EFFECT OF POSITIVE-INDEFINITE MATRIX ON MAGNETICRESONANCE DIFFUSION TENSOR-DERIVED PARAMETERS
2010-10-08ZhangHuailingRenHongrunJinXinanHeQingGaoSong
Zhang Huailing,Ren Hongrun,Jin Xin′an,He Qing,Gao Song
(1.Public Health School,Guangdong Medical College,Dongguan,523909,P.R.China;2.Basic Medical Department,Beijing Medical School,Beijing,100053,P.R.China;3.Radiology Department,Houjie Hospital,Dongguan,523945,P.R.China;4.Medical Physics Department,Peking University Health Science Center,Beijing,100191,P.R.China)
INTRODUCTION
Diffusion magnetic resonance(MR)imaging provides a noninvasive method to investigate the diffusion property of water molecules in vivo,and has been widely used in research and clinical applications,such as ischemic stroke and many kinds of cancers[1].However,the biological tissues in vivo are highly heterogeneous media that consist of various compartments and barriers.During the diffusion-driven displacement,water molecules are impeded by boundaries and other obstacles.In many biological tissues,these obstacles are tightly packed and coherently aligned,e.g. along nerve fibers. It is called the anisotropy,which may contain information about many pathological and physiological changes.The diffusion effect on the MR signal depends on the direction of the applied diffusion sensitive gradient field.Since the diffusion of water molecules in vivo is anisotropic,the diffusion properties are mathematically described as a tensor instead of a single diffusion coefficient.

where the subscripts refer to the orientations of the tissue and diffusion gradient fields,respectively.
The diffusion tensor is a 3×3 full-rank sym-metric matrix.So there are six independent values in one tensor.To obtain the element values in the matrix,at least six diffusion-weighted images(DWIs)in different directions of diffusion gradients plus a T2image are required.For example,diffusion gradient fields with 25 directions can be described by the matrix as follows

Then,25 apparent diffusion coefficient(ADC)values are acquired corresponding to 25 directions,and the following equation can be derived.
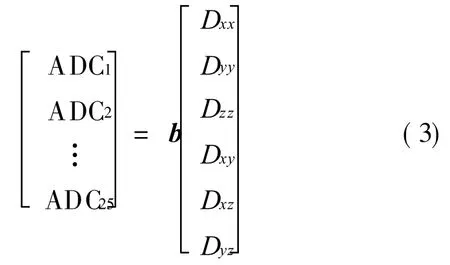
From Eq.(3),six independent values of a tensor can be obtained.
The eigenvalues of the diffusion tensor,ordered asλ1≥λ2≥λ3,can be used to derive various parameters,such as the mean diffusivity(MD)and the fractional anisotropy(FA).

Thevalue of FA falls between[0,1].In the situation where FA=0,the diffusion is isotropic.
Mapping of these parameters can be useful in depicting pathological and physiological changes in different regions of the brain such as the white matter,as well as in other areas such as the cartilageand the myocardium[2].Ideally,all the diffusion tensors are positive-definite matrices(all eigenvalues of the matrix are positive).However,the image noise and the signal loss may result in positive-indefinite matrices[3]. The objective of the study in this paper is to evaluate the effect of a positive-indefinite matrix on the tensor-derived parameters.Based on our findings,a modified algorithm is proposed for calculating the tensorderived parameters.
1 MATERIALSAND METHODS
The images of five healthy subjects are obtained using a GE 1.5T Signa Twinspeed scanner with a maximum gradient strength of 40 m T/m.A quadraturebirdcage coil is used for both excitation and reception.All subjects areasked to avoid moving their heads during the scan.As shown in Fig.1,the diffusion pulse sequence is based on the pulse gradient spin echo(PGSE)with a pair of strong magnetic gradient fields on either sideof theπpulse.For simplicity,the slice-selection gradient fields are omitted in Fig.1.The signal intensity is described by
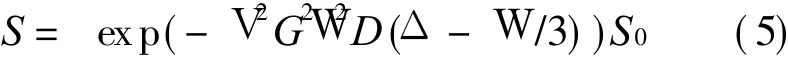
where G is the diffusion magnetic gradient field strength,W the pulse gradient width,Δthe leading edge separation between two pulsed gradients,and S0 the signal intensity without diffusion weighting[4].

Fig.1 Conventional PGSE pulse sequence with diffusion gradient applied along one physical dimension
In addition to T1 and T2 weighted imaging,five slices of tensor data encompassing the corpus callosum and the basal ganglia are acquired using a two-dimensional spin echo planar image(EPI)sequence.The scan parameters are as follows:the acquisition matrix 128×128,field of view FOV=24 cm×24 cm,the time of repetition TR=8 000 ms,the number of excitation NEX=1,the echo time TE=74 ms,the diffusion weighting(b factor)f b=1 000 s/mm2,the slice thickness 5 mm.The diffusion sensitizing gradients are applied in a total of 25 directions.
All images are transferred to a personal computer for offline post-processing,which is carried out by means of the program suit FSL(version 4.04,FMRIB Software Library,Oxford Center for Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Brain,Oxford University,Oxford,UK).Firstly,all DWI images are smoothed with an 8 mm full-width at half maximum smoothing kernel.Secondly,all these images are temporally high-pass filtered with a cutoff period of 100 s.Then,25 DWIs of one slice corresponding to different diffusion gradient directions are registered with T2 image of the same slice.
Data are analyzed by using the homemade software based on MATLAB.The 25 directional ADCs of each pixel are first calculated according to Eq.(5).The diffusion tensor of each pixel and the eigenvalues of the diffusion tensor are then derived by using the algorithm described in theintroduction.Based on the diffusion tensor,an FA image for each sliceis generated using the conventional algorithm[5].In addition,another FA image for each sliceis generated by applying the absolutevalueoperation to all eigenvalues of the diffusion tensor matrix before the calculation of FA.To monitor the affected pixels by the operation,the corresponding pixels in the T2weighted image are colored.
2 RESULTSAND DISCUSSION
Figs.2(a,b)show the FA images calculated by the conventional algorithm and the modified algorithm in this paper,respectively.Substantial differences can be found in Fig.2.FA values of many pixels in Fig.2(a),which are generated by the conventional FA calculation algorithm,are over-estimated,especially in the area of the splenium of the corpus callosum.

Fig.2 FA images of representative subject generated by conventional algorithm and modified algorithm
The reason for the FA value over-estimation is the positive-indefinite diffusion tensor.If one or more eigenvalues are negative,according to Eq.(3),FA is over-estimated.MDis another important tensor-drived parameter.Since MD is the average of three eigenvalues,the positive-indefinite diffusion tensor leads to an under-estimate of MD according to the conventional algorithm.Fig.3 shows the diffusion ellipsoids of positive and negative matrices,where Xiandλiare eigenvectors and eigenvalues,respectively.

Fig.3 Diffusion ellipsoids of positive and negative matrices
The interpretation of the distribution in Fig.4 is straightward.As shown in Fig.4,there are more positive-indefinite diffusion tensors in the area of white matter,such as the genu and the splenium of corpus callosum.The orientation of the fibers in white matter is highly directional.The diffusion of water molecules in these fibers is therefore highly anisotropic[6]. Compared with the main eigenvalue,the other two eigenvalues are close to zero,and it can lead to a positiveindefinite diffusion tensor.There are no fibers in the gray matter,so less diffusion tensors in the gray matter area are positive-indefinite matrices.The diffusion of water molecules in theventricles is an isotropic diffusion.The three eigenvalues are the same,so all the diffusion tensors in the area of the ventricles are positive-definite matrices.

Fig.4 Diffusion tensors of dark area in white matter(positive-indefinite matrices)
A modified algorithm is proposed to calculate the diffusion tensor-derived parameters. The three eigenvalues can be used to describe the axes of a diffusion ellipsoid,whose direction is determined by the eigenvectors.As shown in Fig.3,the sign of eigenvalues cannot influence the direction and the shape of the diffusion ellipsoid.Thus,the absolutevalue operation can be applied to each eigenvalues before calculating the tensordrived parameters.
The FA of many pixels are over-estimated and under-estimated,respectively by the conventional algorithm. Particularly,it is noted that many pixels in Fig.2(a)with erroneous FA values are corrected on the FA image derived by the modified algorithm.
3 CONCLUSION
The conventional algorithm for calculating the diffusion tensor-derived parameters requires all eigenvalues to be positive.When the condition is not met,FA and MD will beincorrectly determined.Since only the magnitudes are concerned without considering the direction of the eigenvalues,it shows that the robustness and the reliability for deriving these parameters can be improved by using the absolute value of eigenvalues.
[1] Paolo G P,Ragini V,Seung-Koo L,et al.Diffusion-tensor M R imaging and tractography:exploring brain microstructure and connectivity[J].Radiology,2007,245(2):367-384.
[2] Wintermark M,Rowley H A,Michael H L.Acute stroke triage to intravenous thrombolysis and other therapies with advanced CT or MR imaging:pro-MR imaging[J].Radiology,2009,251(6):627-633.
[3] Hasan K M,Alexander A L,Narayana P A.Does fractional anisotropy have better noise immunity characteristics than relative anisotropy in diffusion tensor MRI?An analytical approach[J].Magn Reson M ed,2004,51(2):413-417.
[4] Marta M C,Carpenter T,Williams G B.Looking for the optimal DTIacquisition scheme given a maximum scan time:are more b-values a waste of time[J].Magnetic Resonance Imaging,2009,27(2):163-175.
[5] Pierpaoli C,Basser P J.Toward a quantitative assessment of diffusion anisotropy[J].Magn Reson Med,1996,36(4):893-906.
[6] Basser P J,Pajevic S,Pierpaoli C,et al.In vivo fiber tractography using DT-MRI data[J].Magn Reson Med,2000,44(4):625-632.
杂志排行
Transactions of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics的其它文章
- FITTING CORRECTION METHOD OF RING ARTIFACTS FOR RECONSTRUCTING CONE-BEAM CT IMAGES
- IMAGING CHARACTERISTICSOF RAT MODELSOF PARKINSON DISEASE
- MOTOR CORTEX NETWORKSIN STROKE PATIENTS DURING RECOVERY WITH f MRI
- FLUORESCENCE SPECTRUM ANALYSISOF ETHER-WATER SOLUTION BASED ON GAUSSIAN DECOMPOSITION METHOD
- EFFECTIVE DETECTION DEPTH OF NEEDLE-LIKE OPTICAL PROBE
- PREPARATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF WATERSOLUBLE NEAR-INFRARED EMITTING PbSQUANTUM DOTS
