三疣梭子蟹Profilin基因全长cDNA的克隆与表达分析
2010-12-25王日昕
申 望, 叶 茂, 石 戈, 王日昕
(浙江海洋学院 海洋科学学院海洋生物资源及分子工程实验室,浙江 舟山 316004)
三疣梭子蟹Profilin基因全长cDNA的克隆与表达分析
申 望, 叶 茂, 石 戈, 王日昕*
(浙江海洋学院 海洋科学学院海洋生物资源及分子工程实验室,浙江 舟山 316004)
三疣梭子蟹(Portunus trituberculatus)是我国沿海重要养殖品种之一。近年来,养殖病害呈逐年上升趋势,制约了三疣梭子蟹养殖产业的健康可持续发展。克隆三疣梭子蟹免疫相关基因、研究免疫基因的功能和作用机制,可为三疣梭子蟹养殖病害的防治奠定基础。本研究从三疣梭子蟹血细胞全长cDNA文库中克隆了742 bp的profilin基因全长cDNA。该profilin全长cDNA中开放阅读框长375 bp,编码125 aa。推导的三疣梭子蟹profilin理论等电点pI 5.87,氨基酸序列与冈比亚按蚊(Anopheles gambiae)profilin同源性最高,序列一致性为42.9%。荧光定量RT-PCR分析结果显示,在正常的三疣梭子蟹机体中,血细胞profilin表达水平最高,其次为肝胰脏;在致病菌副溶血弧菌(Vibrio parahaemolyticus)诱导后,血细胞中profilin表达量显著上升(P<0.01),表明profilin可能参与了三疣梭子蟹的免疫防御反应,是一个免疫相关因子。
三疣梭子蟹;免疫;基因克隆;Profilin;基因表达
Profilin最初是从牛脾中纯化鉴定的一个与肌动蛋白单体(G-actin)结合的相对分子质量15 k的小分子蛋白质。现有研究表明,profilin普遍存在于真核生物细胞中(Carlsson et al, 1977; Jockusch et al, 2007),与肌动蛋白单体按1:1结合,催化肌动蛋白单体的ADP/ATP核苷交换,生成G-ATP-actin,调节肌动蛋白的动力学活性,影响运动细胞边缘肌动蛋白网络的组装、维持和去组装(Haugwitz et al, 1994; Pollard & Borisy, 2003; Romero et al, 2007),参与肌动蛋白活性基础上的生命活动,如细胞运动、黏附、分裂、形态发生以及细胞内的膜泡运输等。profilin除参与肌动蛋白相关生理活动外,还参与机体的免疫防御反应,是一个免疫相关因子,如海胆体腔细胞经脂多糖诱导后,profilin转录水平显著提高(Smith et al, 1995);人乳腺癌细胞中profilin表达量显著低于正常乳腺上皮细胞中profilin的表达量,通过转染profilin cDNA提高乳腺癌细胞中profilin表达量后,乳腺癌细胞恢复正常生长(Janke et al, 2000);果蝇profilin基因突变的血细胞吞噬活性增强,表明果蝇profilin是一个关键的吞噬活性调节因子(Pearson et al, 2003)。
三疣梭子蟹(Portunus trituberculatus)是我国重要的海产经济蟹类,也是90年代虾病暴发和流行后,作为对虾替代养殖品种发展起来的大宗养殖品种。但近年来由于养殖规模的不断扩大以及养殖集约化程度的不断提高,三疣梭子蟹养殖病害也频频爆发,制约了三疣梭子蟹养殖业的进一步发展(Chen et al, 2005; Li et al, 2008)。克隆三疣梭子蟹免疫相关基因,研究免疫基因的功能和作用机制,可为三疣梭子蟹养殖病害的防治以及遗传育种奠定良好基础。本研究从三疣梭子蟹血细胞全长cDNA文库中克隆了一个profilin基因的全长cDNA序列,对其进行生物信息学分析,并应用荧光定量RT-PCR技术研究了该基因在正常三疣梭子蟹不同组织中的表达水平差异以及致病菌诱导前后血细胞中的表达水平变化,为研究profilin参与的三疣梭子蟹免疫防御反应机制奠定基础。
1 材料与方法
1.1 三疣梭子蟹血细胞全长cDNA文库的构建及profilin基因克隆
三疣梭子蟹采自浙江舟山海域。成年雄性三疣梭子蟹采集后饲养于恒温水族箱(25℃),饲养24 h后,以内含抗凝剂(0.45 mol/L NaCl,0.1 mol/L葡萄糖,26 mmol/L柠檬酸,30 mmol/L柠檬酸钠,10 mmol/L EDTA,pH4.6)的注射器从蟹肢体未硬化部位抽取血淋巴,立即4℃ 2 000 g离心5 min,收集血细胞(Söderhäll & Smith, 1983),采用TRIZOL法提取三疣梭子蟹血细胞总RNA,mRNA的分离根据Invitrogen公司FastTrack® 2.0 Kit试剂盒操作手册进行,通过poly(T)纤维素柱亲和层析,从三疣梭子蟹血细胞总RNA中分离poly A+mRNA。全长cDNA文库的构建按Clontech公司SMART cDNA全长文库构建试剂盒说明书进行,连接载体使用pGEM-T easy T载体,转化菌株为E. coli(DH10B)。文库克隆子测序引物为M13F (5'-TGT AAA ACG ACG GCC AGT-3')和M13R(5'-CAG GAA ACA GCT ATG ACC-3')。测得的ESTs序列通过BLASTX检索GenBank nr数据库寻找同源基因。
1.2 三疣梭子蟹profilin基因的生物信息学分析与系统树构建
在线计算三疣梭子蟹profilin理论分子量及等电点(http://us.expasy.org/ tools/ pi_tool.html; Bjellqvist et al, 1993; Bjellqvist et al, 1994);NetPhos2.0 Server在线分析磷酸化位点(http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/NetPhos/; Blom et al, 1999);TargetP 1.1 Server在线分析亚细胞定位信息(http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TargetP/; Emanuelsson et al, 2000);氨基酸序列比对使用Clustal W(Thompson et al, 1994);以MEGA 4.1软件包(Kumar et al, 2008)中的邻接法(nerghbor-joining method, NJ)构建节肢动物profilin系统树,选择人profilin为外群,参数设置为默认的泊松校正算法,不考虑插入/缺失位点,同时,应用自举检验(bootstrap test)重抽样1 000次估计系统树中节点的自引导值(bootstrap value)。
构建系统树所用节肢动物和人profilin如下:中国明对虾(Fenneropenaeus chinensis,FJ480175)、凡纳滨对虾(Litopenaeus vannamei,ABI93174)、斑节对虾(Penaeus monodon,ABU97474)、家蚕(Bombyx mori,NP_001037108)、黑腹果蝇(Drosophila melanogaster,NP_477016)、冈比亚按蚊(Anopheles gambiae,XP_553744)、蚜虫(Acyrthosiphon pisum,NP_001156129、XP_ 001945869、XP_001945923)、鱼虱(Lepeophtheirus salmonis,ACO12777)、鱼虱(Caligus rogercresseyi,ACO10829)、黑脚硬蜱(Ixodes scapularis,XP_002414739)、无爪螨(Blomia tropicalis,AAQ24553)、棉兰皱皮螨(Suidasia medanensis,AAX34044)、人(Homo sapiens,NP_005013、NP_444252、NP_002619、NP_001025057、NP_955378)。
1.3 Profilin基因表达的荧光定量RT-PCR分析
1.3.1 Profilin基因在三疣梭子蟹不同组织中的表达分析 从5只雄性三疣梭子蟹分别采集等量的血细胞、肌肉、肝胰脏、眼组织,按组织差别将5个体来源的组织合并后提取总RNA。血细胞总RNA提取,按1.1进行;其它组织采集后先液氮研磨,再用TRIZOL 法提取总RNA。以组织总RNA为模板,oligo(dT)18为引物, 按全式金EasyScript Reverse Transcriptase说明书操作反转录合成cDNA第一链。以三疣梭子蟹核糖体蛋白S18(RpS18)为内参基因,采用荧光定量RT-PCR技术研究profilin基因在不同组织中的差异表达。 RpS18基因RT-PCR引物:Ptrs18-F:5'-AGG AGG AGG TTG AGA AGA TTG T-3',Ptrs18-R:5'- GCA GCT TGG TTT CCA GGT AG-3', 扩增片段长度141 bp;profilin基因RT-PCR引物:Ptpro-F:5'-GCA AGA AGG AAA CAA CTG GAG -3',Ptpro-R:5'-GAG GTG GTC AGC CAT ACA GTC-3',扩增片段长度125 bp。RT-PCR反应体系: 第1链cDNA 2μL,SYBR Premix Ex TaqTM(2 ×)12.5μL,上游引物0.5 μL(10 μmol/L),下游引物0.5 μL (10 μmol/L),加9.5 μL去离子水至总体积25 μL。扩增条件:95℃预变性2 min;94℃变性10 s,60℃ 40 s,40个循环。反应在ABI 7500Fast实时定量PCR仪上进行,定量的数据结果采用2-△△Ct法(Livak et al, 2001)进行分析。三疣梭子蟹profilin在不同组织及致病菌诱导前后的相对表达量采用SPSS统计软件进行Ttest检验,P<0. 05认为差异有统计学意义。
1.3.2 三疣梭子蟹血细胞Profilin基因在副溶血弧菌(Vibrio parahaemolyticus)诱导下表达的时空差异分析 副溶血弧菌在LB液体培养基扩大培养后离心收集细菌,无菌去离子水洗涤3次,最后用无菌去离子水稀释到109CFU/mL备用。5只雄性三疣梭子蟹(重250~300 g/只)在恒温水族箱(25℃)暂养24 h后,每只抽取0.3 mL血淋巴,合并后按1.1提取总RNA,然后每只蟹注射50 μL菌液,并在注射菌液后3、6、12、24 h如前所述抽取血淋巴并提取总RNA。实时荧光定量PCR分析操作按1.3.1进行。
2 结 果
2.1 三疣梭子蟹profilin基因克隆与鉴定
用引物M13F和M13R对三疣梭子蟹全长cDNA文库进行初步测序,获得74条ESTs序列,将ESTs序列进行拼接,共得到23条unigene,包含6个序列重叠群(Contigs)和17条Singletons。其中一个包含7条ESTs序列的序列重叠群经BLASTX检索到的同源基因均为profilin,并与冈比亚按蚊profilin(XP_553744)同源性最高,氨基酸序列一致性为42.9%,因此,该基因为三疣梭子蟹的profilin基因。三疣梭子蟹血细胞cDNA文库测序得到的7条profilin ESTs序列仅在3'-UTR末端可能由于加尾时剪切位点不同形成1~3个核苷酸的长度差异,因此,7条profilin ESTs序列应为同一基因的转录产物。三疣梭子蟹profilin基因cDNA一致序列长度为742 bp(不包括polyA,Genbank登录号:GU253912),由66 bp的5'-UTR、375 bp的编码区和301 bp的3'-UTR组成,在3'-UTR末端有加尾信号AATAAA(图1)。编码区推导的氨基酸序列由125个氨基酸残基组成,理论相对分子质量13 739.38,预期等电点pI 5.87,在线磷酸化位点分析显示三疣梭子蟹profilin共有11个可能的磷酸化位点,分别为Ser5/32/38/56/58/71/104/123、Thr84和Tyr6/125。

图 1 三疣梭子蟹profilin的全长cDNA序列和推导的氨基酸序列Fig. 1 The full-length cDNA sequence and deduced amino acid sequence of the profilin from Portunus trituberculatus
蛋白亚细胞定位分析结果表明,推导的三疣梭子蟹profilin蛋白无N 末端信号肽、无线粒体及核定位信号、无内质网停留信号、无过氧化酶体结合信号、无DNA或RNA结合信号、无外分泌信号,表明该profilin蛋白分布于细胞质中,细胞定位特征与引言中所述功能一致。
2.2 Profilin的序列分析比对与系统发生分析
推导的三疣梭子蟹profilin氨基酸序列与6种节肢动物门动物profilin的序列比对结果如图2所示(图2)。三疣梭子蟹profilin与中国明对虾(Fenneropenaeus chinensis,FJ480175)、凡纳滨对虾(Litopenaeus vannamei,ABI93174)、斑节对虾(Penaeus monodon,ABU97474)、家蚕(Bombyx mori,NP_001037108)、黑腹果蝇(Drosophila melanogaster,NP_477016)和冈比亚按蚊(Anopheles gambiae,XP_553744)等profilin的氨基酸一致性分别为35.71 %、36.5 %、34.9 %、40.5 %、38.10 %和42.9 %。
以人的5种profilin亚型为外群构建的节肢动物门profilin NJ系统树如图3所示。有螯亚门(Chelicerata)3个物种的profilin聚在一枝;有颚亚门(Mandibulata)昆虫纲代表物种的profilin聚在一枝,甲壳纲文献报道的5种profilin以及本研究报道的三疣梭子蟹profilin也聚为单独一枝;但在甲壳纲中,3种对虾profilin并未聚为一枝,其中凡纳滨对虾(软甲亚纲,Malacostraca)profilin与颚足亚纲(Maxillopoda)两种鱼虱的profilin亲缘关系更近;三疣梭子蟹与对虾同属软甲亚纲十足目(Decapoda),三疣梭子蟹profilin与中国明对虾、斑节对虾profilin亲缘关系较近,而与凡纳滨对虾profilin亲缘关系较远。
2.3 三疣梭子蟹profilin的表达分析
荧光定量RT-PCR分析结果显示,profilin在未诱导的三疣梭子蟹血细胞、肝胰脏、眼和肌肉中均有表达(图4A)。其中血细胞profilin表达量最高,其次为肝胰脏,相对表达量为血细胞的0.2倍(P<0.01),而在眼和肌肉中profilin表达量极低,相对表达量分别仅为血细胞的0.028倍(P<0.01)和0.002倍(P<0.01)。
以诱导前三疣梭子蟹血细胞profilin表达量为对照,荧光定量RT-PCR分析副溶血弧菌诱导后不同时间血细胞profilin表达量变化结果显示:诱导3、6、12和24 h后,profilin表达量分别相当于与诱导前的1.91倍(P<0.01)、1.21倍(P<0.01)、0.78倍(P<0.01)和0.62倍(P<0.01),表明血细胞中profilin的在副溶血弧菌诱导下表达量上调,后下调(图4B)。

图 2 节肢动物代表性profilin氨基酸序列比对Fig. 2 Multiple sequence alignment of the profilins from arthropod

图 3 NJ法构建的节肢动物profilin的系统发生树Fig. 3 Phylogenetic analysis of the profilins of arthropod by Neighbor-Joining method
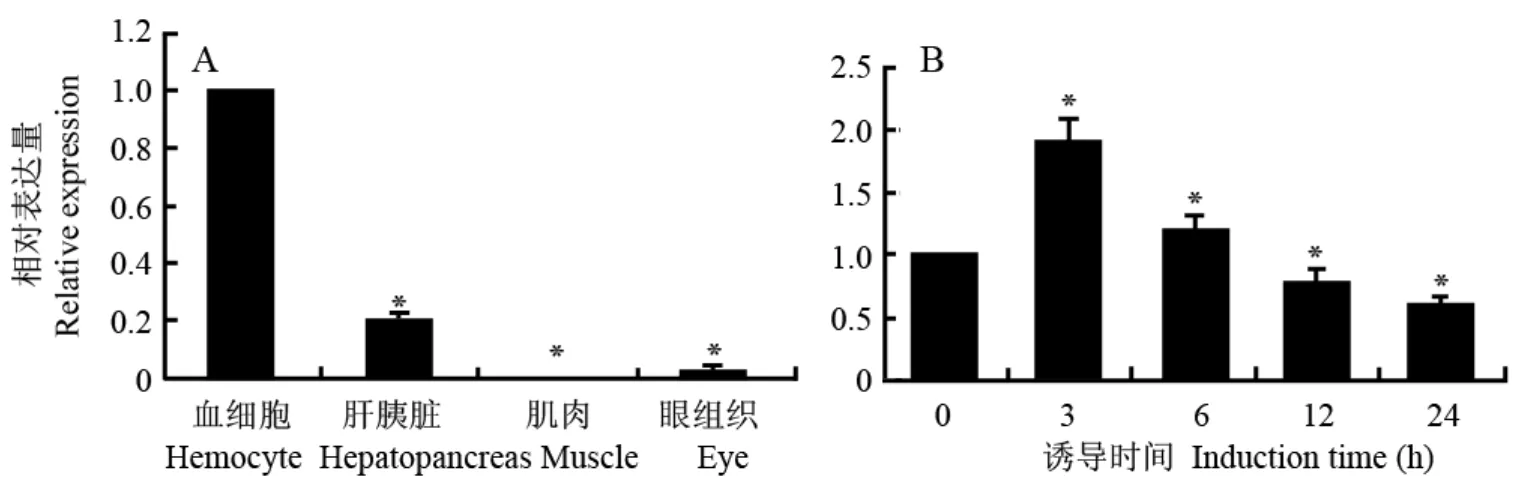
图 4 实时荧光定量RT-PCR分析三疣梭子蟹profilin的差异表达Fig. 4 Differential expression analysis of profilin by Real-time RT-PCR
3 讨 论
已有的大量研究结果表明,profilin是一种普遍存在于真核生物细胞中的小分子蛋白质,迄今为止在真核生物的各个类群,包括真菌、植物、动物等都有大量profilin被报道。同时也发现profilin的氨基酸序列并不保守,来源于不同物种,甚至来源于同一物种的profilin不同异构体之间氨基酸序列同源性都可能较低(Pollard & Quirk, 1994;Obermann et al, 2005)。但profilin的二级结构和三级结构非常保守:4个α螺旋包围在由7个β折叠构成的核心的外部,形成球状结构,在分子表面有三个配体结构域,分别结合肌动蛋白单体(包括肌动蛋白相关蛋白,如ARP2、ARP3)、具有聚pro伸展结构的蛋白质(PLP配体,如Formin蛋白家族)和4,5−二磷脂酰肌醇(PIP2)等三大类配体(Mahoney et al, 1997),构成三个配体结构域的氨基酸序列相对保守(Huang et al, 1996),特别是N末端第三个氨基酸残基Trp3,在所有报道的profilin中仅在人profilin IV中发生突变(Obermann et al, 2005)。本研究克隆的三疣梭子蟹profilin由125个氨基酸残基组成,氨基酸序列比对显示与另6种节肢动物有颚亚门动物的profilin相似性较低,氨基酸一致性只有34.9%~42.9%,但N末端相对较为保守,该区域为PLP配体结合结构域的一部分,同时N末端第三位氨基酸残基也为保守的Trp残基。因此,三疣梭子蟹profilin与已报道的其他物种profilin演化规律一致,氨基酸一级结构保守性较低,但构成配体结合结构域的部分区段较为保守。蛋白亚细胞定位分析结果显示,本研究克隆的三疣梭子蟹profilin定位于细胞质,提示该profilin可能也是通过调节细胞质肌动蛋白的动力学活性参与细胞生理过程。细胞质中profilin在蛋白激酶的催化下,通过磷酸化与去磷酸化修饰的方式调节活性,进而影响细胞骨架的动态变化(Vemuri & Singh, 2001),在线做磷酸化位点分析显示。三疣梭子蟹profilin共有11个可能的磷酸化位点,分别为Ser5/32/38/56/58/71/104/123、Thr84和Tyr6/125,对这些潜在磷酸位点的进一步研究,将有助于了解生理条件下profilin的动态修饰与作用机制。
荧光定量RT-PCR分析三疣梭子蟹profilin组织表达特异性结果显示,本研究克隆的profilin主要在三疣梭子蟹免疫相关组织和器官(血细胞和肝胰脏)中表达,而在眼和肌肉中的表达量极低,分别仅为血细胞中表达量的0.028倍(P<0.01)和0.002倍(P<0.01),与中国明对虾profilin组织表达特异性相似(Kong et al, 2009),提示甲壳类血细胞来源profilin在机体组织中的表达模式可能与甲壳类抗菌肽,如penaeidins、curstin等的表达模式类似,即主要在血细胞中以组成型表达,肌肉、眼等非免疫相关器官中检测到的微量表达可能是组织血管中残留血细胞造成的(Destoumieux et al, 2000; Smith et al, 2008)。三疣梭子蟹致病菌副溶血弧菌诱导后血细胞中profilin表达量显著上调(P<0.01),与对虾白斑病毒(WSSV)诱导后的中国明对虾、斑节对虾血细胞中profilin表达量变化一致(Somboonwiwat et al, 2006; Kong et al, 2009),表明本研究克隆的三疣梭子蟹profilin参与了致病微生物感染后免疫防御反应,是一个免疫相关因子。
真核生物中profilin异构体的种类比较复杂,低等真核生物有1~3种profilin异构体,而高等真核生物中可能更多,例如阿米巴虫(Dictyostelium discoideum)和秀丽线虫(Caenorhabditis elegans)各有三种profilin异构体(Arasada et al, 2007; Polet et al, 2006),脊椎动物目前已报道的profilin有4种类型,即profilin I~IV(Polet et al, 2007),并且不同profilin异构体有不同的组织表达特异性(Obermann et al, 2005; Polet et al, 2006)。甲壳纲已报道的profilin基因较少,在NCBI nr蛋白质数据中仅检索到5个profilin基因,分别来自软甲亚纲的3种对虾和颚足亚纲的两种鱼虱。系统分析显示,三疣梭子蟹profilin与中国明对虾、斑节对虾profilin亲缘关系较近,聚在一枝;而凡纳滨对虾profilin与两种鱼虱的profilin亲缘关系更近,没有与同属于软甲亚纲十足目的中国明对虾、斑节对虾、三疣梭子蟹profilin聚在一枝(图3),与Kong(2009)等报道的对虾profilin聚类关系类似。同时,本研究报道的三疣梭子蟹profilin与中国明对虾、斑节对虾profilin均克隆自血细胞,在外源致病微生物诱导下表达量均上调,参与免疫防御反应,且组织表达特异性研究表明,三疣梭子蟹、中国明对虾profilin主要在免疫相关组织血细胞和肝胰脏中表达(Somboonwiwat et al, 2006; Kong et al, 2009), 而凡纳滨对虾profilin克隆自鳃组织,在虾白斑病毒(WSSV)诱导后表达量下调(Clavero-Salas et al, 2007)。因此,profilin NJ系统树中甲壳纲profilin的系统发生关系提示,三疣梭子蟹、中国明对虾、斑节对虾profilin与凡纳滨对虾profilin可能分属两种不同类型的profilin,甲壳纲动物中应有两种或两种以上profilin异构体,并可能具有不同的组织表达特异性和生理活性。
Arasada R, Gloss A, Tunggal B, Joseph JM, Rieger D, Mondal S, Faix J, Schleicher M, Noegel AA. 2007. Profilin isoforms inDictyostelium discoideum[J].Biochim Biophys Acta, 1773(5): 631-641.
Blom N, Gammeltoft S, Brunak S. 1999. Sequence- and structure-based prediction of eukaryotic protein phosphorylation sites [J].J Mol Biol, 294(5): 1351-1362.
Bjellqvist B, Basse B, Olsen E, Celis JE. 1994. Reference points for comparisons of two-dimensional maps of proteins from different human cell types defined in a pH scale where isoelectric points correlate with polypeptide compositions [J].Electrophoresis, 15: 529-539.
Bjellqvist B, Hughes GJ, Pasquali C, Paquet N, Ravier F, Sanchez JC, Frutiger S, Hochstrasser DF. 1993. The focusing positions of polypeptides in immobilized pH gradients can be predicted from their amino acid sequences [J].Electrophoresis, 14: 1023-1031.
Carlsson L, Nyström NE, Sundkvist I, Markey F, Lindberg U. 1977. Actin polymerizability is influenced by profilin, a low molecular weight protein in non-muscle cells [J].J Biochem Mol Biol, 115: 465-483.
Chen YE, Jin S, Zhao QS. 2005. Causes and prevention ofPortunus trituberculatusdiseases in aquaculture [J].Reserv Fisher, 25(1): 78-79.[陈寅儿, 金 珊, 赵青松. 2005. 梭子蟹养殖中的发病原因与防治对策. 水利渔业, 25(1): 78-79.]
Clavero-Salas A, Sotelo-Mundo RR, Gollas-Galván T, Hernández-López J, Peregrino-Uriarte AB, Muhlia-Almazán A, Yepiz-Plascencia G. 2007. Transcriptome analysis of gills from the white shrimpLitopenaeus vannameiinfected with white spot syndrome virus [J].Fish Shellfish Immunol, 23: 459-472.
Destoumieux D, Munoz M, Cosseau C, Rodriguez J, Bulet P, Comps M, Bachère E. 2000. Penaeidins, antimicrobial peptides with chitin-binding activity, are produced and stored in shrimp granulocytes and released after microbial challenge [J].J Cell Sci, 113(3): 461-469.
Emanuelsson O, Nielsen H, Brunak S, von Heijne G. 2000. Predicting subcellular localization of proteins based on their N-terminal amino acid sequence [J].J Mol Biol, 300: 1005-1016.
Haugwitz M, Noegel AA, Karakesisoglou J, Schleicher M. 1994.Dictyostelium amoebaethat lack G-actinsequestering profilins show defects in F-actin content, cytokinesis, and development [J].Cell, 79: 303-314.
Huang SR, McDowell JM, Weise MJ, Meagher RB. 1996. TheArabidopsisprofilin gene family: Evidence for an ancient split between constitutive and pollen-specific profilin genes [J].Plant Physiol, 111: 115-126.
Janke J, Schlüter K, Jandrig B, Theile M, Kölble K, Arnold W, Grinstein E, Schwartz A, Estevéz-Schwarz L, Schlag PM, Jockusch BM, Scherneck S. 2000. Suppression of tumorigenicity in breast cancer cells by the microfilament protein profilin 1 [J].J Exp Med, 191(10): 1675-1686.
Jockusch B M, Murk K, Rothkegel M. 2007. The profile of profilins [J].Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol, 159: 131-149.
Kong HJ, Hong GE, Cho HK, Nam BH, Kim YO, Kim WJ, Lee SJ, Kim KK. 2009. Cloning of profilin (FcPFN) from the shrimpFenneropenaeus chinensis, a highly expressed protein in white spot syndrome virus (WSSV)-infected shrimp [J].J Appl Genet, 50(3): 245-250.
Kumar S, Nei M, Dudley J, Tamura K. 2008. MEGA: A biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences [J].Brief Bioinform, 9: 299-306.
Li DP, Wang CL, Wu DH. 2008. Primary study on the resistance to emulsification disease related gene ofPortunu strituberculatu[J].J Hydroecol, 1(1): 125-128.[励迪平, 王春琳, 吴丹华. 2008. 三疣梭子蟹抗乳化病相关基因的初步研究. 水生态学杂志, 1(1): 125-128.]
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. 2001. Analysis of relative rene expression data using Real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-△△Ct methods [J].Methods, 25: 402-408.
Mahoney NM, Janmey PA, Almo SC. 1997. Structure of the profilin-poly-l-proline complex involved in morphogenesis and cytoskeletal regulation [J].Nat Struct Biol, 4: 953-960.
Obermann H, Raabe I, Balvers M, Brunswig B, SchulzeW, Kirchhoff C. 2005. Novel testis-expressed profilin IV associated with acrosome biogenesis and spermatid elongation [J].Mol Hum Reprod, 11: 53-64.
Pearson AM, Baksa K, Rämet M M, Protas M, McKee M, Brown D, Ezekowitz RA. 2003. Identification of cytoskeletal regulatory proteins required for efficient phagocytosis inDrosophila[J].Microbes Infect, 5: 815-824.
Polet D, Lambrechts A, Ono K, Mah A, Peelman F, Vandekerckhove J, Baillie DL, Ampe C, Ono S. 2006.Caenorhabditis elegansexpresses three functional profilins in a tissue-specific manner [J].Cell Motil Cytoskeleton, 63(1): 14-28.
Polet D, Lambrechts A, Vandepoele K, Vandekerckhove J, Ampe C. 2007. On the origin and evolution of vertebrate and viral profilins [J].FEBS Lett, 581: 211-217.
Pollard TD, Borisy GG. 2003. Cellular motility driven by assembly and disassembly of actin filaments [J].Cell, 113(4): 549.
Pollard TD, Quirk S. 1994. Profilins, ancient actin binding proteins with highly divergent primary structures [J].Soc Gen Physiol Ser, 49: 117-128.
Romero S, Didry D, Larquet E, Boisset N, Pantaloni D, Carlier MF. 2007. How ATP hydrolysis controls filament assembly from profilin-actin: Implication for formin processivity [J].J Biol Chem, 282: 8435-8445.
Smith LC, Britten RJ, Davidson EH. 1995. Lipopolysaccharide activates the sea urchin immune system [J].Dev Comp Immunol, 19: 217-224.
Smith VJ, Fernandes JMO, Kemp GD, Hauton C. 2008. Crustins: Enigmatic WAP domain-containing antibacterial proteins from crustaceans [J].Dev Comp Immunol, 32: 758-772.
Söderhäll K, Smith VJ. 1983. Separation of the haemocyte populations ofCarcinus maenasand other marine decapods, and prophenoloxidase distribution [J].Dev Comp Immunol, 7: 229-239.
Somboonwiwat K, Supungul P, Rimphanitchayakit V, Aoki T, Hirono I, Tassanakajon A. 2006. Differentially expressed genes in hemocytes ofVibrio harveyi-challenged shrimpPenaeus monodon[J].J Biochem Mol Biol, 39: 26-36.
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ. 1994. CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice [J].Nucleic Acids Res, 22(22): 4673-4680.
Vemuri B, Singh SS. 2001. Protein kinase C isozyme-specific phosphorylation of profilin [J].Cell Signal, 13(6): 433-439.
cDNA Cloning, Characterization and mRNA Expression of a Profilin from the Swimming CrabPortunus trituberculatus
SHEN Wang, YE Mao, SHI Ge, WANG Ri-Xin*
(Laboratory of Marine Biology Resources and Molecular Engineering, Ocean Science College, Zhejiang Ocean University, Zhoushan316004,China)
We isolated and characterized the profilin full-length cDNA from hemocytes of swimming crabPortunus trituberculatus. The profilin cDNA consists of 742 bp and the 375 bp open reading frame encodes a polypeptide of 125 amino acids, having a predicted isoelectric point of 5.87. The deduced amino acid sequence shows 42.9% amino acid sequence identity to the profilin of mosquitoAnopheles gambiae. The profilin mRNA was highly expressed in hemocytes and moderately in hepatopancreas of normal crab. The higher expression of profilin mRNA is observed in crab challenged by the pathogenic bacteriumVibrio parahaemolyticus. These results suggest a potential role for profilin in pathogen host defense mechanisms.
Portunus trituberculatus; Immunity; Gene cloning; Profilin; Gene expression
Q959.223.63; Q349; Q78
A
0254-5853-(2010)03-0261-07
10.3724/SP.J.1141.2010.03261
2009-12-22;接受日期:2010-04-27
国家科技支撑计划(2007BAD43B08);浙江省科技厅重大项目(2007C02001);浙江省面上项目(2009C32019)
∗通讯作者(Corresponding author),E-mail: wangrixin1123@126.com
申望,男,讲师,E-mail: shenwangzs@163.com
book=3,ebook=178
