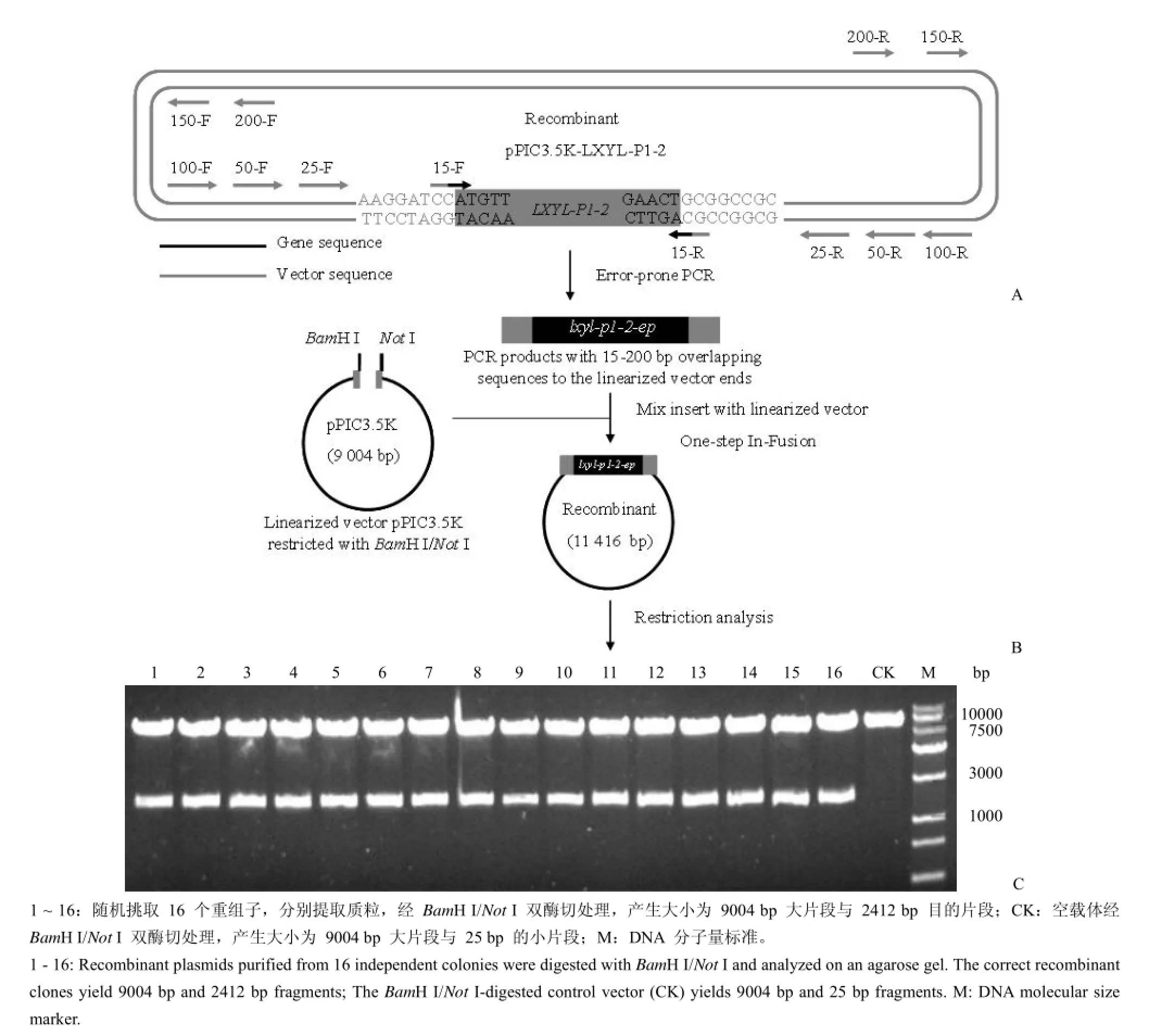
图1 In-Fusion 技术构建糖基水解酶 Lxyl-p1-2 基因突变库示意图(A:引物在原载体上的同源部位;B:In-Fusion 一步法连接;C:重组质粒 BamH I/Not I 酶切鉴定)Figure1 Schematic diagram of construction of Lxyl-p1-2 mutant library by In-Fusion technique (A: Homologous positions of the primers on the original vector; B: One-step ligation by In-Fusion enzyme; C: Restriction analysis of the recombinant plasmids by BamH I/Not I)
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
1.1.1 工具酶和试剂 限制性内切酶、T4 DNA连接酶、Dpn I、Taq DNA 聚合酶、PCR 试剂购自NEB;DNA marker、PCR 产物纯化试剂盒、琼脂糖凝胶 DNA 回收试剂盒购自北京全式金生物技术有限公司;In-Fusion PCR 克隆试剂盒购自淮安百慧生物科技有限公司;引物由 Invitrogen 公司合成;质粒小提试剂盒购自天根生化科技(北京)有限公司;其余试剂均为国产或进口分析纯。
1.1.2 菌株和质粒 大肠杆菌 E.coli TG1 由本实验室保存。重组质粒 pPIC3.5K-LXYL-P1-2 由本实验室构建,巴斯德毕赤酵母 Pichia pastoris GS115、载体 pPIC3.5K 购自 Invitrogen 公司。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 引物设计 In-Fusion 技术的核心是设计引物使目的基因的 5'-末端分别与线性化载体末端至少含有 15 bp 同源序列。如图 1A 所示,根据目的基因两侧的载体区域设计引物,引物的同源序列距离目的基因越远,则扩增得到的 DNA 片段与载体的同源区段越长。所用的上/下游引物序列见表 1,其同源区段的长度分别为:15、25、50、100、150和 200 bp。
1.2.2 Lxyl-p1-2 的易错 PCR 扩增 以含Lxyl-p1-2 基因的重组质粒 pPIC3.5K-LXYL-P1-2为模板,进行易错 PCR 扩增。50 μl 反应体系含有:1 × Taq DNA 聚合酶缓冲液、0.2 mol/L dATP 和dCTP、1 mol/L dGTP 和 dTTP、7 mmol/L MgCl2、0.5 mmol/L MnCl2、上下游引物各 0.4 µmol/L、模板 DNA 1 ng、Taq DNA 聚合酶 3U。PCR 扩增条件:94 ℃ 3 min;94 ℃ 30 s,58 ℃ 30 s,72 ℃ 2 min 30 s,共 30 个循环;72 ℃ 10 min。
易错 PCR 扩增产物命名为 Lxyl-p1-2-ep, Dpn I 消化以彻底去除原始模板质粒 pPIC3.5KLXYL-P1-2[12]。
1.2.3 In-Fusion 连接反应摩尔比的优化 将目的基因和限制性内切酶 BamH I/Not I 双酶切处理的线性化载体按照摩尔比 1∶1、3∶1、5∶1 和 10∶1 的梯度混合均匀,目的基因两端的序列和载体序列间同源区段长度为 15 bp,各梯度载体总量相同,均为 100 ng,加入 In-Fusion 酶 3 μl,补足水至10 μl,25 ℃ 反应 30 min。取 5 μl 连接产物转化大肠杆菌 TG1 感受态细胞,均匀涂布于 LB(含100 μg/ml Amp)固体培养基上,37 ℃ 过夜培养。阳性重组率通过菌落 PCR 测定,以确定最优摩尔比连接体系。
重组子的筛选:从 LB(含 100 μg/ml Amp)平板上挑取单菌落,利用 pPIC3.5K 序列引物5'AOX1 和 3'AOX1 进行菌落 PCR,鉴定阳性转化子。PCR 扩增条件:94 ℃ 3 min;94 ℃ 30 s,55 ℃ 30 s,72 ℃ 2 min 30 s,共 30 个循环;72 ℃10 min。

表1 本研究所用的引物及其序列Table1 The primers and the sequences utilized in this study
定义:阳性重组率(%)=(菌落 PCR 鉴定阳性的单菌落数/LB 板上的全部单菌落数)× 100%。
1.2.4 In-Fusion 克隆时同源区段长度对阳性重组率的影响 为考察不同长度同源区段对阳性重组率的影响,利用表 1 所示的上/下游引物进行 PCR扩增,将扩增产物分别与线性化载体通过 In-Fusion连接,取 5 μl 连接产物转化大肠杆菌 TG1 感受态细胞。阳性重组率通过菌落 PCR 测定,比较不同长度同源区段间阳性重组率的差异。
1.2.5 In-Fusion 法与常规酶切连接法阳性重组率的比较 分别运用常规酶切连接法与 In-Fusion 法构建 Lxyl-p1-2 基因的突变库,比较两种方法的阳性重组率。
重组质粒 pPIC3.5K-LXYL-P1-2 和载体pPIC3.5 分别用 BamH I/Not I 双酶切处理,分别回收目的基因片段(切胶回收)和载体片段(乙醇沉淀回收)。
T4 连接:酶切回收基因片段和载体 pPIC3.5K酶切片段按照摩尔比 5∶1 混合均匀,载体的量为100 ng,T4 DNA ligase 1 μl,10 × T4 DNA ligase Buffer 2 µl,水补至 20 μl,16 ℃ 连接 3 h。取 5 μl连接产物转化大肠杆菌 TG1 感受态细胞。阳性重组率通过菌落 PCR 测定。
2 结果
2.1 Lxyl-p1-2 的易错 PCR 扩增
以含 Lxyl-p1-2 基因的重组质粒 pPIC3.5KLXYL-P1-2 为模板,引物 15-F/15-R、25-F/25-R、50-F/50-R、100-F/100-R、150-F/150-R 和 200-F/ 200-R 通过易错 PCR 扩增分别得到理论值大小为2442、2462、2512、2612、2712 和 2812 bp 的Lxyl-p1-2-ep 基因片段(扩增片段上下游与载体分别含有 15、25、50、100、150 和 200 bp 的重叠序列)(图 2)。

图2 易错 PCR 扩增 Lxyl-p1-2 片段电泳图Figure2 Electrophoresis of error-prone PCR product of Lxyl-p1-2
2.2 In-Fusion 连接反应摩尔比的优化
插入片段与载体的不同摩尔比,结果如图 3所示。在插入片段与载体的比例为 1∶1、3∶1、5∶1和 10∶1 的梯度中,载体的量均为 100 ng。随着插入片段与载体摩尔比的增加,阳性重组率上升明显,当摩尔比增加到 5∶1 时达到峰值,此为最佳摩尔比。
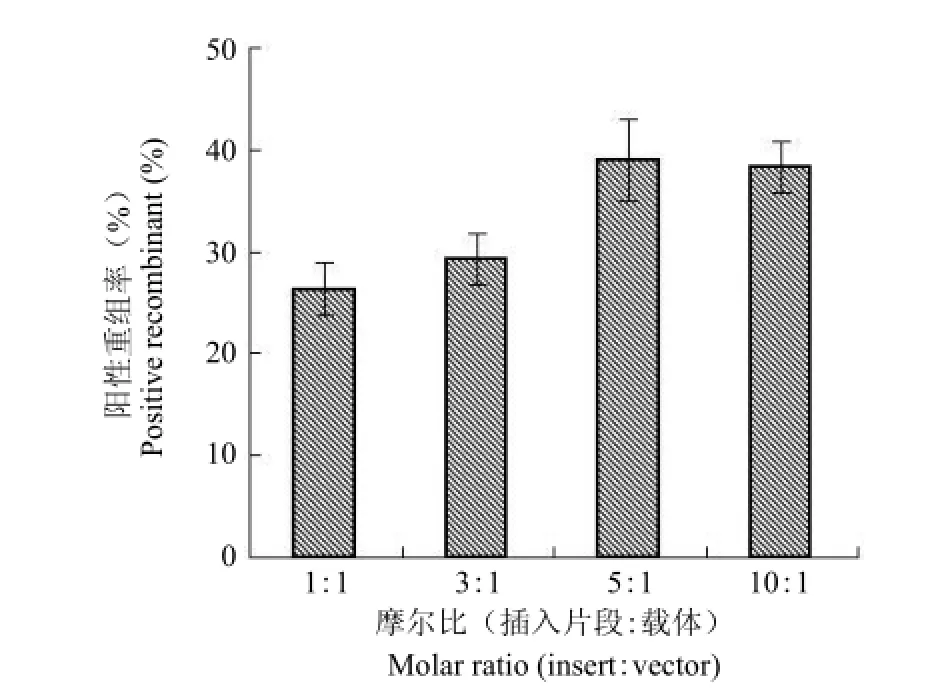
图3 插入片段和载体不同摩尔比阳性重组率比较Figure3 Positive recombinant ratio of In-Fusion assembly using different molar ratio

图4 同源区段长度对 In-Fusion 法重组效率的影响Figure4 Influence of different lengths of the over-lapping sequences on the In-Fusion recombination efficiency
2.3 含有目的基因的重组片段与载体同源区段长度对 In-Fusion 阳性重组率的影响
含有目的基因的重组片段与载体间不同长度同源区段对阳性重组率的影响,结果如图 4 所示:当同源区段长度为 15 ~ 50 bp 时,阳性重组率不高;当同源区段长度为 100 bp 时,阳性重组率为80% ~ 90%,达到最高值;此时如果再继续增加同源区段长度到 150 ~ 200 bp 时,阳性重组率则不再上升。故可选择长度为 100 bp 的同源区段进行In-Fusion 高通量克隆和构建突变库,具有进行后续操作的可行性。
由图 4 可知,传统酶切连接法的阳性重组率仅为 25% ~ 30%,明显低于 In-Fusion 方法的所有实验组,其中,In-Fusion 法同源区段长度为 100 bp组的阳性重组率是传统酶切连接法的 3 倍,而且,与传统酶切连接法通常需要 3 ~ 4 d 相比,In-Fusion 法建库只需 1 ~ 2 d 时间。
3 讨论
In-Fusion 技术是近年来新兴的一种克隆方法,已逐渐应用于长片段 DNA 克隆、多片段克隆和基因突变等研究中[13-14]。在常规的 In-Fusion 技术中,15 bp 的同源区段长度足以满足一般小片段克隆对阳性重组率的要求,例如,Irwin等[9]证实利用In-Fusion 技术将 N2L 基因(553 bp)成功插入到pETBlue-2 载体中,阳性重组率可达 99%。Benoit等[10]探讨了不同长度的 DNA 片段(447 ~ 1200 bp)与不同长度的载体(2824 ~ 5434 bp)间阳性重组率的差别,发现长插入片段与短插入片段相比,阳性重组率较低,且不同大小的插入片段与同样大小的载体间阳性重组率存在较大差异(25% ~ 100%)。我们的实验结果证实:同源区段长度成为影响阳性重组率的重要因素,长片段同源区段与短片段同源区段相比,阳性重组效率上升明显,这与 Sleight等[11]研究一致。进一步的研究发现,对于长度为2.4 kb 的目的基因来说,当 PCR 扩增得到的重组片段与载体的同源区段增加到 100 bp 时,与同源区段为 15 ~ 50 bp 相比,阳性重组率提高至 80% ~90%。
本研究应用 In-Fusion 技术构建糖基水解酶Lxyl-p1-2 基因突变库。构建的重组载体经菌落PCR、酶切鉴定证实易错 PCR 扩增的片段Lxyl-p1-2-ep 被成功插入载体中。现已累计测序超过 100 个克隆,均未发生连接区的碱基突变。目前正进行突变库的筛选工作,已从 2000 株克隆中筛选到 2 株酶活性显著提高的突变株 EP1 和EP2,其酶活性分别比野生型对照增加 0.57 和1.21 倍。在应用易错 PCR 或 DNA 改组等方法进行定向进化研究时,采用 In-Fusion 技术进行建库简便、快速,只需要 PCR、载体酶切和 In-Fusion 连接过程,省略了常规酶切连接法构建过程中亚克隆连接、质粒提取、基因片段与载体酶切、T4 DNA 连接酶连接等多步烦琐且耗时的工作,将建库周期由3 ~ 4 d 缩短为 1 ~ 2 d。另外,一步连接也降低了亚克隆步骤带来的突变基因容量与丰度的损失。本研究关于同源区段长度的实验结果,对于利用该技术进行类似大片段 DNA 的克隆具有借鉴意义,今后要更加关注大于 2.4 kb 长度的基因片段的连接效率,以检验该方法的适用范围。
[1] Festa F, Steel J, Bian X, et al. High-throughput cloning and expression library creation for functional proteomics. Proteomics, 2013, 13(9): 1381-1399.
[2] Kumar A, Singh S. Directed evolution: tailoring biocatalysts for industrial applications. Crit Rev Biotechnol, 2012.
[3] You C, Percival Zhang YH. Easy preparation of a large-size random gene mutagenesis library in Escherichia coli. Anal Biochem, 2012, 428(1):7-12.
[4] You C, Zhang XZ, Zhang YH. Simple cloning via direct transformation of PCR product (DNA Multimer) to Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2012, 78(5):1593-1595.
[5] Miyazaki K. MEGAWHOP cloning: a method of creating random mutagenesis libraries via megaprimer PCR of whole plasmids. Methods Enzymol, 2011, 498:399-406.
[6] Gruet A, Longhi S, Bignon C. One-step generation of error-prone PCR libraries using Gateway® technology. Microb Cell Fact, 2012, 11:14.
[7] Berrow NS, Alderton D, Sainsbury S, et al. A versatile ligation-independent cloning method suitable for high-throughput expression screening applications. Nucleic Acids Res, 2007, 35(6): e45.
[8] Berrow NS, Alderton D, Owens RJ. The precise engineering of expression vectors using high-throughput In-Fusion PCR cloning. Methods Mol Biol, 2009, 498:75-90.
[9] Irwin CR, Farmer A, Willer DO, et al. In-fusion® cloning with vaccinia virus DNA polymerase. Methods Mol Biol, 2012, 890:23-35.
[10] Benoit RM, Wilhelm RN, Scherer-Becker D, et al. An improved method for fast, robust, and seamless integration of DNA fragments into multiple plasmids. Protein Expr Purif, 2006, 45(1):66-71.
[11] Sleight SC, Bartley BA, Lieviant JA, et al. In-Fusion BioBrick assembly and re-engineering. Nucleic Acids Res, 2010, 38(8):2624-2636.
[12] Bryksin AV, Matsumura I. Overlap extension PCR cloning: a simple and reliable way to create recombinant plasmids. Biotechniques, 2010, 48(6):463-465.
[13] Zhu B, Cai G, Hall EO, et al. In-fusion assembly: seamless engineering of multidomain fusion proteins, modular vectors, and mutations. Biotechniques, 2007, 43(3):354-359.
[14] Kushnir S, Marsac Y, Breitling R, et al. Rapid production of functionalized recombinant proteins: marrying ligation independent cloning and in vitro protein ligation. Bioconjug Chem, 2006, 17(3): 610-617.
Effect of the length of homologous sequence on the In-Fusion recombination efficiency
LI Hui-xian, ZHU Ping
Objective To explore the effect of length of homologous sequence between the ends of PCR amplicon (harboring the targeted gene) and the vector on the In-Fusion recombination efficiency, when the template vector is the same as the cloning vector, and to establish an efficient high-throughput cloning method based on In-Fusion technique.Methods With construction of the mutant library of the glycoside hydrolase Lxyl-p1-2 (2.4 kb) as an example, different primers were designed on the basis of the various positions of the vector. The PCR fragments (each harboring the targeted gene) were obtained by error-prone PCR. Each fragment contained two over-lapping sequences (15 - 200 bp in length) at the two ends with each of the corresponding ends of the linearized vector. These PCR amplicons were directionally cloned into the vector pPIC3.5K by In-Fusion technique.Results For the cloning of the 2.4 kb DNA fragments by the In-Fusion method, the highest DNA ligation efficacy was obtained when the over-lapping sequence between the PCR fragments and the linearized vector at any end was 100 bp in length, with the highest recombination rate of around 90%. The recombination rate was three times higher than that of the conventional restriction enzyme cloning method. Moreover, the cloning period was drastically shortened from 3 - 4 d of the conventional method to 1 - 2 d of the present method.Conclusion The optimized length of homologous sequence obtained in this paper may significantly increase the ligation efficacy between the 2.4 kb targeted gene and the vector when the In-Fusion technique was applied. The method is particularly suitable to construct the mutant library in the study of directed evolution.
Directed molecular evolution; In-Fusion technique; Homologous sequence; High-throughput cloning
ZHU Ping, Email: zhuping@imm.ac.cn
10.3969/cmba.j.issn.1673-713X.2013.04.001
国家自然科学基金(31270796);“重大新药创制”国家科技重大专项(2012ZX09301002-001-005);中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金(2012N06)
100050 北京,中国医学科学院北京协和医学院药物研究所天然药物活性物质与功能国家重点实验室/卫生部天然药物生物合成重点实验室
朱平,Email:zhuping@imm.ac.cn
2013-04-22
方法 以糖基水解酶 Lxyl-p1-2(2.4 kb)基因突变库的构建为例,设计引物使目的基因的两端分别与线性化载体末端含有 15 ~ 200 bp 重叠序列,并通过易错 PCR 方法获得含目的基因的 PCR 扩增片段,运用 In-Fusion 技术将 PCR 扩增片段定向克隆至表达载体 pPIC3.5K 中。
结果 对于长度大约为 2.4 kb 的较大片段 DNA 的克隆,PCR 扩增片段的末端与载体间最适同源区段长度约为100 bp,此时连接效率最高,其阳性重组率高达 90% 左右,是常规酶切连接法的 3 倍。与后者相比,该技术将克隆周期由 3 ~ 4 d 缩短为 1 ~ 2 d。
结论 优化的同源区段长度可以显著提高 In-Fusion 技术对于 2.4 kb 目的基因与载体的连接效率,该方法尤其适用于定向进化过程中基因突变库的构建。
Author Affiliat ion: State Key Laboratory of Active Substance and Function of Natural Medicines/ Ministry of Health Key Laboratory of Biosynthesis of Natural Products, Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100050, China
www.cmbp.net.cn Chin Med Biotechnol, 2013, 8(4):241-246
