内镜下支架置入治疗恶性胃出口梗阻的临床应用进展
2012-05-03莺综述许惠利审校
刘 婷 江 莺综述 许惠利审校
恶性胃出口梗阻是进展期胃窦癌,十二指肠乳头癌及周围癌、胰腺癌、肝胆癌引起的胃十二指肠恶性梗阻。早期阶段可表现为早饱、上腹涨,恶心、呕吐,呕吐物含未消化食物而不含胆汁。如不进行有效治疗,随着病程的进展,患者呕吐症状加剧,不能正常饮食,营养不良及脱水,最终加速患者的死亡。恶性肿瘤引起的胃十二指肠梗阻通常被认为是临终表现,患者平均生存期仅为3~4个月。但是目前通过金属支架置入术结合化疗可明显提高患者生活质量及延长生存期。用自膨式金属支架治疗恶性胃出口梗阻是胃空肠吻合术的替代治疗,是继食管、贲门和胆道恶性疾病金属支架治疗后的进一步发展方向,其目的是改善患者的生活质量。与姑息性手术治疗相比,金属支架置入术具有以下优点[1~5]:①不能耐受手术的患者的首选;②创伤小;③恢复时间短,住院时间短;④缩短了不能进食的时间;⑤临床成功率高;⑥并发症发生率低;⑦成本低。但有学者认为目前的数据仍不能说明支架治疗恶性胃出口梗阻的临床效果是肯定的[6]。1992年Truong首先报道采用金属支架治疗1例幽门梗阻患者[7]。过去10年,国内外有许多医院开展了支架治疗恶性胃出口梗阻的技术,从操作技术、支架材料的选择到生物可降解支架、放射性支架等治疗性支架的摸索,自膨式金属支架治疗恶性胃出口梗阻上了新的台阶。
1 操作技术
行支架置入术前,首先要做上消化道造影,以确定狭窄部位的位置和长度。若梗阻比较严重,患者常出现胃潴留。患者胃体明显扩张,支架置入时,易造成推送器在胃大弯处弯曲迂回。故此类患者术前可行胃肠减压以减少胃的扩张。这不仅可以减少支架置入的难度,还可以防止术中返流物的误吸。
在内窥镜与透视结合下行胃十二指肠内支架置入术是最便捷的[8]。而现在,单独内镜或X线监视下就可以放置。操作方法:按常规胃镜检查进行术前准备,患者取左侧卧位,插胃镜,先对食管胃进行常规检查,胃镜在进入胃窦部时可见幽门被肿瘤阻塞,进入狭窄段,内镜先端通过狭窄部至十二指肠降部中下段,确定狭窄部的长度和其上缘距门齿的距离,经活检钳道插入金属导丝,保留金属导丝并防止滑出,退出胃镜,沿导丝插入带支架推送器尽可能接近胃窦恶性狭窄及幽门位置,再从支架推送器下方插入胃镜并右旋转镜身90度,使支架推送器到达十二指肠球部,确认支架在梗阻段的位置后直视下释放支架。支架释放后如位置不佳可调整。观察支架膨胀良好后退镜。目前金属支架置入技术已相当成熟,国内外医院报道即使单独内镜下操作,技术成功率都能有 90% ~100%[9,10]。
2 支架的选择
支架的选择尚未有统一标准。支架的发展由最开始裸露支架到后来的覆盖支架,经历了一段时间的摸索。Chan Gyoo Kim经过80例患者的比较[6],认为裸露支架与覆盖支架的支架阻塞率分别为12% ~25%和0%,支架迁移率分别为2.8% ~11%和21%~26%,支架通畅率和患者的生存期是基本相近的。由上述数据可以看出覆盖支架在阻止肿瘤过度生长,预防支架梗阻的优势是显而易见的。大量覆盖支架被设计。不同的材料被覆盖支架所采用,包括聚氨酯[11]、硅橡胶[12]、尼龙[13]、聚乙烯[14]、聚四氟乙烯[15]等。从单层裸露支架到双层部分覆盖支架,无论是新设计的大杯型的双层部分覆盖支架,还是喇叭形的硅胶管结合镍钛合金记忆支架都拥有覆盖支架本来的优点,此外大杯的裸支架近端及喇叭形的硅胶管开口均能有效地防止支架的迁移[12,14]。
3 临床疗效
恶性胃出口评分作为新型的评价内镜下支架治疗恶性胃出口梗阻后临床疗效的体系[16]。临床成功被定义为在改善梗阻症状和放置支架后1~3 d的口服摄入量,对口服摄入的程度进行了评估,胃出口梗阻评分系统如下:0=无口服;1=完全流质饮食;2=仅软固体饮食;3=完整的饮食可能。支架置入3天内的口服摄入量是判断支架置入术成功与否的标准。支架成功置入后的疗效可以通过以下指标评估:①技术成功率和临床成功率;②并发症;③支架通畅率。
4 并发症
自膨式金属支架置入术的并发症有以下几种:最常见的并发症是支架阻塞和支架移位,占10% ~25%(表1);较轻的并发症有疼痛,占2%;胆道堵塞占1%;严重并发症仅有1%,包括穿孔[23]和出血。穿孔可能与恶性胃出口梗阻支架置入术后放射治疗有关,尚未有与支架置入直接相关的死亡。胃肠道穿孔:操作时应将胃镜内观察与X线定位相结合并根据CT显示的病变部位情况,经胃镜用微波或热极烧灼形成小通后再送入软头硬导丝过狭窄段放置支架。
胃或肠壁损伤出血:与器械粗糙或操作不当有关。选择柔韧好的输送系统并操作轻柔可避免或减少发生率。
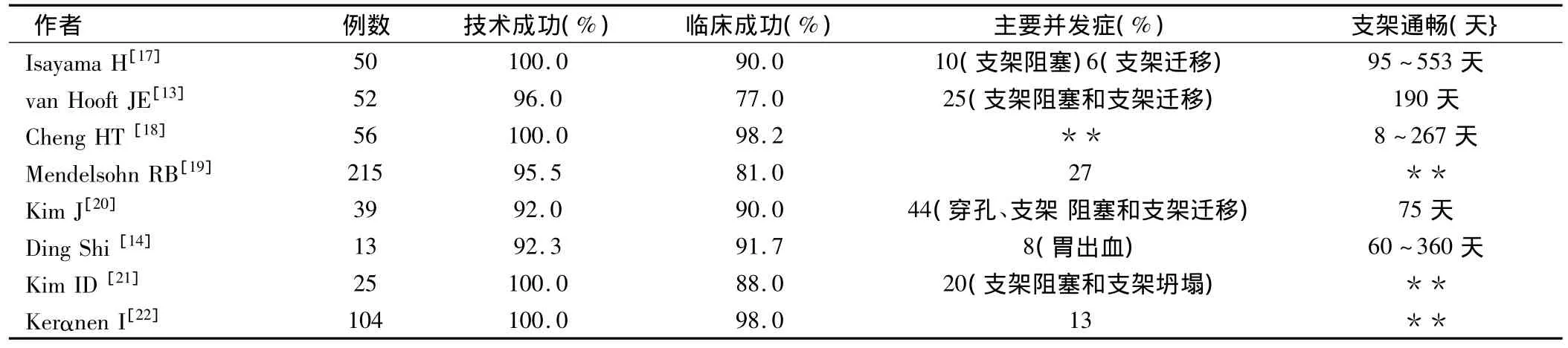
表1 SEMS置入术治疗恶性胃出口梗阻的疗效。
胆道堵塞:使用带膜支架易阻塞胰腺管开口及胆道开口,而裸状支架极少发生,故在进行胰、胆管部位操作时避免使用覆膜支架。
支架移位或脱落:与支架管道径选择不当、支架植入位置不当有关,有与化疗相关的支架移位的报道。而向近端移位的支架可取出后重新放置,远端移位时可胃镜下用异物钳咬住支架近端向上提拉调整位置。
再狭窄:单纯裸支架治疗再狭窄发生时间较早,一般2~3个月即可发生。再狭窄发生时可经原支架再留置同类规格或直径略小的支架,并可多次重复放置。
总之,金属支架置入术是应用微创技术使梗阻的消化道再次通畅,能安全、迅速、有效地缓解胃十二指肠恶性梗阻,为不能手术的患者创造了进一步治疗的机会。但目前金属支架治疗胃十二指肠恶性梗阻对患者的生存期并无明显改善,仅对于生命预期短的患者具有适用性。对于那些有较长生命的患者,胃空肠吻合术更有利于提高患者的生存率[1]。临床上采用化疗结合金属支架治疗不但改善了患者的生活质量,患者的生存期可延长达12月。但是化疗也是引起支架迁移的不确定的诱因。
如何有效抑制恶性肿瘤的生长和恶性肿瘤的并发症,是消化道内支架的研究方向。随着生物可降解支架,药物洗脱性支架和放射性支架等治疗性支架的研制开发[24],金属支架置入术在治疗恶性消化道肿瘤中会起更大的作用。这些支架都从动物实验走向了临床一线,目前生物可降解支架仅用于良性疾病,药物洗脱性支架主要用于冠脉介入术,放射性支架正广泛应用于食管癌[25,26]、胰腺癌[27]。在我国某些医院内镜下植入化疗粒子联合支架置入治疗进展期胃癌恶性胃出口梗阻也在临床探索中。
[1] Suzanne M Jeurnink,Casper HJvan Eijck,EwoutW Steyerberg,etal.stent versus gastrojejunostony for the palliation of gastric outlet obstruction:a systematic review〔J〕.BMC Gastroenterology,2007,doi:10.1186/1471-230X-7-18.
[2] Jeurnink SM,Steyerberg EW,Vleggaar FP,et al.Predictors of survival in patients withmalignant gastric outlet obstruction:a patient-oriented decision approach for palliative treatment〔J〕.Dig Liver Dis,2011,43(7):548.
[3] Jill KJGaidos,Peter V Draganov.Treatmentofmalignantgastric outlet obstruction with endoscopically placed self-expandable metal stents〔J〕.World JGastroenterol,2009,15(35):4365.
[4] Jeurnink SM,Polinder S,Steyerberg EW,et al.Cost comparison of gastrojejunostomy versus duodental srent placement for gastric outlet obstruction〔J〕.JGastroenterol,2010,45(5):537.
[5] Jeurnink SM,Steyerberg EW,van Hooft JE,et al.Surgical gastrojejunostomy or endoscopic stent placement for the palliation ofmalignant gastric outlet obstruction(SUSTENT study):a multicenter randomized trial〔J〕.Gastrointest Endosc,2010 ,71(3):490.
[6] Lene Larssen,AsleW Medhus,Truls Hauge1,et al.Treatment ofmalignant gastric outlet obstruction with stents:An evaluation of the reported variables for clinical outcome〔J〕.BMC Gastroenterology,2009,doi:10.1186/1471-230X-9-45.
[7] Truong S,Bohndorf V,Geller H,et al.Self-expandingmetal stents for palliation of malignant outlet obstruction〔J〕.Endoscopy,1992,24(5):433.
[8] Cheng HT,Tsou YK,Lin CH,et al.Endoscopic metal stents for the palliation ofmalignant upper gastroduodenal obstruction〔J〕.Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am,2011 ,21(3):389.
[9] Chan Gyoo Kim,MD,PhD,Il Ju Choi,MD,PhD,Jong Yeul Lee,MD,et al.covered versus uncovered self-expandablemetallic stents for palliation of malignant pyloric obstruction in gastric cancer patients:a randomized prospective study〔J〕.the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy,2010,doi:10.1016/j.gie.
[10] Jin Hyoung Kim,Ho-Young Song,Ji Hoon Shin,et al.Metallic stent placement in the palliative treatment of malignant gastric outlet obstructions:primary gastric carcinoma versus pancreatic carcinoma〔J〕.Vascular and Interventional Radiology· Original Research,2009,DOI:10.2214/AJR.08.1760.
[11] Kim JH,Song HY,Shin JH,et al.Malignant gastric outlet obstructions:Treatmentwith self-expandable metallic stents〔J〕.Gut Liver,2010,4 Suppl1:S32.
[12] Rueth NM,Andrade RS,Groth SS,et al.Gastric outlet obstruction palliation:a novel stent-based solution〔J〕.Case Rep Gastroenterol,2010,4(2):185.
[13] van Hooft JE,van Montfoort ML,Jeurninu SM,et al.Safey and efficacy of a new non-foreshortening nitionol stent in malignant gastric outlet obstrction(DUONITI study):a prosepective multicenter study〔J〕.Endoscopy,2011,43(8):671.
[14] Ding Shi,Sheng-Hui Liao,Jian-Ping Geng,etal.A newly designed big cup nitinol stent for gastric outlet obstruction〔J〕.World JGastroenterol,2010,16(33):4206.
[15] Sun Mi Lee,MD,Dae Hwan Kang,MD,Gwang Ha Kim,MD,et al.Self-expandablemetallic stents for gastric outlet obstruction resulting from stomach cancer:a preliminary study with a newly designed double-layered pyloric stent〔J〕.Gastrointestinal Endoscopy,2007,66(6):1206.
[16] Yu Kyung Cho,Sang Woo Kim,Kwan Woo Nam,et al.Clinical outcomes of self-expandablemetal stents in palliation ofmalignant anastomotic strictures caused by recurrentgastric cancer〔J〕.World JGastroenterol,2009,15(28):3523.
[17] Isayama H,Sasaki T,Nakai Y,et al.management ofmalignant gastric outlet obstruction with amodified triple-layer coveredmetal stent〔J〕.Gastrointest Endosc,2012,75(4):757.
[18] Cheng HT,Tsou YK,Lin CH,etal.endoscopicmetal stent for the palliation ofmalignant upper gastroduodental obstruction〔J〕.Hepatogastroenterology,2011,58(112):1998.
[19] Mendelsohn RB,Gerdes H,Markowitz AJ,et al.Carcinomatosis is not a contraindication to enteral stenting in selected patients with malignant gastric outlet obstruction〔J〕.Gastrointest Endosc,2011,73(6):1135.
[20] Kim J,Choi IJ,Kim CG,et al.Self-expandable metallic stent placement formalignant obstruction in patients with locally recurrent gastric cancer〔J〕.Surg Endosc,2011 ,25(5):1505.
[21] Kim ID,Kang DH,Choi CW,et al.Prevention of covered enteral stent migration in patientswith malignant gastric outlet obstruction:a pilot study of anchoring with endoscopic clips〔J〕.Scand JGastroenterol,2010,45(1):100.
[22] Keränen I,Udd M,Lepistα A,etal.Outcome for self-expandablemetal stents inmalignantgastroduodenal obstruction:single-center experience with 104 patients〔J〕.Surg Endosc,2010,24(4):891.
[23] Peter HU Lee,Robert Moore,Akshay Raizada,et al.Small bowel perforation after duodenal stent migration:An interesting case of a rare complication〔J〕.World JRadiol,2011,3(6):152.
[24] Mark Terence McLoughlin,Michael Francis Byrne,et al.Endoscopic stenting -where arewe now and where can we go?〔J〕.World JGastroenterol,2008,14(24):3798.
[25] Jin-He Guo,MD Gao-Jun Teng,MD ,Guang-Yu Zhu,MD,et al.Selfexpandable esophageal stent loaded with 125Iseeds initial experience in patients with advanced esophageal cancer〔J〕.Vascular and interwentional radiology,2008 ,247(5):574.
[26] Yan Liu,Jun-lou Liu,Zhen-zhaiCai,etal.A novel approach for treatment of unresectable pancreatic cancer:design of radioactive stents and trial studies on normal pigs〔J〕.Clin Cancer Res,2007,DOI:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0154.
[27] 陈明余,杨建祥,袁明金,等.食管贲门癌术后早期胃出口梗阻的诊治体会〔J〕.实用癌症杂志,1998,13(2):143.
